-
 Anxiety Disorder: Measuring the Impact on Major Depressive Disorder
Anxiety Disorder: Measuring the Impact on Major Depressive Disorder -
 Bullying Experiences Among Lithuanian Adolescents: The Associations Between Subjective Happiness and Well-Being
Bullying Experiences Among Lithuanian Adolescents: The Associations Between Subjective Happiness and Well-Being -
 Predictors of Emotional Exhaustion and Depersonalization in Teachers After the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications for Mental Health and Psychiatric Support in Spanish-Speaking Countries
Predictors of Emotional Exhaustion and Depersonalization in Teachers After the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications for Mental Health and Psychiatric Support in Spanish-Speaking Countries -
 Secondary Traumatic Stress in Interpreters for Refugees: Why Training and Supervision Matter
Secondary Traumatic Stress in Interpreters for Refugees: Why Training and Supervision Matter
Journal Description
Psychiatry International
Psychiatry International
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on psychiatric research and practice, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 28.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Psychiatric Mental Health)
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Neurosciences: Brain Sciences, Neurology International, NeuroSci, Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, Neuroglia, Psychiatry International, Clocks & Sleep and Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.
Impact Factor:
1.1 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
The Youngest Minds in a Warming World: A Review of Climate Change and Child and Adolescent Mental Health
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(4), 119; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6040119 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
Climate change poses a growing threat to the mental health of children and adolescents. This narrative review synthesizes global, interdisciplinary research on the psychological impacts of climate disruption during critical developmental stages, with attention to marginalized populations. We explore three key pathways of
[...] Read more.
Climate change poses a growing threat to the mental health of children and adolescents. This narrative review synthesizes global, interdisciplinary research on the psychological impacts of climate disruption during critical developmental stages, with attention to marginalized populations. We explore three key pathways of harm: direct exposure to environmental disasters, chronic disruption of ecological and social systems, and existential distress such as eco-anxiety. Drawing on eco-social theory and developmental psychopathology, the review highlights how these impacts are shaped by age, geography, identity, and systemic inequities. It identifies both risk and protective factors, emphasizing the importance of caregiving relationships, cultural practices, education, and youth climate engagement. While activism can foster resilience and purpose, it may also incur emotional burdens that require clinical and policy attention. We argue that child and adolescent mental health must be recognized as central to climate justice and adaptation, and we offer urgent recommendations for integrated action across sectors.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Smartphone Addiction in Youth: A Narrative Review of Systematic Evidence and Emerging Strategies
by
Daniele Giansanti
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(4), 118; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6040118 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
Smartphone addiction has emerged as a significant public health concern, particularly among adolescents and young adults. This narrative review, conducted in line with the ANDJ checklist, synthesizes evidence from 25 systematic reviews and meta-analyses, complemented by randomized controlled trials and clinical studies, to
[...] Read more.
Smartphone addiction has emerged as a significant public health concern, particularly among adolescents and young adults. This narrative review, conducted in line with the ANDJ checklist, synthesizes evidence from 25 systematic reviews and meta-analyses, complemented by randomized controlled trials and clinical studies, to provide a structured overview of the field. The study selection flow and publication trends reveal a rapidly expanding research landscape, with most evidence produced in the last decade, reflecting both the ubiquity of smartphones and increasing awareness of their health impacts. The synthesis highlights converging findings across reviews: excessive smartphone use is consistently associated with psychosocial, behavioral, and academic challenges, alongside sleep disturbances and mental health symptoms. Common messages include the recognition of smartphone addiction as a multidimensional phenomenon, while emerging themes point to heterogeneity in definitions, tools, and methodological approaches. Comparative analysis of reviews underscores both shared risk factors—such as emotional dysregulation and social isolation—and differences in study designs and target populations. Importantly, this review identifies critical gaps, including the lack of standardized definitions, limited longitudinal evidence, and scarce cross-cultural validation. At the same time, promising opportunities are noted, from lifestyle-based interventions (e.g., physical activity) to educational and policy-level strategies fostering digital literacy and self-regulation. The post-pandemic context further emphasizes the need for sustained monitoring and adaptive responses. Overall, this review calls for youth-centered, multi-sector interventions aligned with WHO recommendations, supporting coordinated, evidence-based action across health, education, and policy domains.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Not All Bad: A Laboratory Experiment Examining Viewing Images of Nature on Instagram Can Improve Wellbeing and Positive Emotions
by
Christopher Stiff and Lisa J. Orchard
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(4), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6040117 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Instagram is a hugely popular social media site; however, it has also been cited in many times as being a source of low self-esteem, unhappiness, and body dissatisfaction. Despite this, there is potential to use Instagram as a self-care delivery system and create
[...] Read more.
