Telomere Shortening and Its Association with Cell Dysfunction in Lung Diseases
Abstract
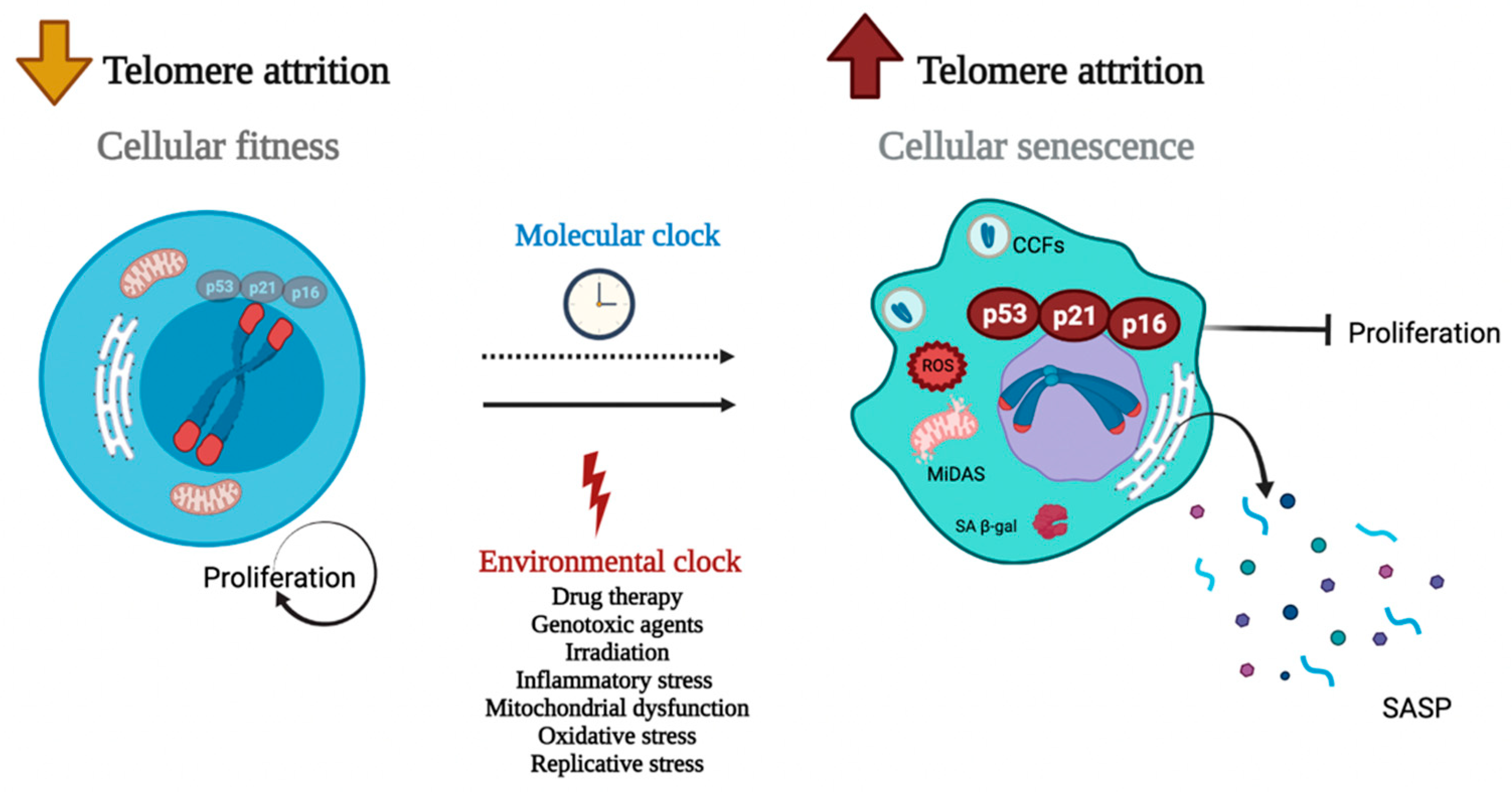
:1. Introduction
2. New Lights on TS and Cell Senescence
3. TS and Lung Disease Development
4. Influence of Immune Cells with Shorter Telomeres on Development of Lung Diseases
5. Immunotherapy, Pharmacology, and Genetic Therapy
6. Conclusions
| Telomeropathies | Gene, Protein Name (S) Related | Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer | TERT, TERC, PARN, TINF2, NAF1, DKC1, RTEL1 | Rapamycin | [154] |
| Prednisone Cyclosporine Cyclophosphamide Dasatinib Quercetin Cycloastragenol (CAG) Danazol | [107,142,147] | ||
| IPF | Nintedanib Pirfenidone Alemtuzumab GRN510 | [121,133,145,152,155,156] | |
| Dyskeratosis congenita | TERT, TERC, DKC1, or TINF2 | Danazol Oxymetholon Nandrolone Cycloastragenol CAG) Etoposide | [142,147,150] |
| Acute interstitial pneumonia Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia Smoking related interstitial lung disease | TERT | NS | [157] [140] [158] |
| Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis Hypersensitivity pneumonitis | TERT, TERC, RTEL1 | NS NS | [141] [159] |
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lange, T. Shelterin: The Protein Complex That Shapes and Safeguards Human Telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a Specific Telomere Terminal Transferase Activity in Tetrahymena Extracts. Cell 1985, 43, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, G.B. The Human Telomere Terminal Transferase Enzyme Is a Ribonucleoprotein That Synthesizes TTAGGG Repeats. Cell 1989, 59, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.R. Beginning to Understand the End of the Chromosome. Cell 2004, 116, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.W.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Prowse, K.R.; Harley, C.B.; West, M.D.; Ho, P.L.C.; Coviello, G.M.; Wright, W.E.; Weinrich, S.L.; Shay, J.W. Specific Association of Human Telomerase Activity with Immortal Cells and Cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Nguyen, L.N.T.; Nguyen, L.N.; Dang, X.; Cao, D.; Khanal, S.; Schank, M.; Thakuri, B.K.C.; Ogbu, S.C.; Morrison, Z.D.; et al. ATM Deficiency Accelerates DNA Damage, Telomere Erosion, and Premature T Cell Aging in HIV-Infected Individuals on Antiretroviral Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Micco, R.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Baker, D.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular Senescence in Ageing: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobon, A.J.; Teixeira, F.M.E.; Sato, M.N. I Mmunosenescence and Inflammaging: Risk Factors of Severe COVID-19 in Older People. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, L. The Limited In Vitro Lifetime of Human Diploid Cell Strains. Exp. Cell Res. 1965, 37, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, A.; Barbi, V.; Gottardi Zamperla, M.; Atlante, S.; Forleo, L.; Nesta, M.; Massetti, M.; Pontecorvi, A.; Nanni, S.; Farsetti, A.; et al. Evidence for Biological Age Acceleration and Telomere Shortening in COVID-19 Survivors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Silva, A.P.; Vieira, E.L.M.; Xavier, G.; Barroso, L.S.S.; Bertola, L.; Martins, E.A.R.; Brietzke, E.M.; Belangero, S.I.N.; Diniz, B.S. Telomere Shortening in Late-life Depression: A Potential Marker of Depression Severity. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichy, E.D.; Ma, N.; Sidibe, D.; Loro, E.; Kocan, J.; Chen, D.Z.; Khurana, T.S.; Hasty, P.; Mourkioti, F. Persistent NF-ΚB Activation in Muscle Stem Cells Induces Proliferation-Independent Telomere Shortening. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibironke, O.; Carranza, C.; Sarkar, S.; Torres, M.; Choi, H.T.; Nwoko, J.; Black, K.; Quintana-Belmares, R.; Osornio-Vargas, Á.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; et al. Urban Air Pollution Particulates Suppress Human T-Cell Responses to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campisi, J.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular Senescence: When Bad Things Happen to Good Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewoye, A.B.; Tampakis, D.; Follenzi, A.; Stolzing, A. Multiparameter Flow Cytometric Detection and Quantification of Senescent Cells in Vitro. Biogerontology 2020, 21, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.-P.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype: The Dark Side of Tumor Suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppé, J.-P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the P53 Tumor Suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgoulis, V.; Adams, P.D.; Alimonti, A.; Bennett, D.C.; Bischof, O.; Bishop, C.; Campisi, J.; Collado, M.; Evangelou, K.; Ferbeyre, G.; et al. Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell 2019, 179, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuła-Pietrasik, J.; Niklas, A.; Uruski, P.; Tykarski, A.; Książek, K. Mechanisms and Significance of Therapy-Induced and Spontaneous Senescence of Cancer Cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, B.-D.; Broude, E.V.; Dokmanovic, M.; Zhu, H.; Ruth, A.; Xuan, Y.; Kandel, E.S.; Lausch, E.; Christov, K.; Roninson, I.B. A Senescence-like Phenotype Distinguishes Tumor Cells That Undergo Terminal Proliferation Arrest after Exposure to Anticancer Agents. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Gower, A.C.; Ding, H.; Giorgadze, N.; Palmer, A.K.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lenburg, M.; et al. The Achilles’ Heel of Senescent Cells: From Transcriptome to Senolytic Drugs. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Delfavero, J.; Csipo, T.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Kiss, T.; Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; Mukli, P.; Toth, P.; Ahire, C.; et al. Treatment with the BCL-2/BCL-XL Inhibitor Senolytic Drug ABT263/Navitoclax Improves Functional Hyperemia in Aged Mice. GeroScience 2021, 43, 2427–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, M.B.; Ayaz-Güner, Ş.; Gunaydin, Z.; Karakukcu, M.; Peluso, G.; Di Bernardo, G.; Özcan, S.; Galderisi, U. Proteomic and Biological Analysis of the Effects of Metformin Senomorphics on the Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 730813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Rayman, M.P.; Zhang, J. Prospective Selective Mechanism of Emerging Senolytic Agents Derived from Flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12418–12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsvari, B.; Nuttall, J.R.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Azithromycin and Roxithromycin Define a New Family of “Senolytic” Drugs That Target Senescent Human Fibroblasts. Aging 2018, 10, 3294–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Bailey, J.T.; Fung, I.T.H.; Kuentzel, M.L.; Chittur, S.V.; Yang, Q. Type I Interferon Signaling Controls the Accumulation and Transcriptomes of Monocytes in the Aged Lung. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimane, L.; Barkane, L.; Igumnova, V.; Kivrane, A.; Zole, E.; Ranka, R. Telomere Length and Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2021, 131, 102144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía-Roldán, I.; Fernandez, R.; Mejía, M.; Juarez, F.; Ramirez-Martinez, G.; Montes, E.; Pruneda, A.K.S.; Martinez-Espinosa, K.; Alarcon-Dionet, A.; Herrera, I.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with the Development of Interstitial Lung Abnormalities. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2003005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, R.D.; Majety, M.; Chen, S. The Aging Transcriptome and Cellular Landscape of the Human Lung in Relation to SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Patra, T.; Vijayamahantesh; Ray, R. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Paracrine Senescence and Leukocyte Adhesion in Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Cárdenes, N.; Sellarés, J.; Bueno, M.; Corey, C.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Peng, Y.; D’Cunha, H.; Sembrat, J.; Nouraie, M.; et al. IPF Lung Fibroblasts Have a Senescent Phenotype. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L1164–L1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Guan, X.; Carraro, G.; Parimon, T.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Mulay, A.; Soukiasian, H.J.; David, G.; Weigt, S.S.; et al. Senescence of Alveolar Type 2 Cells Drives Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, G.; Luckhardt, T.; Antony, V.; Zhou, Y.; Carter, A.B.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, R.-M. Serpine 1 Induces Alveolar Type II Cell Senescence through Activating P53-P21-Rb Pathway in Fibrotic Lung Disease. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssaini, A.; Breau, M.; Kebe, K.; Abid, S.; Marcos, E.; Lipskaia, L.; Rideau, D.; Parpaleix, A.; Huang, J.; Amsellem, V.; et al. MTOR Pathway Activation Drives Lung Cell Senescence and Emphysema. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e93203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, R.; Nakahata, Y.; Shinohara, K.; Bessho, Y. Cellular Senescence Triggers Altered Circadian Clocks With a Prolonged Period and Delayed Phases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 638122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGhatrif, M.; Cingolani, O.; Lakatta, E.G. The Dilemma of Coronavirus Disease 2019, Aging, and Cardiovascular Disease: Insights From Cardiovascular Aging Science. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Sui, J.; Kuhn, J.H.; Moore, M.J.; Luo, S.; Wong, S.-K.; Huang, I.-C.; Xu, K.; Vasilieva, N.; et al. Receptor and Viral Determinants of SARS-Coronavirus Adaptation to Human ACE2. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 Receptor: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Target. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, P.S.; Meijer, P.; Nazgiewicz, A.; Anderson, S.G.; Borthwick, L.A.; Bagnall, J.; Kitchen, G.B.; Lodyga, M.; Begley, N.; Venkateswaran, R.V.; et al. The Circadian Clock Protein REVERBα Inhibits Pulmonary Fibrosis Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Melos, K.I.; Angelini, L.; Burd, C.E.; Robbins, P.D.; Niedernhofer, L.J. Mouse Models of Accelerated Cellular Senescence. In Cellular Senescence; Demaria, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1896, pp. 203–230. ISBN 978-1-4939-8930-0. [Google Scholar]
