Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Smart Energy Systems Design
Printed Edition Available!
A printed edition of this Topical Collection is available
here.
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Surender Reddy Salkuti
Dr. Surender Reddy Salkuti
 Dr. Surender Reddy Salkuti
Dr. Surender Reddy Salkuti
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Railroad and Electrical Engineering, Woosong University, Daejeon 34606, Republic of Korea
Interests: market clearing including renewable energy sources; demand response; smart grid development with integration of wind and solar PV energy sources; artificial intelligence applications in power systems; power system analysis and optimization; energy and environmental economics; multi-objective optimization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We are pleased to announce this collection, entitled “Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: Smart Energy Systems Design”. This issue will be a collection of papers written by researchers who have been invited by the Editorial Board Members.
Smart energy systems that integrate multiple energy sectors are considered a promising paradigm for providing a comprehensive and optimized solution for an achievable, affordable, and sustainable energy system in the near future. Although extensive studies on the definition, implementation and optimization of these systems have been conducted, the design and management of a smart energy system remains a critical challenge. Thus, this collection aims to bring together the most recent research on a variety of exciting topics such as (but not limited to):
- Control and operation of modern power grids;
- Renewable energy power generation connected to the grid–microgrid;
- Energy harvesting and wireless power transfer technologies;
- Electronic equipment related to energy systems;
- Energy storage and electic vehicles;
- Big data and artificial intelligence.
Dr. Surender Reddy Salkuti
Prof. Dr. Dibin Zhu
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Designs is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- smart energy
- energy storage
- smart grid
- electric vehicles
- big data
- artificial intelligence
- energy harvesting
- wireless power transfer
- optimization
Published Papers (15 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Collaborative Control Strategy of Electric–Thermal–Hydrogen-Integrated Energy System Based on Variable-Frequency Division Coefficient
by
Lin He, Weichun Li, Hang Xu, Yue Wu, Qi Wang, Dengke Han, Yuming Liao and Jianyong Zhao
Viewed by 605
Abstract
To address the issues of diverse energy supply demands and power fluctuations in integrated energy systems (IESs), this study takes an IES composed of power-generation units, such as wind and photovoltaic units, along with various energy-storage systems, including electrical, thermal, and hydrogen storage,
[...] Read more.
To address the issues of diverse energy supply demands and power fluctuations in integrated energy systems (IESs), this study takes an IES composed of power-generation units, such as wind and photovoltaic units, along with various energy-storage systems, including electrical, thermal, and hydrogen storage, as the research subject. A collaborative control strategy is proposed for the IES, which comprehensively considers the status of diverse energy-storage systems like battery packs, thermal tanks, and hydrogen tanks. First, a mathematical model of the IES is constructed. Then, a dual-layer collaborative control strategy is designed, considering different operating modes of the IES, which includes a multi-energy-storage power allocation control layer based on second-order power-frequency processing and distribution and an adaptive adjustment layer for adjusting power-frequency coefficients based on adaptive fuzzy control. Finally, MATLAB is used to simulate and validate the proposed strategy. The results indicate that the collaborative control strategy based on variable-frequency coefficients optimizes the allocation of fluctuating power among multiple energy-storage systems, enhances the stability of bus voltage, reduces the deep charge and discharge time of battery packs, and extends the service life of battery packs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditorial
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Smart Energy System Design
by
Surender Reddy Salkuti
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 718
Abstract
The collection series presents various emerging approaches for designing growing renewable energy (RE), energy storage (ES), and smart transportation with electric vehicles (EVs) in the power and automobile industries [...]
Full article
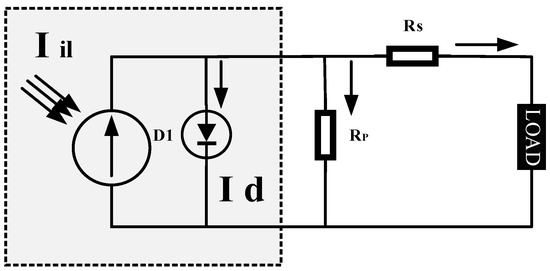
Open AccessArticle
Parameter Identification in Triple-Diode Photovoltaic Modules Using Hybrid Optimization Algorithms
by
Dhiaa Halboot Muhsen, Haider Tarish Haider and Yaarob Al-Nidawi
Viewed by 833
Abstract
Identifying the parameters of a triple-diode electrical circuit structure in PV modules is a critical issue, and it has been regarded as an important research area. Accordingly, in this study, a differential evolution algorithm (DEA) is hybridized with an electromagnetism-like algorithm (EMA) in
[...] Read more.
Identifying the parameters of a triple-diode electrical circuit structure in PV modules is a critical issue, and it has been regarded as an important research area. Accordingly, in this study, a differential evolution algorithm (DEA) is hybridized with an electromagnetism-like algorithm (EMA) in the mutation stage to enhance the reliability and efficiency of the DEA. A new formula is presented to adapt the control parameters (mutation factor and crossover rate) of the DEA. Seven different experimental data sets are used to improve the performance of the proposed differential evolution with an integrated mutation per iteration algorithm (DEIMA). The results of the proposed PV modeling method are evaluated with other state-of-the-art approaches. According to different statistical criteria, the DEIMA demonstrates superiority in terms of root mean square error and main bias error by at least 5.4% and 10%, respectively, as compared to other methods. Furthermore, the DEIMA has an average execution time of 27.69 s, which is less than that of the other methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Energy Access in Rural Indonesia: A Holistic Assessment of a 1 kW Portable Power Generator Based on Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
by
Handrea Bernando Tambunan, Reynolds Widhiyanurrochmansyach, Sabastian Pranindityo and Jayan Sentanuhady
Viewed by 937
Abstract
Hydrogen energy is a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels, offering a clean and sustainable solution to address the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation. Fuel cells provide direct and environmentally friendly conversion of chemical energy from a fuel source into electrical
[...] Read more.
Hydrogen energy is a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels, offering a clean and sustainable solution to address the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation. Fuel cells provide direct and environmentally friendly conversion of chemical energy from a fuel source into electrical energy, emitting only water vapor when utilizing hydrogen from renewable sources. This study delves into the design of a portable proton-exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) device tailored for household use in rural areas. The research focuses on achieving a minimum peak power of 1000 W and a voltage of 220 VAC at 50 Hz for the fuel cell. Employing theoretical calculations derived from existing formulas and literature reviews, various fuel cell components are meticulously assessed, including real power, voltage drop, performance under current load, and pressure drop on the bipolar plate. Additionally, the study encompasses the selection of auxiliary components like converters, inverters, fans, and others. The resultant fuel cell design showcases a device capable of generating a peak power of 1132.32 W with an efficiency rating of 48.66%. Identifying suitable auxiliary components further contributes to developing a practical and efficient portable power solution for rural households.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Systematic Literature Review on AC Microgrids
by
Marcos Gomez-Redondo, Marco Rivera, Javier Muñoz and Patrick Wheeler
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2183
Abstract
The objective of this work is to analyze and compare AC microgrid (ACMG) solutions to introduce the topic to new researchers. The methodology used to achieve this goal is a systematic literature review using five questions: (1) How have ACMGs evolved in five
[...] Read more.
The objective of this work is to analyze and compare AC microgrid (ACMG) solutions to introduce the topic to new researchers. The methodology used to achieve this goal is a systematic literature review using five questions: (1) How have ACMGs evolved in five years? (2) What are the standards for ACMGs? (3) What are the different schemes for connecting MGs to the utility grid? (4) What are the different control schemes in ACMGs? (5) What is an appropriate way to compare results when working with ACMGs? The articles were published in Q1/Q2 journals as based on either the Scimago Journal Rank (SJR) and/or the Journal Citation Report (JCR) between 2018 and 2022 and were from three databases: (1) Web of Science (WoS), (2) Scopus, and (3) IEEE Xplore. Publications not describing pure ACMGs, review papers, publications not related to the questions, and papers describing work that did not meet a quality assessment were excluded, resulting in 34 articles being included in this review. Results show: (1) the energy sources and AC bus nature of microgrids over five years, (2) the identification and quantification of cited standards for microgrids, (3) the pros and cons of different schemes for connecting an AC microgrid to the main grid, (4) the control schemes, classified in a hierarchical control structure, and (5) the simulation tools and experimental benches used in microgrids. Most studies considered a generic energy source and a low-voltage three-phase AC bus, 16 standards were found, and the most cited standard was IEEE Standard 1547. The most common connection scheme to the utility grid was a direct connection, most of the works proposed a modification to a hierarchical control system scheme, and the most common simulation tool was MATLAB. The preferred experimental setup consisted of parallel inverters for testing a control scheme, a prototype when proposing a power electronic system, and a laboratory microgrid for testing fault detection methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Application of Low-Temperature Geothermal Thermoelectric Power Generation (Lotemg–TPG) in Sari Ater Hot Spring, Ciater, Subang, West Java, Indonesia
by
Harapan Marpaung, Supriyadi, Ni Ketut Lasmi, Alamta Singarimbun and Wahyu Srigutomo
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1609
Abstract
The use of surface geothermal manifestations in Indonesia is still very limited as a tourist attraction. Solid-state thermoelectric generator technology is an alternative to converting electrical energy directly from a heat source in the form of low-temperature geothermal manifestation. Low-temperature geothermal thermoelectric power
[...] Read more.
The use of surface geothermal manifestations in Indonesia is still very limited as a tourist attraction. Solid-state thermoelectric generator technology is an alternative to converting electrical energy directly from a heat source in the form of low-temperature geothermal manifestation. Low-temperature geothermal thermoelectric power generation (Lotemg–TPG) was designed, manufactured, and tested to take advantage of this opportunity. It was also applied to the Sari Ater Hot Spring, Ciater. The Lotemg–TPG unit comprises seven M8T modules in two frame blocks equipped with hot- and cold-water circulation channels. The M8T module is the main part of the Lotemg–TPG, which consists of eight TEG elements of type TEG1-241-1.4-1.2, flanked by a hot-side radiator and a cold-side radiator. The measurement results showed that at the temperature difference between the hot-side T
h and the cold-side T
c of ∆
T 17.38 °C, one module can produce 1.30 W of power, so the total power of the Lotemg–TPG unit is around 9.10 W. This result is quite good considering that the heat source is obtained for free, and the device can operate to produce stable electrical power.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
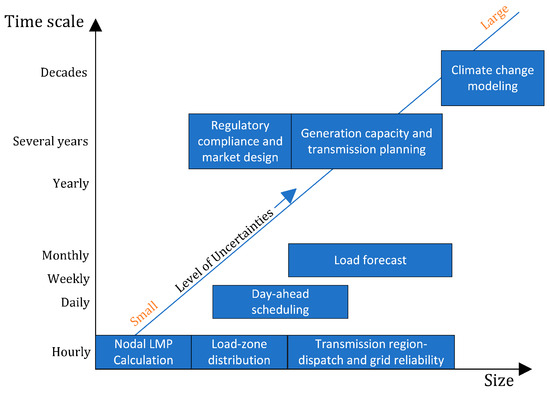
A Review of Uncertainties in Power Systems—Modeling, Impact, and Mitigation
by
Hongji Hu, Samson S. Yu and Hieu Trinh
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4584
Abstract
A comprehensive review of uncertainties in power systems, covering modeling, impact, and mitigation, is essential to understand and manage the challenges faced by the electric grid. Uncertainties in power systems can arise from various sources and can have significant implications for grid reliability,
[...] Read more.
A comprehensive review of uncertainties in power systems, covering modeling, impact, and mitigation, is essential to understand and manage the challenges faced by the electric grid. Uncertainties in power systems can arise from various sources and can have significant implications for grid reliability, stability, and economic efficiency. Australia, susceptible to extreme weather such as wildfires and heavy rainfall, faces vulnerabilities in its power network assets. The decentralized distribution of population centers poses economic challenges in supplying power to remote areas, which is a crucial consideration for the emerging technologies emphasized in this paper. In addition, the evolution of modern power grids, facilitated by deploying the advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), has also brought new challenges to the system due to the risk of cyber-attacks via communication links. However, the existing literature lacks a comprehensive review and analysis of uncertainties in modern power systems, encompassing uncertainties related to weather events, cyber-attacks, and asset management, as well as the advantages and limitations of various mitigation approaches. To fill this void, this review covers a broad spectrum of uncertainties considering their impacts on the power system and explores conventional robust control as well as modern probabilistic and data-driven approaches for modeling and correlating the uncertainty events to the state of the grid for optimal decision making. This article also investigates the development of robust and scenario-based operations, control technologies for microgrids (MGs) and energy storage systems (ESSs), and demand-side frequency control ancillary service (D-FCAS) and reserve provision for frequency regulation to ensure a design of uncertainty-tolerance power system. This review delves into the trade-offs linked with the implementation of mitigation strategies, such as reliability, computational speed, and economic efficiency. It also explores how these strategies may influence the planning and operation of future power grids.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
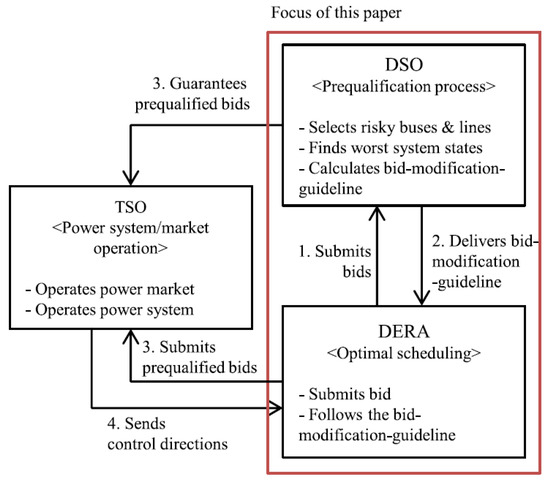
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Field Experiment for a Prequalification Scheme for a Distribution System Operator on Distributed Energy Resource Aggregations
by
Jung-Sung Park and Bal-Ho Kim
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1644
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to summarize and share the field experiment results of KEPCO’s project consortium to create a TSO-DSO-DERA interaction scheme. The field experiment was conducted based on the prequalification algorithm proposed in previous research from the same consortium, and
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this paper is to summarize and share the field experiment results of KEPCO’s project consortium to create a TSO-DSO-DERA interaction scheme. The field experiment was conducted based on the prequalification algorithm proposed in previous research from the same consortium, and was designed to verify the validity of the algorithm under realistic grid conditions. In addition, during the course of the field experiment, it was found that points that were missed or not given much importance in the existing prequalification algorithm could affect the completeness of the overall system, and then practical improvements were made to improve this. The demonstration results confirm that the proposed algorithm is effective in real-world grid environments and can help DSOs to ensure the reliability of the distribution system while supporting DERA’s participation in the wholesale market using the proposed prequalification scheme.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
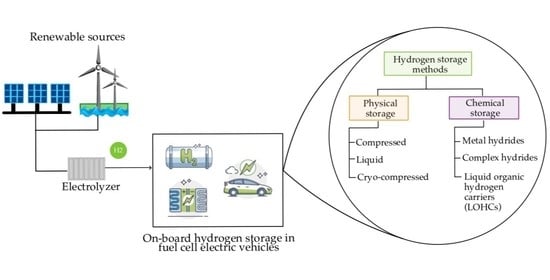
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
The Status of On-Board Hydrogen Storage in Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
by
Julián A. Gómez and Diogo M. F. Santos
Cited by 36 | Viewed by 12311
Abstract
Hydrogen as an energy carrier could help decarbonize industrial, building, and transportation sectors, and be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, power, or heat. One of the numerous ways to solve the climate crisis is to make the vehicles on our roads
[...] Read more.
Hydrogen as an energy carrier could help decarbonize industrial, building, and transportation sectors, and be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, power, or heat. One of the numerous ways to solve the climate crisis is to make the vehicles on our roads as clean as possible. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) have demonstrated a high potential in storing and converting chemical energy into electricity with zero carbon dioxide emissions. This review paper comprehensively assesses hydrogen’s potential as an innovative alternative for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in transportation, particularly for on-board applications. To evaluate the industry’s current status and future challenges, the work analyses the technology behind FCEVs and hydrogen storage approaches for on-board applications, followed by a market review. It has been found that, to achieve long-range autonomy (over 500 km), FCEVs must be capable of storing 5–10 kg of hydrogen in compressed vessels at 700 bar, with Type IV vessels being the primary option in use. Carbon fiber is the most expensive component in vessel manufacturing, contributing to over 50% of the total cost. However, the cost of FCEV storage systems has considerably decreased, with current estimates around 15.7 $/kWh, and is predicted to drop to 8 $/kWh by 2030. In 2021, Toyota, Hyundai, Mercedes-Benz, and Honda were the major car brands offering FCEV technology globally. Although physical and chemical storage technologies are expected to be valuable to the hydrogen economy, compressed hydrogen storage remains the most advanced technology for on-board applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Performance Explorations of a PMS Motor Drive Using an ANN-Based MPPT Controller for Solar-Battery Powered Electric Vehicles
by
Anjuru Viswa Teja, Wahab Razia Sultana and Surender Reddy Salkuti
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2139
Abstract
Solar energy can function as a supplementary power supply for other renewable energy sources. On average, Vellore region experiences approximately six hours of daily sunshine throughout the year. Solar photovoltaic (PV) modules are necessary to monitor and fulfill the energy requirements of a
[...] Read more.
Solar energy can function as a supplementary power supply for other renewable energy sources. On average, Vellore region experiences approximately six hours of daily sunshine throughout the year. Solar photovoltaic (PV) modules are necessary to monitor and fulfill the energy requirements of a given day. An artificial neural network (ANN) based maximum power point tracking (MPPT) controller is utilised to regulate the solar photovoltaic (PV) array and enhance its output. The utilisation of this controller can enhance the efficiency of the module even in severe circumstances, where reduced current and torque ripples will be observed on the opposite end. The motorised vehicle has the capability to function at its highest torque level in different load scenarios as a result. The proposed method is expected to provide advantages in various electric vehicle (EV) applications that require consistent velocity and optimal torque to satisfy the load conditions. The study employs a solar battery that is linked to an SVPWM inverter and subsequently a DC-DC boost converter to supply power to the load. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) based Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) control system is proposed for a solar battery powered Electric Vehicle (EV) and the system’s performance is evaluated by collecting and analysing data under adjustable load conditions to obtain constant parameters such as speed and torque. The MATLAB
® Simulink
® model was utilised for this purpose.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
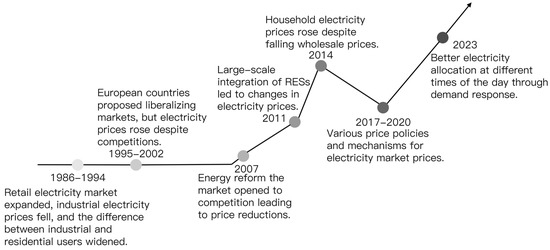
Electricity Pricing and Its Role in Modern Smart Energy System Design: A Review
by
Jiaqi Liu, Hongji Hu, Samson S. Yu and Hieu Trinh
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4904
Abstract
Energy is the foundation for human survival and socio-economic development, and electricity is a key form of energy. Electricity prices are a key factor affecting the interests of various stakeholders in the electricity market, playing a significant role in the sustainable development of
[...] Read more.
Energy is the foundation for human survival and socio-economic development, and electricity is a key form of energy. Electricity prices are a key factor affecting the interests of various stakeholders in the electricity market, playing a significant role in the sustainable development of energy and the environment. As the number of distributed energy resources (DERs) increases, today’s power systems no longer rely on a vertical market model and fixed electricity pricing scheme but instead depend on power dispatch and dynamic pricing to match supply and demand. This can help prevent significant fluctuations in supply–load imbalance and maintain system stability. Modern power grids have evolved by integrating information, communication, and intelligent control technologies with traditional power systems, giving rise to the concept of smart electric grids. Choosing an appropriate pricing scheme to manage large-scale DERs and controllable loads in today’s power grid become very important. However, the existing literature lacks a comprehensive review of electricity pricing in power systems and its transformative impact on shaping the energy landscape. To fill this void, this paper provides a survey on the developments, methods, and frameworks related to electricity pricing and energy trading. The review mainly considers the development of pricing in a centralized power grid, peer-to-peer (P2P) and microgrid-to-microgrid (M2M) energy trading and sharing, and various pricing methods. The review will cover the pricing schemes in modern power systems, particularly with respect to renewable energy sources (RESs) and batteries, as well as controllable load applications, and the impact of pricing schemes based on demand-side ancillary services (DSAS) for grid frequency support. Lastly, this review article describes the current frameworks and limitations of electricity pricing in the current energy market, as well as future research directions. This review should offer a great overview and deep insights into today’s electricity market and how pricing methods will drive and facilitate the future establishment of smart energy systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
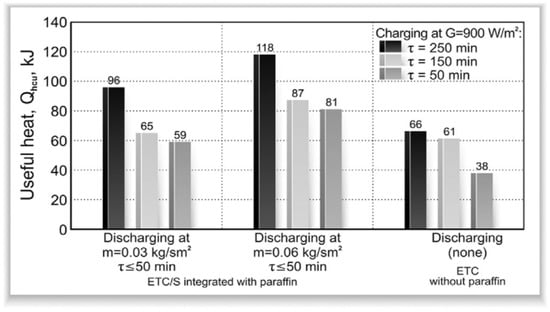
Recent Advances, Development, and Impact of Using Phase Change Materials as Thermal Energy Storage in Different Solar Energy Systems: A Review
by
Farhan Lafta Rashid, Mudhar A. Al-Obaidi, Anmar Dulaimi, Haitham Y. Bahlol and Ala Hasan
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 4958
Abstract
The efficient utilization of solar energy technology is significantly enhanced by the application of energy storage, which plays an essential role. Nowadays, a wide variety of applications deal with energy storage. Due to the intermittent nature of solar radiation, phase change materials are
[...] Read more.
The efficient utilization of solar energy technology is significantly enhanced by the application of energy storage, which plays an essential role. Nowadays, a wide variety of applications deal with energy storage. Due to the intermittent nature of solar radiation, phase change materials are excellent options for use in several types of solar energy systems. This overview of the relevant literature thoroughly discusses the applications of phase change materials, including solar collectors, solar stills, solar ponds, solar air heaters, and solar chimneys. Despite the complexity of their availability and high costs, phase change materials are utilized in the majority of solar energy techniques because of the considerable technical improvements they provide. While numerous studies have investigated the progress of phase change materials used in solar energy applications such as photovoltaic systems, it is vital to understand the conceptual knowledge of employing phase change materials in various types of solar thermal energy systems. Investigations into the use of phase change materials in solar applications for the purpose of storing thermal energy are still being carried out to upgrade the overall performance. This paper briefly reviews recently published studies between 2016 and 2023 that utilized phase change materials as thermal energy storage in different solar energy systems by collecting more than 74 examples from the open literature. This study focuses on demonstrating the maturity of phase change materials and their integration into solar energy applications. Based on the findings, proposals for new research projects are made.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
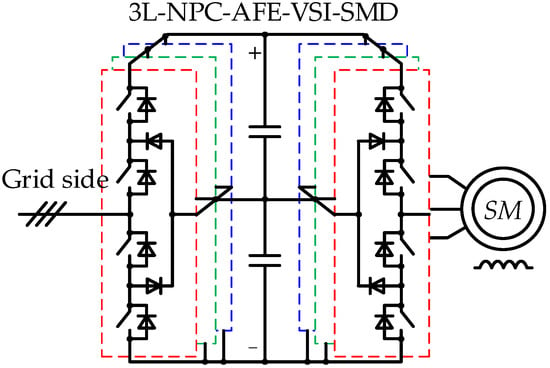
Control over Grid Reactive Power by Using a Powerful Regenerative Controlled-Speed Synchronous Motor Drive
by
Aleksandr S. Maklakov, Aleksandr A. Nikolaev and Tatyana A. Lisovskaya
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2244
Abstract
The authors propose a technique for reactive power compensation using a powerful regenerative controlled-speed synchronous motor drive (SMD) based on a three-level (3L) neutral point clamped (NPC) active front-end rectifier (AFE) and a voltage source inverter (VSI). The review of technical solutions for
[...] Read more.
The authors propose a technique for reactive power compensation using a powerful regenerative controlled-speed synchronous motor drive (SMD) based on a three-level (3L) neutral point clamped (NPC) active front-end rectifier (AFE) and a voltage source inverter (VSI). The review of technical solutions for reactive power compensation showed that the limitations on the transmitted reactive power in the system under consideration still have not been studied. The paper provides a mathematical description and proposes synthesis-friendly block diagrams of the mathematical 3L-NPC-AFE-VSI and SMD models. The developed models allow defining the instantaneous values of the total 3L-NPC-AFE power consumed from the grid depending on the SMD load diagram. It is noted that the 3L-NPC-AFE-VSI-SMD system is designed without considering the opportunities for reactive power generation. It was determined that the limit value of reactive power generated by a 3L-NPC-AFE depends on the DC link voltage, the grid current consumption and the modulation index. The possibility of reactive power compensation by the SMD system through a 3L-NPC-AFE was experimentally tested on the main drive of a metal plate hot rolling mill. The analysis of the results obtained showed that during the breakdown, an SMD can generate reactive power equal to 16% of the total rated power using a 3L-NPC-AFE at a rated DC link voltage and without overcurrent. It was shown that generating reactive power is expedient in low-load SMD operation modes or at idle. Research in this area is promising due to the widespread use of high-power SMD based on a 3L-NPC-AFE-VSI and the tightening of requirements for energy saving and efficiency and supply voltage quality. The proposed reactive power control technique can be used as part of an industrial smart grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
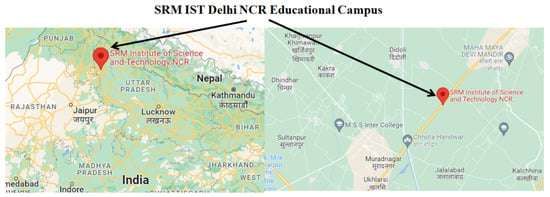
Technical and 2E Analysis of Hybrid Energy Generating System with Hydrogen Production for SRM IST Delhi-NCR Campus
by
Shilpa Sambhi, Himanshu Sharma, Vikas Bhadoria, Pankaj Kumar, Georgios Fotis and Lambros Ekonomou
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2475
Abstract
This work intends to perform technical and 2E (economic & environmental) analysis for the proposed hybrid energy generating system for a part load at SRM IST at the Delhi-NCR campus, India. The investigation has been done for electricity generation and hydrogen production through
[...] Read more.
This work intends to perform technical and 2E (economic & environmental) analysis for the proposed hybrid energy generating system for a part load at SRM IST at the Delhi-NCR campus, India. The investigation has been done for electricity generation and hydrogen production through renewable energy sources, mainly solar energy. It is in line with the Indian Government’s initiatives. The proposed hybrid system has to meet the electric load demand of 400 kWh/day with a peak load of 74.27 kW and hydrogen load demand of 10 kg/day with a peak demand of 1.86 kg/h. The analysis has been performed for both on-grid and off-grid conditions. As a result, optimum results have been obtained off-grid condition, with $0.408 per kWh cost of energy, $16.6 per kg cost of hydrogen, low O&M cost ($21,955 per year), a high renewable fraction (99.8%), and low greenhouse emissions (247 kg/year). In addition, sensitivity analysis has been performed between—(1) the solar PV array size & the number of battery strings, with NPC, renewable fraction & CO
2 emissions as sensitivity variables, and (2) reformer capacity & hydrogen tank capacity, with NPC as sensitivity variable.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Hybrid Control and Energy Management of a Residential System Integrating Vehicle-to-Home Technology
by
Khadija El Harouri, Soumia El Hani, Nisrine Naseri, Elhoussin Elbouchikhi, Mohamed Benbouzid and Sondes Skander-Mustapha
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2841
Abstract
Electric vehicles (EV) and photovoltaic (PV) systems are increasingly becoming environmentally friendly and more affordable solutions for consumers. This article discusses the integration of PV and EV in a residential system to meet the requirements of residential loads taking into account the PV
[...] Read more.
Electric vehicles (EV) and photovoltaic (PV) systems are increasingly becoming environmentally friendly and more affordable solutions for consumers. This article discusses the integration of PV and EV in a residential system to meet the requirements of residential loads taking into account the PV supplied power, availability and the state of charge (SOC) of EVs. A hybrid control model has been proposed to control the residential system. The combined PI-Fuzzy logic controller is employed to control the buck-boost bi-directional converter. The DC-AC grid-side converter is controlled by the ADRC controller. The effectiveness of PI-Fuzzy logic controller in reducing voltage and current ripples and ADRC controller in rejecting disturbances is demonstrated in each case. A rule-based energy management strategy has been proposed to control the flow of energy between the components of the residential system. The suggested energy management system (EMS) covers every scenario that might occur. Whether the EV is linked to the home or not, and also takes into account the owner using the EV in an emergency situation. The EV operates in two modes, Home-to-Vehicle (H2V) mode and Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) mode, depending on the power produced by the PV and the conditions related to the EV. All possible scenarios are tested and validated. The simulation results show that the proposed EMS is a reliable solution that can reduce the power grid intervention.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures