Journal Description
Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all types of dementia, with particular interest on Alzheimer’s disease, published quarterly online by MDPI. The Panhellenic Federation of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders (PFADRD) is affiliated with the JDAD and its members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 19 days; acceptance to publication in 4 days (median values for MDPI journals in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- JDAD is a companion journal of Brain Sciences.
- Journal Cluster of Neurosciences: Brain Sciences, Neurology International, NeuroSci, Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, Neuroglia, Psychiatry International, Clocks & Sleep and Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.
Latest Articles
Neuroimaging Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2040037 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Alzheimer’s disease accounts for approximately 50% to 80% of all causes of dementia. Co-existence of AD with other diseases causing dementia poses a diagnostic challenge, as we are still far from diagnosing AD accurately in order to manage it appropriately. Neuroimaging techniques, not
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease accounts for approximately 50% to 80% of all causes of dementia. Co-existence of AD with other diseases causing dementia poses a diagnostic challenge, as we are still far from diagnosing AD accurately in order to manage it appropriately. Neuroimaging techniques, not only help diagnose AD but also consistently feature in diagnostic and research criteria for AD as biomarkers. Molecular biomarkers including positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and structural biomarkers including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), have been used in various therapeutic and prognostic studies in AD. This review highlights the recent advances in neuroimaging biomarkers, including molecular biomarkers (PET and SPECT tracers) and structural biomarkers (MRI), for AD. For the purpose of this review, molecular biomarkers have been further subcategorized into non-specific radiotracers (FDG-PET and blood flow SPECT) and specific amyloid- and tau-related radiotracers. The aim of this review is to discuss the recent advances and evidence of molecular and structural biomarkers of AD.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Navigating Language in Dementia Care: Bilingualism, Communication, and the Untapped Potential of Speech-Language Pathologists
by
Weifeng Han
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2040036 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aim: As the global population ages, the number of bilingual individuals living with dementia is increasing, yet their communication needs remain underrepresented in both clinical practice and research. This evidence review examines the intersection of language regression, communication challenges, and cultural–linguistic identity in
[...] Read more.
Aim: As the global population ages, the number of bilingual individuals living with dementia is increasing, yet their communication needs remain underrepresented in both clinical practice and research. This evidence review examines the intersection of language regression, communication challenges, and cultural–linguistic identity in bilingual dementia, with a particular focus on the role of speech–language pathologists (SLPs). Methods: Twelve peer-reviewed studies were critically reviewed and thematically analysed across four domains: (1) language regression and retention in bilingual dementia, (2) communication challenges in bilingual dementia care, (3) the marginal role of speech–language pathology, and (4) cultural–linguistic identity and health equity. The included studies span clinical case reports, experimental research, qualitative caregiver studies, and systematic reviews, with bilingual populations across Asia, Europe, North America, and the Middle East. Results: Findings reveal that language deterioration in bilingual dementia is dynamic and highly individualised, often influenced by language history, emotional context, and usage patterns. Caregivers and clinicians face persistent communication breakdowns, particularly in linguistically mismatched settings. Despite their specialised expertise in communication, SLPs remain largely peripheral in dementia care, constrained by systemic, educational, and methodological barriers. Moreover, linguistic and cultural identity play a critical role in how dementia is experienced and managed, yet are rarely integrated into care frameworks. Conclusions: This review highlights a significant knowledge–practice gap in bilingual dementia care and underscores the need to embed culturally and linguistically responsive communication practices, especially through speech–language therapy, at the centre of bilingual dementia care and support. It outlines key research and practice directions to advance equity, accuracy, and relational care in this growing population.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Patient Diagnosis Alzheimer’s Disease with Multi-Stage Features Fusion Network and Structural MRI
by
Thi My Tien Nguyen and Ngoc Thang Bui
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2040035 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Timely intervention and effective control of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) have been shown to limit memory loss and preserve cognitive function and the ability to perform simple activities in older adults. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are one of the most
[...] Read more.
Background: Timely intervention and effective control of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) have been shown to limit memory loss and preserve cognitive function and the ability to perform simple activities in older adults. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are one of the most common and effective methods for early detection of AD. With the rapid development of deep learning (DL) algorithms, AD detection based on deep learning has wide applications. Methods: In this research, we have developed an AD detection method based on three-dimensional (3D) convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for 3D MRI images, which can achieve strong accuracy when compared with traditional 3D CNN models. The proposed model has four main blocks, and the multi-layer fusion functionality of each block was used to improve the efficiency of the proposed model. The performance of the proposed model was compared with three different pre-trained 3D CNN architectures (i.e., 3D ResNet-18, 3D InceptionResNet-v2, and 3D Efficientnet-b2) in both tasks of multi-/binary-class classification of AD. Results: Our model achieved impressive classification results of 91.4% for binary-class as well as 80.6% for multi-class classification on the Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS) database. Conclusions: Such results serve to demonstrate that multi-stage feature fusion of 3D CNN is an effective solution to improve the accuracy of diagnosis of AD with 3D MRI, thus enabling earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Virtual Team-Based Care Planning for Older Adults with Dementia: Enablers, Barriers, and Lessons from Hospital-to-Long-Term Care Transitions
by
Lillian Hung, Paulina Santaella, Denise Connelly, Mariko Sakamoto, Jim Mann, Ian Chan, Karen Lok Yi Wong, Mona Upreti, Harleen Hundal, Marie Lee Yous and Joanne Collins
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2040034 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Transitions from hospital to long-term care (LTC) facilities are critical periods for older adults living with dementia, often involving complex medical, cognitive, and psychosocial needs. Virtual team-based care has emerged as a promising strategy to improve communication, coordination, and continuity of care
[...] Read more.
Background: Transitions from hospital to long-term care (LTC) facilities are critical periods for older adults living with dementia, often involving complex medical, cognitive, and psychosocial needs. Virtual team-based care has emerged as a promising strategy to improve communication, coordination, and continuity of care during these transitions. However, there is limited evidence on how such approaches are implemented in practice, particularly with respect to inclusion, equity, and engagement of older adults and families. Objective: This study aimed to identify the enablers and barriers to delivering virtual team-based care to support older adults with dementia in transitioning from hospital to LTC. Methods: We conducted a qualitative study using semi-structured interviews, focus groups, and a policy review. Data were collected from 60 participants, including healthcare providers, older adults, and family care partners across hospital and LTC settings in British Columbia, Canada. Thematic analysis was conducted using a hybrid inductive and deductive approach. Eighteen institutional policies and guidelines on virtual care and dementia transitions were reviewed to contextualize findings. Results: Four themes were identified: (1) enhancing communication and collaboration, (2) engaging families in care planning, (3) digital access and literacy, and (4) organizational readiness and infrastructure. While virtual huddles and secure messaging platforms supported timely coordination, implementation was inconsistent due to infrastructure limitations, unclear protocols, and staffing pressures. Institutional policies emphasized privacy and security but lacked guidance for inclusive engagement of older adults and families. Many participants described limited access to reliable technology, a lack of training, and the absence of tools tailored for individuals with cognitive impairment. Conclusions: Virtual care has the potential to support more coordinated and inclusive transitions for people with dementia, but its success depends on more than technology. Structured protocols, inclusive policies, and leadership commitment are essential to ensure equitable access and meaningful engagement. The proposed VIRTUAL framework offers practical tips for strengthening virtual team-based care by embedding ethical, relational, and infrastructural readiness across settings.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Teaching Dementia Care Using a Competency-Based Approach in Physical Therapy Education: Findings from a Pilot Study
by
Amie Marie Jasper, Heather Bushnell, Jayne Josephsen and Mohammed Ata
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030033 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: With the expected growth in the number of people with dementia and the effect it has on their daily life, physical therapists will be required to provide competent care across all settings for people with dementia. This study aimed to explore
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: With the expected growth in the number of people with dementia and the effect it has on their daily life, physical therapists will be required to provide competent care across all settings for people with dementia. This study aimed to explore the effects of a competency-based education (CBE) intervention consisting of interprofessional education (IPE) and experiential learning on perceived dementia care competence and confidence among physical therapy students and to determine recruitment and retention rates of the multi-phasic study. Methods: A total of 13 sixth-semester Doctor of Physical Therapy students participated in IPE (Phase 1) and experiential learning (Phase 2) and completed the Dementia Care Competency Model (DCCM) 2.0 and Confidence in Dementia Scale (CODE) at three time points (pre-test and after Phases 1 and 2). Results: The recruitment and retention rates were 89% and 36%, respectively. The DCCM 2.0 (F-test = 10.57, partial eta squared = 0.66) and the CODE (F-test = 21.27, partial eta squared = 0.80) showed large effect sizes between the three measurement time points. Conclusions: The findings of this study suggest that CBE facilitates the development of core dementia care competencies of interprofessional collaborative practice and person-centered care, as well as practitioner confidence development in dementia care.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Therapeutic Modalities Targeting Tau Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease
by
Thomas Gabriel Schreiner, Liviu Iacob, Carmen Vasilache and Oliver Daniel Schreiner
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030032 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most frequent neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, is characterized by two key pathological features: extracellular amyloid beta plaques and intracellular highly phosphorylated tau protein aggregates known as neurofibrillary tangles. While in the last decades intensive research related to anti-amyloid disease-modifying therapies
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most frequent neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, is characterized by two key pathological features: extracellular amyloid beta plaques and intracellular highly phosphorylated tau protein aggregates known as neurofibrillary tangles. While in the last decades intensive research related to anti-amyloid disease-modifying therapies for AD was conducted, there has been less interest in treatments targeting tau protein. However, this paradigm is slowly changing, as recent studies have shown the increasing importance of tau protein in the onset and evolution of AD. In this context, this review aims to offer a practical overview of currently available therapies targeting tau protein and future research directions. The first part of the manuscript highlights the pathophysiological basics of tau protein aggregation and tau-related kinase dysregulations, considering their role in physiological versus AD conditions. Subsequently, the most relevant classes of drugs modulating tau protein formation, aggregation, and post-translational modifications are presented, with appropriate examples from clinical trials. Finally, unexplored research directions regarding tau-targeting therapies are discussed, with active and passive immunotherapies a promising research direction. Therapies targeting tau protein are a valuable treatment modality in AD, with current drug classes expected to diversify soon.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
An Analysis of the Relationship Between the APOE4 Allele Count, Age of Onset, and Cognitive Impairment Prevalence in the NACC Database: Evaluating the Nigerian Paradox
by
Richard Hunt Bobo, Sheida Riahi, Vaghawan Prasad Ojha and Shantia Yarahmadian
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030031 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: This study analyzes the database of the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC) to examine the correlation between the age of onset and the prevalence of cognitive impairment with the number of subjects carrying APOE4 alleles. The research also evaluates the interaction of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study analyzes the database of the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC) to examine the correlation between the age of onset and the prevalence of cognitive impairment with the number of subjects carrying APOE4 alleles. The research also evaluates the interaction of race and gender in the effect of APOE4 on cognition and age of onset to determine whether the findings support or refute the Nigerian paradox. This paradox refers to the observed resistance of Nigerians to the increasing prevalence of cognitive impairment associated with a higher APOE4 count. Methods: The NACC67 dataset consists of 195,196 rows and 1024 columns, yielding data from 40,210 individual subjects, including information on race, gender, APOE alleles, and cognitive impairment. Among these subjects, 24,673 had recorded data on the age when cognitive decline was first observed. Logistic regression, Chi-square tests, and ANOVA analyses were performed to explore these relationships. The hypotheses tested were as follows: (1) that the APOE4 count is associated with both the prevalence and earlier onset of cognitive impairment and (2) whether the Nigerian paradox (a resistance to APOE4-associated cognitive impairment) could be observed in racial groups represented in the NACC dataset. Results: The results showed a significant positive association between cognitive impairment and the APOE4 count. A logistic regression analysis assessed potential interactions between race or gender and the relationship between the APOE4 count, cognitive impairment prevalence, and the age of onset. No significant interactions were observed among White, Black, Asian, and “Other” racial groups. Across all racial groups except for Pacific Islanders, an increase in APOE4 count was associated with an earlier onset of cognitive impairment and a higher prevalence of the condition. A statistically significant correlation between APOE4 count and age of onset was found only in Black and White individuals. The female gender, the White race, and a higher APOE4 count were associated with a greater prevalence of cognitive impairment and an earlier onset. However, gender and race did not significantly modify the effect of the APOE4 count on cognitive impairment. Conclusions: These findings do not support the Nigerian paradox in White, Black, Asian, and “Other” racial groups, comprising a total of 39,660 subjects. The association between APOE4 and the age of cognitive decline remained consistent across gender and racial groups.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Establishing a Digitally Enabled Healthcare Framework for Enhanced Prevention, Risk Identification, and Relief for Dementia and Frailty
by
George Manias, Spiridon Likothanassis, Emmanouil Alexakis, Athos Antoniades, Camillo Marra, Guido Maria Giuffrè, Emily Charalambous, Dimitrios Tsolis, George Tsirogiannis, Dimitrios Koutsomitropoulos, Anastasios Giannaros, Dimitrios Tsoukalos, Kalliopi Klelia Lykothanasi, Paris Vogazianos, Spyridon Kleftakis, Dimitris Vrachnos, Konstantinos Charilaou, Jacopo Lenkowicz, Noemi Martellacci, Andrada Mihaela Tudor, Nemania Borovits, Mirella Sangiovanni, Willem-Jan van den Heuvel, on behalf of the COMFORTage Consortium and Dimosthenis Kyriazisadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030030 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
During the last decade, artificial intelligence (AI) has enabled key technological innovations within the modern dementia and frailty healthcare and prevention landscape. This has boosted the impact of technology in the clinical setting, enabling earlier diagnosis with improved specificity and sensitivity, leading to
[...] Read more.