- Alessio, N.; Aprile, D.; Cappabianca, S.; Peluso, G.; Di Bernardo, G.; Galderisi, U. Different Stages of Quiescence, Senescence, and Cell Stress Identified by Molecular Algorithm Based on the Expression of Ki67, RPS6, and Beta-Galactosidase Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basisty, N.; Kale, A.; Jeon, O.H.; Kuehnemann, C.; Payne, T.; Rao, C.; Holtz, A.; Shah, S.; Sharma, V.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. A Proteomic Atlas of Senescence-Associated Secretomes for Aging Biomarker Development. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohli, J.; Wang, B.; Brandenburg, S.M.; Basisty, N.; Evangelou, K.; Varela-Eirin, M.; Campisi, J.; Schilling, B.; Gorgoulis, V.; Demaria, M. Algorithmic Assessment of Cellular Senescence in Experimental and Clinical Specimens. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 2471–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; Nehme, J.; Demaria, M. Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, O.; Agrawal, A.; Porat, Z.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Alon, U. Senescent Cell Turnover Slows with Age Providing an Explanation for the Gompertz Law. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biran, A.; Zada, L.; Abou Karam, P.; Vadai, E.; Roitman, L.; Ovadya, Y.; Porat, Z.; Krizhanovsky, V. Quantitative Identification of Senescent Cells in Aging and Disease. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, S.; Cardaci, S.; Montagna, C.; Di Giacomo, G.; De Zio, D.; Bordi, M.; Maiani, E.; Campello, S.; Borreca, A.; Puca, A.A.; et al. S-Nitrosylation Drives Cell Senescence and Aging in Mammals by Controlling Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3388–E3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, P.-Y.; Liu, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chou, W.-H.; Huang, M.-C. Shortened Leukocyte Telomere Length in Young Adults Who Use Methamphetamine. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang-Chien, J.; Huang, J.-L.; Tsai, H.-J.; Wang, S.-L.; Kuo, M.-L.; Yao, T.-C. Particulate Matter Causes Telomere Shortening and Increase in Cellular Senescence Markers in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, S.; De Meyer, T.; Van Oostveldt, P. Telomere Attrition as Ageing Biomarker. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar]
- Slusher, A.L.; Zúñiga, T.M.; Acevedo, E.O. Inflamm-Aging Is Associated with Lower Plasma PTX3 Concentrations and an Impaired Capacity of PBMCs to Express HTERT Following LPS Stimulation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 2324193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic Inflammation (Inflammaging) and Its Potential Contribution to Age-Associated Diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A New Immune–Metabolic Viewpoint for Age-Related Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Le, W.; Xie, L.; Li, H.; Wen, W.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Ye, J.; et al. A Human Circulating Immune Cell Landscape in Aging and COVID-19. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 740–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorenjak, V.; Petrelis, A.M.; Stathopoulou, M.G.; Toupance, S.; Kumar, S.; Labat, C.; Masson, C.; Murray, H.; Lamont, J.; Fitzgerald, P.; et al. A Genetic Determinant of VEGF-A Levels Is Associated with Telomere Attrition. Aging 2021, 13, 23517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurk, D.; Wilson, C.; Passos, J.F.; Oakley, F.; Correia-Melo, C.; Greaves, L.; Saretzki, G.; Fox, C.; Lawless, C.; Anderson, R.; et al. Chronic Inflammation Induces Telomere Dysfunction and Accelerates Ageing in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.S.; Wu, Y.; Okobi, Q.; Adekoya, D.; Atefi, M.; Clarke, O.; Dutta, P.; Vadgama, J.V. Proinflammatory Cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α Increased Telomerase Activity through NF-κ B/STAT1/STAT3 Activation, and Withaferin A Inhibited the Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5958429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Luo, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, C.; Dai, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Ma, W.; Songyang, Z.; Huang, Y. MiR-185 Targets POT1 to Induce Telomere Dysfunction and Cellular Senescence. Aging 2020, 12, 14791–14807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Horikawa, I.; Fujita, K.; Afshar, Y.; Kokko, A.; Laiho, P.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Harris, C.C. Functional Diversity of Human Protection of Telomeres 1 Isoforms in Telomere Protection and Cellular Senescence. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11677–11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, P.; Jia, S.; Takasugi, T.; Tesmer, V.M.; Nandakumar, J.; Chen, Y.; Chang, S. Distinct Functions of POT1 Proteins Contribute to the Regulation of Telomerase Recruitment to Telomeres. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glousker, G.; Briod, A.; Quadroni, M.; Lingner, J. Human Shelterin Protein POT 1 Prevents Severe Telomere Instability Induced by Homology-directed DNA Repair. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, W.; Hockemeyer, D.; Kibe, T.; de Lange, T. Functional Dissection of Human and Mouse POT1 Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Qian, Y.; Ding, T.; Wei, L.; Cao, S. Shorter Telomere Length of T-Cells in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Lung Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Planas-Cerezales, L.; Arias-Salgado, E.G.; Buendia-Roldán, I.; Montes-Worboys, A.; López, C.E.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Hernaiz, P.L.; Sanuy, R.L.; Leiro-Fernandez, V.; Vilarnau, E.B.; et al. Predictive Factors and Prognostic Effect of Telomere Shortening in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Telomeric Clinical Implications in IPF. Respirology 2019, 24, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machahua, C.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Ocaña-Guzman, R.; Molina-Molina, M.; Pardo, A.; Chavez-Galan, L.; Selman, M. CD4+T Cells in Ageing-Associated Interstitial Lung Abnormalities Show Evidence of pro-Inflammatory Phenotypic and Functional Profile. Thorax 2021, 76, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.M.; Lee, X.W.; Wang, X. Telomere Shortening in Human Diseases. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3180–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Telomere-Driven Diseases and Telomere-Targeting Therapies. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, J.W. Telomeres and Aging. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, M.N.; Armstrong, G.N.; Gramatges, M.M.; Bertuch, A.A.; Jhangiani, S.N.; Doddapaneni, H.; Lewis, L.; Tombrello, J.; Tsavachidis, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Germline Mutations in Shelterin Complex Genes Are Associated with Familial Glioma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, dju384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codd, V.; Nelson, C.P.; Albrecht, E.; Mangino, M.; Deelen, J.; Buxton, J.L.; Hottenga, J.J.; Fischer, K.; Esko, T.; Surakka, I.; et al. Identification of Seven Loci Affecting Mean Telomere Length and Their Association with Disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pooley, K.A.; Bojesen, S.E.; Weischer, M.; Nielsen, S.F.; Thompson, D.; Amin Al Olama, A.; Michailidou, K.; Tyrer, J.P.; Benlloch, S.; Brown, J.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Scan (GWAS) for Mean Telomere Length within the COGS Project: Identified Loci Show Little Association with Hormone-Related Cancer Risk. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 5056–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, T.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Gong, K. Telomere Shortening Is Associated with Genetic Anticipation in Chinese Von Hippel–Lindau Disease Families. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3802–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacNeil, D.E.; Lambert-Lanteigne, P.; Autexier, C. N-Terminal Residues of Human Dyskerin Are Required for Interactions with Telomerase RNA That Prevent RNA Degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5368–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meiners, S.; Eickelberg, O.; Königshoff, M. Hallmarks of the Ageing Lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 807–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.-C.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short Telomeres Are a Risk Factor for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghisays, F.; Garzia, A.; Wang, H.; Canasto-Chibuque, C.; Hohl, M.; Savage, S.A.; Tuschl, T.; Petrini, J.H.J. RTEL1 Influences the Abundance and Localization of TERRA RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Deng, Z.; Vladimirova, O.; Gulve, N.; Johnson, F.B.; Drosopoulos, W.C.; Schildkraut, C.L.; Lieberman, P.M. TERRA G-Quadruplex RNA Interaction with TRF2 GAR Domain Is Required for Telomere Integrity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzalin, C.M.; Reichenbach, P.; Khoriauli, L.; Giulotto, E.; Lingner, J. Telomeric Repeat–Containing RNA and RNA Surveillance Factors at Mammalian Chromosome Ends. Science 2007, 318, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeftner, S.; Blasco, M.A. Developmentally Regulated Transcription of Mammalian Telomeres by DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase II. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Dahmane, N.; Tsai, K.; Wang, P.; Williams, D.R.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Showe, L.C.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Q.; et al. Telomeric Repeat-Containing RNA (TERRA) Constitutes a Nucleoprotein Component of Extracellular Inflammatory Exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6293–E6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najarro, K.; Nguyen, H.; Chen, G.; Xu, M.; Alcorta, S.; Yao, X.; Zukley, L.; Metter, E.J.; Truong, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Telomere Length as an Indicator of the Robustness of B- and T-Cell Response to Influenza in Older Adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, N.P.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Hodes, R.J. Human Naive and Memory T Lymphocytes Differ in Telomeric Length and Replicative Potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11091–11094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Effros, R.B.; Boucher, N.; Porter, V.; Zhu, X.; Spaulding, C.; Walford, R.L.; Kronenberg, M.; Cohen, D.; Schächter, F. Decline in CD28+ T Cells in Centenarians and in Long-Term T Cell Cultures: A Possible Cause for Both in Vivo and in Vitro Immunosenescence. Exp. Gerontol. 1994, 29, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsinprasert, W.; Chanhom, N.; Suvichapanich, S.; Wattanapokayakit, S.; Mahasirimongkol, S.; Chantratita, W.; Jittikoon, J. Leukocyte Telomere Length as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Su, X.; Da, M.; Yang, Z.; Duan, W.; Mo, X. Association between Leucocyte Telomere Length and Cardiovascular Disease in a Large General Population in the United States. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Gerdes, N.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Figulla, H.R. Circulating Levels of Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines in Overweight Adolescents. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 958403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-Y.; Chang, S.-F.; Chang, T.-Y.; Su, H.-M.; Lu, S.-C. Synergistic Effects of Electronegative-LDL- and Palmitic-Acid-Triggered IL-1β Production in Macrophages via LOX-1- and Voltage-Gated-Potassium-Channel-Dependent Pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 97, 108767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Lee, A.-S.; Lu, L.-S.; Ke, L.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Dong, J.-W.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chu, C.-S.; Chan, H.-C.; et al. Human Electronegative LDL Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Premature Senescence of Vascular Cells in Vivo. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, D.; Kuang, X.; Xiao, J.; Yu, Q.; Lu, X.; Li, W.; Xie, B.; et al. Serum IL-1β and IL-17 Levels in Patients with COPD: Associations with Clinical Parameters. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2017, 12, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, M.-C.; Cheng, L.; Liang, M.; Ji, H.; Fu, J. Blockade of LOX-1 Prevents Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Inflammation and Injury in Mice. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Zglinicki, T. Oxidative Stress Shortens Telomeres. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfeir, A.; Kosiyatrakul, S.T.; Hockemeyer, D.; MacRae, S.L.; Karlseder, J.; Schildkraut, C.L.; de Lange, T. Mammalian Telomeres Resemble Fragile Sites and Require TRF1 for Efficient Replication. Cell 2009, 138, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikawa, S.; Kawanishi, S. Site-Specific DNA Damage at GGG Sequence by Oxidative Stress May Accelerate Telomere Shortening. FEBS Lett. 1999, 453, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikawa, S.; Tada-Oikawa, S.; Kawanishi, S. Site-Specific DNA Damage at the GGG Sequence by UVA Involves Acceleration of Telomere Shortening. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4763–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Telomere Dysfunction Disturbs Macrophage Mitochondrial Metabolism and the NLRP3 Inflammasome through the PGC-1α/TNFAIP3 Axis. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3493–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.-C. Association between Shortened Telomere Length and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Z. Für Rheumatol. 2018, 77, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Green, G.; Zhuo, H.; Liu, K.D.; Kangelaris, K.N.; Gomez, A.; Jauregui, A.; Vessel, K.; Ke, S.; et al. Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Telomere Length Is Associated with Survival of Sepsis Patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, M.S.; Cheng, N.-L.; Kim, J.; An, J.; Dong, F.; Yang, Q.; Zou, I.; Weng, N. Human T Cell Differentiation Negatively Regulates Telomerase Expression Resulting in Reduced Activation-Induced Proliferation and Survival. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, C.L.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Talbot, C.C.; Abraham, R.S.; Hamm, D.; Gable, D.L.; Kanakry, C.G.; Applegate, C.D.; Siliciano, J.; Jackson, J.B.; et al. Short Telomere Syndromes Cause a Primary T Cell Immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5222–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyoh, S.; Venkatesan, N.; Poon, A.H.; Nishioka, M.; Lin, T.-Y.; Baglole, C.J.; Eidelman, D.H.; Hamid, Q. Are Leukocytes in Asthmatic Patients Aging Faster? A Study of Telomere Length and Disease Severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 480–482.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro-Hermida, S.; Martínez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Short and Dysfunctional Telomeres Protect from Allergen-induced Airway Inflammation. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, K.T.S.; Wong, R.S.; Tsang, H.-W.; Chua, G.T.; Chan, D.; Chan, K.C.; Wong, W.H.S.; Yam, J.C.; Ho, M.; Tham, C.C.; et al. Impact of Snoring on Telomere Shortening in Adolescents with Atopic Diseases. Genes 2021, 12, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Newton, C.A.; Arnould, I.; Elicker, B.M.; Henry, T.S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Golden, J.A.; Jones, K.D.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; et al. The MUC5B Promoter Polymorphism and Telomere Length in Patients with Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: An Observational Cohort-Control Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; de Punder, K.; Buss, C.; Wadhwa, P.D. The Fetal Programming of Telomere Biology Hypothesis: An Update. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnung Scholten, R.; Møller, P.; Jovanovic Andersen, Z.; Dehlendorff, C.; Khan, J.; Brandt, J.; Ketzel, M.; Knudsen, L.E.; Mathiesen, L. Telomere Length in Newborns Is Associated with Exposure to Low Levels of Air Pollution during Pregnancy. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzakhani, H.; De Vivo, I.; Leeder, J.S.; Gaedigk, R.; Vyhlidal, C.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Tantisira, K. Early Pregnancy Intrauterine Fetal Exposure to Maternal Smoking and Impact on Fetal Telomere Length. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 218, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Hu, K.; Su, H.; Shi, F.; Kong, L.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J. Increased CD8+CD28+ T Cells Independently Predict Better Early Response to Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Patients with Lung Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, B.; Bilgi, O.; Gümüs, M.; Erikçi, A.A.; Sayan, Ö.; Türken, O.; Kandemir, E.G.; Öztürk, A.; Yaylacı, M. CD8+CD28− Cells and CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells in the Peripheral Blood of Advanced Stage Lung Cancer Patients. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jing, W.; An, N.; Li, A.; Yan, W.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J. Prognostic Significance of Peripheral CD8+CD28+ and CD8+CD28− T Cells in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Chemo(Radio)Therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, E.; Tedone, E.; O’Hara, R.; Cornelius, C.; Lai, T.-P.; Ludlow, A.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. The Maintenance of Telomere Length in CD28+ T Cells During T Lymphocyte Stimulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Planas-Cerezales, L.; Arias-Salgado, E.G.; Berastegui, C.; Montes-Worboys, A.; González-Montelongo, R.; Lorenzo-Salazar, J.M.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Garcia-Moyano, M.; Dorca, J.; Flores, C.; et al. Lung Transplant Improves Survival and Quality of Life Regardless of Telomere Dysfunction. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 695919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Tian, L.; Bian, T.; Zhao, H.; Tao, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, Q.; Hou, H. The Role of CD28 in the Prognosis of Young Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, G.M.A.; Wills, M.R.; Appay, V.; O’Callaghan, C.; Murphy, M.; Smith, N.; Sissons, P.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Bell, J.I.; Moss, P.A.H. Functional Heterogeneity and High Frequencies of Cytomegalovirus-Specific CD8+ T Lymphocytes in Healthy Seropositive Donors. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8140–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naikawadi, R.P.; Disayabutr, S.; Mallavia, B.; Donne, M.L.; Green, G.; La, J.L.; Rock, J.R.; Looney, M.R.; Wolters, P.J. Telomere Dysfunction in Alveolar Epithelial Cells Causes Lung Remodeling and Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuda, R.; Aoshiba, K.; Matsushima, H.; Ogura, T.; Okudela, K.; Ohashi, K. Cellular Senescence and Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype: Comparison of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease, and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Batenburg, A.A.; Kazemier, K.M.; van Oosterhout, M.F.M.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C.; Goldschmeding, R.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Telomere Shortening and DNA Damage in Culprit Cells of Different Types of Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 691–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, C.; Povedano, J.M.; Serrano, R.; Benitez-Buelga, C.; Popkes, M.; Formentini, I.; Bobadilla, M.; Bosch, F.; Blasco, M.A. Telomerase Gene Therapy Rescues Telomere Length, Bone Marrow Aplasia, and Survival in Mice with Aplastic Anemia. Blood 2016, 127, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waisberg, D.R.; Barbas-Filho, J.V.; Parra, E.R.; Fernezlian, S.; Ribeiro de Carvalho, C.R.; Kairalla, R.A.; Capelozzi, V.L. Abnormal Expression of Telomerase/Apoptosis Limits Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell Replication in the Early Remodeling of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia/Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Quintero, B.; Buendía-Roldán, I.; Ramírez-Salazar, E.G.; Balderas-Martínez, Y.I.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, S.L.; Martínez-Espinosa, K.; Selman, M. Circulating MicroRNA Signature Associated to Interstitial Lung Abnormalities in Respiratory Asymptomatic Subjects. Cells 2020, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Miao, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Qu, K.; Liu, C. MiR-34a Induces Cellular Senescence via Modulation of Telomerase Activity in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting FoxM1/c-Myc Pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3988–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Gonzalez De Los Santos, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Rinke, A.E.; Kim, K.K.; Phan, S.H. Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Ameliorates Lung Fibrosis by Protecting Alveolar Epithelial Cells against Senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8861–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro-Hermida, S.; Autilio, C.; Martínez, P.; Bosch, F.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Blasco, M.A. Telomerase Treatment Prevents Lung Profibrotic Pathologies Associated with Physiological Aging. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202002120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, M.A.; Balderas-Martínez, Y.I.; Buendía-Roldan, I.; Abdala-Valencia, H.; Nam, K.; Jain, M.; Bhorade, S.; Bharat, A.; Reyfman, P.A.; Ridge, K.M.; et al. Inflammatory Pathways Are Upregulated in the Nasal Epithelium in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Cox, M.J.; Willis-Owen, S.A.G.; Mallia, P.; Russell, K.E.; Russell, A.-M.; Murphy, E.; Johnston, S.L.; Schwartz, D.A.; Wells, A.U.; et al. The Role of Bacteria in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Speckmann, C.; Sahoo, S.S.; Rizzi, M.; Hirabayashi, S.; Karow, A.; Serwas, N.K.; Hoemberg, M.; Damatova, N.; Schindler, D.; Vannier, J.-B.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Heterogeneity of RTEL1 Deficiency. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borie, R.; Bouvry, D.; Cottin, V.; Gauvain, C.; Cazes, A.; Debray, M.-P.; Cadranel, J.; Dieude, P.; Degot, T.; Dominique, S.; et al. Regulator of Telomere Length 1 (RTEL1) Mutations Are Associated with Heterogeneous Pulmonary and Extra-Pulmonary Phenotypes. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Glousker, G.; Lamm, N.; Tawil, S.; Hourvitz, N.; Smoom, R.; Revy, P.; Tzfati, Y. Full Length RTEL1 Is Required for the Elongation of the Single-Stranded Telomeric Overhang by Telomerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 7239–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballew, B.J.; Joseph, V.; De, S.; Sarek, G.; Vannier, J.-B.; Stracker, T.; Schrader, K.A.; Small, T.N.; O’Reilly, R.; Manschreck, C.; et al. A Recessive Founder Mutation in Regulator of Telomere Elongation Helicase 1, RTEL1, Underlies Severe Immunodeficiency and Features of Hoyeraal Hreidarsson Syndrome. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cagsin, H.; Uzan, A.; Tosun, O.; Rasmussen, F.; Serakinci, N. Tissue-Specific Ultra-Short Telomeres in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2020, 15, 2751–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.H.; Kim, J.; Lim, M.N.; Bak, S.H.; Kim, W.J. Correlation between Telomere Length and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease–Related Phenotypes: Results from the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Dusty Areas (CODA) Cohort. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2021, 84, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba-Lanús, E.; Cazorla-Rivero, S.; García-Bello, M.A.; Mayato, D.; Gonzalvo, F.; Ayra-Plasencia, J.; Celli, B.; Casanova, C. Telomere Length Dynamics over 10-Years and Related Outcomes in Patients with COPD. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsellem, V.; Gary-Bobo, G.; Marcos, E.; Maitre, B.; Chaar, V.; Validire, P.; Stern, J.-B.; Noureddine, H.; Sapin, E.; Rideau, D.; et al. Telomere Dysfunction Causes Sustained Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Sundar, I.K.; Tormos, A.M.; Lerner, C.A.; Gerloff, J.; Yao, H.; Rahman, I. Shelterin Telomere Protection Protein 1 Reduction Causes Telomere Attrition and Cellular Senescence via Sirtuin 1 Deacetylase in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benetos, A.; Lai, T.-P.; Toupance, S.; Labat, C.; Verhulst, S.; Gautier, S.; Ungeheuer, M.-N.; Perret-Guillaume, C.; Levy, D.; Susser, E.; et al. The Nexus Between Telomere Length and Lymphocyte Count in Seniors Hospitalized With COVID-19. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, e97–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vazquez, R.; Guío-Carrión, A.; Zapatero-Gaviria, A.; Martínez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Shorter Telomere Lengths in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Disease. Aging 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Codd, V.; Raisi-Estabragh, Z.; Musicha, C.; Bountziouka, V.; Kaptoge, S.; Allara, E.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Butterworth, A.S.; Wood, A.M.; et al. Shorter Leukocyte Telomere Length Is Associated with Adverse COVID-19 Outcomes: A Cohort Study in UK Biobank. EBioMedicine 2021, 70, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omran, H.M.; Almaliki, M.S. Influence of NAD+ as an Ageing-Related Immunomodulator on COVID 19 Infection: A Hypothesis. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wei, J.; Riethman, H.; Baur, J.A.; Voglauer, R.; Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Telomere Length Regulates ISG15 Expression in Human Cells. Aging 2009, 1, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Lee, J.-H.; Parker, Z.M.; Acharya, D.; Chiang, J.J.; van Gent, M.; Riedl, W.; Davis-Gardner, M.E.; Wies, E.; Chiang, C.; et al. ISG15-Dependent Activation of the Sensor MDA5 Is Antagonized by the SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease to Evade Host Innate Immunity. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimura-Omori, M.; Kiyohara, C.; Yanagihara, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ogata-Suetsugu, S.; Harada, E.; Hamada, N.; Tsuda, T.; Takata, S.; Shimabukuro, I.; et al. Association between Telomere-Related Polymorphisms and the Risk of IPF and COPD as a Precursor Lesion of Lung Cancer: Findings from the Fukuoka Tobacco-Related Lung Disease (FOLD) Registry. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arish, N.; Petukhov, D.; Wallach-Dayan, S.B. The Role of Telomerase and Telomeres in Interstitial Lung Diseases: From Molecules to Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chambers, D.C.; Lutzky, V.P.; Apte, S.H.; Godbolt, D.; Feenstra, J.; Mackintosh, J. Successful Treatment of Telomeropathy-related Interstitial Lung Disease with Immunosuppression and Danazol. Respirol. Case Rep. 2020, 8, e00607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiri, K.D.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Weissler, J.C.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Shay, J.W.; Garcia, C.K. Adult-Onset Pulmonary Fibrosis Caused by Mutations in Telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cronkhite, J.T.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Chin, K.M.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere Shortening in Familial and Sporadic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justet, A.; Klay, D.; Porcher, R.; Cottin, V.; Ahmad, K.; Molina Molina, M.; Nunes, H.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Naccache, J.M.; Manali, E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Carrying a Telomere-Related Gene Mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A Phase 3 Trial of Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Cycloastragenol: An Exciting Novel Candidate for Age-associated Diseases (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsley, D.M.; Dumitriu, B.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Weinstein, B.; Chen, C.; Hardy, N.; Mihalek, A.D.; Lingala, S.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Danazol Treatment for Telomere Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khincha, P.P.; Wentzensen, I.M.; Giri, N.; Alter, B.P.; Savage, S.A. Response to Androgen Therapy in Patients with Dyskeratosis Congenita. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 165, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieri, M.; Kirschner, M.; Tometten, M.; Abels, A.; Rolles, B.; Isfort, S.; Panse, J.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; Beier, F. Comparable Effects of the Androgen Derivatives Danazol, Oxymetholone and Nandrolone on Telomerase Activity in Human Primary Hematopoietic Cells from Patients with Dyskeratosis Congenita. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieri, M.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; Beier, F. Treatment of Telomeropathies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2021, 34, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, J.J.; Fudge, N.J.; Gallant, M.E.; Grant, M.D. Proximity of Cytomegalovirus-Specific CD8+ T Cells to Replicative Senescence in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Individuals. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, D.; Khanal, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Nguyen, L.N.; Nguyen, L.N.T.; Dang, X.; Schank, M.; Thakuri, B.K.C.; et al. A Matter of Life or Death: Productively Infected and Bystander CD4 T Cells in Early HIV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 626431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara-Romeo, I.; Martinez, P.; Saraswati, S.; Whittemore, K.; Graña-Castro, O.; Thelma Poluha, L.; Serrano, R.; Hernandez-Encinas, E.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Maria Flores, J.; et al. The MTOR Pathway Is Necessary for Survival of Mice with Short Telomeres. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fauce, S.R.; Jamieson, B.D.; Chin, A.C.; Mitsuyasu, R.T.; Parish, S.T.; Ng, H.L.; Ramirez Kitchen, C.M.; Yang, O.O.; Harley, C.B.; Effros, R.B. Telomerase-Based Pharmacologic Enhancement of Antiviral Function of Human CD8+ T Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7400–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newton, C.A.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; Kozlitina, J.; Glazer, C.S.; Aravena, C.; Meyer, K.; Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere-Related Lung Fibrosis Is Diagnostically Heterogeneous but Uniformly Progressive. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gansner, J.M.; Rosas, I.O. Telomeres in Lung Disease. Transl. Res. 2013, 162, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGroder, C.F.; Zhang, D.; Choudhury, M.A.; Salvatore, M.M.; D’Souza, B.M.; Hoffman, E.A.; Wei, Y.; Baldwin, M.R.; Garcia, C.K. Pulmonary Fibrosis 4 Months after COVID-19 Is Associated with Severity of Illness and Blood Leucocyte Telomere Length. Thorax 2021, 76, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, D.S.; Nawrot, T.S. Ageing at the Level of Telomeres in Association to Residential Landscape and Air Pollution at Home and Work: A Review of the Current Evidence. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 298, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz, A.; Flores-Gonzalez, J.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Chavez-Galan, L. Telomere Shortening and Its Association with Cell Dysfunction in Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010425
Ruiz A, Flores-Gonzalez J, Buendia-Roldan I, Chavez-Galan L. Telomere Shortening and Its Association with Cell Dysfunction in Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010425
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz, Andy, Julio Flores-Gonzalez, Ivette Buendia-Roldan, and Leslie Chavez-Galan. 2022. "Telomere Shortening and Its Association with Cell Dysfunction in Lung Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010425
APA StyleRuiz, A., Flores-Gonzalez, J., Buendia-Roldan, I., & Chavez-Galan, L. (2022). Telomere Shortening and Its Association with Cell Dysfunction in Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010425









