-
 Design of an Array to Evaluate Biomarkers of Response to Biological Treatments in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Design of an Array to Evaluate Biomarkers of Response to Biological Treatments in Inflammatory Bowel Disease -
 Old and New Analgesic Acetaminophen: Pharmacological Mechanisms Compared with Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Old and New Analgesic Acetaminophen: Pharmacological Mechanisms Compared with Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs -
 Assessing the Pharmacological and Pharmacogenomic Data of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy Outcomes in the Clinical Setting
Assessing the Pharmacological and Pharmacogenomic Data of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy Outcomes in the Clinical Setting
Journal Description
Future Pharmacology
Future Pharmacology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on pharmacology, drug discovery, and therapeutics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), EBSCO, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Pharmacology and Pharmacy)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Future Pharmacology is a companion journal of Pharmaceutics.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
Galantamine as a Potential Treatment for Peripheral Nerve Injuries: Emphasis on Non-Systemic Delivery
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040063 (registering DOI) - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
Peripheral nerve injuries can lead to significant functional impairments, and treatment options remain limited. Galantamine, widely used for cognitive disorders, has shown potential effects on the peripheral nervous system, making it a candidate for new therapeutic approaches. The narrative review explores the use
[...] Read more.
Peripheral nerve injuries can lead to significant functional impairments, and treatment options remain limited. Galantamine, widely used for cognitive disorders, has shown potential effects on the peripheral nervous system, making it a candidate for new therapeutic approaches. The narrative review explores the use of galantamine for peripheral nerve injuries, with a focus on transdermal and iontophoretic delivery methods. Searches in scientific databases revealed no peer-reviewed publications addressing this specific application. As a result, the review expanded to include printed and offline sources and a broader timeframe to capture earlier reports. Available evidence from Bulgaria suggests that galantamine ampules have been applied via iontophoresis for peripheral neuropathy. However, this approach is not documented in established scientific databases, and information on its safety and effectiveness is limited. Overall, research on transdermal galantamine for peripheral nerve injuries is still scarce. More studies are needed to better understand its potential benefits and to optimize safe delivery methods.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Cannabidiol Modulates the Effects of Levetiracetam on Seizure Parameters and Behavioral Outcomes in Pentylenetetrazol-Kindled Rats
by
Emília Simon, Noémi Miklós, Sorana-Denisa Frandeș, Melinda Kolcsar and Zsolt Gáll
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040062 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The antiseizure effects of cannabidiol (CBD) were extensively studied when used as a monotherapy. However, there is conflicting evidence regarding its use in combination with levetiracetam (LEV). Methods: This study explored the effects of chronic co-administration of CBD and LEV
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The antiseizure effects of cannabidiol (CBD) were extensively studied when used as a monotherapy. However, there is conflicting evidence regarding its use in combination with levetiracetam (LEV). Methods: This study explored the effects of chronic co-administration of CBD and LEV in a pentylenetetrazole-kindling rat model to evaluate potential antiseizure and neuropsychiatric interactions. Male and female Wistar rats (n = 48) were divided into four treatment groups: one control and three treated by receiving LEV 300 mg/kg and LEV + CBD at 10 and 60 mg/kg, respectively. Seizure parameters were assessed using the Racine scale, and behavior was evaluated using the open field (OF), novel object recognition (NOR), and social interaction (SI) tests. Results: While both combinations, LEV + CBD 10 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg, significantly reduced maximal seizure intensity, the LEV + CBD 10 mg/kg attenuated LEV’s anti-kindling effect. Additionally, only LEV + CBD 60 mg/kg reduced seizure duration compared to LEV alone (p = 0.0002). In behavioral assessments, LEV + CBD 10 mg/kg showed anxiolytic effects in the OF test by increasing central activity (p = 0.0141). In contrast, the LEV + CBD 60 mg/kg impaired social behavior in both sexes (p = 0.0019). LEV improved the cognitive performance of female rats in the NOR test (p = 0.0301), but this improvement was not observed in LEV + CBD groups. Conclusions: CBD exhibited dose-dependent effects when combined with LEV: low doses might offer anxiolytic effects but promote kindling, and high doses enhance seizure control but potentially worsen social interaction. The results support the therapeutic potential of LEV-CBD co-treatment, while highlighting the need for careful dose optimization when considering CBD as an adjunctive therapy.
Full article
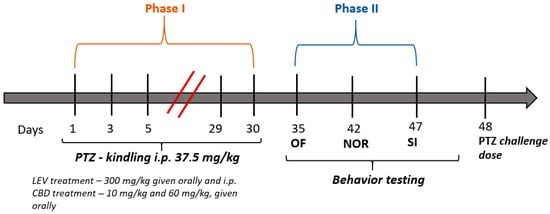
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness and Safety of Linezolid as Continuous Infusion Versus Intermittent Infusion in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
by
Ligia-Ancuța Hui, Ana-Maria Vlase, Elisabeta Ioana Hirișcău, Constantin Bodolea, Andrei-Mihai Bălan, Laurian Vlase and Adina Popa
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040061 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Linezolid is a reserve antibiotic used to treat infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria with resistance genes. In critically ill patients, high intra- and interindividual variability has been observed, prompting the search for alternative methods to reduce this variability and achieve the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Linezolid is a reserve antibiotic used to treat infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria with resistance genes. In critically ill patients, high intra- and interindividual variability has been observed, prompting the search for alternative methods to reduce this variability and achieve the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic indices necessary for a favorable efficacy–safety balance. Aim of the study: We wished to compare the safety and effectiveness of a continuous infusion (CI) versus an intermittent infusion (II) of linezolid in patients requiring intensive care. Materials and Methods: This study, registered under the number NCT05801484), was a prospective, open-label, single-center, two-arm study. Data on hematologic safety and effectiveness were collected and compared between patients receiving CI and II, respectively, at the same daily dose of linezolid (1200 mg). Results: Twenty-nine patients from the intensive care unit were included, divided into two groups. No statistically significant difference was found in 30-day mortality between the groups, nor in the likelihood of post-treatment culture negativity. However, a significantly greater reduction in C-reactive protein levels was observed in the CI group compared to the II group. Regarding safety, at CrCl < 60 mL/min, the decrease in platelets was statistically significant in group II but not in group CI. Additionally, at the 30-day follow-up, recovery from thrombocytopenia was better in the CI group. Conclusions: Continuous infusion of linezolid proved to be non-inferior to intermittent infusion at the same daily dose in terms of effectiveness. Furthermore, a lower risk of adverse reactions was identified with continuous infusion.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Superoxide Anion Generation, Its Pathological Cellular and Molecular Roles and Pharmacological Targeting in Inflammatory Pain: Lessons from the Potassium Superoxide Model
by
Beatriz Hoffmann Sales Bianchini, Geovana Martelossi-Cebinelli, Jessica Aparecida Carneiro, Fernanda Soares Rasquel-Oliveira, Rubia Casagrande and Waldiceu A. Verri
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040060 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are formed by the incomplete reduction of oxygen and play a crucial role in both physiological function and pathological process, being controlled by enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems. However, excessive ROS production can exceed the body’s antioxidant capacity, resulting
[...] Read more.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are formed by the incomplete reduction of oxygen and play a crucial role in both physiological function and pathological process, being controlled by enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems. However, excessive ROS production can exceed the body’s antioxidant capacity, resulting in oxidative stress and causing cell death and oxidation of important biomolecules. In this context, the inhibition and/or modulation of ROS has been shown to be effective in reducing pain, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Among ROS, superoxide anion (O2•−) is the first free radical to be formed through the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) or by specific enzymes systems, such as the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) complex. O2•− plays a significant role in the development and maintenance of pain associated with inflammatory conditions through direct or indirect activation of primary nociceptive neurons and, consequently, peripheral and central sensitization. Experimentally, potassium superoxide (KO2, a O2●− donor) is used to initiate O2●− mediated inflammatory and nociceptive responses, making it important for studying the mechanisms associated with ROS-induced pain and evaluating potential therapeutic molecules. This review addresses the production and regulation of O2•−, highlighting its biosynthesis, redox control, and its physiological and pathological roles in the development of inflammatory pain, as well as the pharmacological therapies under development aimed at its generation and/or action.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Bidirectional Regulation of Nitric Oxide and Endothelin-1 in Cerebral Vasospasm: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives
by
Katrin Becker and Kaihui Lu
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040059 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cerebral vasospasm (CVS) following a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a critical complication driven by imbalances between vasodilators and vasoconstrictors. This review explores the bidirectional interplay between nitric oxide (NO) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) in CVS pathogenesis. NO, a potent vasodilator mainly produced by endothelial
[...] Read more.
Cerebral vasospasm (CVS) following a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a critical complication driven by imbalances between vasodilators and vasoconstrictors. This review explores the bidirectional interplay between nitric oxide (NO) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) in CVS pathogenesis. NO, a potent vasodilator mainly produced by endothelial and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (eNOS/nNOS) under normal physiological conditions, is scavenged early after SAH by hemoglobin derivatives, leading to microcirculatory dysfunction, pericyte constriction, and impaired neurovascular coupling. Conversely, ET-1 exacerbates vasoconstriction by suppressing NO synthesis via ROS-dependent eNOS uncoupling and Rho-kinase activation. The NO/ET-1 axis further influences delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) through mechanisms like 20-HETE-mediated cGMP suppression and oxidative stress. Emerging therapies—including NO donors, NOS gene therapy, and ET-1 receptor antagonists—aim to restore this balance. Understanding these pathways offers translational potential for mitigating CVS and improving outcomes post-SAH.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Decoding Anticancer Drug Response: Comparison of Data-Driven and Pathway-Guided Prediction Models
by
Efstathios Pateras, Ioannis S. Vizirianakis, Mingrui Zhang, Georgios Aivaliotis, Georgios Tzimagiorgis and Andigoni Malousi
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040058 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objective: Predicting pharmacological response in cancer remains a key challenge in precision oncology due to intertumoral heterogeneity and the complexity of drug–gene interactions. While machine learning models using multi-omics data have shown promise in predicting pharmacological response, selecting the features with the highest
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Predicting pharmacological response in cancer remains a key challenge in precision oncology due to intertumoral heterogeneity and the complexity of drug–gene interactions. While machine learning models using multi-omics data have shown promise in predicting pharmacological response, selecting the features with the highest predictive power critically affects model performance and biological interpretability. This study aims to compare computational and biologically informed gene selection strategies for predicting drug response in cancer cell lines and to propose a feature selection strategy that optimizes performance. Methods: Using gene expression and drug response data, we trained models on both data-driven and biologically informed gene sets based on the drug target pathways to predict IC50 values for seven anticancer drugs. Several feature selection methods were tested on gene expression profiles of cancer cell lines, including Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) with Support Vector Regression (SVR) against gene sets derived from drug-specific pathways in KEGG and CTD databases. The predictability was comparatively analyzed using both AUC and IC50 values and further assessed on proteomics data. Results: RFE with SVR outperformed other computational methods, while pathway-based gene sets showed lower performance compared to data-driven methods. The integration of computational and biologically informed gene sets consistently improved prediction accuracy across several anticancer drugs, while the predictive value of the corresponding proteomic features was significantly lower compared with the mRNA profiles. Conclusions: Integrating biological knowledge into feature selection enhances both the accuracy and interpretability of drug response prediction models. Integrative approaches offer a more robust and generalizable framework with potential applications in biomarker discovery, drug repurposing, and personalized treatment strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Tyrphostin A9 and Structurally Related Tyrphostins on Colorectal Carcinoma Cells
by
Lubna H. Tahtamouni, Ayah Y. Almasri, Marya A. Hamad, Nour A. Hussein, Khaled M. Saleh, Salem R. Yasin, Rainer Schobert and Bernhard Biersack
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040057 - 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is among the most commonly diagnosed cancers in both men and women. Although CRC mortality is generally decreasing, new therapeutic options are needed for unresponsive subgroups of CRC patients. Methods: A series of known and new tyrphostin derivatives was
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is among the most commonly diagnosed cancers in both men and women. Although CRC mortality is generally decreasing, new therapeutic options are needed for unresponsive subgroups of CRC patients. Methods: A series of known and new tyrphostin derivatives was tested for their efficacy against three CRC cell lines with varying KRAS, p53, and/or BRAF statuses. Growth inhibition, apoptosis induction, and inhibition of EGFR and VEGFR-2 were investigated. Results: Tyrphostin A9, the known RG13022-related tyrphostin 1a and its dichlorido(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) complex 1b, and the new SF5-substituted compounds 2a and 2b showed selective antiproliferative activity against KRAS-mutant HCT-116 CRC cells expressing wildtype p53, while p53-knockout HCT-116 and KRAS-wildtype BRAF/p53-mutant HT-29 CRC cells were distinctly less sensitive. In HCT-116 cells, only tyrphostin A9 increased mRNA expression of caspases 3 and 8, as well as the kinases MEK1 and MEK2, whereas 2a reduced caspase 8 mRNA levels. Tyrphostin A9 increased caspase 3 activity and induced apoptosis in HCT-116 p53-wildtype cells while simultaneously inhibiting the receptor tyrosine kinases EGFR and VEGFR-2 at low nanomolar concentrations. Conclusions: Tyrphostin A9 could be a promising therapeutic option for the treatment of KRAS-mutant CRC that expresses wildtype p53.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Avendaño-Briseño et al. Thallium Toxicity: Mechanisms of Action, Available Therapies, and Experimental Models. Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5, 49
by
Karla Alejandra Avendaño-Briseño, Jorge Escutia-Martínez, José Pedraza-Chaverri and Estefani Yaquelin Hernández-Cruz
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040056 - 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
In the original publication [1], during the revisions and restructuring of the manuscript, the following references were inadvertently removed by the authors and were not cited:103 [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Integration of Deep Learning with Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation for Novel TNF-α-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
by
Muhammad Yasir, Jinyoung Park, Eun-Taek Han, Jin-Hee Han, Won Sun Park, Jongseon Choe and Wanjoo Chun
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040055 - 23 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a key regulator of inflammatory responses, and its biological activity is dependent on proteolytic processing by the tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme (TACE), also known as ADAM17. Aberrant TACE activity has been associated with various inflammatory and immune-mediated
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a key regulator of inflammatory responses, and its biological activity is dependent on proteolytic processing by the tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme (TACE), also known as ADAM17. Aberrant TACE activity has been associated with various inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases, positioning it as a compelling target for therapeutic intervention. Methods: While our previous study explored TACE inhibition via repositioned FDA-approved drugs, the present study aims to examine previously untested chemical scaffolds from the Enamine compound library, seeking first-in-class TACE inhibitors. We employed an integrated in silico workflow that combined ligand-based virtual screening using a graph convolutional network (GCN) model trained on known TACE inhibitors with structure-based methodologies, including molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, and binding free energy calculations. Results: Several enamine-derived compounds demonstrated strong predicted inhibitory potential, favorable docking scores, and stable interactions with the TACE active site. Among them, Z1459964184, Z2242870510, and Z1450394746 emerged as lead candidates based on their highly stable 300 ns RMSD and robust hydrogen bonding profile as compared to the reference compound BMS-561392. Conclusions: This study highlights the utilization of deep learning-driven screening combined with extended 300 ns molecular simulations to identify novel small-molecule scaffolds for TACE inhibition and supports further exploration of these hits as potential anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Unveiling Biocompatibility: Comprehensive Study on Epoxy–Polyetheramine-Based Polymeric Nanogels in CHO-K1 Cell Line
by
Natalia Nascimento Silveira, Heber Eduardo Andrada, Julia Mirian Paulino, Naiara Cristina da Silva Boaretto, Eduardo Ferreira Molina and Raquel Alves dos Santos
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030054 - 18 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Backgorund/Objectives: Advances in nanotechnology have enabled conventional compounds with low bioavailability to achieve their full therapeutic potential by ensuring targeted tissue delivery. In this context, polymeric nanogels have emerged as a promising option for drug delivery due to their high loading capacity and
[...] Read more.
Backgorund/Objectives: Advances in nanotechnology have enabled conventional compounds with low bioavailability to achieve their full therapeutic potential by ensuring targeted tissue delivery. In this context, polymeric nanogels have emerged as a promising option for drug delivery due to their high loading capacity and excellent in vivo stability. Objectives: Given the growing potential of nanogels in drug delivery, their cytotoxicity and genotoxicity must be evaluated to ensure safety in biotechnological applications. This study assessed the genotoxic safety of nanogels synthesized via the reaction of Jeffamine® T-5000 polyoxypropylene triamine (PPO) monomers (Huntsman Chemical, The Woodlands, TX, USA) and poly (ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (DPEG) in varying proportions: 1:1 (Nano11), 1:3 (Nano13), and 2:3 (Nano23) PPO/DPEG. Additionally, we determined which of the two components exhibited lower toxicity against the CHO-K1 cell line (Chinese hamster ovary). Methods: To achieve this, short- and long-term cytotoxicity experiments were conducted using the XTT colorimetric assay and clonogenic survival assay, alongside the micronucleus test and comet assay for genotoxicity analysis. Results: The cytotoxicity assays (XTT, clonogenic, and trypan blue) indicated that the nanogels did not exhibit cytotoxic effects at concentrations up to 100 μg/mL, while the genotoxicity assays revealed no evidence of DNA or chromosomal damage at these levels. Conclusions: These findings underscore the safety profile of Jeffamine® T-5000 as an effective carrier, demonstrating its compatibility with DPEG and positioning it as a highly promising and innovative solution for advanced drug delivery systems.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Altered Antimicrobial Activity and Selectivity of Dihydro-Protoberberines over Their Corresponding Protoberberines
by
Juan Ostos-Hernandez, Hannah Bhakta, Caleb VanArragon, Lanna Sirhan, Danielle Orozco-Nunnelly and Jeffrey Pruet
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030053 - 17 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria and fungi, or “superbugs”, makes the development of new antimicrobial compounds of continued importance. In this context, we have explored structural variants of the plant-derived phytocompound berberine, seeking higher antimicrobial activity and selectivity. Our prior work prepared
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria and fungi, or “superbugs”, makes the development of new antimicrobial compounds of continued importance. In this context, we have explored structural variants of the plant-derived phytocompound berberine, seeking higher antimicrobial activity and selectivity. Our prior work prepared fourteen protoberberine variants (B1–B14), and found that a partially reduced dihydro-protoberberine (B14) was significantly more active against Gram-positive bacteria. To further investigate this trend, we prepared a series of protoberberines and related dihydro-protoberberines, with the goal of better understanding the effects of the partial reduction of the protoberberine core. Methods: Protoberberines were prepared from a cyclization between glyoxal and substituted N-benzyl-phenethylamines, prepared by reductive amination. Dihydro-derivatives were obtained via NaBH4 reduction. Biological activity was assessed with a Kirby–Bauer assay to determine zones of inhibition against a panel of twelve microorganisms. Cytotoxicity was also assessed using an MTT assay against a T84 human colon carcinoma cell line. Results: The majority of the prepared compounds showed greater Gram-positive antibacterial activity compared to original berberine, and nearly all dihydro-protoberberines had improved Gram-positive antibacterial activity over their unreduced form. Additionally, the reduced variants were less active against fungi, indicating a step towards higher microbial selectivity. All variants showed greater potency against cancer cells. Conclusions: The present work highlights a significant improvement in antibacterial activity and selectivity for this set of dihydro-protoberberines over their unreduced counterparts.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation with Vitis vinifera Leaf Extract: A Combined Experimental and Computational Pharmacological Study
by
Sanja Djakovic, Marina Nikolic, Ivan Srejovic, Nikola Nedeljkovic, Marko Karovic, Jovana Bradic, Marijana Andjic, Vladimir Jakovljevic and Milos Nikolic
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030052 - 14 Sep 2025
Abstract
Objectives: Our study aimed to examine the antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential of the lyophilized aqueous leaf extract of Vitis vinifera. Methods: The antioxidant capacity of the extract was evaluated using the DPPH and FRAP assays. The in vivo phase of
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Our study aimed to examine the antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential of the lyophilized aqueous leaf extract of Vitis vinifera. Methods: The antioxidant capacity of the extract was evaluated using the DPPH and FRAP assays. The in vivo phase of the study included 40 male Wistar albino rats. One half of the animals were used to induce the carrageenan model of acute inflammation, while the other half were used for examination of the extract effect on the redox state. Rats from the experimental group drank tap water containing 150 mg/kg Vitis vinifera extract for 14 days, while control animals received saline at the same volume. The molecular docking studies of polyphenols present in the leaf extract were conducted in AutoDock Vina. Results: In vitro assessment of the antioxidative capacity of the applied extract revealed significant free radical scavenging activity (IC50 value 11.63 µg/mL), along with a pronounced ferric reducing ability (0.143 at 700 nm). Moreover, animal treatment with the extract led to significant paw edema inhibition (30.34%, 35.06%, and 41.54% in the second, third, and fourth hours, respectively) and to pro-oxidative marker reduction. Additionally, Vitis vinifera extract significantly increased catalase activity and glutathione levels. The in silico results showed that rutin binds to cyclooxygenase 1 (−8.2 kcal/mol) and 2 (−8.3 kcal/mol), as well as to antioxidant enzymes (catalase: −8.6 kcal/mol, SOD: −7.4 kcal/mol), indicating its key role in mediating the biological activity of the tested extract. Conclusions: This study highlights the significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of V. vinifera lyophilized aqueous leaf extract from the Serbian market, supported by both in vivo and in silico analyses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in the Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nanoparticle-Based Strategies to Enhance Catecholaminergic Drug Delivery for Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Advances, Challenges, and Therapeutic Opportunities
by
Luis E. Cobos-Puc, María del C. Rodríguez-Salazar, Sonia Y. Silva-Belmares and Hilda Aguayo-Morales
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030051 - 11 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Neuropsychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, depression, and Alzheimer’s disease are characterized by deficits in catecholaminergic neurotransmission. Conventional pharmacotherapies have several limitations, including poor blood–brain barrier permeability, rapid peripheral metabolism, systemic toxicity, and suboptimal brain bioavailability. This review evaluates nanoparticle-based strategies that
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Neuropsychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, depression, and Alzheimer’s disease are characterized by deficits in catecholaminergic neurotransmission. Conventional pharmacotherapies have several limitations, including poor blood–brain barrier permeability, rapid peripheral metabolism, systemic toxicity, and suboptimal brain bioavailability. This review evaluates nanoparticle-based strategies that can overcome these limitations by enhancing the delivery of catecholaminergic drugs to the central nervous system (CNS). Methods: A narrative synthesis was conducted based on a comprehensive review of research articles published by July 2025. Articles were retrieved from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. The studies examined nanoformulations of catecholaminergic agents with a focus on CNS delivery, BBB penetration, toxicity, and therapeutic outcomes in neuropsychiatric disease models. Results: Evidence shows that nanoparticle platforms can stabilize drugs and extend their release time. They can also enable BBB penetration. These platforms reduce peripheral side effects and improve behavioral and neurochemical outcomes in preclinical models. Conclusions: Nanoparticles are a promising strategy for optimizing pharmacotherapy for CNS disorders associated with catecholamine deficiencies. However, more research is needed on their long-term safety, bioaccumulation, and clinical feasibility before they can be widely adopted.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
AI-Driven Image Analysis for Precision Screening Transposon-Mediated Transgenesis of NFκB eGFP Reporter System in Zebrafish
by
Yui Iwata, Aoi Mori, Kana Shinogi, Kanako Nishino, Saori Matsuoka, Yuki Kushida, Yuki Satoda, Akiyoshi Shimizu, Fumihiro Terami, Toru Nonomura, Shunichi Kitajima and Toshio Tanaka
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030050 - 31 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Zebrafish-based drug discovery systems provide significant advantages over mammalian models for high-throughput in vivo screening. Among these, the NF-κB eGFP reporter system significantly enhances drug discovery in zebrafish by enabling real-time, high-resolution monitoring of pathway activity in live organisms, thereby streamlining mechanistic
[...] Read more.
Background: Zebrafish-based drug discovery systems provide significant advantages over mammalian models for high-throughput in vivo screening. Among these, the NF-κB eGFP reporter system significantly enhances drug discovery in zebrafish by enabling real-time, high-resolution monitoring of pathway activity in live organisms, thereby streamlining mechanistic studies and high-throughput screening. Methods: We developed a novel AI (Quantifish and Orange software)-based zebrafish precision individualized 96-well ZF plates (0–7 dpf) and individualized MT tanks (8 dpf–4 mpf) protocol for the transposon-mediated transgenesis of the NFκB eGFP reporter system. Results: One-cell stage embryos were administered NFκB reporter construct and Tol2 transposase mRNA via microinjection and transferred to separate wells of a 96-well ZF plate. Bright-field and fluorescence images of each well were captured at 5 dpf in the F0, F1, and F2 generations using the automated confocal high-content imager CQ1. The Quantifish software was used for the automated detection and segmentation of zebrafish larval fluorescence intensity in specific regions of interest. Quantitative data on the fluorescence intensity and distribution patterns were measured in Quantifish, and advanced statistical and machine learning methods were applied using Orange. Imaging data with eGFP expression results were assessed to evaluate the efficiency of the transgenic protocol. Discussion: This AI-enhanced precision protocol allows for high-throughput screening and quantitative analysis of NFκB reporter transgenesis in zebrafish, enabling the efficient identification and characterization of stable transgenic lines that exhibit tissue-specific expression of the NF-κB reporter, such as lines with induced expression restricted to the retina following LPS stimulation. This approach streamlines the evaluation of regulatory elements, enhances data consistency, and reduces animal use, making it a valuable tool for zebrafish drug discovery.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Thallium Toxicity: Mechanisms of Action, Available Therapies, and Experimental Models
by
Karla Alejandra Avendaño-Briseño, Jorge Escutia-Martínez, José Pedraza-Chaverri and Estefani Yaquelin Hernández-Cruz
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030049 - 30 Aug 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
Thallium (Tl) is a non-essential and highly toxic heavy metal capable of replacing potassium (K+) in biological systems, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inhibition of protein synthesis. In humans, the estimated oral lethal dose ranges from 10 to 15
[...] Read more.
Thallium (Tl) is a non-essential and highly toxic heavy metal capable of replacing potassium (K+) in biological systems, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inhibition of protein synthesis. In humans, the estimated oral lethal dose ranges from 10 to 15 mg/kg, with acute mortality rates of 6–15% and chronic neurological sequelae in up to 55% of survivors. Environmental releases of thallium of up to 5000 metric tons annually from industrial and mining activities, combined with its high oral bioavailability and nonspecific multisystemic symptoms, underscore the urgent need for more effective therapeutic strategies. This review summarizes current evidence on Tl toxicity, including its mechanisms of action, clinical manifestations, and available treatments. It emphasizes the strategic selection of biological models: simple organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster enable high-throughput screening and early biomarker detection; zebrafish (Danio rerio) provide vertebrate-level evaluation of multi-organ effects; and rodent models offer systemic toxicokinetic and therapeutic validation. Human-derived organoids and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) systems recreate tissue-specific microenvironments, allowing translational assessment of mitochondrial, neuronal, and cardiac toxicity. Integrating these models within a tiered and complementary framework, alongside environmental and clinical surveillance, can accelerate the development of targeted treatments and strengthen public health responses to Tl exposure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Intercellular Communication: Implications for Drug Discovery and Targeted Therapies
by
Mst. Afsana Mimi and Md. Mahmudul Hasan
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030048 - 30 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are mediators of intercellular communication and serve as promising tools for drug discovery and targeted therapies. These lipid bilayer-bound nanovesicles facilitate the transfer of functional proteins, RNAs, lipids, and other biomolecules between cells, thereby influencing various physiological and pathological processes.
[...] Read more.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are mediators of intercellular communication and serve as promising tools for drug discovery and targeted therapies. These lipid bilayer-bound nanovesicles facilitate the transfer of functional proteins, RNAs, lipids, and other biomolecules between cells, thereby influencing various physiological and pathological processes. This review outlines the molecular mechanisms governing EV biogenesis and cargo sorting, emphasizing the role of key regulatory proteins in modulating selective protein packaging. We explore the critical involvement of EVs in various disease microenvironments, including cancer progression, neurodegeneration, and immunological modulation. Their ability to cross biological barriers and deliver bioactive cargo makes them desirable candidates for precise drug delivery systems, especially in neurological and oncological disorders. Moreover, this review highlights advances in engineering EVs for the delivery of RNA therapeutics, CRISPR-Cas systems, and targeted small molecules. The utility of EVs as diagnostic tools in liquid biopsies and their integration into personalized medicine and companion diagnostics are also discussed. Patient-derived EVs offer dynamic insights into disease states and enable real-time treatment stratification. Despite their potential, challenges such as scalable isolation, cargo heterogeneity, and regulatory ambiguity remain significant hurdles. Recent studies have reported novel pharmacological approaches targeting EV biogenesis, secretion, and uptake pathways, with emerging regulators showing promise as drug targets for modulating EV cargo. Future directions include the standardization of EV analytics, scalable biomanufacturing, and the classification of EV-based therapeutics under evolving regulatory frameworks. This review emphasizes the multifaceted roles of EVs and their transformative potential as therapeutic platforms and biomarker reservoirs in next-generation precision medicine.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of an Aminochalcone-Loaded Hydrogel Against Candida spp.
by
Emmanuely de Oliveira Chaves dos Santos, Pedro Luiz Rosalen, Joice Graciani, Josy Goldoni Lazarini, Maria Ligia Rodrigues Macedo, Diego Romário-Silva, Mayara Aparecida Rocha Garcia, Suzana Gonçalves Carvalho, Paola da Mata Siqueira Mesut, Ana Claudia Castelã Nascimento Prates, Luis Octávio Regasini, Marlus Chorilli, Rafael Leonardo Xediek Consani and Janaina de Cássia Orlandi Sardi
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030047 - 28 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background: Prosthetic candidiasis remains a significant clinical challenge, particularly due to the ability of Candida species to form resilient biofilms on dental prostheses, which limits the efficacy of conventional antifungal treatments. In this context, developing strategies to prevent or reduce biofilm formation is
[...] Read more.
Background: Prosthetic candidiasis remains a significant clinical challenge, particularly due to the ability of Candida species to form resilient biofilms on dental prostheses, which limits the efficacy of conventional antifungal treatments. In this context, developing strategies to prevent or reduce biofilm formation is essential. Objectives This study investigates the antifungal and antibiofilm potential of a hydrogel formulation incorporating aminochalcone AM-35 as a candidate for the prevention and treatment of prosthetic candidiasis. Methods: To achieve this, experiments were conducted to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of aminochalcone AM-35 against Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis strains. AM-35 was incorporated into a hydrogel, which was subsequently tested on biofilms formed by these yeast species, both individually and in combination. The experimental disks were sterilized and incubated with C. albicans, C. tropicalis, and a mixture of both strains for 120 h to allow biofilm maturation. After contamination, the samples were divided into four experimental groups: Group 1: Hydrogel; Group 2: Hydrogel+AM-35; Group 3: Sodium hypochlorite (positive control); and Group 4: No treatment. The samples were then subjected to a sonication process to disaggregate the cells, which were then cultured on plates for colony-forming unit (CFU/mL) counts. The hydrogel’s toxicity was evaluated in vivo using the Galleria mellonella model. Results: The hydrogel formulation demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity, with an MIC of 7.8 μg/mL for C. albicans and 3.9 μg/mL for C. tropicalis. Treatment with the hydrogel at a concentration of 39 μg/mL resulted in a significant reduction in the formation and viability of mixed-species biofilms (p < 0.05). Additionally, the results indicated robust activity against C. albicans and C. tropicalis without presenting toxicity in the Galleria mellonella model. In conclusion, the hydrogel formulation exhibited effective antibiofilm activity, significantly reducing the microbial load. Conclusions: These findings open new possibilities for the development of alternative treatments for prosthetic candidiasis. The research suggests that the use of chalcone-based compounds may represent a promising approach in combating fungal infections in dentistry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Fisher-Bautista et al. Genetic Markers Associated with Ferroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases. Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5, 37
by
Brandon Fisher-Bautista, Gabriela Fonseca-Camarillo and Alfredo Cruz-Gregorio
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030046 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
There was an error in the original publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Co-Administration of Levetiracetam or Brivaracetam with Ethanol on the Associative Learning and Anxiety Level of Rats
by
Ewa Zwierzyńska and Bogusława Pietrzak
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030045 - 21 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Ethanol intake leads to cognitive deficits. Recent research demonstrated that a dysregulation of synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) expression seems to be linked to anxiety and memory disorders. Levetiracetam and brivaracetam are two antiseizure drugs that affect the SV2A protein. This study
[...] Read more.
Background: Ethanol intake leads to cognitive deficits. Recent research demonstrated that a dysregulation of synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) expression seems to be linked to anxiety and memory disorders. Levetiracetam and brivaracetam are two antiseizure drugs that affect the SV2A protein. This study aimed to assess the impact of these drugs on associative learning and anxiety-like behaviors in ethanol-treated rats. Methods: Adult male Wistar rats (n = 64) were given brivaracetam or levetiracetam via i.g. for three weeks at doses of 300 mg/kg or 6 mg/kg, respectively. Ethanol was administered as a 20% solution twice a day, via i.g., at a morning dose of 1.5 g/kg b.w. and an afternoon dose of 3.5 g/kg b.w. Additionally, 5% ethanol was available ad libitum between 4:00 p.m. and 8:00 a.m. Associative learning was evaluated using the passive avoidance test during the alcohol administration period, as well as the contextual fear conditioning and cued fear conditioning tests during the withdrawal period. The level of anxiety was determined using the elevated plus maze test in withdrawal rats. Results: Ethanol consumption resulted in impaired associative memory, and its withdrawal was linked to increased anxiety levels. Levetiracetam enhanced memory performance in the passive avoidance test, but brivaracetam disturbed memory associated with unpleasant stimuli in the contextual fear conditioning. Additionally, withdrawal-induced disturbance of locomotor activity persisted, particularly in animals receiving levetiracetam in the elevated plus maze. Conclusions: Levetiracetam appears to provide certain beneficial effects, whereas brivaracetam may worsen memory disturbances in rats.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Curcumin Nanoparticles Against Aquatic Bacterial Pathogens
by
Edith Dube and Grace Emily Okuthe
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(3), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030044 - 19 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bacterial diseases are a major constraint to aquaculture productivity, driving extensive antibiotic use and raising concerns over antimicrobial resistance, environmental contamination, and food safety. Curcumin, a polyphenolic compound from Curcuma longa, exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities but is limited by poor
[...] Read more.
Bacterial diseases are a major constraint to aquaculture productivity, driving extensive antibiotic use and raising concerns over antimicrobial resistance, environmental contamination, and food safety. Curcumin, a polyphenolic compound from Curcuma longa, exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities but is limited by poor water solubility, instability, and low bioavailability. This review was conducted through a literature search of Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar using targeted keywords, including curcumin nanoparticles, antibacterial, aquatic pathogens, nanotechnology, synthesis, and disease control. Titles and abstracts were screened for relevance, followed by full-text evaluation of selected studies. Key findings were critically analyzed and incorporated into the review. Findings from the literature indicate that curcumin nanoparticles, synthesized via milling, anti-solvent precipitation, ionic gelation, emulsification, spray drying, and metal/polymer nanocomposite formation, exhibit enhanced antibacterial activity against aquatic pathogens, including Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus. Optimally engineered curcumin nanoparticles (<100 nm, being mostly spherical, highly negatively charged) can penetrate bacterial membranes, disrupt biofilms, lower minimum inhibitory concentrations, and improve in vivo fish survival. Practical applications include dietary supplementation to boost fish immunity and growth, water disinfection to reduce pathogen loads, immersion therapy for external infections, and antimicrobial coatings for aquaculture equipment and surfaces, resulting in reduced infections and outbreaks, reduced mortality, improved water quality, and decreased antibiotic dependence. In conclusion, curcumin nanoparticles and curcumin-based nanocomposites present a versatile, eco-friendly approach to sustainable aquaculture disease management. However, further field-scale validation, safety assessment, and cost-effective production methods are necessary to enable commercial adoption.
Full article
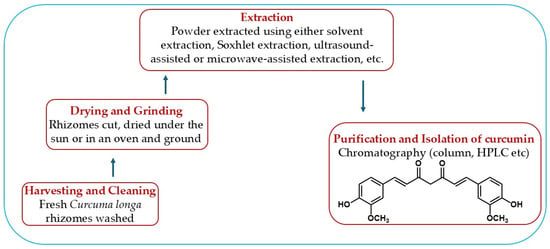
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, Sci. Pharm., Molecules, Future Pharmacology, Biomolecules
Natural Products and Drug Discovery—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Sonia Piacente, Marta MenegazziDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology: From First-in-Human to Precision Dosing
Guest Editors: Giovanni Gori, Antonello Di PaoloDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Transdiagnostic Psychopharmacology: Bridging Mechanisms Across Mental Disorders
Guest Editor: Felix KesslerDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Proteins or Peptides as Effective Weapons in Antimicrobial and Cancer Therapy
Guest Editors: Nidia M. León-Sicairos, Gerardo Ramírez-RicoDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Recent Advances in the Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
Guest Editors: Ivan M. Srejović, Nikola Nedeljkovic, Miloš NikolićDeadline: 28 February 2026