During the last decade, artificial intelligence (AI) has enabled key technological innovations within the modern dementia and frailty healthcare and prevention landscape. This has boosted the impact of technology in the clinical setting, enabling earlier diagnosis with improved specificity and sensitivity, leading to accurate and time-efficient support that has driven the development of preventative interventions minimizing the risk and rate of progression. Background/Objectives: The rapid ageing of the European population places a substantial strain on the current healthcare system and imposes several challenges. COMFORTage is the joint effort of medical experts (i.e., neurologists, psychiatrists, neuropsychologists, nurses, and memory clinics), social scientists and humanists, technical experts (i.e., data scientists, AI experts, and robotic experts), digital innovation hubs (DIHs), and living labs (LLs) to establish a pan-European framework for community-based, integrated, and people-centric prevention, monitoring, and progression-managing solutions for dementia and frailty. Its main goal is to introduce an integrated and digitally enabled framework that will facilitate the provision of personalized and integrated care prevention and intervention strategies on dementia and frailty, by piloting novel technologies and producing quantified evidence on the impact to individuals’ wellbeing and quality of life. Methods: A robust and comprehensive design approach adopted through this framework provides the guidelines, tools, and methodologies necessary to empower stakeholders by enhancing their health and digital literacy. The integration of the initial information from 13 pilots across 8 European countries demonstrates the scalability and adaptability of this approach across diverse healthcare systems. Through a systematic analysis, it aims to streamline healthcare processes, reduce health inequalities in modern communities, and foster healthy and active ageing by leveraging evidence-based insights and real-world implementations across multiple regions. Results: Emerging technologies are integrated with societal and clinical innovations, as well as with advanced and evidence-based care models, toward the introduction of a comprehensive global coordination framework that: (a) improves individuals’ adherence to risk mitigation and prevention strategies; (b) delivers targeted and personalized recommendations; (c) supports societal, lifestyle, and behavioral changes; (d) empowers individuals toward their health and digital literacy; and (e) fosters inclusiveness and promotes equality of access to health and care services. Conclusions: The proposed framework is designed to enable earlier diagnosis and improved prognosis coupled with personalized prevention interventions. It capitalizes on the integration of technical, clinical, and social innovations and is deployed in 13 real-world pilots to empirically assess its potential impact, ensuring robust validation across diverse healthcare settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Microglial Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapies
by
Emine Erdag and Ismail Celil Haskologlu
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030029 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal loss. Although amyloid-β plaques and neurofibrillary tangles have been the historical hallmarks of AD pathology, growing evidence highlights microglial-mediated neuroinflammation as a central driver of disease
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal loss. Although amyloid-β plaques and neurofibrillary tangles have been the historical hallmarks of AD pathology, growing evidence highlights microglial-mediated neuroinflammation as a central driver of disease onset and progression. This review aims to provide an updated overview of the dual roles of microglia in AD, from their protective functions to their contribution to chronic inflammation and neurodegeneration. Methods: This review synthesizes findings from recent experimental and clinical studies to examine the molecular mechanisms underlying microglial activation and dysfunction in AD. Key areas of focus include microglial signaling pathways, gut–brain axis interactions, and immunometabolic regulation. The review also evaluates emerging immunomodulatory therapeutic strategies designed to restore microglial homeostasis. Results: Recent studies reveal that microglia undergo a dynamic transition from a homeostatic to a reactive state in AD, contributing to sustained neuroinflammation and impaired clearance of pathological aggregates. Molecular mechanisms such as TREM2 signaling, NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and metabolic reprogramming play critical roles in this process. Additionally, gut microbiota alterations and systemic inflammation have been shown to influence microglial function, further exacerbating disease pathology. Conclusions: Targeting microglial dysfunction through immunomodulatory strategies holds promise as a disease-modifying approach in AD. Therapeutic avenues under investigation include natural compounds, synthetic modulators, immunotherapies, and microbiota-based interventions. A deeper mechanistic understanding of microglial regulation may open new translational pathways for the development of effective treatments for AD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Precision Nutrition for Dementia: Exploring the Potential in Mitigating Dementia Progression
by
Tara J. Jewell, Michelle Minehan, Jackson Williams and Nathan M. D’Cunha
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030028 - 14 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Precision nutrition is a tailored dietary approach that considers an individual’s genetic and metabolic profile, lifestyle factors, and specific nutritional needs to improve health and potentially modify disease progression. While research is ongoing into precision nutrition approaches for preventing dementia, there is no
[...] Read more.
Precision nutrition is a tailored dietary approach that considers an individual’s genetic and metabolic profile, lifestyle factors, and specific nutritional needs to improve health and potentially modify disease progression. While research is ongoing into precision nutrition approaches for preventing dementia, there is no evidence on its targeted application to slow dementia-related disease progression and mitigate functional and cognitive decline. This narrative review addresses this gap by synthesising evidence on nutrient–gene interactions, genotype, gut microbiome, nutritional status and the interplay between metabolic pathways implicated in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration to modify disease progression in a protective or therapeutic manner. Understanding and addressing comorbidities that share pathological mechanisms with dementia have the potential to enhance the understanding of precision nutrition to inform more effective, tailored approaches to slow dementia progression. To increase the robustness of precision nutrition trials for people with dementia, further research is needed into biomarker discovery, multi-omics technologies, and increasing mechanistic research to map the precise biological pathways underpinning the interactions between diet, gene expression, and neuroinflammation. Moreover, there is a need to evaluate the feasibility of precision nutrition for people experiencing cognitive impairment. Addressing these gaps will determine if people with dementia can benefit from precision nutrition and, subsequently, improve their quality of life and health outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Reducing Neuroinflammation and Risk of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease by Reducing Dietary Lipopolysaccharides, Arachidonic Acid, and Advanced Glycation End Products
by
Steven Blake, Luciana Baroni, Panida Piboolnurak, Thomas Harding, Maile Harding and Catherine Blake
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030027 - 11 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), arachidonic acid (AA), and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are higher in the brain of subjects affected by cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), compared to a healthy brain. Methods: In this narrative review, articles were selected with
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), arachidonic acid (AA), and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are higher in the brain of subjects affected by cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), compared to a healthy brain. Methods: In this narrative review, articles were selected with data on these three key dietary compounds relevant to neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in order to provide practical dietary advice to reduce the risk of diseases affecting cognition. Results: Triggered by LPS and AGEs in food, inflammatory cytokines can enter the brain and stimulate microglial activation, inflammation, and oxidative damage. AA can elicit neuroinflammation by increasing leukotriene-A4 and prostaglandin-E2 production. Increased levels of neuroinflammation are associated with poorer cognition in AD. Discussion: A dietary reduction of LPS, AA, and AGEs could slow progression and reduce the risk of cognitive impairment and AD by reducing neuroinflammation through several mechanisms. The avoidance of foods that are highest in LPS, AGEs, and AA (dairy products, pork, poultry, beef, and seafood) and the emphasis on foods lowest in LPS, AGEs, and AA (fruits, vegetables, boiled whole grains, beans, raw nuts, and seeds) can reduce neuroinflammation and risk of cognitive impairment and AD. Conclusions: Reduction of chronic neuroinflammation with dietary changes may represent a novel approach to the treatment of AD and cognitive decline.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Implementation of the Memory Support System for Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Feasibility Survey Study
by
Suraj Brar, Mirou Jaana, Octavio A. Santos, Nicholas Kassabri, Lisa Sweet, Frank Knoefel, Melanie Chandler, Atul Jaiswal and Neil W. Thomas
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030026 - 7 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), a condition between normal aging and dementia, is characterized by cognitive changes that do not significantly affect instrumental activities of daily living. The Memory Support System (MSS), an evidence-based behavioral intervention developed by the Mayo Clinic, has been
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), a condition between normal aging and dementia, is characterized by cognitive changes that do not significantly affect instrumental activities of daily living. The Memory Support System (MSS), an evidence-based behavioral intervention developed by the Mayo Clinic, has been shown to aid those living with MCI and their support partners in coping with cognitive challenges. However, the MSS has not been offered clinically within the Canadian context. Therefore, we conducted a study assessing the feasibility of the MSS from the perspectives of individuals living with MCI and their support partners. Methods: Participants from an institutional registry of research participants, patients, and support partners at a memory clinic, as well as members of a local Dementia Society, were approached to complete an online or paper version of a survey assessing feasibility dimensions. Responses were compared between and within groups for differences in mean scores and associations between linked binary choice response questions. Results: A total of 77 responses were received; 39 surveys were completed by participants with MCI, and 38 by support partners. Respondents found the MSS to be acceptable and practical. On average, participants thought it would be more difficult to train in using the MSS than support partners. Both groups expressed interest in the intervention. On average, participants with MCI and support partners preferred virtual MSS training to in-person and indicated more interest in participating in training over six weeks as compared to two weeks. Conclusions: Flexibility in duration and format when offering the MSS are important considerations when offering the intervention as part of a clinical program. Future research should evaluate cost-effectiveness (e.g., financial, staff resources, etc.) of the MSS approach if it were to be institutionalized in the Ontario healthcare system.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Aβ1-42 Oligomer Injection Model: Understanding Neural Dysfunction and Contextual Memory Deficits in Dorsal CA1
by
Min-Kaung-Wint-Mon and Dai Mitsushima
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030025 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The transgenic animals have been yielding invaluable insights into amyloid pathology by replicating the key features of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, there is no clear relationship between senile plaques and memory deficits. Instead, cognitive impairment and synaptic dysfunction are particularly linked to a
[...] Read more.
The transgenic animals have been yielding invaluable insights into amyloid pathology by replicating the key features of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, there is no clear relationship between senile plaques and memory deficits. Instead, cognitive impairment and synaptic dysfunction are particularly linked to a rise in Aβ1-42 oligomer level. Thus, injection of Aβ1-42 oligomers into a specific brain region is considered an alternative approach to investigate the effects of increased soluble Aβ species without any plaques, offering higher controllability, credibility and validity compared to the transgenic model. The hippocampal CA1 (cornu ammonis 1) region is selectively affected in the early stage of AD and specific targeting of CA1 region directly links Aβ oligomer-related pathology with memory impairment in early AD. Next, the inhibitory avoidance (IA) task, a learning paradigm to assess the synaptic basis of CA1-dependent contextual learning, triggers training-dependent synaptic plasticity similar to in vitro HFS (high-frequency stimulation). Given its reliability in assessing contextual memory and synaptic plasticity, this task provides an effective framework for studying early stage AD-related memory deficit. Therefore, in this review, we will focus on why Aβ1-42 oligomer injection is a valid in vivo model to investigate the early stage of AD and why dorsal CA1 region serves as a target area to understand the adverse effects of Aβ1-42 oligomers on contextual learning through the IA task.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Gray Matter Volume Associations with Montreal Cognitive Assessment Domains in an ADNI Cohort of Early-Onset Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease
by
Minos Kritikos, Taulant Rama, Vania Zubair, Chuan Huang, Christopher Christodoulou, Allen P. F. Chen, Roman Kotov, Frank D. Mann and on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030024 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment are standard, efficient, and swift clinical and research tools used when interrogating cognitively impairing (CI) conditions, such as Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the associations between gross
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment are standard, efficient, and swift clinical and research tools used when interrogating cognitively impairing (CI) conditions, such as Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the associations between gross cognitive impairment (CI) as compared to domain-specific functioning and underlying neuroanatomical correlates have not been investigated among individuals with early-onset Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) or Alzheimer’s disease (EOAD), who can benefit greatly from early diagnosis and intervention strategies. Methods: We analyzed T1-weighted MRIs and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores from the ADNI database in individuals < 65 years old who were either cognitively normal (CN) or had MCI or EOAD. Gray matter volume (GMV) was estimated in voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and ROI-parcellation general linear models examining associations with individual MoCA scores after adjusting for demographic covariates. Results: Results from 120 subjects (44 CN, 62 MCI, and 14 EOAD), identified significant global but also individually distinct domain-specific topographical signatures spanning the temporal, parietal, limbic, occipital, frontal lobes, and cingulate gyri. Conclusions: The results highlight neural correlates of cognitive functioning in a sample of young patients representative of the AD continuum, in addition to studying the structural MRI and functional cognitive difference.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Physical Activity Patterns Between Individuals with Early-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitively Healthy Adults
by
Léonie Moll, Michèle Häner, Roland Rössler and Sabine Krumm
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030023 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Physical activity (PA) has been shown to prevent Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by reducing amyloid accumulation, lowering inflammatory factors, and increasing hippocampal grey matter. While high lifetime PA engagement is associated with a reduced risk of AD, the relationship between specific types of
[...] Read more.
Background: Physical activity (PA) has been shown to prevent Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by reducing amyloid accumulation, lowering inflammatory factors, and increasing hippocampal grey matter. While high lifetime PA engagement is associated with a reduced risk of AD, the relationship between specific types of PA and early-stage AD remains unclear. As AD primarily affects cognitive function before physical capabilities, PA engagement—an important factor in PA—needs further investigation. Objectives: This study explores the potential association between current participation in open-skill sports (OSSs) versus closed-skill sports (CSSs) and early-stage AD. Methods: The sample (N = 128) included a cognitively healthy (HC, n = 78) group and an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) group, combining amnestic mild cognitive impairment due to AD patients (n = 22) and early-stage Alzheimer’s dementia patients (n = 28), reflecting the continuum of progression from aMCI to dAD (n = 50). PA was assessed with the Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly questionnaire, specifically focusing on PA within the last seven days. The statistical analyses included Mann–Whitney U tests and backwards stepwise logistic regression models. Results: Key predictors of group classification (AD vs. NC) included sex, high frequency of PA, and high duration of PA, each for the last seven days. Participation in OSS was significantly associated with medium PA frequency, high PA duration, both within the last seven days, and age, but not with diagnostic status. No statistically significant differences in PA levels (OSSs or CSSs) executed within the last seven days were observed between the AD and HC groups. Conclusions: Participation in OSSs or CSSs within the last seven days was only a marginally significant predictor of AD vs. HC status, and a diagnosis of AD was not predictive of OSS participation within the last seven days. Given the protective role of PA in AD, future research should aim to identify specific PA types that effectively support cognitive health in older adults with early cognitive decline.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dilemmas in Implementing Advance Directives of Patients with Advanced Dementia
by
Norman L. Cantor, William Choi and Michael J. Young
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030022 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: To avoid becoming mired in prolonged deep dementia, some people seek to hasten death by advance instructions rejecting life-sustaining medical intervention (LSMI) at a point of cognitive decline they define in advance as unacceptable. When the time comes to implement such advance
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: To avoid becoming mired in prolonged deep dementia, some people seek to hasten death by advance instructions rejecting life-sustaining medical intervention (LSMI) at a point of cognitive decline they define in advance as unacceptable. When the time comes to implement such advance instructions and to allow the person in advanced dementia to die, many clinicians experience moral and ethical qualms. The decision makers face a clash between people’s legally recognized self-determination prerogative to control their post-competence medical fate and the decision makers’ conviction that humane treatment dictates sustaining the well-being, i.e., the physical “best interests,” of the patient who no longer recalls prior instructions grounded in concerns about personal dignity. The authors’ objective here is to provide guidance in resolving this anguishing dilemma confronting medical decision makers. Methods: The authors construct and analyze a case scenario involving a patient in a state of advanced dementia with a clear advance instruction rejecting LSMI at the current point of debilitation, but who is not ostensibly suffering, is experiencing a modicum of life satisfaction, and is making life-affirming utterances. The two lead authors present contrasting views on whether legal and moral factors impel the implementation of the advance directive rejecting treatment or rather dictate life-sustaining medical intervention. Results: At this early stage of jurisprudence involving persons in advanced dementia, there can be no definitive resolution of the difficult legal/moral clash confronting decision makers. Some sources would conclude that persons are legally entitled to define precipitous mental decline and complete dependence on others as intolerably undignified and inconsistent with their self-defined life narrative. Other sources would be guided by humane respect for the contemporary well-being of a non-suffering patient, especially one making life-affirming utterances. Conclusion: Through the lens of this illuminating case and contrasting analyses, readers should better understand how clinicians should weigh advance directives against shifting care preferences subsequently articulated by persons with advanced dementia.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Outdoor-Based Care and Support Programs for Community-Dwelling People Living with Dementia and Their Care Partners: A Scoping Review
by
Anthea Innes, Mason McLeod, Equity Burke, Dylan Lu, Constance Dupuis and Vanina Dal Bello-Haas
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030021 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: How to best assist people living with dementia (PLWD) and their care partners to maximize quality of life and quality of living, through appropriate and effective non-pharmaceutical approaches, remains a focus of dementia societies and organizations worldwide. This scoping review explored
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: How to best assist people living with dementia (PLWD) and their care partners to maximize quality of life and quality of living, through appropriate and effective non-pharmaceutical approaches, remains a focus of dementia societies and organizations worldwide. This scoping review explored the types, opportunities, benefits and challenges of outdoor-based care and support programs for community-dwelling PLWD and their care partners. Methods: The methodological framework proposed by Arksey & O’Malley (2005) and modified by Levac et al. (2010) was followed. Four research databases were searched from January 2000 to November 2024; 2817 articles were retrieved and 20 met inclusion criteria and underwent data extraction. Results: Program types included the following: nature-based, care farm, green care farm, and farm-based dementia care programs, representing more than half of the included articles; health walks; and outdoor horticulture/garden/gardening programs. The number of PLWD participants ranged from 4 to 136. The total number of care partner participants was 151 and the total number of service provider participants was 87. The essence of, and connections with, nature and the outdoors had notable relevance and value for PLWD. Reported benefits, assessed quantitatively and qualitatively, were numerous and those in the social domain were reported most often. Identified challenges and barriers were related to risks and safety and program development, and implementation and delivery. Conclusions: The noteworthy potential of outdoor-based care and support programs to promote and enhance the quality of life and quality of living of community-dwelling PLWD and their care partners was elucidated. As most PLWD prefer to, and do, continue to reside in their homes, including those with advancing symptoms, the findings have significant relevance and implications for real-world practice and policy. Future research addressing current gaps will strengthen this growing field of dementia research.
Full article
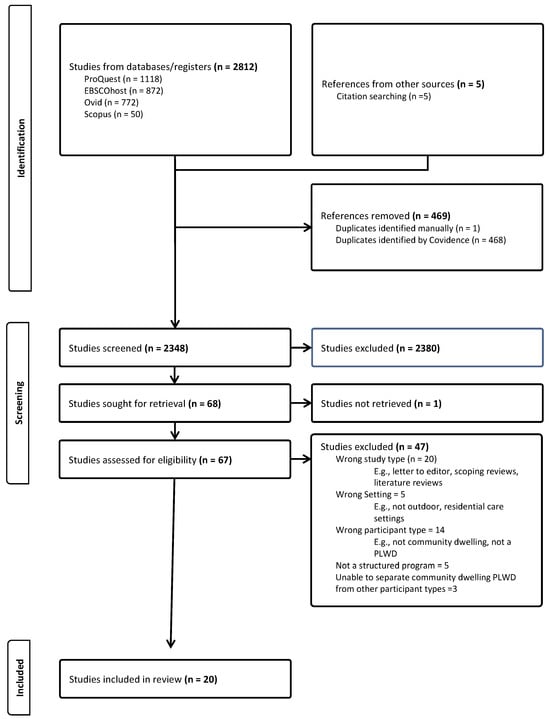
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Alzheimer’s Disease Lipidome: Elevated Cortical Levels of Glycerolipids in Subjects with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) but Not in Non-Demented Alzheimer’s Neuropathology (NDAN) Subjects
by
Paul L. Wood, John E. Cebak and Aaron W. Beger
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(3), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2030020 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Abnormal brain glycerolipid metabolism has been reported for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This includes both diacylglycerols (DGs) and monogalactosyl-DGs (MGDGs), which are elevated in AD subjects. While DGs are also elevated in subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), MGDGs have not yet
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Abnormal brain glycerolipid metabolism has been reported for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This includes both diacylglycerols (DGs) and monogalactosyl-DGs (MGDGs), which are elevated in AD subjects. While DGs are also elevated in subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), MGDGs have not yet been examined at this early stage of cognitive impairment. Methods: MGDG, triacylglycerol (TG), and ether glycerolipid levels in the cerebral cortex gray matter of controls, MCI, and non-demented Alzheimer’s neuropathology (NDAN) subjects were monitored by high-resolution mass spectrometry (<2 ppm mass error). Results: MGDG, MGDG ether, DG ether, and TG levels were elevated in the cerebral cortex of MCI but not NDAN subjects. Conclusions: A diverse array of glycerolipids was elevated in MCI subjects, suggesting a role in cognitive dysfunction. This suggestion is further supported by the maintenance of normal glycerolipid levels in NDAN subjects with amyloid accumulation but not cognitive deficits. Our data clearly indicate that while complex lipid alterations occur in MCI subjects, relative to controls 20 years younger, no such lipid alterations occur in NDAN subjects. While amyloid deposition in MCI is not involved in the observed lipid alterations, other ongoing neuropathologies may contribute to changes in lipid dynamics and vice versa.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating the Measurement Precision of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) for Cognitive Screening in Parkinson’s Disease Through Item Response Theory
by
Pedro Renato de Paula Brandão, Danilo Assis Pereira, Brenda Hanae Bentes Koshimoto, Vanderci Borges, Henrique Ballalai Ferraz, Artur Francisco Schumacher Schuh, Carlos Roberto de Mello Rieder, Maira Rozenfeld Olchik, Ignacio F. Mata, Vitor Tumas and Bruno Lopes Santos-Lobato
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2020019 - 6 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is widely used to evaluate global cognitive function; however, its precision in measurement in heterogeneous populations—especially among patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD)—remains underexplored. Methods: In this multicenter cross-sectional study, we examined the psychometric properties of
[...] Read more.
Background: The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is widely used to evaluate global cognitive function; however, its precision in measurement in heterogeneous populations—especially among patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD)—remains underexplored. Methods: In this multicenter cross-sectional study, we examined the psychometric properties of the Brazilian Portuguese MoCA in 484 PD patients (age range, 26–90 years; mean ± SD, 59.9 ± 11.1 years; disease duration range, 1–35 years; mean ± SD, 8.7 ± 5.4 years) using Item Response Theory (IRT). The Graded Response Model (GRM) was employed to estimate item difficulty and discrimination parameters, and differential item functioning (DIF) concerning age and education was investigated via a Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC) model. Results: The MoCA demonstrated essential unidimensionality and robust model fit. GRM analyses revealed that items within the Attention and Naming domains had high discrimination, indicating sensitivity to subtle cognitive deficits, while Memory items exhibited lower discrimination. Orientation items showed low difficulty thresholds, suggesting a propensity for ceiling effects. The MIMIC model further indicated that age and education significantly influenced overall scores: increasing age was associated with lower performance, whereas higher educational attainment correlated with better outcomes, particularly in Memory Recall and Executive/Visuospatial domains, even after accounting for their modest inverse relationship. Conclusions: Our findings support the validity of the Brazilian Portuguese MoCA for cognitive screening in PD while highlighting item-level biases linked to age and education. These results advocate for using education-adjusted norms and computerized scoring algorithms that incorporate item parameters, ultimately enhancing the reliability and fairness of cognitive assessments in diverse clinical populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Objective and Subjective Measures of Cognitive Decline in Highly Educated Older Adults: A 10-Year Longitudinal Study
by
Odelia Elkana, Meitav Levy, Yael Tal Bicovsky, Noy Tal, Noga Oren and Elissa L. Ash
J. Dement. Alzheimer's Dis. 2025, 2(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/jdad2020018 - 5 Jun 2025
Abstract
Background: The timely detection of cognitive decline in highly educated adults is challenging due to their resilient cognitive abilities and the limited sensitivity of neuropsychological tests for this group. Therefore, evaluating subjective facets such as subjective cognitive decline (SCD) becomes imperative, potentially enabling
[...] Read more.
Background: The timely detection of cognitive decline in highly educated adults is challenging due to their resilient cognitive abilities and the limited sensitivity of neuropsychological tests for this group. Therefore, evaluating subjective facets such as subjective cognitive decline (SCD) becomes imperative, potentially enabling the early identification of cognitive decline. Objective: Our primary objective was to identify effective methods, both objective and subjective, for the early detection of cognitive decline in highly educated older adults. A secondary objective was to translate and validate a Hebrew adaptation of the SCD questionnaire. Methods: Initially (T0), the study included 28 highly educated participants (mean age = 72.6, SD = 4.54; mean education 17.6, SD = 3.41). By the final evaluation (T7), 20 participants remained. Annual assessments involved objective neuropsychological tests and self-report questionnaires evaluating depression, anxiety, and SCD with changes analyzed over time using repeated measures ANOVA. Results: Significant declines were observed in the following objective neuropsychological tests: Rey–Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (ROCFT) copy, F(3,57) = 9.05, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.32, and Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) trial six, F(1,19) = 7.32, p < 0.05, ηp2 = 0.28, which is consistent with previous findings. The Hebrew SCD questionnaire demonstrated high reliability and validity and was highly correlated with cognitive decline. Conclusions: The ROCFT copy and the Hebrew SCD questionnaire can serve as valuable indicators for the early detection of cognitive decline in highly educated older adults.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapies for Neurodegenerative Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Neurology International, NeuroSci, JDAD
Impacts of Sex Hormones on Memory and Aging
Topic Editors: Carolina Villada, Vanesa Hidalgo, Caroline GurvichDeadline: 25 May 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JDAD
Risk Factors, Intervention and Prevention of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
Guest Editors: Muhammad Sohail Khan, Muhammad IkramDeadline: 31 May 2026







