A New Space-to-Ground Microwave-Based Two-Way Time Synchronization Method for Next-Generation Space Atomic Clocks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A New Method for Space-to-Ground Two-Way Time Synchronization
2.1. New Generation of Space Time-Frequency Loads
- High-performance space atomic clock (Allan deviation better than 10−17 @ 1 day);
- Precise orbit determination of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers;
- Microwave link module for code and carrier phase measurements;
- Laser link module.
2.2. Space-to-Ground Two-Way Time Synchronization Principle Based on a Single Frequency Mode
2.3. Various Error Corrections of High-Precision Space-to-Ground Time Synchronization
2.3.1. Motion Delay Error Correction
2.3.2. Correction of Periodic Relativistic Error Effect
2.3.3. Gravitational Time Delay Error Correction
3. Simulation Test and Performance Analysis
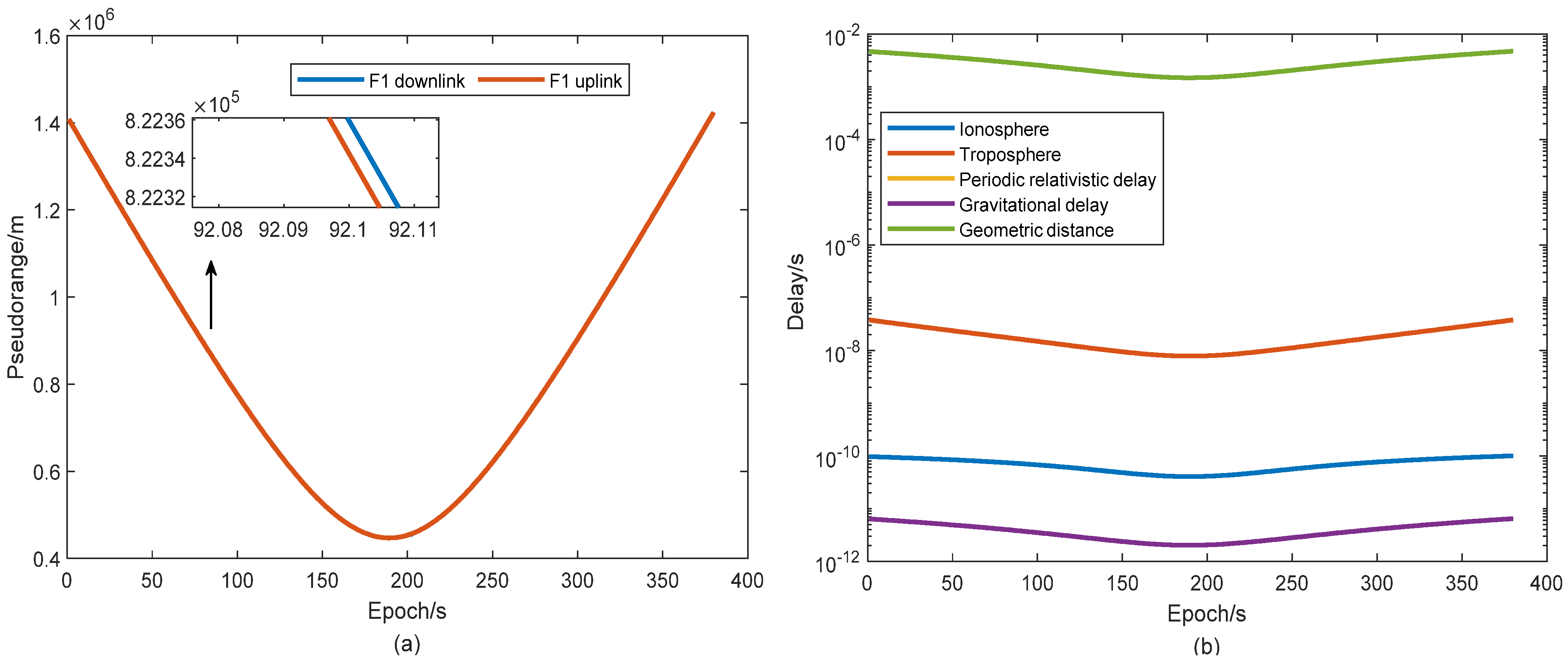
3.1. Low-Orbit Spacecraft-to-Ground Station Simulation Experiment
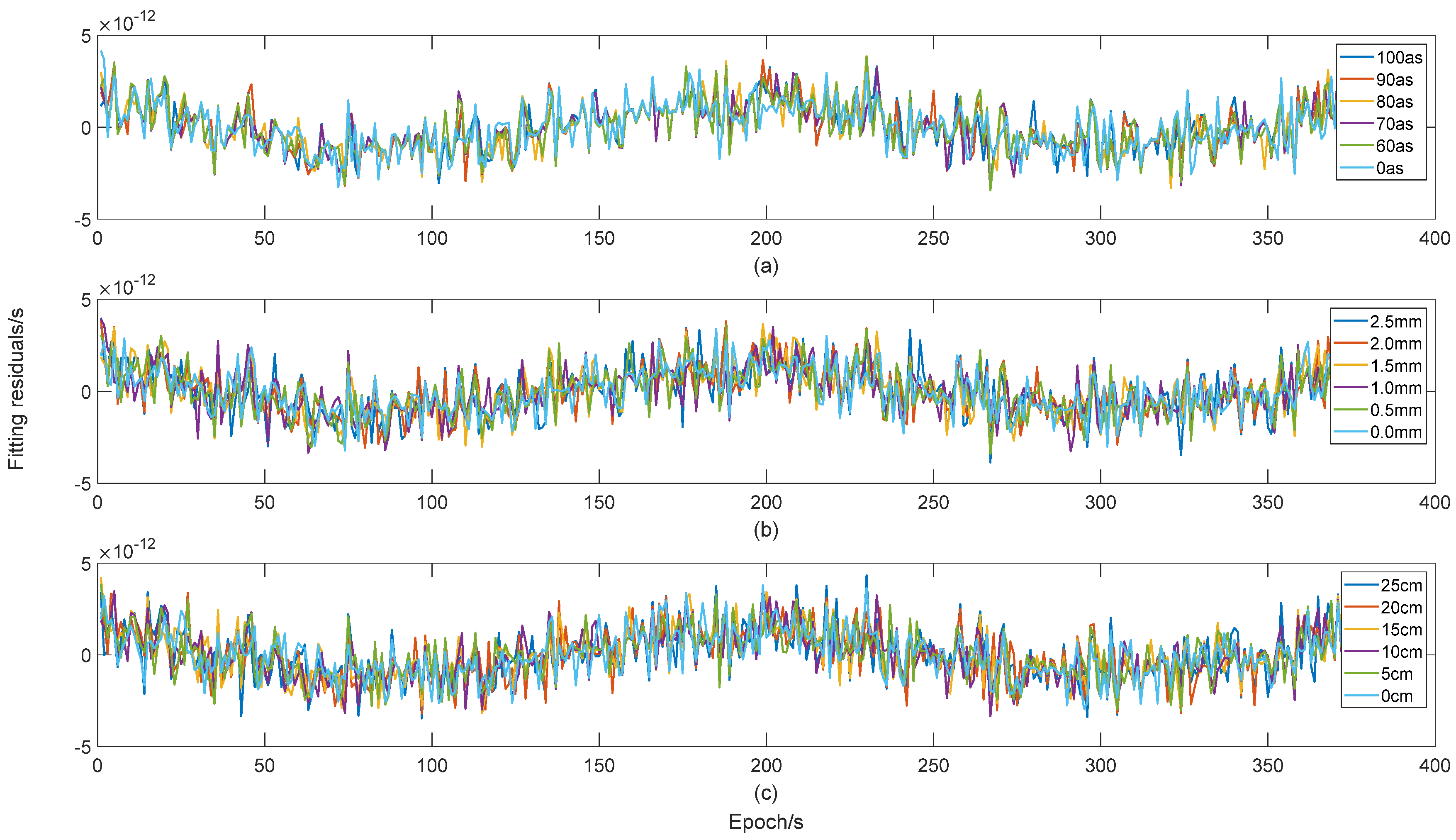
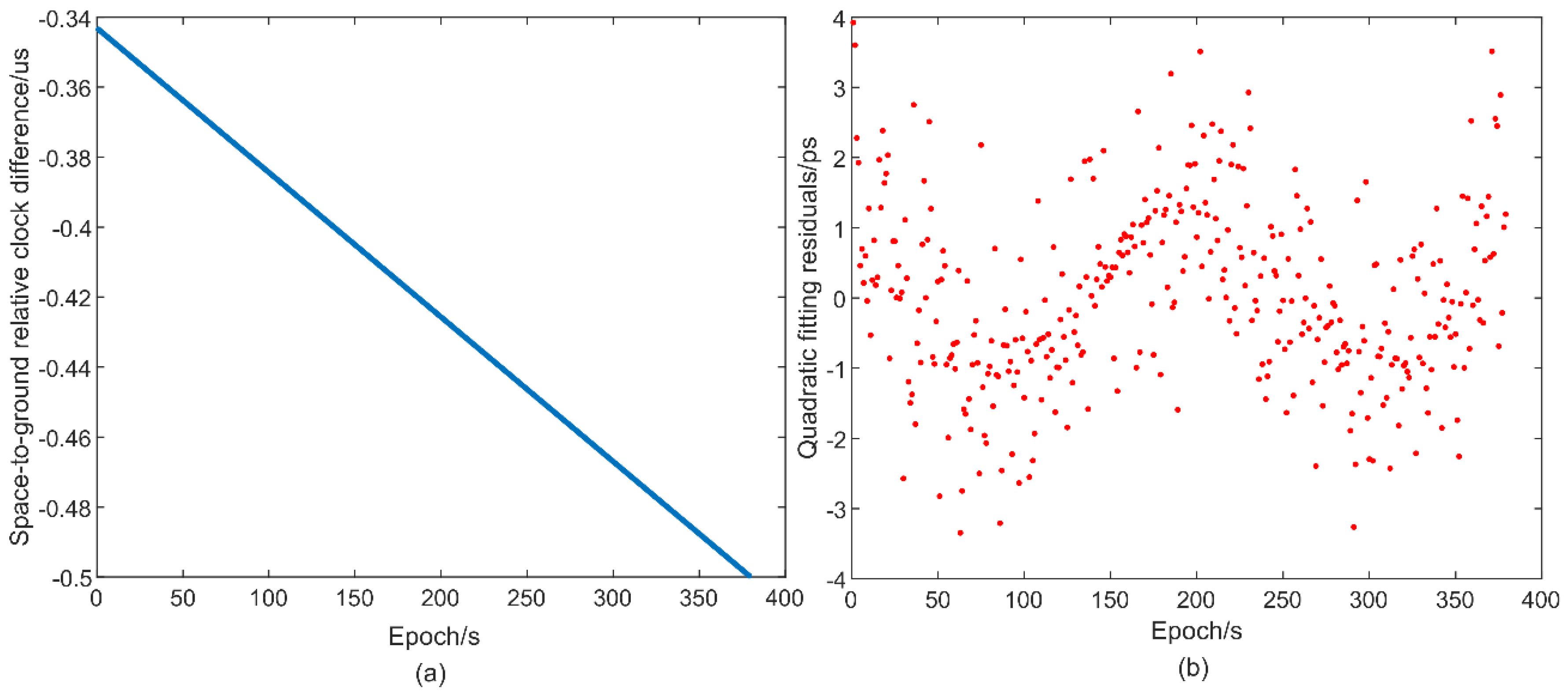
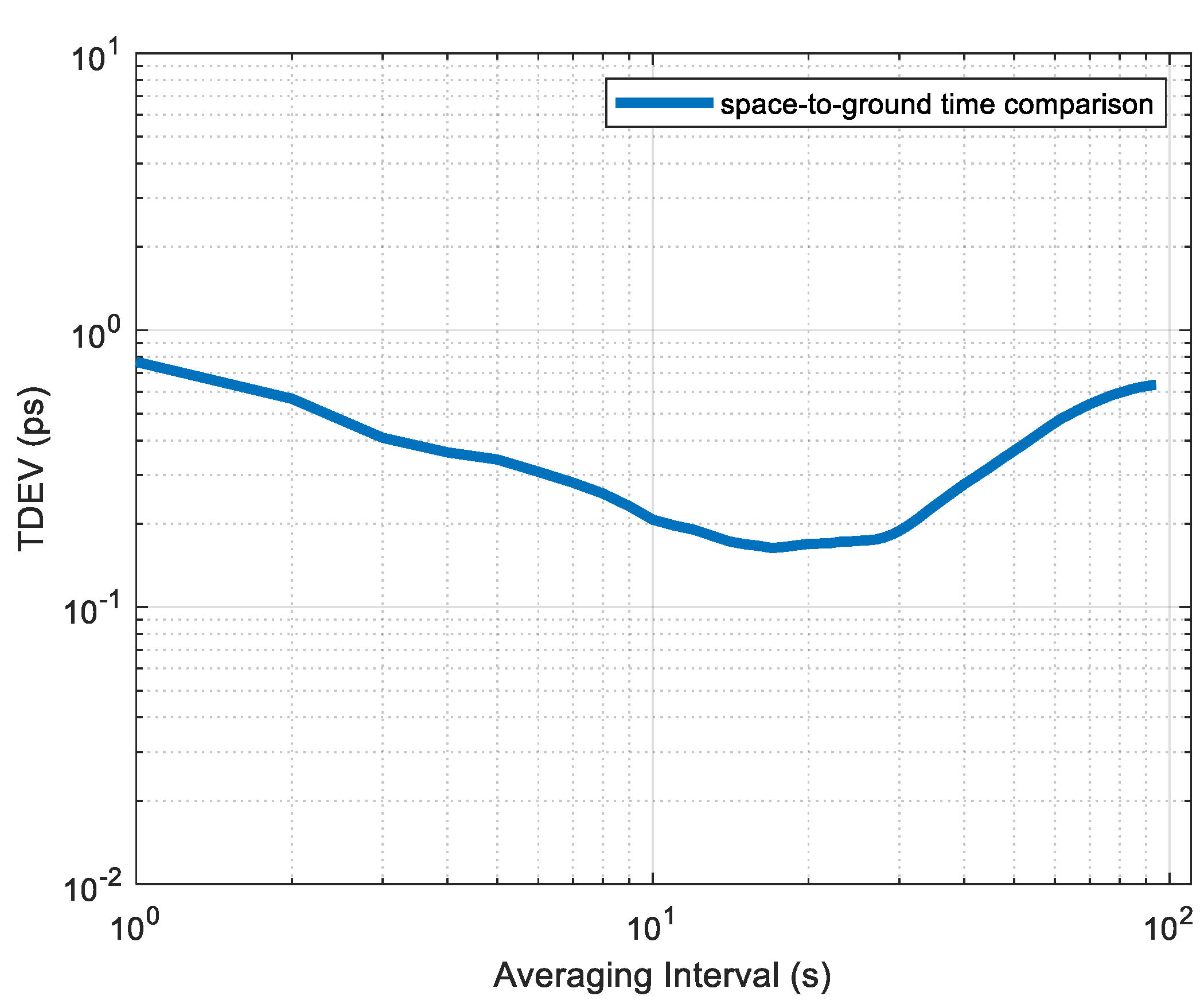
3.2. Space-to-Ground Time Synchronization Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, L. Fiber-based joint time and frequency dissemination via star-shaped commercial telecommunication network. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 080601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Tang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G. Time synchronization of new-generation BDS satellites using inter-satellite link measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Meng, W.; Han, W.; Xie, Y.; Ren, X.; Hu, X.; Dong, W. Advances in Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space of Europe and Ultraprecise Time and Frequency Transfer. Prog. Astron. 2016, 34, 221. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, P.; Abgrall, M.; Jentsch, C.; Lemonde, P. Design of the cold atom PHARAO space clock and initial test results. Appl. Phys. B. 2006, 84, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciapuoti, L.; Salomon, C. Space clocks and fundamental tests: The ACES experiment. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2009, 172, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. System design and key technologies of high accuracy time and frequency microwave link for spaces station. Telecommun. Eng. 2017, 57, 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, P.; Massonnet, D.; Cacciapuoti, L.; Salomon, C. The ACES/PHARAO space mission. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2015, 16, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savalle, E.; Guerlin, C.; Delva, P.; Meynadier, F.; Poncin-Lafitte, C.L.; Wolf, P. Gravitational redshift test with the future ACES mission. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 36, 245004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heb, M.P.; Stringhetti, L.; Hummelsberger, B.; Hausner, K.; Stalford, R.; Nasca, R.; Cacciapuoti, L.; Much, R.; Feltham, S.; Vudali, T. The ACES mission: System development and test status. Acta Astronaut. 2011, 29, 929–938. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciapuoti, L.; Much, R.; Feltham, S.; Nasca, R.; Vudali, T.; Hess, M.P.; Stringhetti, L.; Salomon, C. ACES status at completion of the engineering models phase. In Proceedings of the 2010 European Frequency and Time Forum, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 13–16 April 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, P.; Meynadier, F.; Le Poncin-Lafitte, C.; Laurent, P.; Wolf, P. Time and frequency transfer with a MicroWave Link in the ACES/PHARAO mission. In Proceedings of the 2012 European Frequency and Time Forum, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Origlia, S.; Pramod, M.S.; Schiller, S.; Singh, Y.; Viswam, S.; Bongs, K.; Hafner, S.; Berbers, S.; Dorscher, S.; Al-Masoudi, A. An optical lattice clock breadboard demonstrator for the I-SOC mission on the ISS. In Proceedings of the Lasers & Electro-optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference IEEE, Munich, Germany, 25–29 June 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Shi, W. Development of Deep Space Radio Ranging and Velocity Measurement Technology. J. Deep. Space Explor. 2018, 5, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Michalak, G.; Glaser, S.; Neumayer, K.H.; König, R. Precise orbit and Earth parameter determination supported by LEO satellites, inter-satellite links and synchronized clocks of a future GNSS. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4753–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, A.; Hess, M.P.; Kehrer, J.; Schafer, W.; Kufner, M.; Siccardi, M.; Cacciapuoti, L.; Aguilar Sanches, I.; Feltham, S. The ACES Microwave Link: Instrument Design and Test Results. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium Joint with the 21st European Frequency and Time Forum, Geneva, Switzerland, 29 May–1 June 2007; p. 1295. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X. Super-high accurate new metho d of common-view time comparison based on space station. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Satellite-ground two-way measuring method and performance evaluation of BDS-3 inter-satellite link system. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 157530–157540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X. Effect of Orbit Error on Space Station Time Comparison and Calibrating Method. J. Astronaut. 2019, 40, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Meynadier, F.; Delva, P.; Le Poncin Lafitte, C.; Guerlin, C.; Laurent, P.; Wolf, P. ACES Micro-wave link data analysis: Status update. In Proceedings of the Journées Systèmes De Référence Spatio Temporels Scientific Developments from Highly Accurate Space Time Reference Systems, Paris, France, 16–18 September 2013; pp. 134–135. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciapuoti, L. I-SOC Scientific Requirement. 2017. Available online: http://www.exphy.uni-duesseldorf.de/PDF/SCI-ESA-HRE-ESR-ISOC_Iss.1.1_Approved.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Pütz, C.; He, M.P.; Hummelsberger, B.; Hausner, K.; Prochazka, I. Aces mission status and outlook. In Proceedings of the 62nd International Astronautical Congress, Cape Town, South Africa, 3–7 October 2011; Volume 1, pp. 495–508. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciapuoti, L.; Armano, M.; Much, R.; Sy, O.; Salomon, C. Testing gravity with cold-atom clocks in space: The ACES mission. Eur. Phys. J. D 2020, 74, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Z. Research on Communication Delay Model for Narrow Beam Inter-satellite Links in a TDMA System. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2017 Proceedings, Shanghai, China, 23–25 May 2017; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hobiger, T.; Piester, D.; Baron, P. A correction model of dispersive troposphere delays for the ACES microwave link. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Li, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G.; Chang, Z.; Wu, S. System error calibration for time division multiple access inter-satellite payload of new-generation Beidou satellites. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J. Research on Determination and Time Synchronizing of Navigation Satellite Based on Crosslinks; National University of Defense Technology: Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Gao, S.; Pan, Z.; Han, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, X. A SatelliteGround Precise Time Synchronization Method and Analysis on Time Delay Error Caused by Motion. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2021 Proceedings, Nanchang, China, 26–28 May 2021; Volume 3, pp. 158–171. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Kang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. The Principle and Method of Beidou Satellite Navigation and Positioning; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Gao, S.; Yang, J.; Xiao, F.; Fang, Y.; Feng, S. Relativistic Effect in the Two-Way Time Comparison Between Navigation Satellites. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2021 Proceedings, Nanchang, China, 26–28 May 2021; Volume 3, pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wu, H.; Zhou, M.; Qi, J. Orbit Engineering Application and STK Simulation for Microsatellite; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H. Research on method of Satellite-Ground Time Synchronization Base on Ka Band ISL System of BDS; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Tao, E.; Xu, K. Centimeter-Level Orbit Determination for TG02 Spacelab Using Onboard GNSS Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meynadier, F.; Delva, P.; Poncin-Lafitte, C.L.; Guerlin, C.; Wolf, P. Atomic clock ensemble in space (ACES) data analysis. Class. Quantum Gravity 2018, 35, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinbach, U.; Schon, S. Improved GPS receiver clock modeling for kinematic orbit determination of the GRACE satellites. In Proceedings of the 2012 European Frequency and Time Forum, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 157–160. [Google Scholar]



| Arc | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chain Construction Start Time | 04:46:49 | 06:24:10 | 08:02:08 | 09:38:54 | 11:15:38 |
| Chain Construction End Time | 04:53:08 | 06:29:42 | 08:06:38 | 09:44:40 | 11:21:26 |
| Number of Epochs (s) | 380 | 333 | 271 | 347 | 359 |
| Attitude Error (as) | 0 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Way Time Synchronization Accuracy (ps) | 1.2732 | 1.2733 | 1.2822 | 1.3111 | 1.3167 | 1.3272 |
| Phase Centre Calibration Error (mm) | 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Way Time Synchronization Accuracy (ps) | 1.2295 | 1.2776 | 1.2930 | 1.3102 | 1.3469 | 1.3860 |
| Orbit Determination Error (cm) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Way Time Synchronization Accuracy (ps) | 1.2707 | 1.2825 | 1.2930 | 1.3495 | 1.3874 | 1.4352 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Gao, S.; Bai, Y.; Pan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. A New Space-to-Ground Microwave-Based Two-Way Time Synchronization Method for Next-Generation Space Atomic Clocks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030528
Guo Y, Gao S, Bai Y, Pan Z, Liu Y, Lu X, Zhang S. A New Space-to-Ground Microwave-Based Two-Way Time Synchronization Method for Next-Generation Space Atomic Clocks. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030528
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yanming, Shuaihe Gao, Yan Bai, Zhibing Pan, Yinhua Liu, Xiaochun Lu, and Shougang Zhang. 2022. "A New Space-to-Ground Microwave-Based Two-Way Time Synchronization Method for Next-Generation Space Atomic Clocks" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030528
APA StyleGuo, Y., Gao, S., Bai, Y., Pan, Z., Liu, Y., Lu, X., & Zhang, S. (2022). A New Space-to-Ground Microwave-Based Two-Way Time Synchronization Method for Next-Generation Space Atomic Clocks. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030528








