Epidemiological Lifestyle Analysis and Infection Prevention in Public Health
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Mariusz Gujski
Prof. Dr. Mariusz Gujski
 Prof. Dr. Mariusz Gujski
Prof. Dr. Mariusz Gujski
E-Mail
Collection Editor
Department of Public Health, Medical University of Warsaw, 02-097 Warsaw, Poland
Interests: health care systems; evidence based health policy and public health; preventive medicine; health promotion; cancer control policies
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Mateusz Jankowski
Dr. Mateusz Jankowski
 Dr. Mateusz Jankowski
Dr. Mateusz Jankowski
E-Mail
Collection Editor
Department of Population Health, School of Public Health, Centre of Postgraduate Medical Education, 01-826 Warsaw, Poland
Interests: tobacco control; tobacco related diseases; e-cigarettes; heated tobacco products; lifestyle medicine; prevention programmes; health policy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Lifestyle factors have a significant impact on general health. Lifestyle-related risk factors can be modified through evidence-based public health programs. Epidemiological lifestyle analysis may provide important evidence supporting lifestyle medicine and its importance in public health research.
Public health can also significantly benefit from infection prevention. The economic burden of healthcare-associated infection is meaningful in low- and middle-income countries. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrates the importance of infection prevention. There is a need to exchange international experiences in the field of the healthcare organization model limiting the transmission of infections and educational activities on the prevention of infections.
This Topical Collection aims to present the diversity and progress of research in the field of epidemiological lifestyle analysis as well as evidence-based public health interventions to prevent the spread of infections.
In this Topical Collection, we invite researchers in epidemiology, public health, management, quality assurance, preventive medicine, health economics, and other social sciences to submit high-quality original papers or systematical reviews related to the issues in this research area.
Prof. Dr. Mariusz Gujski
Dr. Mateusz Jankowski
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Risk factors
- Health risk assessment
- Lifestyle medicine
- Preventive medicine
- Health promotion
- Hygiene
- Infection prevention
Published Papers (29 papers)
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Urban Rail Transit Epidemic Prevention Measures on Passengers’ Safety Perception
by
Pengxiang Ding, Suwei Feng and Jianning Jiang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3004
Abstract
In 2020, COVID-19 triggered concern about the safety of public transport. To meet passengers’ expectations regarding safety, the public transport department has stepped up its pandemic prevention services. Some prevention services require passengers to follow mandatory requirements. However, whether and to what extent
[...] Read more.
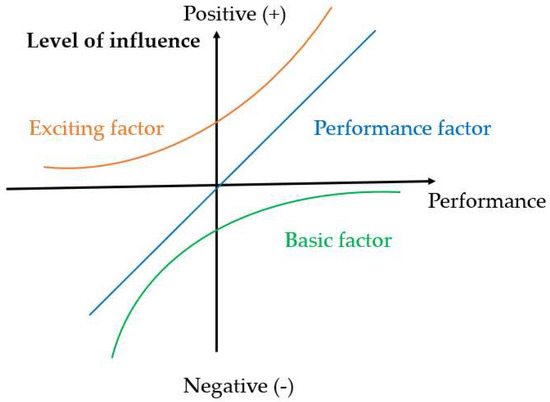
In 2020, COVID-19 triggered concern about the safety of public transport. To meet passengers’ expectations regarding safety, the public transport department has stepped up its pandemic prevention services. Some prevention services require passengers to follow mandatory requirements. However, whether and to what extent these requirements affect passenger satisfaction with public transportation services remains unclear. This study aims to construct an integrated framework to explore the direct and indirect relationships between four constructs (regular services quality, pandemic prevention service, psychological distance, and safety perception) and passengers’ satisfaction in the context of urban rail transit services. Based on survey data collected from 500 passengers on the Shanghai Metro, this paper examines the relationships between routine service, pandemic prevention measures, safety perceptions, and satisfaction with the service. The results from the structural equation model indicate that routine service (0.608), pandemic prevention measures (0.56), and safety perception (0.05) have positive effects on passenger satisfaction. Psychological distance negatively impacts safety perception (−0.949) and has indirect effects on passenger satisfaction. Further, in order to identify the service improvements that public transportation departments should focus on, we use the three-factor theory to identify the services that should be improved: Basic factors, such as “punctual arrival of metros”, “treatment of harmful garbage”, “increasing frequency of platform disinfection”, and “measurement of station temperature” should be treated as the first priority. As the second improvement priority, “the planning of metro stations can accommodate my travel scope” can be considered. Last, public transportation departments can enhance the exciting factor by installing “metro entrance signs” when resources are available.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Severity and Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection Compared with Primary Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Jie Deng, Yirui Ma, Qiao Liu, Min Du, Min Liu and Jue Liu
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 4599
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) reinfection has brought new challenges to the global prevention and control of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic; however, current studies suggest that there is still great uncertainty about the risk of severe COVID-19 and poor outcomes
[...] Read more.
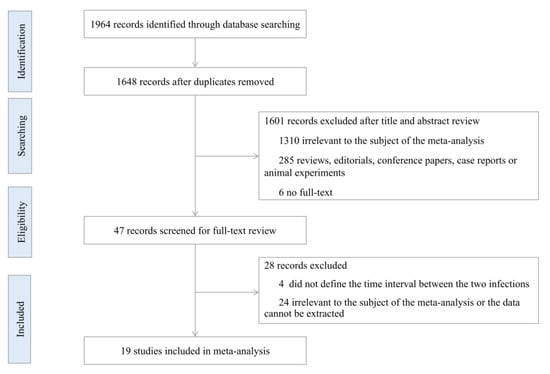
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) reinfection has brought new challenges to the global prevention and control of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic; however, current studies suggest that there is still great uncertainty about the risk of severe COVID-19 and poor outcomes after SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. Random-effects inverse-variance models were used to evaluate the pooled prevalence (PP) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) of severity, outcomes and symptoms of reinfection. Random-effects were used to estimate the pooled odds ratios (OR) and its 95%CI of severity and outcomes between reinfections and primary infections. Nineteen studies involving a total of 34,375 cases of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and 5,264,720 cases of SARS-CoV-2 primary infection were included in this meta-analysis. Among those SARS-CoV-2 reinfection cases, 41.77% (95%CI, 19.23–64.31%) were asymptomatic, and 51.83% (95%CI, 23.90–79.76%) were symptomatic, only 0.58% (95%CI, 0.031–1.14%) manifested as severe illness, and 0.04% (95%CI, 0.009–0.078%) manifested as critical illness. The PPs for SARS-CoV-2 reinfection-related hospitalization, admission to ICU, and death were, respectively, 15.48% (95%CI, 11.98–18.97%), 3.58% (95%CI, 0.39–6.77%), 2.96% (95%CI, 1.25–4.67%). Compared with SARS-CoV-2 primary infection cases, reinfection cases were more likely to present with mild illness (OR = 7.01, 95%CI, 5.83–8.44), and the risk of severe illness was reduced by 86% (OR = 0.14, 95%CI, 0.11–0.16). Primary infection provided some protection against reinfection and reduces the risk of symptomatic infection and severe illness. Reinfection did not contribute to extra risk of hospitalization, ICU, or death. It is suggested to scientifically understand the risk of reinfection of SARS-CoV-2, strengthen public health education, maintain healthy habits, and reduce the risk of reinfection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Habits, and Food Labels Use—A Representative Cross-Sectional Survey among Adults in Poland
by
Adam Żarnowski, Mateusz Jankowski and Mariusz Gujski
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3836
Abstract
An unhealthy diet is an important risk factor for disability and premature death. This study aimed to assess nutrition knowledge, dietary habits, and food label use among adults in Poland as well as to identify factors associated with diet-related behaviors. A cross-sectional survey
[...] Read more.
An unhealthy diet is an important risk factor for disability and premature death. This study aimed to assess nutrition knowledge, dietary habits, and food label use among adults in Poland as well as to identify factors associated with diet-related behaviors. A cross-sectional survey was carried out in July 2020 on a non-probability quota-based sample of 1070 adult citizens of Poland. The most common sources of nutrition knowledge were news websites (41.8%) or family/friends (32.4%). Over one-quarter of adults in Poland were on a diet (28.7%). Over one-tenth of respondents (11.9%) consumed less than three meals per day. Half of the respondents (50.3%) declared that they use food labels when shopping, and 15.4% checked the nutrition information on restaurant menus. Female gender (OR:1.70; 95%CI:1.26–2.29;
p < 0.001), presence of chronic diseases (OR:1.83; 95%CI:1.37–2.44;
p < 0.001), regular physical activity (
p < 0.001), and being a non-smoker (OR:1.45; 95%CI:1.02–2.06;
p = 0.04) were significantly associated with higher odds of being on a diet. Females (OR:1.63; 95%CI:1.24–2.15;
p < 0.001), respondents with higher education (OR:1.53; 95%CI:1.17–2.01;
p = 0.002), those who had never been married (OR:1.49; 95%CI:1.07–2.07;
p = 0.02), respondents with chronic diseases (OR:1.73; 95%CI:1.30–2.31;
p < 0.001), those with regular physical activity (
p < 0.05), as well as non-smokers (OR:1.42; 95%CI:1.04–1.95;
p = 0.03) had higher odds of checking the food labels. This study showed a significant gap in nutrition knowledge among adults in Poland.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
How Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Affect Population Mobility in Taiwan?
by
Shih-Feng Liu, Hui-Chuan Chang, Jui-Fang Liu and Ho-Chang Kuo
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2755
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) impairs the free movement of human beings. The study aims to determine how the COVID-19 pandemic affected population mobility. Methods: The study obtained Google COVID-19 population mobility report and e Taiwan COVID-19 pandemic information from Our World in Data.
[...] Read more.
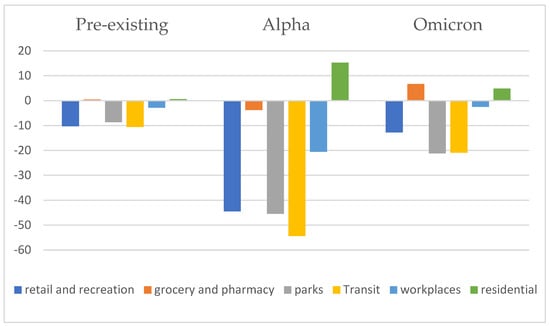
Background: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) impairs the free movement of human beings. The study aims to determine how the COVID-19 pandemic affected population mobility. Methods: The study obtained Google COVID-19 population mobility report and e Taiwan COVID-19 pandemic information from Our World in Data. Results: During the Alpha wave, transit decreased the most, with an average difference of >50%, followed by parks, workplaces, groceries, and pharmacies. During the Omicron wave, the average population flow in parks and transit decreased by about 20%. During the pre-existing wave, the average population visits of transit decreased by 10% at the most, followed by parks and workplaces. The peak of daily new confirmed cases per million (7-day rolling average) was 25.02, 6.39, and 0.81 for Alpha, Omicron, and the pre-existing wave, respectively. Daily new confirmed cases per million people correlated with the change in population visits of various places (all
p < 0.001). The reproduction rate (7-day rolling average) correlated with the change of population visits of most places, except retail and recreation. We conclude the Alpha variant affected more individuals than Omicron and pre-existing type. Furthermore, changes in population visits in transit were most impacted. This change was consistent with daily new confirmed cases per million people and reproduction rate (7-day rolling average). Conclusion: The Alpha variant affected more individuals than the Omicron and pre-existing types. Furthermore, changes in population visits in transit locations were most impacted. This change was consistent with the daily new number of confirmed cases per million people and the 7-day rolling average reproduction rate.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiological Analysis of Diabetes-Related Hospitalization in Poland before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic, 2014–2020
by
Kuba Sękowski, Justyna Grudziąż-Sękowska, Paweł Goryński, Jarosław Pinkas and Mateusz Jankowski
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3556
Abstract
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide. The study aimed to present an epidemiological analysis of hospitalization related to diabetes mellitus in Poland between 2014 and 2020 as well as to analyze changes in diabetes-related hospital admissions before and during
[...] Read more.
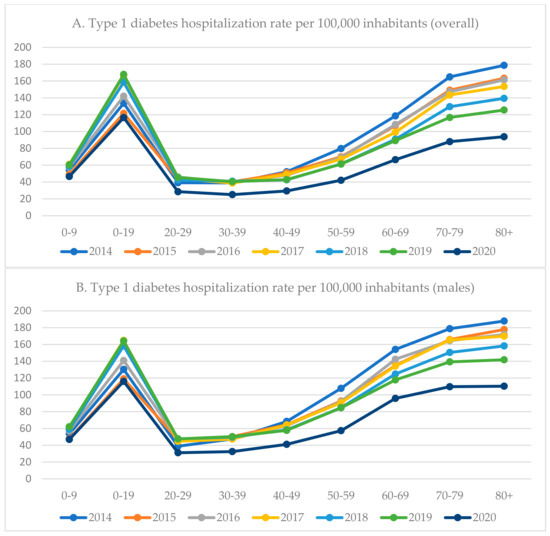
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide. The study aimed to present an epidemiological analysis of hospitalization related to diabetes mellitus in Poland between 2014 and 2020 as well as to analyze changes in diabetes-related hospital admissions before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. This study is a retrospective analysis of the national registry dataset of hospital discharge reports on diabetes-related hospitalizations in Poland between 2014 and 2020. The number of diabetes-related hospitalizations varied from 76,220 in 2016 to 45,159 in 2020. The hospitalization rate per 100,000 has decreased from 74.6 in 2019 to 53.0 in 2020 among patients with type 1 diabetes (percentage change: −28.9%). An even greater drop was observed among patients with type 2 diabetes: from 99.4 in 2019 to 61.6 in 2020 (percentage change: −38%). Both among patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, a decrease in hospitalization rate was higher among females than males (−31.6% vs. −26.7% and −40.9% vs. −35.2% respectively). When compared to 2019, in 2020, the in-hospital mortality rate increased by 66.7% (60.0% among males and 65.2% among females) among patients hospitalized with type 1 diabetes and by 48.5% (55.2% among females and 42.1% among males) among patients hospitalized with type 2 diabetes. Markable differences in hospitalization rate, duration of hospitalization, as well as in-hospital mortality rate by gender, were observed, which reveal health inequalities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
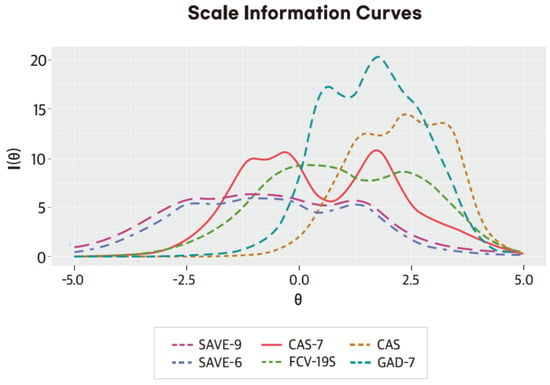
Applicability and Psychometric Comparison of the General-Population Viral Anxiety Rating Scales among Healthcare Workers in the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Changnam Kim, Oli Ahmed, Washington Allysson Dantas Silva, C. Hyung Keun Park, Soyoung Yoo and Seockhoon Chung
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2362
Abstract
We aimed to explore the reliability and validity of viral anxiety rating scales (developed for the general population) among healthcare workers. In addition, we compared the psychometric properties of rating scales in accordance with the Generalized Anxiety Scale-7 items (GAD-7) during this COVID-19
[...] Read more.
We aimed to explore the reliability and validity of viral anxiety rating scales (developed for the general population) among healthcare workers. In addition, we compared the psychometric properties of rating scales in accordance with the Generalized Anxiety Scale-7 items (GAD-7) during this COVID-19 pandemic. The viral anxiety of 330 healthcare workers was measured with Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics—9 items (SAVE-9), SAVE-6, Coronavirus Anxiety Scale (CAS), Fear of COVID-19 Scale (FCV-19S), and COVID-19 Anxiety Scale (CAS-7). Factor analyses, item response theory, and Rasch model analyses were conducted to confirm the construct validities of the scales and compare the psychometric properties of rating scales. The receiver operating curve (ROC) analysis examined the cutoff scores of rating scales in accordance with a mild degree of generalized anxiety. The SAVE-9, SAVE-6, CAS, FCV-19S, and CAS-7 scales showed good reliability of internal consistency among healthcare workers. Their construct validity and convergent validity of each scale were similarly good. Furthermore, in comparing the psychometric properties of rating scales, we observed that the CAS scale was the most discriminating and difficult among the scales. The CAS and FCV-19S provided more information and were more efficient than the SAVE-9, SAVE-6, and CAS-7 scales when they were used to measure healthcare workers’ viral anxiety. Viral anxiety rating scales can be applied to healthcare workers with good reliability and validity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
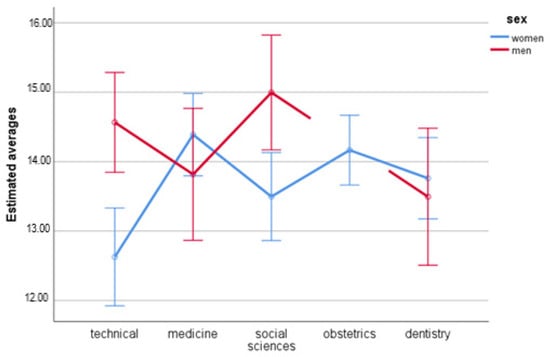
Quality of Life Assessment in Students from Polish Universities during the COVID-19 Pandemic According to WHO Quality of Life Questionnaire
by
Agata Trzcionka, Marta Włodarczyk-Sielicka, Piotr Surmiak, Anna Szymańska, Artur Pohl and Marta Tanasiewicz
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2932
Abstract
The outbreak of COVID-19 in December 2019 in China influenced the lives of people all over the world. Many had to face the completely new situation of lockdown. These changes influenced many aspects of life. Students’ quality of life changed as well. The
[...] Read more.
The outbreak of COVID-19 in December 2019 in China influenced the lives of people all over the world. Many had to face the completely new situation of lockdown. These changes influenced many aspects of life. Students’ quality of life changed as well. The aim of the study was to assess the differences in the quality of life of students with regard to the field of study and the knowledge regarding medicine. The study population consisted of 500 students from three Polish universities (Medical University of Silesia, Maritime University of Szczecin and Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznań). Study participants were invited to fill in an online cross-sectional quality of life questionnaire (WHOQOL-BREF) created by the World Health Organization (WHO). The analysis was done using the IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0 programme. The obtained results showed differences in respondents’ reactions in two domains. The lowest resistance to the critical situation was observed in women who studied at the technical university. Higher values of resistance were observed in women studying medical sciences.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Level of Knowledge, Beliefs and Acceptance of HPV Vaccine: A Cross-Sectional Study in Romania
by
Toader Septimiu Voidăzan, Mihaela Alexandra Budianu, Florin Francisc Rozsnyai, Zsolt Kovacs, Cosmina Cristina Uzun and Nicoleta Neagu
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 4767
Abstract
(1) Background: The infection with Human papilloma virus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection and it has been associated with cervical cancer (CC) in 99.7% of the cases. In Romania, CC is the second most common, with incidence (22.6%
000)
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The infection with Human papilloma virus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection and it has been associated with cervical cancer (CC) in 99.7% of the cases. In Romania, CC is the second most common, with incidence (22.6%
000) and mortality rates (9.6%
000) three times higher than any other European country. Our aim was to assess the level of knowledge regarding HPV infection among parents, highschool students, medical students and doctors, with an emphasis on their main source of information—the Internet. (2) Methods: We applied five questionnaires to six categories of respondents: parents of pupils in the 6th–8th grades, medical students, doctors, boys in the 11th–12th grades, girls in the 11th–12th grades and their mothers. (3) Results: We included a total of 3108 respondents. 83.83% of all respondents had known about HPV infection. The level of information about HPV infection and vaccination was either satisfactory, poor or very poor. Their main source of information varied depending on the respondent profile and professional activity. Medical students were informed by doctors and healthcare professionals (53.0%), doctors gathered their information from books, journals and specialized brochures (61.6%). For the other categories of respondents, the Internet was the main source of information. Most respondents answered that doctors and healthcare professionals should provide information on HPV infection and vaccination, but very few of them actually seeked information from their general practitioner. (4) Conclusions: Population adherence to the appropriate preventative programs, as well as relevant information disseminated by the medical staff are key elements towards reducing the risk of HPV-associated cancers. An important role could also be played by schools, where teachers and school doctors could provide relevant information on the general aspects of HPV infection. Additionally, sex education classes and parent-teacher meetings should cover the main characteristics of HPV infection and what preventative measures can be employed against it.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
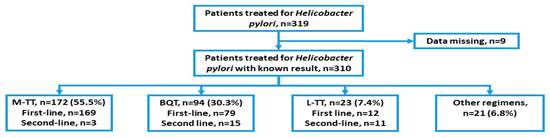
Comparative Effectiveness of Various Eradication Regimens for Helicobacter Pylori Infection in the Northeastern Region of Poland
by
Justyna Wasielica-Berger, Patryk Gugnacki, Maryla Mlynarczyk, Pawel Rogalski, Agnieszka Swidnicka-Siergiejko, Stefania Antonowicz, Michalina Krzyzak, Dominik Maslach, Andrzej Dabrowski and Jaroslaw Daniluk
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3887
Abstract
Purpose: Due to the lack of systematic data on antibiotic sensitivity, the treatment of the highly prevalent and pathogenic
Helicobacter pylori (
H. pylori) infection still poses a significant problem. Therefore, the aim of our study was to compare the efficacy of
[...] Read more.
Purpose: Due to the lack of systematic data on antibiotic sensitivity, the treatment of the highly prevalent and pathogenic
Helicobacter pylori (
H. pylori) infection still poses a significant problem. Therefore, the aim of our study was to compare the efficacy of the three most commonly used anti-
H. pylori therapies in northeastern Poland. Patients and Methods: This was a retrospective, single-center study performed on 289 outpatients with an
H. pylori infection. Patients received one of the following three treatment regimens: (1) bismuth quadruple therapy (BQT) for 10 days, (2) metronidazole-based triple therapy (M-TT) for 10 or 14 days, and (3) levofloxacin-based triple therapy (L-TT) for 10 or 14 days. Results: BQT, M-TT, and L-TT accounted for 93.2% of prescribed anti-
H. pylori therapies. The overall success rate for all treatment regimens was 84.1% (243/289). The effectiveness of first- and second-line therapy was similar and reached 83.8% and 86.2%, respectively. The efficacy of the individual treatment regimens was as follows: (1) BQT—89.4% (84/94), (2) M-TT—80.6% (112/139) and 78.8% (26/33) for 10 and 14 days, respectively, and (3) L-TT—84.6% (11/13) and 100% (10/10) for 10 and 14 days, respectively. The overall duration of treatment and type and dose of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) had no effect on the treatment efficacy. Conclusions: In the northeastern part of Poland, 10-day BQT and 10- or 14-day L-TT are effective treatment regimens for
H. pylori eradication and have appear to be superior to M-TT. Practitioners in our clinic followed mostly local anti-
H. pylori therapy guidelines.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Relationship between Dietary Behaviors and Physical Activity and the Components of Metabolic Syndrome: A Case-Control Study
by
Małgorzata Godala, Michalina Krzyżak, Dominik Maślach and Ewelina Gaszyńska
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3743
Abstract
Poor diet and low physical activity play an important role in the etiopathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. The aim of this study was to analyze the association between nutrient intake, groups of food products and physical exercise undertaken and the components of metabolic syndrome
[...] Read more.
Poor diet and low physical activity play an important role in the etiopathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. The aim of this study was to analyze the association between nutrient intake, groups of food products and physical exercise undertaken and the components of metabolic syndrome (MS). The study included 330 patients with MS, and the control group comprised of 270 subjects without MS. The food intake was assessed using 24-h dietary recall, and a 13-item Food Frequency Questionnaire. To assess nutrition knowledge, a Beliefs and Eating Habits Questionnaire was used. The level of physical activity was assessed using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire. Three patterns of behavior were identified: Prudent-Active, Western-Sedentary, and NotPrudent-notWestern-lowActive. In the Prudent-Active group, as compared to the NotPrudent-notWestern-lowActive subjects, the risk of central obesity, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL cholesterol and hyperglycemia occurrence was lower. There was also a lower proportion of patients with MS. As compared to the NotPrudent-notWestern-lowActive subjects, in the Prudent-Active group there was more than a two times higher chance of subjects with a high level of nutrition knowledge. Western diets have been proven to exert a detrimental effect on the components of MS. When designing intervention programs, education of patients with MS on dietary habits and physical activity should be considered.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Healthcare Utilization and Adherence to Treatment Recommendations among Children with Type 1 Diabetes in Poland during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Justyna Grudziąż-Sękowska, Kuba Sękowski and Bartosz Kobuszewski
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3853
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) is, next to obesity and asthma, the most common chronic disease in children in Poland. The results of T1D treatment strongly depend on the patient’s compliance with therapeutic recommendations, which entails the use of necessary health services. Based
[...] Read more.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) is, next to obesity and asthma, the most common chronic disease in children in Poland. The results of T1D treatment strongly depend on the patient’s compliance with therapeutic recommendations, which entails the use of necessary health services. Based on a retrospective analysis of the data on health services provided in 2016–2020 to over 15.5 thousand patients with T1D in Poland, we assessed the compliance of the actual model of treatment of T1D in children with the current guidelines. It was found that only about 50% of patients received the number of diabetes consultations corresponding to the recognized standards, with about 15% of children with T1D remaining outside the public healthcare system. In the case of many outpatient services (ophthalmological, neurological, mental health), the number of consultations was extremely low—one order of magnitude lower than in general population and dropped even lower in 2020. This shows that the health needs of children with T1D are not being met within the public healthcare system. The COVID-19 pandemic caused significant limitations in access to healthcare in Poland. Compared to the pre-pandemic period there was a significant decrease (−27% compared to 2019) in the number of hospitalizations, and a substantial increase (+22% compared to 2019) in the number of diabetic ketoacidoses (DKA) cases. The proportion of hospitalizations caused by DKA rose to 8.9% compared to 7.3% in 2019.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Resting Metabolic Rate in Women with Endocrine and Osteoporotic Disorders in Relation to Nutritional Status, Diet and 25(OH)D Concentration
by
Małgorzata Godala, Ewa Sewerynek, Dominik Maślach, Michalina Krzyżak and Ewelina Gaszyńska
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2642
Abstract
There are speculations that vitamin D may be an important regulator of the energy metabolism. The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of serum 25(OH)D concentration and nutritional status on the resting metabolic rate. The study group consisted of 223
[...] Read more.
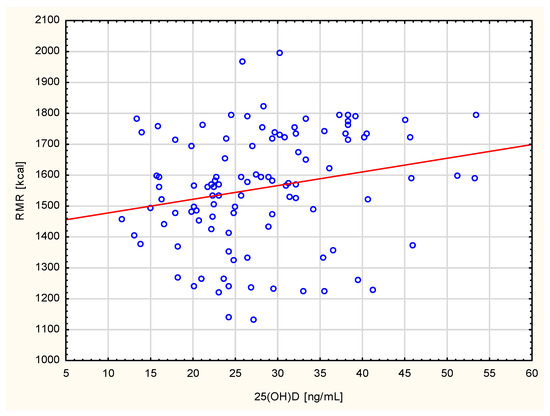
There are speculations that vitamin D may be an important regulator of the energy metabolism. The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of serum 25(OH)D concentration and nutritional status on the resting metabolic rate. The study group consisted of 223 women with endocrine and/or osteoporotic disorders. The control group consisted of 108 women, clinically healthy. The total 25(OH)D concentration level was measured with an assay using chemiluminescent immunoassay technology. Indirect calorimetry was applied to assess the resting metabolic rate. The mean resting metabolic rate was significantly lower in the group of women with metabolic disorders than in the control group. A correlation was found between serum 25(OH)D levels in healthy subjects and the resting metabolic rate. Significantly higher resting metabolic rate was found in women with normal serum 25(OH)D levels in comparison to subjects with deficient vitamin D levels. The control group demonstrated a relationship between body fat tissue and fat-free body mass and the resting metabolic rate. Both 25(OH)D concentration and body composition were factors influencing the resting metabolic rate in the group of healthy subjects. More research is needed to clarify the relationship between vitamin D status and metabolic rate in individuals with endocrine and osteoporotic disorders.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Use of Antidepressant and Antianxiety Pharmaceuticals as Well as Sick Leave in Poland
by
Dominika Krupa, Marcin Czech, Jarosław Pinkas and Anna Mosiołek
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3575
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a major upheaval to the lives of people and placed a strain on societal mental health. The aim of this research is to estimate the impact of the pandemic on the mental condition of the Polish population measured through
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a major upheaval to the lives of people and placed a strain on societal mental health. The aim of this research is to estimate the impact of the pandemic on the mental condition of the Polish population measured through the consumption of relevant medication and medical leave of absence from the workplace. Methods: We analyzed national-level data on the consumption of pharmaceuticals used in clinical practice in Poland in the treatment of depression and anxiety alongside medical absence in the workplace using the Interrupted Time Series model to estimate the significance of the pandemic. Results: We found no significant change regarding the consumption of pharmaceuticals with the development of the pandemic. Conversely, medical leaves of absence for psychiatric reasons increased significantly with the onset of COVID-19. The influence was strongest in the diagnosis of anxiety or reaction to severe stress and weakest in recurrent depression. Conclusion: The pandemic had a significant influence on the ability to work for psychiatric patients in Poland but did not change pharmaceutical use. Physicians should consider the mental health of patients impacted by the anti-epidemic measures. Further study is needed to fully understand the long-term impact of the pandemic on mental health in Poland.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
HPV Vaccination: Polish-Language Facebook Discourse Analysis
by
Karolina Sobeczek, Mariusz Gujski and Filip Raciborski
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3819
Abstract
Social media platforms are widely used for spreading vaccine-related information. The objectives of this paper are to characterize Polish-language human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination discourse on Facebook and to trace the possible influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on changes in the HPV vaccination debate.
[...] Read more.
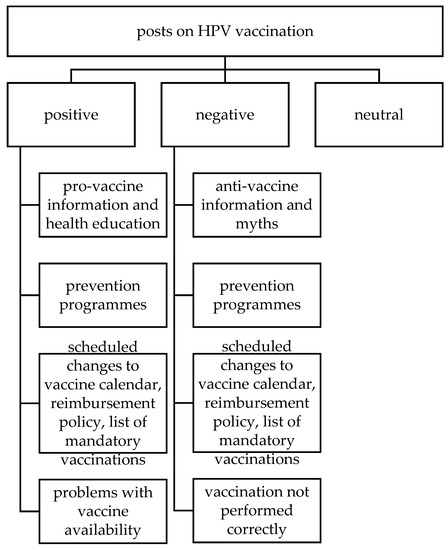
Social media platforms are widely used for spreading vaccine-related information. The objectives of this paper are to characterize Polish-language human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination discourse on Facebook and to trace the possible influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on changes in the HPV vaccination debate. A quantitative and qualitative analysis was carried out based on data collected with a tool for internet monitoring and social media analysis. We found that the discourse about HPV vaccination bearing negative sentiment is centralized. There are leaders whose posts generate the bulk of anti-vaccine traffic and who possess relatively greater capability to influence recipients’ opinions. At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic vaccination debate intensified, but there is no unequivocal evidence to suggest that interest in the HPV vaccination topic changed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge and Perceptions Regarding Coronavirus (COVID-19) among Pediatric Dentists during Lockdown Period
by
Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni, Sivakumar Nuvvula, Jaya Chandra Bhumireddy, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Priya Verma, Rishitha Sajja, Abdullah Alassaf, Basim Almulhim, Sara Alghamdi, Anupam Saha, Virinder Goyal and Srinivas Namineni
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3811
Abstract
Aim: To assess the knowledge and perceptions of COVID-19 among pediatric dentists based on their dependent source of information. Methods: A descriptive-analytical cross-sectional survey using a self-administered questionnaire with 23 questions was sent via Google forms to pediatric dentists. All participants were divided
[...] Read more.
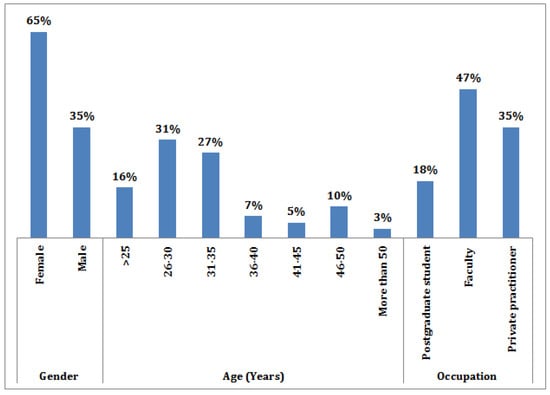
Aim: To assess the knowledge and perceptions of COVID-19 among pediatric dentists based on their dependent source of information. Methods: A descriptive-analytical cross-sectional survey using a self-administered questionnaire with 23 questions was sent via Google forms to pediatric dentists. All participants were divided into three groups [postgraduate residents (PGs), private practitioners (PP), and faculty (F)]. The comparison of knowledge and perception scores was made based on occupation, source of information, and descriptive statistics used for the analysis using SPSS 21.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Results: A total of 291 pediatric dentists completed the survey, and the majority of them were females (65%). Overall, good mean scores were obtained for knowledge (9.2 ± 1.07) and perceptions (5.6 ± 1.5). The majority of the participants used health authorities (45%) to obtain updates on COVID-19, while social media (35.1%) and both (19.6%) accounted for the next two. A statistically significant difference (
p < 0.05) was found among different pediatric dentists groups for relying on the source of information. Conclusion: Overall good pediatric dentists showed sufficient knowledge regarding COVID-19. The pediatric dentists’ age, occupation, and source of information influenced knowledge regarding COVID-19, whereas perceptions were influenced by age and gender of the participants. Health authorities successfully educated pediatric dentists than the social media
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge and Attitude of Polish Dental Healthcare Professionals during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Anna Turska-Szybka, Maria Prokopczyk, Piotr Winkielman and Dorota Olczak-Kowalczyk
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3431
Abstract
Objectives: This study analyzed Polish dentists’ knowledge of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the main problems in their work during the early phase of the pandemic. Methods: Dentists responded to an online anonymous survey consisting of 57 questions relating to socio-demographics, knowledge about COVID-19,
[...] Read more.
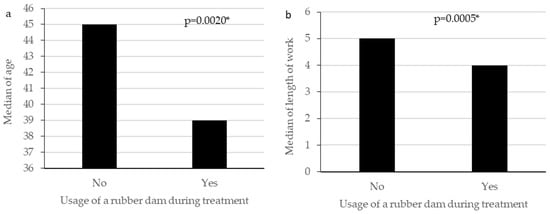
Objectives: This study analyzed Polish dentists’ knowledge of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the main problems in their work during the early phase of the pandemic. Methods: Dentists responded to an online anonymous survey consisting of 57 questions relating to socio-demographics, knowledge about COVID-19, and office procedures. The obtained data were analyzed using basic descriptive statistics, significance of dependencies and Chi square and Mann–Whitney tests;
p < 0.05. Results: Ultimately, responses from 730 dentists were included. The mean age was 43.62 ± 11.57. Almost 3/4 of the respondents followed the information on COVID-19. A total of 95.5% had knowledge about COVID-19. Genetic testing was the basic test according to 69.2%. Further, 56.0% were concerned about the pandemic, and 23.6% were significantly anxious. In addition, 42.1% considered a risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace as very high. A total of 84.0% admitted patients performing a triage and using personal protective equipment (PPE). Further, 44.5% planned to become vaccinated. Continuing the work during the pandemic was strongly correlated with age, sector, and location and duration of work. Conclusions: Most Polish dentists follow the information on the COVID-19 protocol and have sufficient knowledge about COVID-19. Dentists are concerned and anxious about the situation. The vast majority admitted patients during the pandemic and use PPE. Only almost half plan to be vaccinated.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Organization of a Hospital Ward Aimed at Admitting Patients with SARS-CoV-2: An Economic and Epidemiological Perspective
by
Artur Z. Białoszewski, Dorota Gołąb-Bełtowicz and Monika Raulinajtys-Grzybek
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2924
Abstract
The SARS-CoV-2 epidemic requires dynamic action on the part of the entire health care system to provide infected patients whose condition requires hospitalization with access to appropriate medical care and infrastructure, including oxygen devices and ventilators. The demand for specialized inpatient care has
[...] Read more.
The SARS-CoV-2 epidemic requires dynamic action on the part of the entire health care system to provide infected patients whose condition requires hospitalization with access to appropriate medical care and infrastructure, including oxygen devices and ventilators. The demand for specialized inpatient care has increased rapidly and in many areas exceeds the resources available to date. Individual hospitals must make investment and organizational decisions to increase their capacity to handle patients with SARS-CoV-2. The aim of the article is to present the organizational and investment steps taken to establish and maintain an infectious hospital ward as well as the clinical and financial consequences of this decision. The study was conducted in a hospital ward that was launched at the end of October 2020 to care for patients with SARS-CoV-2. A case study method was used. The department was characterized taking into account its importance for: (1) the regional level of health coverage of the population, (2) the organization of the hospital’s activities, (3) the financial and economic situation of the hospital.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The German Translation of the Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics-9 (SAVE-9) Scale: Results from Healthcare Workers during the Second Wave of COVID-19
by
Julia König, Seockhoon Chung, Verena Ertl, Bettina K. Doering, Hannah Comtesse, Johanna Unterhitzenberger and Antonia Barke
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4189
Abstract
Healthcare workers (HCW) are among those most directly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. Most research with this group has used ad hoc measures, which limits comparability across samples. The Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics-9 scale (SAVE-9) is a nine-item scale first developed
[...] Read more.
Healthcare workers (HCW) are among those most directly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. Most research with this group has used ad hoc measures, which limits comparability across samples. The Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics-9 scale (SAVE-9) is a nine-item scale first developed in Korea, and has since been translated into several languages. We report on data collected from 484 German HCW between November 2020 and March 2021, during the “second wave” of coronavirus infections. We conducted item analysis, confirmatory factor analysis on the previously found factor solutions of the SAVE-9, examined correlations with established measures of depression, generalized anxiety, and insomnia, and compared scores between different groups of HCW. The psychometric properties of the German SAVE-9 were satisfactory and comparable to previous findings from Korea and Russia. Correlations with mental health measures were positive, as expected. We found some significant differences between groups of HCW on the SAVE-9 which were consistent with the literature but did not appear on the other mental health measures. This suggests that the SAVE-9 taps into specifically work-related stress, which may make it a helpful instrument in this research area.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
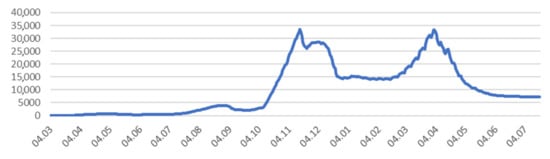
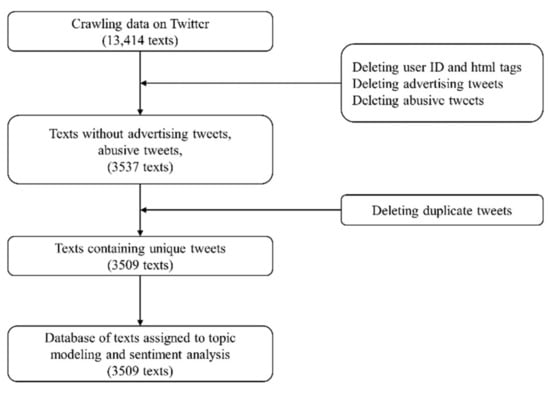
Text Mining Approaches to Analyze Public Sentiment Changes Regarding COVID-19 Vaccines on Social Media in Korea
by
Jae-Geum Shim, Kyoung-Ho Ryu, Sung Hyun Lee, Eun-Ah Cho, Yoon Ju Lee and Jin Hee Ahn
Cited by 44 | Viewed by 5524
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the entire world, resulting in a tremendous change to people’s lifestyles. We investigated the Korean public response to COVID-19 vaccines on social media from 23 February 2021 to 22 March 2021. We collected tweets related to COVID-19 vaccines
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the entire world, resulting in a tremendous change to people’s lifestyles. We investigated the Korean public response to COVID-19 vaccines on social media from 23 February 2021 to 22 March 2021. We collected tweets related to COVID-19 vaccines using the Korean words for “coronavirus” and “vaccines” as keywords. A topic analysis was performed to interpret and classify the tweets, and a sentiment analysis was conducted to analyze public emotions displayed within the retrieved tweets. Out of a total of 13,414 tweets, 3509 were analyzed after preprocessing. Eight topics were extracted using the Latent Dirichlet Allocation model, and the most frequently tweeted topic was vaccine hesitation, consisting of fear, flu, safety of vaccination, time course, and degree of symptoms. The sentiment analysis revealed a similar ratio of positive and negative tweets immediately before and after the commencement of vaccinations, but negative tweets were prominent after the increase in the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases. The public’s anticipation, disappointment, and fear regarding vaccinations are considered to be reflected in the tweets. However, long-term trend analysis will be needed in the future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
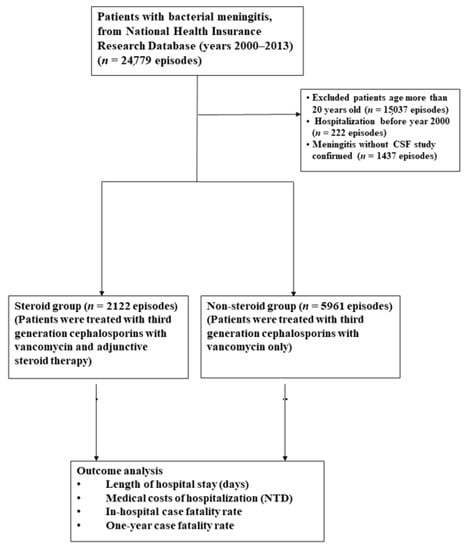
Nationwide Population-Based Epidemiological Study for Outcomes of Adjunctive Steroid Therapy in Pediatric Patients with Bacterial Meningitis in Taiwan
by
Dong-Yi Hsieh, Yun-Ru Lai, Chia-Yi Lien, Wen-Neng Chang, Chih-Cheng Huang, Ben-Chung Cheng, Chia-Te Kung and Cheng-Hsien Lu
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3196
Abstract
Although corticosteroids can serve as an effective anti-inflammatory adjuvant therapy, the role of adjunctive steroid therapy in pediatric bacterial meningitis in Taiwan remains under-investigated. Cases of acute bacterial meningitis, aged between 1 month and 20 years, were divided into a steroid group (empirical
[...] Read more.
Although corticosteroids can serve as an effective anti-inflammatory adjuvant therapy, the role of adjunctive steroid therapy in pediatric bacterial meningitis in Taiwan remains under-investigated. Cases of acute bacterial meningitis, aged between 1 month and 20 years, were divided into a steroid group (empirical antibiotics with adjunctive steroid therapy) and a non-steroid group (empirical antibiotics only). Data were identified from the annual hospitalization discharge claims of the National Health Insurance Research Database using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes. Of the 8083 episodes enrolled in this study, 26% (2122/8083) and 74% (5961/8083) were divided into the steroid and non-steroid groups, respectively. The fatality rates were 7.9% in the steroid group and 1.7% in the non-steroid group during hospitalization (
p < 0.0001). In the steroid and non-steroid groups, the median length of hospital stay was 13 and 6 days, respectively (
p < 0.0001). Medical costs (median (interquartile range)) of hospitalization were 77,941 (26,647–237,540) and 26,653 (14,287–53,421) New Taiwan dollars in the steroid and non-steroid groups, respectively (
p < 0.0001). The steroid group had a more fulminant course at baseline, a higher fatality rate, length of hospital stay, and medical cost of hospitalization. Therefore, the beneficial effects of the adjunctive use of corticosteroids in pediatric bacterial meningitis are inconclusive, and additional prospective multicenter investigations are required to clarify this issue.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
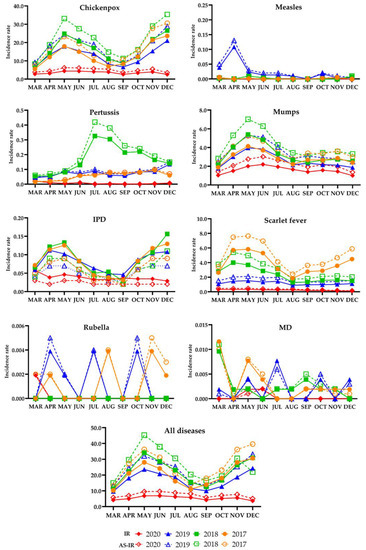
Infectious Respiratory Diseases Decreased during the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea
by
Da Hae Kim, Thi Mai Nguyen and Jin Hee Kim
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 3763
Abstract
Infectious respiratory diseases are highly contagious and very common, and thus can be considered as one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. We followed up the incidence rates (IRs) of eight infectious respiratory diseases, including chickenpox, measles, pertussis, mumps, invasive
[...] Read more.
Infectious respiratory diseases are highly contagious and very common, and thus can be considered as one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. We followed up the incidence rates (IRs) of eight infectious respiratory diseases, including chickenpox, measles, pertussis, mumps, invasive pneumococcal disease, scarlet fever, rubella, and meningococcal disease, after COVID-19 mitigation measures were implemented in South Korea, and then compared those with the IRs in the corresponding periods in the previous 3 years. Overall, the IRs of these diseases before and after age- or sex-standardization significantly decreased in the intervention period compared with the pre-intervention periods (
p < 0.05 for all eight diseases). However, the difference in the IRs of all eight diseases between the IRs before and after age-standardization was significant (
p < 0.05 for all periods), while it was not significant with regard to sex-standardization. The incidence rate ratios for eight diseases in the pre-intervention period compared with the intervention period ranged from 3.1 to 4.1. These results showed the positive effects of the mitigation measures on preventing the development of respiratory infectious diseases, regardless of age or sex, but we need to consider the age-structure of the population to calculate the effect size. In the future, some of these measures could be applied nationwide to prevent the occurrence or to reduce the transmission during outbreaks of these infections. This study provides evidence for strengthening the infectious disease management policies in South Korea.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
How the Intensity of Night Shift Work Affects Breast Cancer Risk
by
Marta Szkiela, Ewa Kusideł, Teresa Makowiec-Dąbrowska and Dorota Kaleta
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 6405
Abstract
Background—In 2019, the IARC concluded that “night shift work is probably carcinogenic to humans (Group 2A), based on limited evidence from human epidemiological studies and sufficient evidence of cancer and strong mechanistic evidence in experimental Animals.” The negative health consequences of night shift
[...] Read more.
Background—In 2019, the IARC concluded that “night shift work is probably carcinogenic to humans (Group 2A), based on limited evidence from human epidemiological studies and sufficient evidence of cancer and strong mechanistic evidence in experimental Animals.” The negative health consequences of night shift work may depend on how the night shifts are scheduled. The aim of this study was to investigate how the characteristics of night work affect the risk of developing breast cancer. Methods—A case–control study was conducted in 2015–2019 in the Lodz region. The case group included 494 women with breast cancer, while the control group included 515 healthy women. Results—Night work was found to be the third most important factor regarding breast cancer after a high BMI and a short or no breastfeeding period and before factors such as early menstruation, late menopause, no pregnancy, and smoking. The harmful effects of night work were influenced by its intensity, frequency, rotation, and the number of night shift years worked. Night work increases the breast cancer risk by 2.34 times, and high-intensity night work increases the breast cancer risk by 2.66 times. Conclusions—Appropriate ergonomic recommendations for night shift work for employers should be considered.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Indonesian Residents toward COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Survey
by
Muhammad Muslih, Henny Dwi Susanti, Yohanes Andy Rias and Min-Huey Chung
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 5486
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a pandemic. We examined the KAP’s relationship with factors associated with practice toward the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia. This cross-sectional survey study was conducted between March and April 2020 and included 1033 participants. Knowledge scores of COVID-19
[...] Read more.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a pandemic. We examined the KAP’s relationship with factors associated with practice toward the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia. This cross-sectional survey study was conducted between March and April 2020 and included 1033 participants. Knowledge scores of COVID-19 were positively associated with wearing a mask when leaving home (odds ratio (OR): 1.22,
p < 0.05). Although men had a lower knowledge score, they were less likely to go to a crowded place compared with women (OR: 0.79,
p < 0.05). However, women (OR: 1.25,
p < 0.05) were more likely than men to wear a mask when leaving home. Furthermore, men (OR: 3.32,
p < 0.05) were more likely than women to have a positive attitude toward COVID-19. Indonesian residents had satisfactory knowledge, demonstrated a positive attitude, and followed appropriate practices toward the pandemic. More educated individuals had a more positive attitude. Men and women differed with respect to their knowledge-based practices. Men were less likely to go to crowded places, and women were more likely to wear a mask when leaving home. Furthermore, men were more likely to wear a mask when leaving home than women when men had the attitude that Indonesia can win against COVID-19.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
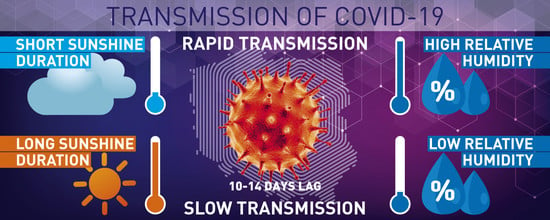
Impact of Meteorological Conditions on the Dynamics of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Poland
by
Bogdan Bochenek, Mateusz Jankowski, Marta Gruszczynska, Grzegorz Nykiel, Maciej Gruszczynski, Adam Jaczewski, Michal Ziemianski, Robert Pyrc, Mariusz Figurski and Jarosław Pinkas
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5293
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the novel coronavirus. The role of environmental factors in COVID-19 transmission is unclear. This study aimed to analyze the correlation between meteorological conditions (temperature, relative humidity, sunshine duration, wind speed) and dynamics of
[...] Read more.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the novel coronavirus. The role of environmental factors in COVID-19 transmission is unclear. This study aimed to analyze the correlation between meteorological conditions (temperature, relative humidity, sunshine duration, wind speed) and dynamics of the COVID-19 pandemic in Poland. Data on a daily number of laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases and the number of COVID-19-related deaths were gatheredfrom the official governmental website. Meteorological observations from 55 synoptic stations in Poland were used. Moreover, reports on the movement of people across different categories of places were collected. A cross-correlation function, principal component analysis and random forest were applied. Maximum temperature, sunshine duration, relative humidity and variability of mean daily temperature affected the dynamics of the COVID-19 pandemic. An increase intemperature and sunshine hours decreased the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases. The occurrence of high humidity caused an increase in the number of COVID-19 cases 14 days later. Decreased sunshine duration and increased air humidity had a negative impact on the number of COVID-19-related deaths. Our study provides information that may be used by policymakers to support the decision-making process in nonpharmaceutical interventions against COVID-19.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
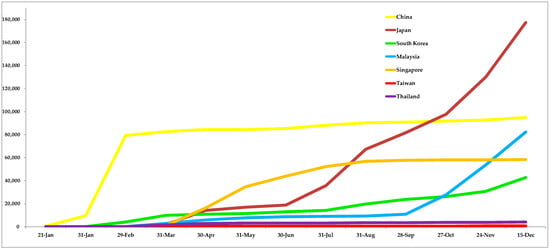
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness of Epidemic Preventive Policies and Hospital Strategies in Combating COVID-19 Outbreak in Taiwan
by
Ting Wan Tan, Han Ling Tan, Man Na Chang, Wen Shu Lin and Chih Ming Chang
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 5429
Abstract
(1) Background: The implementation of effective control measures in a timely fashion is crucial to control the epidemic outbreak of COVID-19. In this study, we aimed to analyze the control measures implemented during the COVID-19 outbreak, as well as evaluating the responses and
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The implementation of effective control measures in a timely fashion is crucial to control the epidemic outbreak of COVID-19. In this study, we aimed to analyze the control measures implemented during the COVID-19 outbreak, as well as evaluating the responses and outcomes at different phases for epidemic control in Taiwan. (2) Methods: This case study reviewed responses to COVID-19 and the effectiveness of a range of control measures implemented for epidemic control in Taiwan and assessed all laboratory-confirmed cases between 11 January until 20 December 2020, inclusive of these dates. The confirmation of COVID-19 infection was defined as the positive result of a reverse-transcriptase–polymerase-chain-reaction test taken from a nasopharyngeal swab. Test results were reported by the Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. The incidence rate, mortality rate, and testing rate were compiled, and the risk ratio was provided to gain insights into the effectiveness of prevention measures. (3) Results and Discussion: This study presents retrospective data on the COVID-19 incidence rate in Taiwan, combined with the vital preventive control measures, in a timeline of the early stage of the epidemic that occurred in Taiwan. The implementation of multiple strategy control measures and the assistance of technologies to control the COVID-19 epidemic in Taiwan led to a relatively slower trend in the outbreak compared to the neighboring countries. In Taiwan, 766 confirmed patients were included, comprised of 88.1% imported cases and 7.2% local transmission cases, within the studied period. The incidence rate of COVID-19 in Taiwan during the studied period was 32 per million people, with a mortality rate of 0.3 per million people. Our analysis showed a significantly raised incidence risk ratio in the countries of interest in comparison to Taiwan during the study period; in the range of 1.9 to 947.5. The outbreak was brought under control through epidemic policies and hospital strategies implemented by the Taiwan Government. (4) Conclusion: Taiwan’s preventive strategies resulted in a drastically lower risk for Taiwan nationals of contracting COVID-19 when new pharmaceutical drug or vaccines were not yet available. The preventive strategies employed by Taiwan could serve as a guide and reference for future epidemic control strategies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
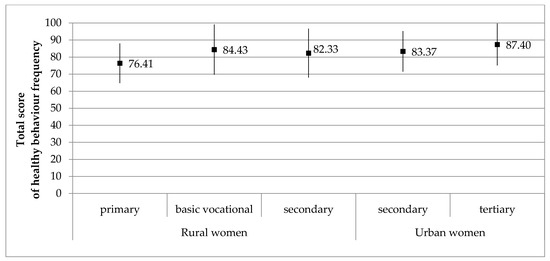
Depressive Symptoms and Healthy Behavior Frequency in Polish Postmenopausal Women from Urban and Rural Areas
by
Mariusz Gujski, Dorota Raczkiewicz, Ewa Humeniuk, Beata Sarecka-Hujar, Artur Wdowiak and Iwona Bojar
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2935
Abstract
The objective of this study was to determine whether the severity of depressive symptoms was linked to healthy behaviors in Polish postmenopausal women and whether the strength of the link differed between women living in urban versus rural settings. The study was conducted
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to determine whether the severity of depressive symptoms was linked to healthy behaviors in Polish postmenopausal women and whether the strength of the link differed between women living in urban versus rural settings. The study was conducted in 2018 in the Lublin region of Poland and included 396 postmenopausal women (239 living in rural areas and 157 in urban areas). The severity of depressive symptoms was evaluated by the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and the frequency of healthy behaviors was assessed using the Inventory of Healthy Behaviors. Postmenopausal women living in rural areas underwent menopause significantly earlier, were more often widowed, more often obese, more often less educated, and less likely to have never married when compared to those living in urban areas. Importantly, rural postmenopausal women endorsed more depressive symptoms (
p = 0.049). There was a negative correlation between the severity of depressive symptoms and age in urban postmenopausal women (r = −0.174,
p = 0.029), but this was not evident in rural women (r = −0.034,
p = 0.600). The frequency of healthy behaviors was significantly lower in rural postmenopausal women, especially with respect to nutritional habits. A positive correlation was found between the frequency of healthy behaviors and the level of education in both sets of women (
p = 0.034 and
p = 0.045, respectively). To summarize, we found a significant link between healthy behaviors and depressive symptoms in postmenopausal women. We also found that this link was more evident in rural than in urban women.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Tobacco and E-Cigarettes Point of Sale Advertising—Assessing Compliance with Tobacco Advertising, Promotion and Sponsorship Bans in Poland
by
Kinga Polanska and Dorota Kaleta
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3833
Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate compliance with the ban on tobacco and e-cigarette products advertising at point of sale (POS) before and after amendment of the Polish Tobacco Control Act. Data were collected, using an observation checklist, between March and
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to evaluate compliance with the ban on tobacco and e-cigarette products advertising at point of sale (POS) before and after amendment of the Polish Tobacco Control Act. Data were collected, using an observation checklist, between March and October 2014 (
n = 1450 POS) and between March and October 2019 (
n = 1320 POS). Ban on tobacco and e-cigarette advertising at POS is commonly violated in Poland. In all POS, at least one form (including tobacco products display) of tobacco advertising was found in 2014 and in 2019. The most common types of tobacco advertising in 2014 were change and counter mats (61%, 42%), posters (38%) and illuminated banners (37%). In 2019, a decrease in promoting tobacco products in the form of mats (
p ≤ 0.001), posters and boards (
p < 0.001) but an increase in video screens were observed (from 8% in 2014 to 30% in 2019;
p < 0.001). A significant increase in the presence of any e-cigarette ads, including e-cigarette displays, illuminated banners and video screens, was observed in 2019 as compared to 2014 (90% vs. 30%; 89% vs. 20%; 31% vs. 2%; 31% vs. 0.5%;
p < 0.001). The minimum age or a no-sale-to-minors signs for tobacco and e-cigarettes were not sufficiently placed in POS to comply with the Act. Poor enforcement of the ban on tobacco and e-cigarette ads at POS provides the tobacco industry with an opportunity to promote their products using unlawful ways. There is a need to educate the public, retailers and civil society with respect to their legal responsibilities and roles.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of Acinetobacter baumannii Activity in Vascular Surgery Units through Epidemiological Management Based on the Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Genotyping
by
Anna Szczypta, Katarzyna Talaga-Ćwiertnia, Małgorzata Kielar, Paweł Krzyściak, Anna Gajewska, Mirosław Szura, Małgorzata Bulanda and Agnieszka Chmielarczyk
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3912
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The genus
Acinetobacter demonstrates resistance to antibiotics and has been shown to spread in the hospital environment causing epidemic outbreaks among hospitalized patients. The objectives of the present study was to investigate the antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, and clonality among
Acinetobacter baumannii
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The genus
Acinetobacter demonstrates resistance to antibiotics and has been shown to spread in the hospital environment causing epidemic outbreaks among hospitalized patients. The objectives of the present study was to investigate the antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, and clonality among
Acinetobacter baumannii strains. Materials and Methods: The study involved 6 (I Outbreak) and 3 (II Outbreak)
A. baumannii strains isolated from patients hospitalized in vascular surgery unit. Results: All tested
A. baumannii strains were extensively drug resistant (XDR) and all the isolates were carbapenem-resistant and among them, all carried the
blaOXA-51 gene, the
blaOXA-24 gene, as well as the
blaOXA-23 gene. All of the investigated strains had the ability to form a biofilm, but all of them produced less biofilm than the reference strain. Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) showed that all strains belonged to the ST2 clone. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) divided the tested outbreak strains into two clones (A and B). Conclusion: This study shows a nosocomial spread of XDR
A. baumannii ST2 having the
blaOXA-51 gene, the
blaOXA-24 gene, as well as the
blaOXA-23 gene, low biofilm formers, that was prevalent in the vascular surgery unit. To identify the current situation of vascular surgery departments targeted epidemiological investigation was needed. Effective implementation of infection control prevented the spread of the epidemic outbreaks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
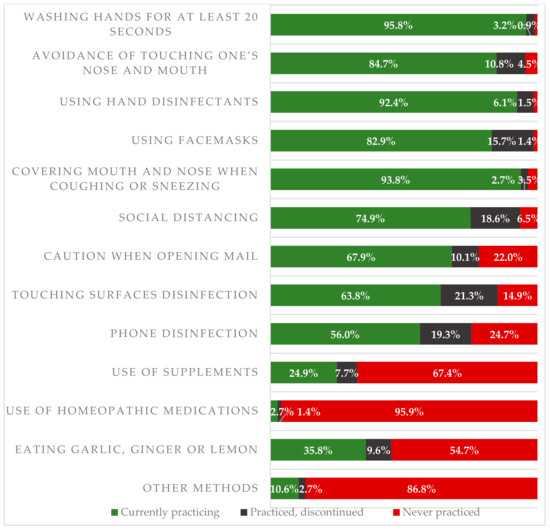
Open AccessArticle
Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Police Officers in Poland—Implications for Public Health Policies
by
Filip Raciborski, Mateusz Jankowski, Mariusz Gujski, Jarosław Pinkas, Piotr Samel-Kowalik, Artur Zaczyński, Igor Pańkowski, Kamil Rakocy and Waldemar Wierzba
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3464
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to characterize sources of knowledge on the means of prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infections as well as to assess the methods of preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among police employees in Poland and their potential impact on the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aimed to characterize sources of knowledge on the means of prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infections as well as to assess the methods of preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among police employees in Poland and their potential impact on the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Methods: The study consisted of two phases: questionnaire and laboratory tests for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The questionnaire included 30 questions related to risk factors, knowledge about SARS-CoV-2, and methods of infection prevention. Results: Data were obtained from 5082 police employees. The most common source of knowledge for a daily update on SARS-CoV-2 infection prevention was the Internet (42.6%), television (40.3%), and radio (39.7%). The most commonly used methods of SARS-CoV-2 infection included washing one’s hands for at least 20 s (95.8%), wearing facemasks (82.9%), and physical distancing (74.9%). Results of IgG tests were lower in police units where the overall compliance with the preventive measures was higher (
p < 0.01). Women were more likely to exercise SARS-CoV-2 infection prevention behaviors compared to men. Compliance with the recommended protective measures increased with age. Conclusions: Lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG seropositivity rates were observed in police units with better overall compliance with the preventive measures, suggesting the key importance of group rather than individual behaviors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures