Journal Description
International Journal of Financial Studies
International Journal of Financial Studies
is an international, peer-reviewed, scholarly open access journal on financial market, instruments, policy, and management research published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), EconLit, EconBiz, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Business, Finance) / CiteScore - Q2 (Finance)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
The Measurement and Characteristic Analysis of the Chinese Financial Cycle
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 187; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040187 - 3 Oct 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In this paper, based on Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity (GARCH) model, five financial serials are dynamically weighted, and then China’s Financial Conditions Index is synthesized to measure China’s financial cycle. After that, using the monthly data of 2000–2023 as sample space, this paper
[...] Read more.
In this paper, based on Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity (GARCH) model, five financial serials are dynamically weighted, and then China’s Financial Conditions Index is synthesized to measure China’s financial cycle. After that, using the monthly data of 2000–2023 as sample space, this paper utilizes the Markov Switching (MS) model to analyze the characteristics of China’s financial cycle and to investigate the four-zone system. Then, the Vector Autoregression (VAR) model focuses on investigating the macroeconomic effects of China’s financial cycle. The findings are as follows: Firstly, the dynamic weighting approach based on GARCH model is more suitable for valuating China’s financial cycle. Secondly, China’s financial cycle has a strong inertia at the state of transition and the imbalance of China’s overall financial situation is very common. Additionally, China’s financial cycle is distinctly characterized by the double asymmetry of fewer contractions and more expansions, shorter expansions, and longer expansions. Thirdly, China’s financial expansion offers a nine-month short-term stimulus to output and exerts lasting upward pressure on prices.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Spot Volatility Measurement Using a Change-Point Duration Model in the High-Frequency Market
by
Zhicheng Li, Haipeng Xing and Yan Wang
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 186; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040186 - 3 Oct 2025
Abstract
Modeling high-frequency volatility is an important topic of market microstructure, as it provides the empirical tools to measure and analyze the rapid price movements. Yet, volatility at a high frequency often exhibits abrupt shifts driven by news and trading activity, making accurate estimation
[...] Read more.
Modeling high-frequency volatility is an important topic of market microstructure, as it provides the empirical tools to measure and analyze the rapid price movements. Yet, volatility at a high frequency often exhibits abrupt shifts driven by news and trading activity, making accurate estimation challenging. This study develops a change-point duration (CPD) model to estimate spot volatility, in which price-change intensities remain constant between events but may shift at random change points. Using simulations and empirical analysis of Nasdaq limit order book data, we demonstrate that the CPD model achieves a favorable balance between responsiveness to sudden shocks and stability in volatility dynamics. Moreover, it outperforms benchmark approaches, including the classical autoregressive conditional duration model, nonparametric duration-based estimators, and candlestick-based measures. These findings highlight the CPD framework as an effective tool for volatility estimation in high-frequency trading environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Market Microstructure and Liquidity)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Climate Risk on Corporate Financialization—Based on Empirical Evidence of Chinese A-Share Listed Companies
by
Hongjian Lu, Jingjing Tang and Zhengge Song
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 185; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040185 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Climate risk, as a significant factor affecting human sustainable development, has emerged as a focal topic of concern for governments and all sectors of society. Using a dataset from China’s Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share markets spanning 2007 to 2019, this study empirically examines
[...] Read more.
Climate risk, as a significant factor affecting human sustainable development, has emerged as a focal topic of concern for governments and all sectors of society. Using a dataset from China’s Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share markets spanning 2007 to 2019, this study empirically examines how climate risk influences corporate financialization. The empirical results show that heightened climate risk significantly reduces the level of corporate financialization, a finding that remains robust across multiple tests. Further heterogeneity analyses indicate that the suppressive effect of climate risk is particularly evident among state-owned enterprises, firms operating in intensely competitive industries, and those located in regions subject to more stringent environmental policies. Mechanism analysis suggests that climate risk inhibits corporate financialization primarily by intensifying firms’ financing constraints while simultaneously stimulating their innovation capacity. These findings imply that corporate financialization in China is largely driven by profit-maximizing behaviors rooted in “investment substitution” and “real-sector intermediation” motives. Collectively, this research enhances understanding of the channels through which climate risk impacts corporate financial behavior and offers valuable empirical insights for policymakers aiming to optimize climate regulations and redirect financial resources toward productive real-sector activities.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Financial Mismatch on Corporate ESG Performance: Evidence from Chinese A-Share Companies
by
Xiaoli Li, Wenxin Heng, Hangyu Zeng and Chengyi Xian
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 184; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040184 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
This study examines the effect of financial mismatch on corporate ESG performance in the context of China’s developmental strategy and its dual-carbon goals. Using panel data for Chinese A-share firms spanning 2009–2023 and employing fixed-effects regression models, we find that financial mismatch significantly
[...] Read more.
This study examines the effect of financial mismatch on corporate ESG performance in the context of China’s developmental strategy and its dual-carbon goals. Using panel data for Chinese A-share firms spanning 2009–2023 and employing fixed-effects regression models, we find that financial mismatch significantly weakens ESG performance. Further analysis reveals that this negative effect mainly operates through three channels: increased financing constraints, weakened internal control quality, and reduced innovation capability. The results remain robust across a series of alternative specifications and sensitivity tests. This study contributes to the literature by identifying financial mismatch as a key determinant of ESG outcomes and by clarifying the mechanisms through which it exerts influence. From a practical perspective, the findings suggest that alleviating financial mismatch by fostering patient capital, improving internal governance structures, and supporting firms’ green and sustainable investments is essential for enhancing corporate ESG performance and achieving China’s dual-carbon targets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends in Corporate Finance: ESG, Climate Risk, and Other Contemporary Issues)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Compliance with the Euro Area Financial Criteria and Economic Convergence in the European Union over the Period 2000–2023
by
Constantin Duguleana, Liliana Duguleana, Klára-Dalma Deszke and Mihai Bogdan Alexandrescu
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 183; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040183 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The two groups of EU economies, the euro area and the non-euro area, are statistically analyzed taking into account the fulfillment of the euro area financial criteria and economic performance over the period 2000–2023. Compliance with financial criteria, economic performance, and their significant
[...] Read more.
The two groups of EU economies, the euro area and the non-euro area, are statistically analyzed taking into account the fulfillment of the euro area financial criteria and economic performance over the period 2000–2023. Compliance with financial criteria, economic performance, and their significant influencing factors are presented comparatively for the two groups of countries. The long-run equilibrium between economic growth and its factors is identified by econometric approaches with the error correction model (ECM) and autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) models for the two data panels. In the short term, economic shocks are taken into account to compare their different influences on economic growth within the two groups of countries. The GMM system is used to model economic convergence at the EU level over the period under review. Comparisons between GDP growth and its theoretical values from econometric models have led to interesting conclusions regarding the existence and characteristics of economic convergence at the group and EU level. EU countries outside the euro area have higher economic growth rates than euro area economies over the period 2000–2023. In the long run, investment brings a higher increase in economic development in EU countries outside the euro area than in euro area countries. Economic shocks have been felt more deeply on economic growth in the euro area than in the non-euro area. The speed of adjustment towards long-run equilibrium in econometric models is slower for non-euro area economies than in the euro area over a one-year period. At the level of the European Monetary Union, change policies have a faster impact on economic development and a faster speed of adjustment towards equilibrium.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Financial Inclusion in Zimbabwe: Lessons from the Commercial Banking Sector
by
Auxilia Kawara, Binganidzo Muchara and Huibrecht M. van der Poll
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 182; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040182 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Financial institutions, researchers, and policymakers are taking steps to promote financial inclusion, a crucial aspect for social and economic development. This study explores the extent of financial inclusion (FI) in Zimbabwe’s commercial banks. This study employed a mixed-methods approach. A relationship mapping was
[...] Read more.
Financial institutions, researchers, and policymakers are taking steps to promote financial inclusion, a crucial aspect for social and economic development. This study explores the extent of financial inclusion (FI) in Zimbabwe’s commercial banks. This study employed a mixed-methods approach. A relationship mapping was conducted on the bank customers’ survey, and a thematic analysis was performed on bank executives to evaluate bank challenges and strategies. The findings confirmed positive strides towards achieving financial inclusion. Gaps in financial inclusion were identified in the high rate of people using informal channels and the limited policies in creating a conducive environment for financial inclusion. The study contributes to the ongoing debate by the World Bank in support of financial inclusion as an effective solution for countries like Zimbabwe, which is experiencing a severe macro crisis. The study adds to the emerging financial inclusion literature, proposing solutions to reduce financial exclusion in developing economies. Based on the study findings, policymakers should create a conducive environment for commercial banks and consumers of financial products and services in Zimbabwe.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Is U.S. CEO Equity and Cash Compensation Aligned with Agency Theory to Maximize Shareholder Returns?
by
Gurupdesh Pandher, David Koslowsky and Yosef Bonaparte
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 181; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040181 - 30 Sep 2025
Abstract
Recent international studies on CEO pay in Europe, Japan, and South Korea reveal significant differences from the U.S. in the use and effectiveness of equity-based CEO compensation, raising questions about the ability of conventional contracts based on agency theory to align with actual
[...] Read more.
Recent international studies on CEO pay in Europe, Japan, and South Korea reveal significant differences from the U.S. in the use and effectiveness of equity-based CEO compensation, raising questions about the ability of conventional contracts based on agency theory to align with actual CEO compensation practices. Our study contributes to this debate by evaluating nine hypotheses from an extended principal–agent framework in which CEO equity and cash incentives are jointly determined in the shareholder return-maximizing contract. The extended model also incorporates the noisy market valuation relationship between firm income and its market equity value, and distinguishes between firm ‘business risk’ and ‘equity risk’. Our empirical results show that CEO cash incentives increase with firm growth prospects and equity risk and decline with firm business risk and firm scale as predicted by the model; meanwhile, CEO equity incentives are partially consistent. Overall, given the dominance of equity compensation in U.S. CEO pay, our results show that cash pay tied to firm business performance (e.g., operating cash flow) is efficient and plays an important role in aligning CEO and shareholder interests and reducing corporate governance risks associated with agency misalignment.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Role of ESG Committee on Indonesian Companies in Promoting Sustainable Practice to Creditors: Symbolic or Substantive?
by
Muhammad Putra Aprullah, Yossi Diantimala, Muhammad Arfan and Irsyadillah Irsyadillah
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(4), 180; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13040180 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
This study investigates whether the presence of an ESG committee in promoting sustainable practices is symbolic or substantive to creditors when setting costs. With unbalanced panel data, the study used 1518 company-year observations from non-financial firms listed on the IDX period 2018 to
[...] Read more.
This study investigates whether the presence of an ESG committee in promoting sustainable practices is symbolic or substantive to creditors when setting costs. With unbalanced panel data, the study used 1518 company-year observations from non-financial firms listed on the IDX period 2018 to 2023. The hypothesis testing of this study was conducted by using moderated regression analysis (MRA). Hypothesis testing using a fixed effects model indicates that ESG disclosure can significantly lower the cost of debt. The role of the ESG committee is to act as a quasi-moderator for the relationship between ESG disclosure and the cost of debt. While the presence of an ESG committee can significantly reduce the cost of debt, the committee itself weakens the relationship between ESG disclosure and the cost of debt. Therefore, these findings suggest that the role of the ESG committee in promoting ESG disclosure to creditors in determining the cost of debt is becoming more substantive, moving away from a merely symbolic role that focuses on maintaining the company’s reputation and strengthening substantive management to control governance risk. The results of this study are expected to contribute to formulating policies that strengthen the role of ESG committees in improving corporate governance and sustainability practices by providing stakeholders with important and relevant ESG disclosure information for investment and funding decisions.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Financing Constraints and High-Quality Development of Chinese Listed Firms: Mechanisms of Investment Efficiency and Contingent Factors
by
Jun Yan, Zexia Zhao and Yan Liu
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 179; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030179 - 18 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Against the backdrop of tightened credit conditions, external financing constraints have increasingly become an important factor affecting enterprises’ high-quality development. This study focuses on the impact of financing constraints on the high-quality development of Chinese listed firms and constructs an analytical framework involving
[...] Read more.
Against the backdrop of tightened credit conditions, external financing constraints have increasingly become an important factor affecting enterprises’ high-quality development. This study focuses on the impact of financing constraints on the high-quality development of Chinese listed firms and constructs an analytical framework involving investment efficiency as a mediator and contextual factors such as managerial effectiveness and internal control quality as moderators. Using a longitudinal dataset of China’s A-share listed companies from 2007 to 2021, multivariate regression and mediation effect tests are conducted. The observational findings reveal a statistically meaningful U-shaped association between financial constraints and the high-quality development of enterprises. Further analysis confirms that investment efficiency partially mediates the relationship between financing constraints and high-quality development, while managerial effectiveness and internal control quality play significant moderating roles in this relationship. Additionally, the study reveals heterogeneous impacts of financing constraints on high-quality development across different regions. These findings provide insights into how enterprises can mitigate the adverse effects of financing constraints and promote high-quality development.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Road to Tax Collection Digitalization: An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Digital Payment Systems in Nigeria and the Role of Macroeconomic Factors
by
Cordelia Onyinyechi Omodero and Gbenga Ekundayo
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 178; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030178 - 17 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global movement towards a cashless society has prompted the payment of tax obligations through digital platforms and sources. In this international race to ensure that transaction payments are not hindered by the lack of physical cash, Nigeria is also making progress. Therefore,
[...] Read more.
The global movement towards a cashless society has prompted the payment of tax obligations through digital platforms and sources. In this international race to ensure that transaction payments are not hindered by the lack of physical cash, Nigeria is also making progress. Therefore, the focus of this study is to assess the implications of digital payment systems in enhancing the effectiveness of tax revenue collection in Nigeria. The analysis spans from the first quarter of 2009 to the fourth quarter of 2023, utilizing the Autoregressive Distributed Lag and Error Correction Model. The research uses the most active digital payment systems that have been in operation during the study period. These electronic payment types include digital cheques (CHQs), Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), Point-of-Sales (POSs), Mobile payment (MPY), and Web-based payment (WPY). These are the predictor variables, while the tax revenue collection (TXC) during this period is the dependent variable. The control variables include information and telecommunication technology penetration rate (ICTPR), inflation, and gross domestic product. The outcomes of this study reveal that, over the long term, a percentage change in CHQs, ATMs, MPY, and ICTPR is linked to a decline of 8.1%, 12.5%, 6.7%, and 22.4% in TXC, respectively. In contrast, WPY indicates a 7.2% positive increase in TXC while inflation exerts a positive increase of 46.7%. The Error Correction Model (ECM) suggests that the deviations from the long-term equilibrium in earlier years are being corrected at a rate of 3.9% in the current year. In the short term, it is noted that digital payment systems do not influence TXC. On the other hand, GDP maintains a significant negative influence on TXC, in both the long- and short-term. Given these results, the study recommends the establishment of a robust information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure to enhance effective tax collection, even from rural areas and the informal sector. It is also important for the government to develop strategies that will bring the informal sector into the tax net.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modeling Market Expectations of Profitability Mean Reversion: A Comparative Analysis of Adjustment Models
by
Miroslava Vlčková and Tomáš Buus
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 177; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030177 - 17 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper investigates how market expectations regarding profitability mean reversion are reflected in stock prices. We propose a model that infers implicit expectations of future earnings using publicly available share prices based on the assumption that markets efficiently incorporate forward-looking information. The study
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates how market expectations regarding profitability mean reversion are reflected in stock prices. We propose a model that infers implicit expectations of future earnings using publicly available share prices based on the assumption that markets efficiently incorporate forward-looking information. The study compares several adjustment models, including the classical partial adjustment framework and a mean reversion model, to identify the most suitable mechanism to capture the dynamics of expected earnings. Special attention is paid to the statistical characteristics of accounting data and ratio-based measures, which influence model performance. Using a dataset covering a twenty-year period, we find that the mean reversion model consistently outperforms partial adjustment models in explaining the behavior of cyclical and random components converging toward a long-term trend. The findings suggest that market prices embed rational expectations of profitability reversion, especially in periods of above average performance. These results align with previous research and provide a robust framework for understanding how earnings expectations are formed and adjusted in financial markets.
Full article
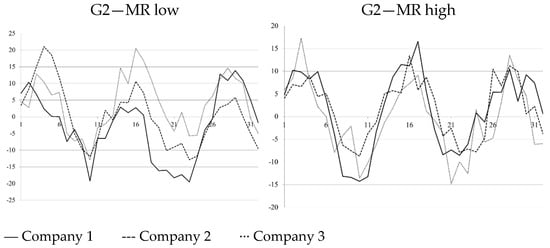
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Generational Insights into Herding Behavior: The Moderating Role of Investment Experience in Shaping Decisions Among Generations X, Y, and Z
by
Abdul Syukur, Amron Amron, Fery Riyanto, Febrianur Ibnu Fitroh Sukono Putra and Rifal Richard Pangemanan
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 176; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030176 - 16 Sep 2025
Abstract
Understanding generational differences in herding behavior is crucial for policymakers, financial educators, and market regulators, particularly in emerging markets where retail investor participation is rapidly growing. This study investigates the influence of herding behavior on investment decision-making among Generations X, Y, and Z
[...] Read more.
Understanding generational differences in herding behavior is crucial for policymakers, financial educators, and market regulators, particularly in emerging markets where retail investor participation is rapidly growing. This study investigates the influence of herding behavior on investment decision-making among Generations X, Y, and Z in Indonesia, as well as the moderating role of investment experience. Using a multi-group structural equation modeling (SEM) approach with data from 1293 retail investors, the research compares behavioral tendencies across cohorts. Results reveal that herding behavior has a positive and significant impact on investment decision-making in all generations, with the strongest effect observed in Generation X, followed by Generation Z and Generation Y. Investment experience significantly weakens herding behavior’s influence for Generation X but shows no significant moderating effect for Generations Y and Z, suggesting that psychological and social influences, particularly from digital platforms, may outweigh experiential learning in younger cohorts. These findings align with behavioral finance theory, which explains herding as a cognitive and emotional bias heightened by market uncertainty. The results provide practical implications for designing targeted financial education programs and regulatory measures to promote independent decision-making and reduce susceptibility to biased market information, especially among younger generations in digitally driven investment environments.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Fear of Missing out (FOMO), Loss Aversion, and Herd Behavior in Gold Investment Decisions: A Study in the Vietnamese Market
by
Xuan Hung Nguyen, Dieu Anh Bui, Nam Anh Le and Quynh Trang Nguyen
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 175; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030175 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigates the influence of FOMO, loss aversion, and herd behavior on gold investment decisions in the Vietnamese market. Employing data collected from 727 investors and the Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) method, the analysis results confirm the pivotal role
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the influence of FOMO, loss aversion, and herd behavior on gold investment decisions in the Vietnamese market. Employing data collected from 727 investors and the Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) method, the analysis results confirm the pivotal role of FOMO, with both direct and indirect impacts on gold investment decisions. Notably, both loss aversion and herd behavior positively influence FOMO, thereby indirectly encouraging relatively hasty and inadequately considered investment decisions. The study also finds that FOMO has a negative relationship with anticipated regret but is positively correlated with subjective expected pleasure. Furthermore, as determined through Multi-Group Analysis (MGA), psychological messages featuring “self-decision” or “risk warning” demonstrate a significant moderating role, potentially reducing or enhancing the influence of FOMO on investment decisions. These findings contribute to enriching behavioral finance theory and provide an empirical basis for developing effective risk management policies and gold market regulation aimed at mitigating the negative impacts of FOMO.
Full article
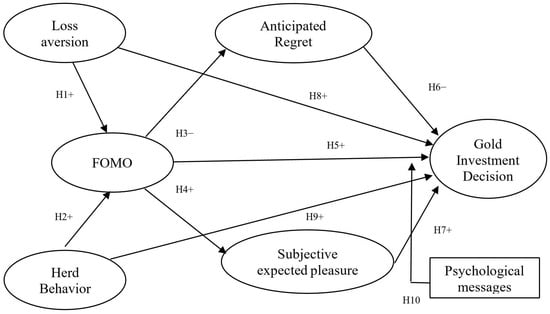
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bank Risk-Taking During COVID-19: The Role of Private and Public Ownership in GCC
by
Abdullah Aldousari, Ahmed Mohammed and Sarah Lindop
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 174; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030174 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
This study explores the ownership–risk relationship in the GCC emerging economies during the COVID-19 pandemic, examining 44 commercial banks classified as private and publicly owned banks. The two-stage least squares (2SLS) method is employed to identify endogeneity issues, with robustness checks using panel
[...] Read more.
This study explores the ownership–risk relationship in the GCC emerging economies during the COVID-19 pandemic, examining 44 commercial banks classified as private and publicly owned banks. The two-stage least squares (2SLS) method is employed to identify endogeneity issues, with robustness checks using panel data techniques. We analyzed the ownership–risk relationship, including non-linear and interaction effects. The results reveal that public ownership exhibits an inverted U-shaped relationship with NPLs, where moderate public concentration increases credit risk, while high public control marginally reduces it. Private ownership is linked to higher risk once bank-specific characteristics are controlled, reflecting riskier lending driven by profitability motives. We show that public banks demonstrate resilience due to stable deposits and implicit backing, whereas private banks are more vulnerable to systemic shocks. The impact of ownership structure on credit risk is context-dependent, reflecting heterogeneous ownership objectives in the GCC.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Capital Structure Theories in US Corporate Divestitures: A Study on Spin-Off Firms
by
Xian Chen, Sanjib Guha and Tahsina Haque Simu
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 173; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030173 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Some giant US conglomerates are now undergoing corporate spin-offs or are considering such spin-offs in the near future. Corporate spin-offs offer a unique opportunity to assess corporate capital structure decisions. The leverage ratio of the spin-off firms represents their initial capital structure. We
[...] Read more.
Some giant US conglomerates are now undergoing corporate spin-offs or are considering such spin-offs in the near future. Corporate spin-offs offer a unique opportunity to assess corporate capital structure decisions. The leverage ratio of the spin-off firms represents their initial capital structure. We investigate the capital structure of corporate spin-offs and find evidence that they adhere to the trade-off theory. This study provides evidence that the subsidiary firms tend to aim for a target capital ratio during the sample period. The results indicate that the partial adjustment model with firm fixed effects is a good fit for the data sample. The parent companies in corporate spin-offs exhibit a similar pattern but with a slower adjustment speed. The tendency to target capital ratios is observable in both market value and book value leverage measures for the parent and subsidiary firms. Indicators of the pecking order assumption do not possess statistically significant coefficients. Changes in share price affect market debt ratios in the short term. With alternative definitions of leverage, the estimated adjustment speeds vary. In the case of longer horizons, the results align with a continuous rate of adjustment.
Full article
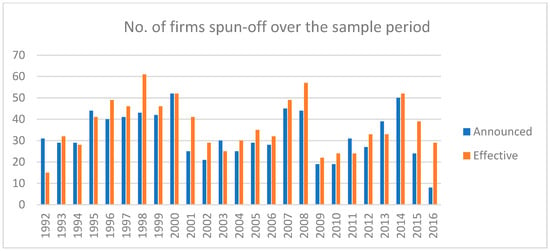
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Philosophy of Financial Performance: A Bibliometric and Conceptual Review
by
Ionela Munteanu, Liliana Ionescu-Feleagă, Bogdan Ștefan Ionescu, Alexandra-Maria Spânu and Mircea Iosif Rus
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 172; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030172 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Financial performance research has increasingly intersected with philosophical debates on ethics, sustainability, and stakeholder value, yet a clear framework linking these perspectives to actionable financial metrics remains underdeveloped. This study aims to explore how philosophical perspectives (normative, epistemological, and behavioral) inform the evolving
[...] Read more.
Financial performance research has increasingly intersected with philosophical debates on ethics, sustainability, and stakeholder value, yet a clear framework linking these perspectives to actionable financial metrics remains underdeveloped. This study aims to explore how philosophical perspectives (normative, epistemological, and behavioral) inform the evolving concept of financial performance, using bibliometric and science mapping techniques to analyze key research trends from 2006 to 2023. The analysis identifies four dominant thematic areas: corporate social responsibility (CSR), organizational performance, ethical governance, and circular economy innovation. We synthesize these into a practical framework that connects each theme to measurable financial indicators, enabling managers to refine capital allocation, investors to incorporate non-financial drivers into valuation models, and policymakers to design sustainability reporting standards that integrate both economic and ethical considerations. By bridging philosophical insights and financial decision-making tools, this study contributes to both the theoretical development and applied practice of performance assessment in finance.
Full article
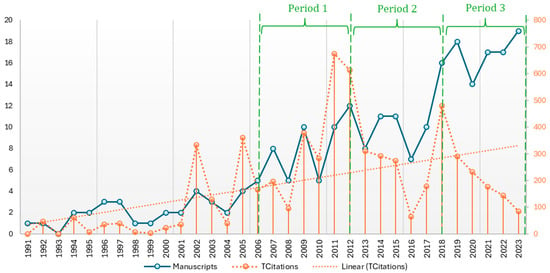
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
When Financial Awareness Meets Reality: Financial Literacy and Gen Z’s Entrepreneurship Interest
by
Eva Kicova, Jakub Michulek, Olga Ponisciakova and Juraj Fabus
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 171; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030171 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Financial literacy is a key competence for responsible decision-making and entrepreneurial readiness. This study looks at how Generation Z’s entrepreneurial participation is impacted by objective, subjective, and calibrated FL. The alignment of perceived and actual knowledge or calibration is highlighted as an understudied
[...] Read more.
Financial literacy is a key competence for responsible decision-making and entrepreneurial readiness. This study looks at how Generation Z’s entrepreneurial participation is impacted by objective, subjective, and calibrated FL. The alignment of perceived and actual knowledge or calibration is highlighted as an understudied factor that influences entrepreneurial behaviour. A mixed-methods approach was applied, combining a survey of 403 Slovak students with structured interviews with secondary school and university teachers. Quantitative analysis used Chi-square tests, Cramer’s V, sign schemes, and MLR. Qualitative interviews provided contextual insights into educational gaps and perceived barriers to entrepreneurship. The findings confirm that a higher financial literacy is positively related to entrepreneurial interest. Objective literacy has a slightly greater predictive value than self-assessed literacy, while calibration emerged as the strongest predictor: realistically, financially literate individuals displayed the highest entrepreneurial engagement, whereas both over- and underestimation of financial knowledge reduced it. Interviews highlighted insufficient financial education, limited practical experience, and fear of risk as major obstacles. By combining three aspects of financial literacy with business goals and offering fresh data from Slovakia, this study makes a contribution to the literature. In similar situations, it makes suggestions for enhancing financial education to support Generation Z’s entrepreneurial potential.
Full article
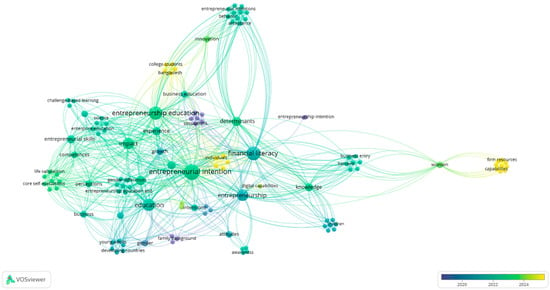
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predicting the Canadian Yield Curve Using Machine Learning Techniques
by
Ali Rayeni and Hosein Naderi
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 170; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030170 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study applies machine learning methods to predict the Canadian yield curve using a comprehensive set of macroeconomic variables. Lagged values of the yield curve and a wide array of Canadian and international macroeconomic variables are utilized across various machine learning models. Hyperparameters
[...] Read more.
This study applies machine learning methods to predict the Canadian yield curve using a comprehensive set of macroeconomic variables. Lagged values of the yield curve and a wide array of Canadian and international macroeconomic variables are utilized across various machine learning models. Hyperparameters are estimated to minimize mispricing across government bonds with different maturities. The Group Lasso algorithm outperforms the other models studied, followed by Lasso. In addition, the majority of the models outperform the Random Walk benchmark. The feature importance analysis reveals that oil prices, bond-related factors, labor market conditions, banks’ balance sheets, and manufacturing-related factors significantly drive yield curve predictions. This study is one of the few that uses such a broad array of macroeconomic variables to examine Canadian macro-level outcomes. It provides valuable insights for policymakers and market participants, with its feature importance analysis highlighting key drivers of the yield curve.
Full article
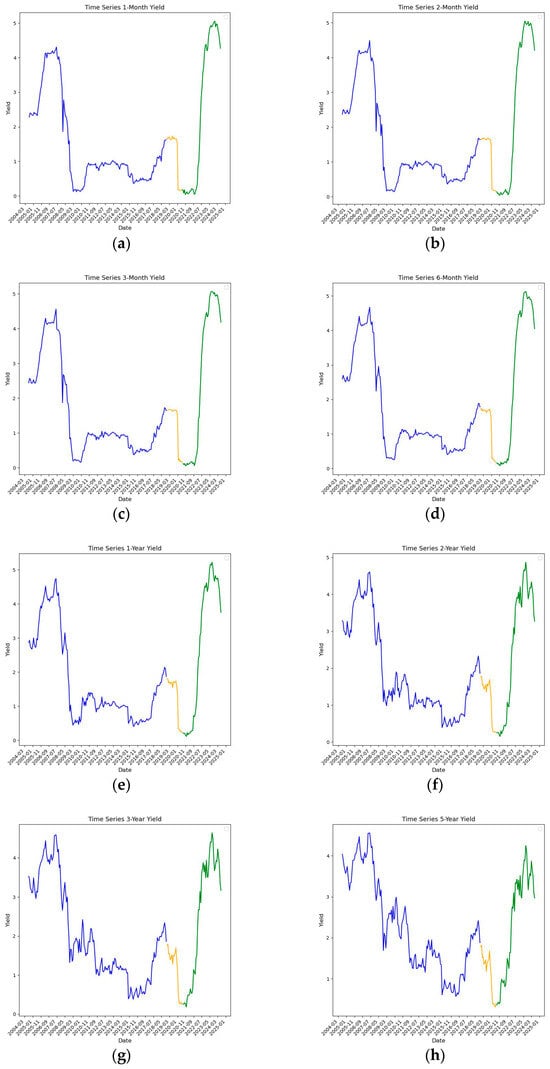
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Dynamics of Cryptocurrencies, DeFi Tokens, and Tech Stocks: Lessons from the FTX Collapse
by
Nader Naifar and Mohammed S. Makni
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 169; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030169 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The FTX collapse marked a significant shock to global crypto markets, prompting concerns about systemic contagion. This paper investigates the dynamic connectedness between cryptocurrencies, DeFi tokens, and tech stocks, focusing on the systemic impact of the FTX collapse. We decompose total, internal, and
[...] Read more.
The FTX collapse marked a significant shock to global crypto markets, prompting concerns about systemic contagion. This paper investigates the dynamic connectedness between cryptocurrencies, DeFi tokens, and tech stocks, focusing on the systemic impact of the FTX collapse. We decompose total, internal, and external connectedness across asset groups using a time-varying parameter VAR model. The results show that post-FTX, Bitcoin and Ethereum intensified their roles as core shock transmitters, while Tether consistently acted as a volatility absorber. DeFi tokens exhibited heightened intra-group spillovers and occasional external influence, reflecting structural fragility. Tech stocks remained largely insulated, with reduced cross-market linkages. Network visualizations confirm a post-crisis fragmentation, characterized by denser internal crypto-DeFi ties and weaker inter-group contagion. These findings have important policy implications for regulators, investors, and system designers, indicating the need for targeted risk monitoring and governance within decentralized finance.
Full article
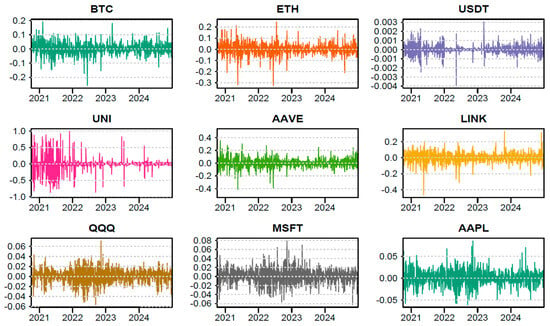
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Liquidity on TE and Performance of Japanese ETFs
by
Atsuyuki Naka, Jiayuan Tian and Seungho Shin
Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13(3), 168; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030168 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study identifies a nonlinear relationship among liquidity, tracking error, and risk-adjusted performance in JETFs. Collecting daily data for 1077 JETFs from January 2008 to April 2022, we find a concave association, whereby both highly liquid and highly illiquid JETFs exhibit lower risk-adjusted
[...] Read more.
This study identifies a nonlinear relationship among liquidity, tracking error, and risk-adjusted performance in JETFs. Collecting daily data for 1077 JETFs from January 2008 to April 2022, we find a concave association, whereby both highly liquid and highly illiquid JETFs exhibit lower risk-adjusted returns and higher tracking errors. Employing quantile regression, we further show that smaller, less liquid JETFs tend to deliver superior risk-adjusted performance. When comparing across listing venues—Japan, the U.S., Ireland, and Luxembourg—we find that the impact of liquidity on performance is most pronounced in the Japanese market, which also shows the highest average tracking error. In contrast, U.S.-listed JETFs offer the lowest tracking error. These results suggest that investors may benefit from choosing smaller JETFs listed in Japan.
Full article
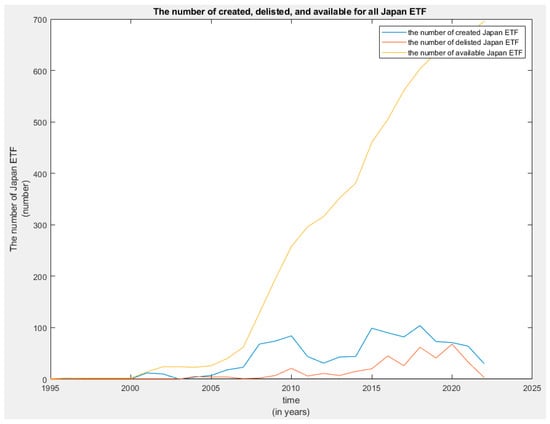
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Economies, Sustainability, Urban Science, IJFS
The Multidimensional Synergy Measures to Achieve Sustainable Regional Socio-Economic Development
Topic Editors: Zaijun Li, Lei Jiang, Rufei MaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Economies, IJFS, JRFM, Risks, Sustainability
Insurance and Risk Management Advances in the 4A Era—AI, Aging, Abruptions, and Adoptions
Topic Editors: Xiaojun Shi, Lingyan Suo, Feng Gao, Baorui DuDeadline: 30 May 2026
Topic in
Economies, IJFS, Sustainability, Businesses, JRFM
Sustainable and Green Finance
Topic Editors: Otilia Manta, Maria PalazzoDeadline: 31 October 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
IJFS
Advancing Financial Stability and Performance Through AI and Digital Transformation
Guest Editor: Hassan ObeidDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
IJFS
Modern Financial Econometrics
Guest Editors: Nikolaos Giannakopoulos, Nikos KanellosDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
IJFS
Financial Stability in Light of Market Fluctuations
Guest Editors: Miguel A. Alonso Neira, Carolina Cosculluela-Martínez, Víctor Espinosa LoyolaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
IJFS
Sports Finance (2nd Edition)
Guest Editor: Rodney PaulDeadline: 31 December 2025









