- Article
Design and Synthesis of Fused Derivatives of 7-Hydroxycoumarin (Umbelliferone) with the Flavonol Quercetin and the Flavone Luteolin-Analysis of Their Antioxidant and Physicochemical Properties
- Panagiotis Theodosis-Nobelos,
- Georgios Papagiouvannis and
- Samvel Sirakanyan
- + 6 authors
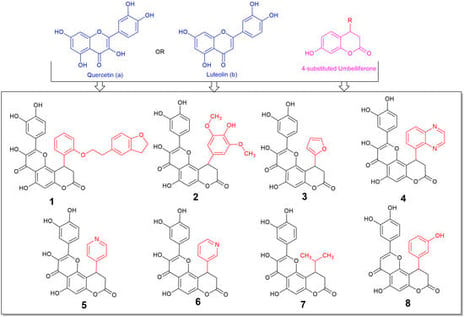
Oxidative stress seems to be part of many deranged processes in the organism, affecting multiple degenerative conditions at a cellular and tissue level. Coumarins and flavonoids comprise two main categories of naturally derived compounds with multiple effects and applications. Our aim in this paper is the design of compounds with increased antioxidant activity with the conjugation of two moieties with highly antioxidant potency in the frame of one molecule. A series of novel derivatives, comprising fusion of 7-hydroxycoumarin (Umbelliferone) and Quercetin (flavonol) have been synthesized using classical organic chemistry methods. Additionally, one novel flavone derivative was prepared for comparison. The novel compounds were tested for their radical, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS) scavenging, their reductive activity, and their labile metal chelating potency, as well as with in silico tools. All of them were more active, in most cases, than reference molecules Trolox and vitamin C. The most active compound 2 reached IC50 of 4.03 and 43.75 μM for ABTS and DPPH, respectively (up to three times lower than that of Trolox). Compound 1 was of equal to vitamin C activity in H2O2 scavenging, whilst compound 3 was up to 6.4 times more active than Trolox in NO scavenging. Since our designed compounds seem to exhibit high antioxidant potential, scavenging reactive nitrogen and oxygen species, which are accumulated and promote the progression of inflammatory conditions, and have reductive and metal chelating abilities, they can be considered as potential candidates for protection in cases of oxidative stress derived toxicity.
3 February 2026