- Review
Compositional Design of High-Entropy Alloys: Advances in Structural and Hydrogen Storage Materials
- Shaopeng Wu,
- Dongxin Wang and
- Cheng Zhang
- + 5 authors
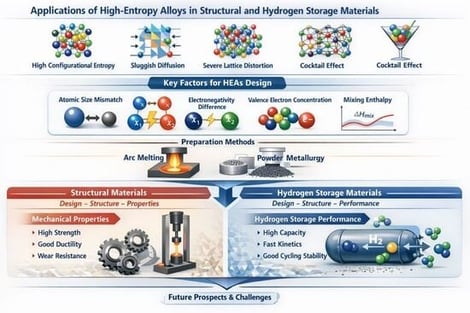
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) present a vast compositional design space, characterized by four core effects—high configurational entropy, sluggish diffusion, severe lattice distortion, and the cocktail effect—which collectively underpin their exceptional potential for both structural and hydrogen storage applications. This mini-review synthesizes recent advances in the compositional design of HEAs with emphasis on structural materials and hydrogen storage. Firstly, it provides an overview of the definition of HEAs and the roles of principal alloying elements, then synthesizes solid solution formation rules based on representative descriptors—atomic size mismatch, electronegativity difference, valence electron concentration, mixing enthalpy, and mixing entropy—together with their applicability limits and common failure scenarios. A brief introduction is provided to the preparation methods of arc melting and powder metallurgy, which have a strong interaction with the composition. The design–structure–property links are then consolidated for structural materials (mechanical properties) and for hydrogen storage materials (hydrogen storage performance). Furthermore, the rules for the combined design of control systems for HEAs and the associated challenges were further discussed, and the future development prospects of HEAs in structural materials and hydrogen storage were also envisioned.
7 January 2026