Instagram is a hugely popular social media site; however, it has also been cited in many times as being a source of low self-esteem, unhappiness, and body dissatisfaction. Despite this, there is potential to use Instagram as a self-care delivery system and create positive changes in users’ mental health by showing them a specific type of image. In this paper, we use Stress Reduction Theory to demonstrate that viewing images of nature on Instagram can improve well-being (H1), by increasing feelings of connectedness with nature (H2). Furthermore, we posit this same influence will elicit more altruistic behaviour from users (H3). In a laboratory experiment, participants accessed images using either the #naturephotography hashtag, or a control hashtag (#bookshelves). Analyses showed that, in line with the proposed positive effects of SRT, viewing natural images improved well-being and positive emotions, and this was at least partially mediated by increased connectedness to nature. Future studies that use a more longitudinal approach, and examine how images can be presented within a more robust psychiatric intervention are then discussed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Postpartum Depression in Saudi Arabia: A Narrative Review of Prevalence, Knowledge, Risk Factors, and Quality-of-Life Impact
by
Amena H. Alhemyari, Batool A. Alabdrabalnabi, Abdullah M. Alotaibi, Abdulmajeed A. Alenazi and Abdulaziz M. Althwanay
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(4), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6040116 - 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background and Objective: Postpartum depression (PPD) is a prevalent psychiatric condition with significant consequences for maternal, paternal, and infant well-being. In Saudi Arabia, some reported prevalence rates exceed global averages. This narrative review synthesizes the current literature on the prevalence, risk factors, awareness,
[...] Read more.
Background and Objective: Postpartum depression (PPD) is a prevalent psychiatric condition with significant consequences for maternal, paternal, and infant well-being. In Saudi Arabia, some reported prevalence rates exceed global averages. This narrative review synthesizes the current literature on the prevalence, risk factors, awareness, and quality-of-life impact of PPD in Saudi Arabia. The aim is to identify methodological inconsistencies, highlight the risk factors, and guide future research and policy. Method: A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. Studies published between 2010 and May 2025 were included if they addressed PPD in Saudi Arabia and the inclusion criteria were met. 38 articles were selected for full-text analysis and incorporation in the study. Results: PPD prevalence in Saudi Arabia ranges from 5.1% to 75.7%, with regional variation attributed to inconsistent methodologies, screening instruments, and diagnostic cutoffs. Risk factors encompass psychiatric history, marital conflict, limited social support, low income, cesarean delivery, unplanned pregnancy, anemia, and sleep disturbance. Nutritional and newborn-related predictors were inconsistently reported. Awareness among the public and healthcare professionals remains limited, and paternal postpartum depression is underrecognized. PPD exerts a pronounced negative impact on maternal quality of life, spanning physical, psychological, and social domains. Conclusions: PPD poses a substantial public health burden in Saudi Arabia. Routine screening with validated tools, integrated perinatal mental health services, and targeted public education campaigns may help address diagnostic delays and stigma. Future studies must adopt standardized diagnostic criteria and longitudinal designs to generate nationally representative prevalence estimates and evaluate preventive strategies.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Hidden Challenge: Male Eating Disorders in the Middle East: A Systematic Review of Prevalence and Cultural Factors
by
Tariq A. Alalwan, Simone Perna, Ayesha Rafique, Sabika Allehdan, Iolanda Cioffi and Mariangela Rondanelli
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 115; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030115 - 16 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Middle Eastern males face unique eating disorder (ED) risks due to cultural transitions from traditional masculine ideals that emphasized functional strength to Western aesthetic standards. Male EDs in Middle Eastern populations constitute an emerging public health concern that has received limited systematic research
[...] Read more.
Middle Eastern males face unique eating disorder (ED) risks due to cultural transitions from traditional masculine ideals that emphasized functional strength to Western aesthetic standards. Male EDs in Middle Eastern populations constitute an emerging public health concern that has received limited systematic research attention, despite increasing clinical recognition. This systematic review synthesized available epidemiological data on ED prevalence among Middle Eastern males to examine regional patterns and associated risk factors. We conducted a systematic review following PRISMA guidelines by searching PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases for studies published between 2000 and 2023 that examined EDs in males aged 15 years and above across Middle Eastern countries. Thirteen studies encompassing 5236 male participants from 11 countries met the inclusion criteria. ED prevalence demonstrated substantial variation from 2.2% to 81.4% depending on population and assessment methodology, with Gulf Cooperation Council countries showing consistently higher rates. Age-stratified analysis revealed the highest rates among adolescents aged 15–18 years (mean: 35.0%) compared to adults over 25 years (mean: 2.1%), with university students showing intermediate levels (mean: 29.0%). Muscle dysmorphia emerged as particularly prevalent among bodybuilders (5.7–81.4%), while university students showed rates of 9.7–49.1%. Depression, body dissatisfaction, and cultural transition stress were consistently identified as correlates across multiple populations. These findings underscore late adolescence as a critical risk period and highlight the urgent need for culturally adapted diagnostic tools, healthcare provider training, and region-specific prevention strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Depression Severity and Its Predictors: Findings from a Nationally Representative Canadian Sample
by
Eric D. Tessier, