Current Density Limit of DC Grounding Facilities Considering Impact on Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
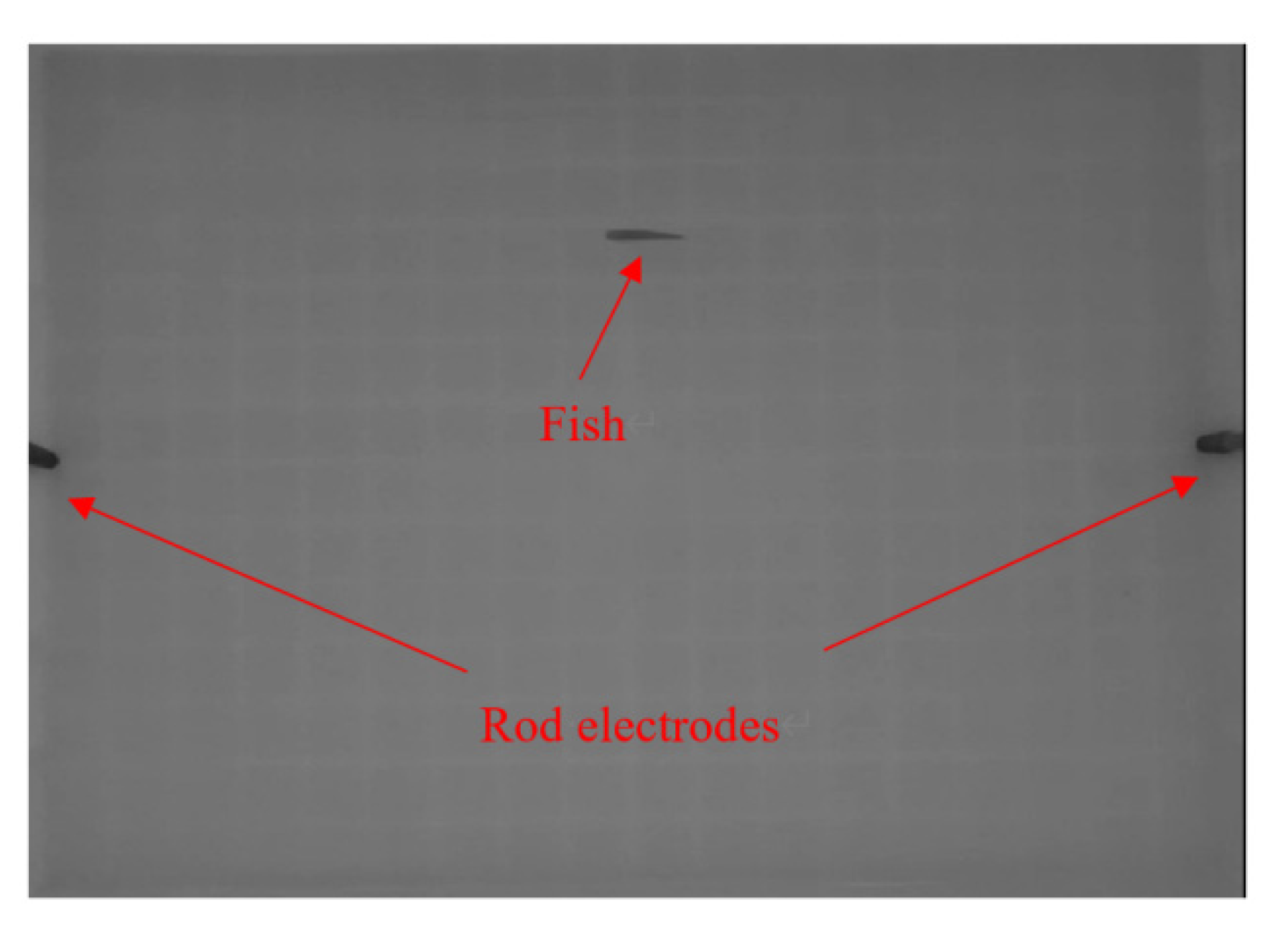
2.1. Design of Experiment
2.2. Choice of Fish
- Short in length to ensure that the length of the water tank used in the experiment would not affect the fish behavior and that the fish would be able to swim freely;
- Small in size, which is convenient for breeding, domestication, and experimental purposes;
- Lacking sensitivity to water quality to ensure that survival behaviors would not be triggered by slight changes in water quality;
- Present in abundance, meaning not rare or endangered, to ensure that the species could be easily obtained.
2.3. Processing Program for Object Recognition and Tracking
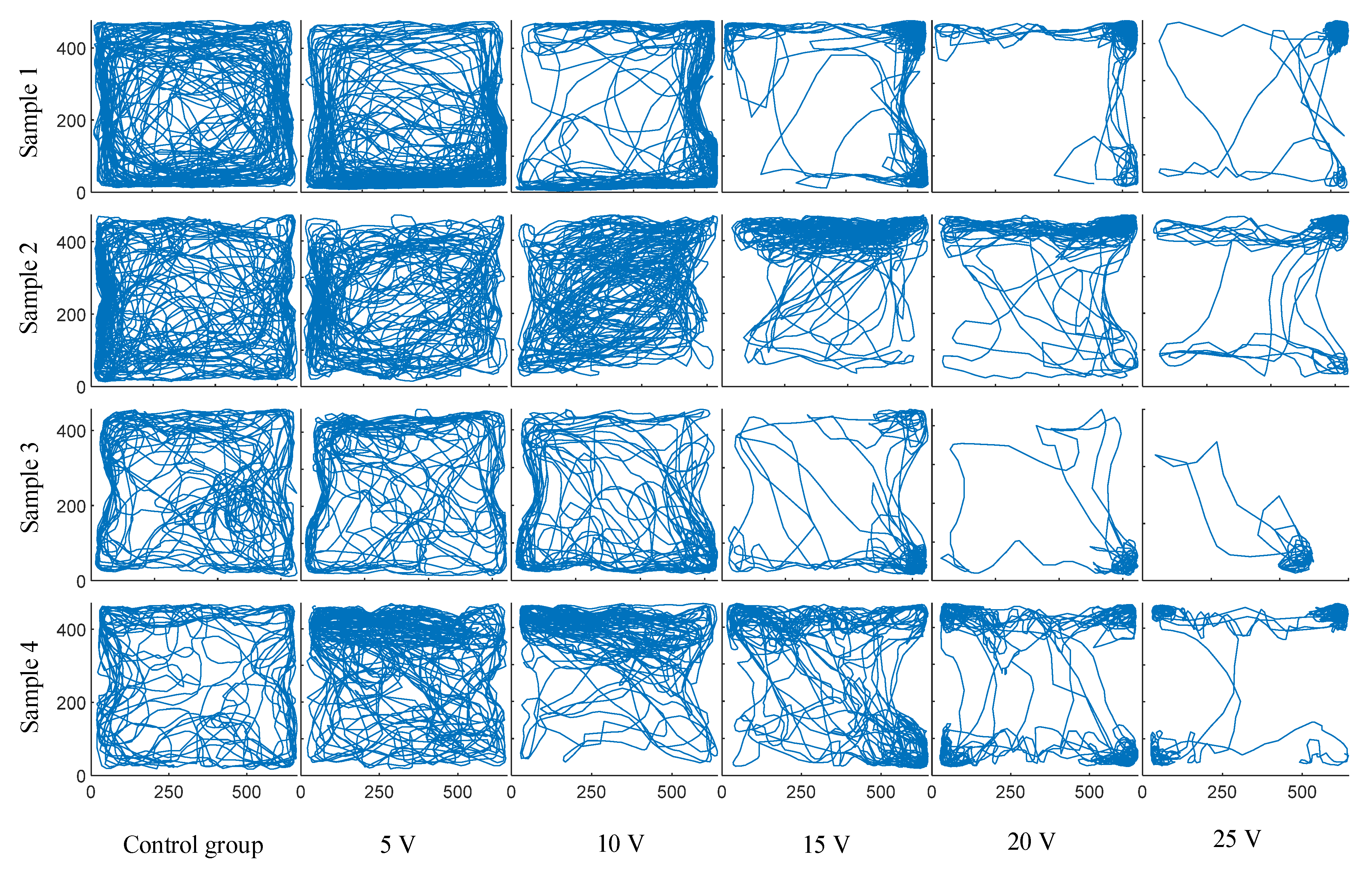
3. Results
4. Discussion
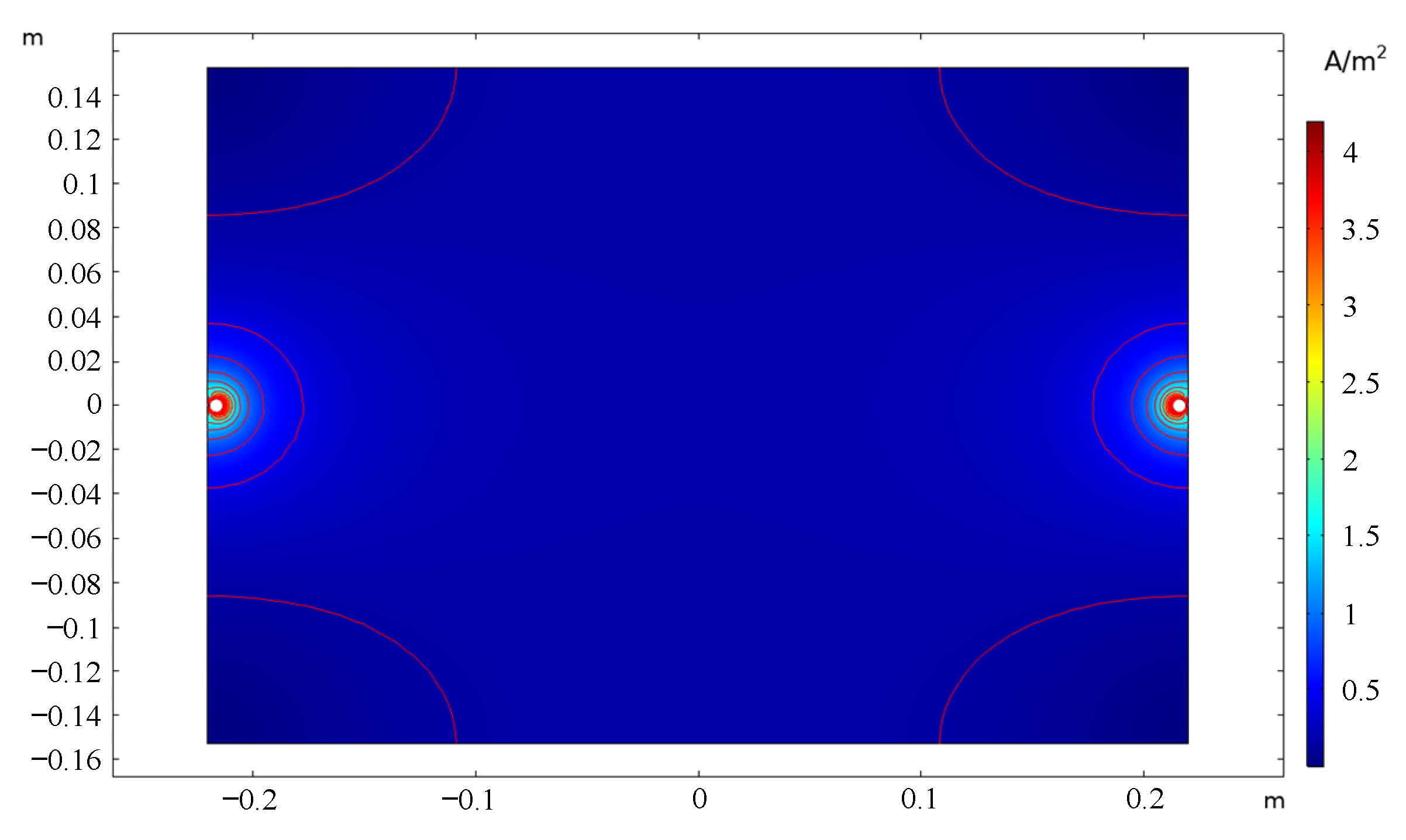
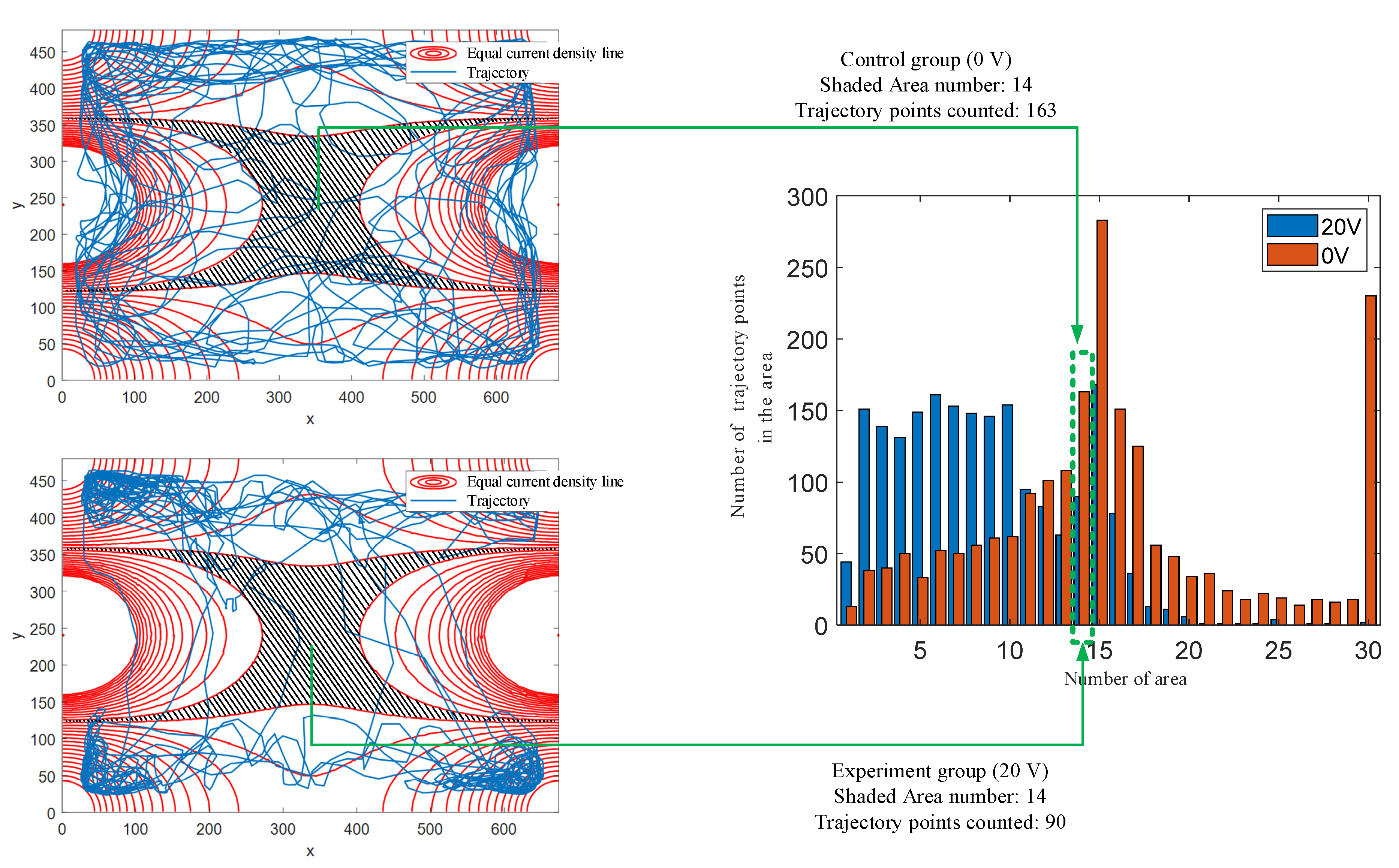
4.1. Statistical Analysis of Trajectory Changes through Current Density Calculation
4.2. Explanation of Trajectory and Statistical Results
4.3. Threshold of Turning Behavior
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marzinotto, M.; Mazzanti, G.; Nervi, M. Ground/sea return with electrode systems for HVDC transmission. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 100, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D. DC Stray Current in Rail Transit Systems and Cathodic Protection [History]. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2015, 22, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, A.; Liu, M.; Lin, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, L. A Multiple Section Model of Stray Current of DC Metro Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2020, 36, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-H. Analysis of Rail Potential and Stray Currents in a Direct-Current Transit System. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henyey, E.; Kynard, B.; Zhuang, P. Use of electronarcosis to immobilize juvenile lake and shortnose sturgeons for handling and the effects on their behavior. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterritt, D.A.; Elliott, S.T.; Schmidt, A.E. Electrical Anesthesia for Immobilizing Adult Coho Salmon in Freshwater. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1994, 14, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inger, R.; Attrill, M.J.; Bearhop, S.; Broderick, A.; Grecian, J.; Hodgson, D.J.; Mills, C.; Sheehan, E.; Votier, S.; Witt, M.; et al. Marine renewable energy: Potential benefits to biodiversity? An urgent call for research. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhman, M.C.; Sigray, P.; Westerberg, H. Offshore Windmills and the Effects of Electromagnetic Fields on Fish. AMBIO 2007, 36, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, L.; Sundqvist, F.; Bergström, U. Effects of an offshore wind farm on temporal and spatial patterns in the demersal fish community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 485, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrulewicz, E.; Napierska, R.; Otremba, Z. The environmental effects of the installation and functioning of the submarine SwePol Link HVDC transmission line: A case study of the Polish Marine Area of the Baltic Sea. J. Sea Res. 2003, 49, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.M.; Zhang, G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xing, B.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, S. Behavioral response of catfish in weak electric field. Mar. Fish. 2012, 2, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.W.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B.; Song, J. Avoidance behavior of Siberian Juvenile Sturgeon to dipole electric field. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2016, 40, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Prel, E. Effect of voltage gradient in an electrical field on threshold indices of fish response. Acta Ichthyol. et Piscat. 1991, 21, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TB675; General Guidelines for HVDC Electrode Design. CIGRE: Paris, France, 2017.
- IEC/TS 62344; Design of earth electrode stations for high-voltage direct current (HVDC) links-General guidelines. Commission I E: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Faugstad, K.; O’Brien, M.; Smith, M.; Zavahir, M. An Environmental Survey on the Operation and Impact of HVDC Electrode; CIGRE: Osaka, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Poléo, A.B.A.; Johannessen, H.; Harboe, M. High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Sea Cable and Sea Electrodes. Effects on Marine Life; University of Oslo: Oslo, Norway, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Marin Miljöanalys, A.B. Environmental Investigation Programme for Baltic Cable-Impact on Natural Habitat; Marin Miljöanalys AB: Göteborg, Sweden, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; He, J.; Zeng, R.; Wu, J. Effect of Coke Bed on the Electrical Performance of HVDC Ground Electrode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4594–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, G.; Martirano, L.; Parise, L.; Celozzi, S.; Araneo, R. Simplified conservative testing method of touch and step voltages by multiple auxiliary electrodes at reduced distance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Sheshyekani, K.; Alemi, M.R. The Effect of Frequency Dependence of Soil Electrical Parameters on the Lightning Performance of Grounding Systems. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2012, 55, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, S.; Slaoui, F. Modelling and simulation of heat dissipation due to HVDC ground electrodes using the finite element method. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT ASIA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–23 May 2014; pp. 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.S.; Teng, Y.; Cai, H.S.; Hu, S.M.; Jing, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, H.; Lan, L.; Lu, H.L. Experimental Study on Gas Evolution Characteristics of DC Deep Well Grounding Electrodes. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57450–57458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, B.; He, J. Influence of Coke Bed on HVDC Grounding Electrode Heat Dissipation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zha, Z.; Tan, B.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lan, L. Numerical Simulation and Field Test of the Transient Temperature Rise of HVdc Grounding Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2017, 33, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Evaluation of the Interference Effects of HVDC Grounding Current on a Buried Pipeline. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cao, F.; Zeng, R.; He, J.; Meng, X.; Liao, Y.; Li, R. DC Current Distribution in Both AC Power Grids and Pipelines Near HVDC Grounding Electrode Considering Their Interaction. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2019, 34, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, X.; Tan, B.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, X. Potential Compensation Method for Restraining the DC Bias of Transformers During HVDC Monopolar Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 31, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Yu, Z.; He, J.; Zhang, B.; Niu, B. Study on Restraining DC Neutral Current of Transformer During HVDC Monopolar Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, B. Vibration and Audible Noise Characteristics of AC Transformer Caused by HVDC System Under Monopole Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 27, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 39649; Laboratory Animal-Quality Control of Laboratory Fish. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Kato, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Ohkawa, M.; Muramoto, K.; Oyama, O.; Watanabe, A.; Nakashima, H.; Nemoto, T.; Sugitani, K. A computer image processing system for quantification of zebrafish behavior. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Yuan, X.Y.; Hui, P.; Zhao, J. Toxic effects of cadmium chloride exposure on neurobehavior of zebrafish larvae. Asian J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 8, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.G. Fish Behavior in Electric Field. China Fish. 1960, 11, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.C.; Lu, W.H.; Qian, X.R.; Chen, Z.Y. A preliminary study of crucian carp behavior under the strong DC field. Zhejiang Fish. Coll. 1994, 4, 282–286. [Google Scholar]





| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 28 |
| Conductivity (S/m) | 0.045 |
| pH | 7.25 |
| Subjects | Condition | Reaction | Threshold | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catfish | DC | Preference | 5.0 ± 0.1 mV/cm | [11] |
| Catfish | DC | Fear | 40 mV/cm | [11] |
| Siberian sturgeon | Dipole | Avoidance | 10 ± 1.0 μV/cm | [12] |
| fish | DC | Slight irritation | 0.02–0.05 mA/cm2 | [34] |
| Crucian, perch, and carp | DC | Anesthesia | 0.2–0.5 mA/cm2 | [34] |
| Crucian | DC | Anesthesia | 60 V/m | [35] |
| Crucian | DC | Stunned | 120 V/m | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Xu, K.; Tan, B.; Tong, X.; Teng, Y.; Li, C.; Lan, L.; Wen, X. Current Density Limit of DC Grounding Facilities Considering Impact on Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Sustainability 2022, 14, 3942. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14073942
Lu H, Chen J, Li G, Xu K, Tan B, Tong X, Teng Y, Li C, Lan L, Wen X. Current Density Limit of DC Grounding Facilities Considering Impact on Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Sustainability. 2022; 14(7):3942. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14073942
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Hailiang, Jiahao Chen, Guanhua Li, Kai Xu, Bo Tan, Xuefang Tong, Yun Teng, Chun Li, Lei Lan, and Xishan Wen. 2022. "Current Density Limit of DC Grounding Facilities Considering Impact on Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio)" Sustainability 14, no. 7: 3942. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14073942
APA StyleLu, H., Chen, J., Li, G., Xu, K., Tan, B., Tong, X., Teng, Y., Li, C., Lan, L., & Wen, X. (2022). Current Density Limit of DC Grounding Facilities Considering Impact on Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Sustainability, 14(7), 3942. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14073942






