Advances in Ship Design
A special issue of Journal of Marine Science and Engineering (ISSN 2077-1312). This special issue belongs to the section "Ocean Engineering".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (31 December 2021) | Viewed by 13928
Special Issue Editors
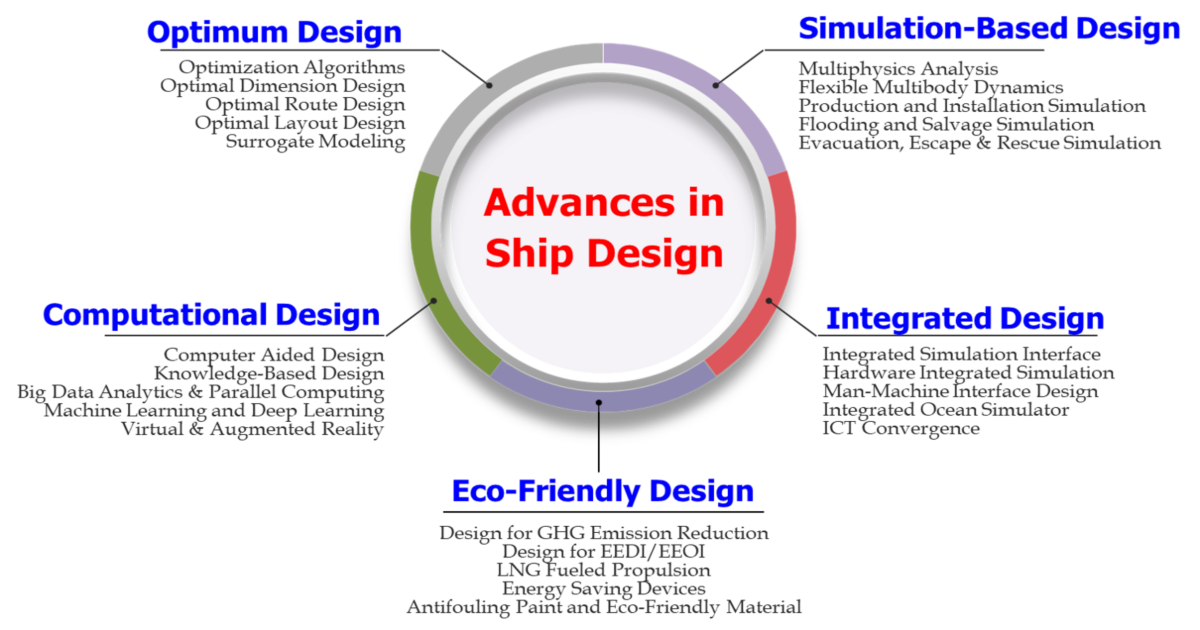
Interests: design theory and methodology; optimum design; simulation-based design (numerical simulation, multibody dynamics); computational design (CAD, big data analytics, machine learning, virtual reality/augmented reality); integrated design (integrated simulation)
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Up to now, ship design has played a pivotal role in realizing safe and efficient ships. Despite such importance, some of the processes of ship design are still carried out by hand, which acts as an obstacle to increasing productivity. In recent times, various technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data are being developed and, due to advances in these new technologies, ship design also has the potential to further develop. Therefore, this SI was proposed to allow us to share such content with each other. Any papers incorporating the latest technology and practice in addition to the traditional ship design theory are welcome, so I hope that excellent papers from interested researchers will be submitted.
Please do not hesitate to contact us and Zara ([email protected]) if you have any queries.
Prof. Dr. Myung-Il Roh
Prof. Dr. Kazuo Hiekata
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Design theory and methodology
- Artifical intelligence for design
- Big data analytics for design
- Optimum design
- Simulation-based design
- Computational design
- Integrated design
- Design for GHG emission reduction






