Basic Studies Aiming at Orius minutus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) Mass-Rearing
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect and Experimental Conditions
2.2. Effect of Moisture on Development
2.3. Selection of Artificial Oviposition Substrates
2.4. Oviposition Substrate Preference Using Cork Sheets
2.5. Hatch Rate and Moisture Supply of Artificial Oviposition Substrate
2.6. Effect of Diet on Development and Reproduction
2.7. Cost Analysis of Plant-Free Rearing System
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Moisture on Development
3.2. Selection of Artificial Oviposition Substrates
3.3. Oviposition Substrate Preference Using Cork Sheets
3.4. Hatch Rate and Moisture Supply of Artificial Oviposition Substrates
3.5. Effect of Diet on Development and Reproduction
3.6. Cost Analysis of the Plant-Free Rearing System
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishimori, T.; Miura, K.; Seko, T. Rearing Orius strigicollis (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on an alternative diet of brine shrimp, Artemia salina (Anostraca: Artemiidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2016, 51, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.B.; Bueno, V.H.P.; Montes, F.C.; van Lenteren, J.C. Population growth of three mirid predatory bugs feeding on eggs and larvae of Tuta absoluta on tomato. BioControl 2016, 61, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenteren, J.C.; Bolckmans, K.; Köhl, J.; Ravensberg, W.J.; Urbaneja, A. Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: Plenty of new opportunities. Entomophaga 2018, 63, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Lenteren, J.C. The state of commercial augmentative biological control: Plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. Entomophaga 2012, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, C.L.R.-V.D.; Hemerik, L.; Van Der Werf, W.; De Jong, P.W.; Van Lenteren, J.C. Life history of the harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis: A global meta-analysis. BioControl 2017, 62, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceryngier, P.; Nedvěd, O.; Grez, A.A.; Riddick, E.W.; Roy, H.E.; Martin, G.S.; Steenberg, T.; Vesely, P.; Zaviezo, T.; Zúñiga-Reinoso, Á.; et al. Predators and parasitoids of the harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis, in its native range and invaded areas. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 1009–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohno, K.; Kashio, T. Development and prey consumption of Orius sauteri (Poppius) and O. minutus (L.) (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) fed on Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1998, 33, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silveira, L.C.P.; Paes Bueno, V.H.; van Lenteren, J.C. Orius insidiosus as biological control agent of thrips in greenhouse chry-santhemums in the tropics. Bull. Insectology 2004, 57, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, T.S.; Hwang, M.R.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, A.S.; Won, H.S.; Hong, D.K.; Cho, J.R.; Ham, E.H. Greenhouse whitefly and thrips management model using natural enemies in semi-forcing culture of Tamato. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 56, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agricultural Products Quality Management Service Home Page. Available online: https://www.naqs.go.kr/contents/contentsTab.do?menuId=MN50068 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Ham, E.H.; Jun, H.J.; Lim, U.T.; Lee, Y.S. Biological control effect of “Natural Enemy in First method” by growers: Potential applications in pest management without monitoring. In Proceedings of the Second International Congress of Biological Control, Davos, Switzerland, 26–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency Home Page. Available online: https://www.qia.go.kr/bbs/lawAnn/viewLawWebAction.do?id=180550&type=0 (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Honda, J.Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Hirose, Y. Development, reproduction and longevity of Orius minutus and Orius sauteri (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) when reared on Ephestia kuehniella eggs. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1998, 33, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.A.A.; Nouri-Ganbalani, G. Assessing the potential for biological control of potato field pests in Ardabil, Iran: Functional responses of Orius niger (Wolf.) and O. minutus (L.) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). J. Pest Sci. 2010, 83, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.A.A. Efficiency of Orius minutus for control of Tetranychus urticaeon selected potato cultivars. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Yi, W.X.; Zheng, C.Y. Predatory and control ability of Orius minutus to the diamindback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutelli-dae). Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2017, 28, 3403–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Sarker, S.; Ham, E.; Lee, J.-S.; Lim, U.T. Development and Fecundity of Orius minutus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) and O. laevigatus Reared on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Nakata, T. Effect of photoperiod on reproductive diapause in the predatory bugs, Orius sauteri (Poppius) and O. minutus (Linnaeus) (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1998, 33, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuda, M.; Shima, K. Relative importance of weather and density dependence on the dispersal and on-plant activity of the predator Orius minutus. Popul. Ecol. 2002, 44, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, S. Development, Prey Consumption, and Fecundity of Orius minutus (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) when Fed on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Acarol. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 15, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, Q.F.; Li, Q.; Jiang, C.X.; Wang, H.J. Effects of temperature on the development and reproduction of Orius minutus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2016, 59, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, T.; Fujiwara-Tsujii, N.; Yasui, H.; Matsuyama, S. Female Sex Pheromone in Trails of the Minute Pirate Bug, Orius minutus (L). J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Taniai, K.; Maeda, T. The mating systems of three species of minute pirate bug, Orius sauteri, O. minutus, and O. strigicollis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2019, 167, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Forest Service (KFS). Development of Environment-Friendly Garden Pest Management Tactics and Its Application Method, 1st ed.; R202000077; Korea Forest Service: Daejeon, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bonte, M.; De Clercq, P. Impact of Artificial Rearing Systems on the Developmental and Reproductive Fitness of the Predatory Bug, Orius laevigatus. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Clercq, P.; Degheele, D. A meat-based diet for rearing the predatory stinkbugs Podisus maculiventris and Podisus sagitta [Het.: Pentatomidae]. BioControl 1992, 37, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constant, B.; Grenier, S.; Bonnot, G. Artificial Substrate for Egg Laying and Embryonic Development by the Predatory Bug Macrolophus caliginosus (Heteroptera: Miridae). Biol. Control. 1996, 7, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Gho, H.G.; Han, M.W.; Lee, G.S. Biological characteristics and mass rearing system for Cadra cautella (Walker) as a substitute diet for natural enemies. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2003, 42, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.; Richards, P.; Nadel, H.; Ferguson, G. A rearing method for the production of large numbers of the insidious flower bug, Orius insidiosus (say) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Can. Entomol. 1995, 127, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Puysseleyr, V.; Höfte, M.; De Clercq, P. Continuous rearing of the predatory anthocorid Orius laevigatus without plant materials. J. Appl. Entomol. 2014, 138, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañé, C.; Zalom, F. Artificial Oviposition Substrate for Rearing Orius insidiosus (Hemiptera, Anthocoridae). Biol. Control. 1994, 4, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Puysseleyr, V.; De Man, S.; Höfte, M.; De Clercq, P. Plantless rearing of the zoophytophagous bug Nesidiocoris tenuis. BioControl 2012, 58, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.G. Reproductive ecology of predaceous Heteroptera. Biol. Control. 2011, 59, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C. Insect Bioecology and Nutrition for Integrated Pest Management, 1st ed.; Panizzi, A.R., Parra, J.R.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4398-3708-5. [Google Scholar]
- Arijs, Y.; De Clercq, P. Liver-based artificial diets for the production of Orius laevigatus. BioControl 2004, 49, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasini, M.G.; van Lenteren, J.C.; Burgio, G. Biological traits and predation capacity of four Orius species on two prey spe-cies. Bull. Insectology 2004, 57, 79–93. [Google Scholar]
- Arijs, Y.; De Clercq, P. Rearing Orius laevigatus on Cysts of the Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana. Biol. Control. 2001, 21, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F. Optimization an Optimal Artificial Diet for the Predatory Bug Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongo, T.; Obayashi, N. Use of Diapause Eggs of Brine Shrimp, Artemia salina (Linne) for Artificial Diet of Coccinelid Beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas). Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1997, 41, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantornhout, I.; Minnaert, H.; Tirry, L.; de Clercq, P. Effect of pollen, natural prey and factitious prey on the development of Iphiseius degenerans. BioControl 2004, 49, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddick, E.W.; Wu, Z.; Rojas, G. Potential utilization of Artemia franciscana eggs as food for Coleomegilla maculata. BioControl 2014, 59, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. The SAS System for Windows 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2015; Available online: https://welcome.oda.sas.com (accessed on 30 May 2020).
- Rural Development Administration (RDA). Rearing Standard and Specifications for Beneficial Insect (II), 1st ed.; Rural Development Administration: Jeonju-si, Korea, 2014; pp. 8–23. ISBN 978-894-802-785-3. [Google Scholar]
- Armer, C.A.; Wiedenmann, R.N.; Bush, D.R. Plant feeding site selection on soybean by the facultatively phytophagous predator Orius insidiosus. Èntomol. Exp. Appl. 1998, 86, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, R.A. Colony maintenance and mass-rearing: Using cold storage technology for extending the shelf-life of insects. In Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests; Vreysen, M.J.B., Robinson, A.S., Hendrichs, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 149–162. ISBN 978-1-4020-6059-5. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Ramos, J.A. Mass Production of Beneficial Organisms; Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Shapiro-Ilan, D.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 711–742. ISBN 978-0-12-391453-8. [Google Scholar]
- Delobel, A.G.L. Humidity effects on Atherigona soccata: Egg development and hatch. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1983, 33, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, M.P.; Bourgeois, G.; Brodeur, J.; Boivin, G. Effect of Soil Temperature and Moisture on Survival of Eggs and First-Instar Larvae of Delia radicum. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, M. Feeding and ovipositing on plants by an omnivorous insect predator. Oecologia 1996, 105, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.C.; Debolt, J.W. Rearing Geocoris punctipes (Heteroptera, Lygaeidae) on insect eggs. Southwest. Entomology 1983, 8, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq, P.; Arijs, Y.; Van Meir, T.; Van Stappen, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Dewettinck, K.; Rey, M.; Grenier, S.; Febvay, G. Nutritional value of brine shrimp cysts as a factitious food for Orius laevigatus (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2005, 15, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L.R. Cannibalism in Natural Populations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1975, 6, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, G.A. The Evolution and Dynamics of Intraspecific Predation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1981, 12, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, M.A.; Crespi, B.J. Cannibalism: Ecology and Evolution among Diverse Taxa; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Schausberger, P. Cannibalism among phytoseiid mites: A review. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2003, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandekerkhove, B.; Parmentier, L.; Van Stappen, G.; Grenier, S.; Febvay, G.; Rey, M.; De Clercq, P. Artemiacysts as an alternative food for the predatory bug Macrolophus pygmaeus. J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 133, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, H.; Law, J.H.; Winzerling, J.J. Iron Metabolism in Insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, B. Iron homeostasis in insects: Insights from Drosophila studies. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.Q.; Winzerling, J.J. Insect ferritins: Typical or atypical? Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2010, 1800, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hentze, M.W.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Galy, B.; Camaschella, C. Two to Tango: Regulation of Mammalian Iron Metabolism. Cell 2010, 142, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geiser, D.L.; Winzerling, J.J. Insect transferrins: Multifunctional proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2011, 1820, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkov, B.; Georgieva, T. Insect iron binding proteins: Insights from the genomes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
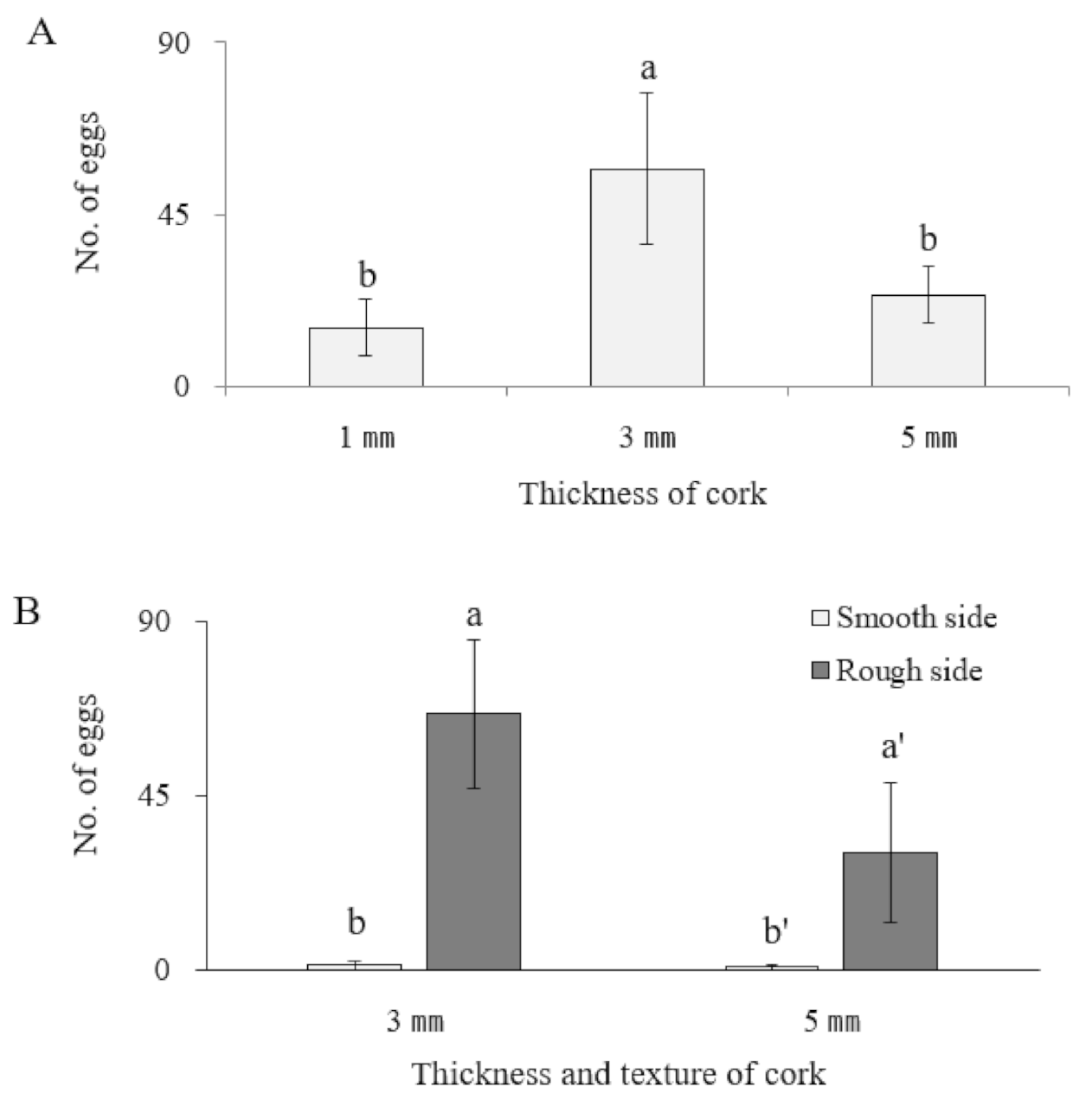
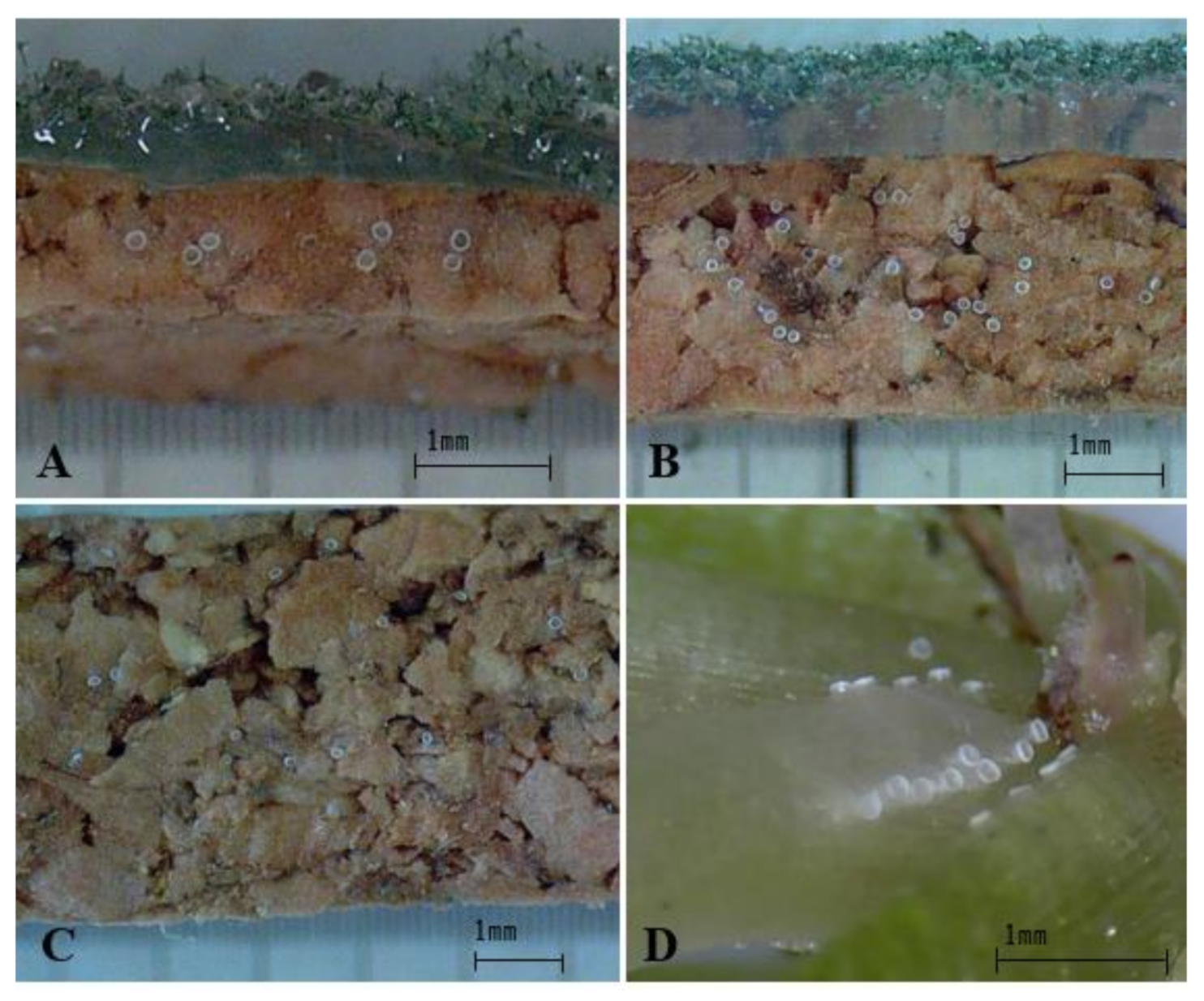




| Treatment | Developmental Time (Days) | Nymphal Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Plant | 11.7 ± 0.6 | 93.3 ± 9.4 |
| Plant and water dome | 11.9 ± 0.99 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Plant and honey-water dome | 12.1 ± 0.4 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Water dome | 12.9 ± 0.1 | 86.7 ± 9.4 |
| Honey-water dome | 12.7 ± 0.1 | 86.7 ± 18.9 |
| Control (no moisture source) | 0 |
| Oviposition Substrate | No. of Eggs | Egg Hatch (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cork | 13.1 ± 2.4 a | 0 b |
| Rubber band | 4.1 ± 4.7 b | 0 b |
| Plant | 12.3 ± 4.1 a | 71.6 ± 0.9 a |
| Treatment | Oviposition Substrate 1 | n 2 | Moisture Source 3 | Egg Hatch (%) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Cork sheet | 149 | Oasis, vermiculite, and buckwheat husk with water | 72.8 ± 3.6 a |
| T2 | Cork sheet | 144 | Vermiculite and buckwheat husk with water | 34.7 ± 4.6 c |
| T3 | Cork sheet | 233 | Oasis with water | 68.8 ± 4.1 a |
| T4 | Cork sheet | 157 | Oasis with water (only after egg-laying) | 51.5 ± 4.1 b |
| T5 | Cork sheet | 213 | 0 d | |
| Control | Plant | 166 | 71.6 ± 0.9 a |
| Diet 2 | Developmental Time (Days) | Survival (%) | % Egg Laying Females | No. of Eggs Deposited per Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 12.1 ± 0.4 (15) a | 72.7 ± 3.8 (167) a | 92.6 ± 6.4 (27) a | 3.8 ± 0.7 (25) a |
| I | 14.0 ± 0.2 (15) a | 67.5 ± 3.7 (167) a | 100.0 ± 0.0 (28) a | 4.8 ± 0.2 (28) a |
| G | 19.9 ± 2.2 (16) b | 11.4 ± 1.3 (174) b | 0 (19) b | - |
| Diets (for Nymph/Adult) 2 | Fecundity (± S.D.) for Ten Days after Egg Laying/Generation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| E/E | 62.9 ± 9.3 (27) a | 63.7 ± 7.5 (25) a | 63.6 ± 12.2 (21) a | 68.8 ± 12.7 (17) a | 76.9 ± 5.7 (18) a |
| I/I | 36.4 ± 6.2 (64) b | 25.3 ± 9.8 (26) b | 39.3 ± 7.1 (24) b | 27.2 ± 0.9 (48) b | 22.4 ± 3.2 (56) c |
| G/G | - | - | - | - | - |
| E/I | 44.7 ± 3.6 (64) b | 36.1 ± 2.8 (66) b | 31.6 ± 4.1 (62) b | 32.5 ± 3.9 (50) b | 21.6 ± 4.1 (70) c |
| E/G | 13.2 ± 2.0 (62) c | 21.8 ± 4.2 (62) b | 28.8 ± 5.4 (42) b | 11.4 ± 2.7 (48) c | 9.0 ± 0.6 (64) c |
| E+I/E+I | 69.0 ± 0.2 (70) a | 68.7 ± 5.5 (62) a | 62.4 ± 4.1 (70) a | 60.5 ± 2.3 (62) a | 53.5 ± 6.2 (70) b |
| E+G/E+G | 73.9 ± 3.7 (72) a | 74.0 ± 2.2 (68) a | 44.4 ± 5.5 (66) ab | 66.5 ± 2.1 (70) a | 63.2 ± 3.4 (22) b |
| Treatment | Survival (%) | Developmental Time (Days) | Fecundity/Day | Hatching Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rearing on plants | 92.3 ± 4.7 (109) a | 19.6 ± 0.6 (109) a | 73.1 ± 8.3 (35) a | 71.6 ± 0.9 (166) a |
| Plant-free rearing | 90.1 ± 5.1 (33) a | 19.2 ± 0.2 (33) a | 78.3 ± 7.1 (25) a | 72.8 ± 3.6 (149) a |
| Mass-Rearing Model of RDA (2014) 1 | Plant-Free Rearing Model |
|---|---|
| Total Cost $507.42 | Total Cost $149.67 |
|
|
| Soil (50 L): $8.22 × 1 ea. = $8.22 | Oasis (23 × 11 × 8 cm): $0.63 × 2 ea. = $1.26 |
| Rearing box (49 × 38 × 8 cm): $3.02 × 2 ea. = $6.04 | |
| Cage (50 × 47 × 37 cm): $83.89 × 2 ea. = $167.77 Compound fertilizer (1 kg): $10.07 × 1 ea. = $10.07 | |
|
Iron-coated Brine Shrimp eggs: $0.16 × 30 g = $4.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jun, H.-J.; Kim, K.-S.; Ham, E.-H. Basic Studies Aiming at Orius minutus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) Mass-Rearing. Insects 2022, 13, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010077
Jun H-J, Kim K-S, Ham E-H. Basic Studies Aiming at Orius minutus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) Mass-Rearing. Insects. 2022; 13(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010077
Chicago/Turabian StyleJun, Hye-Jeong, Kyoung-Su Kim, and Eun-Hye Ham. 2022. "Basic Studies Aiming at Orius minutus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) Mass-Rearing" Insects 13, no. 1: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010077





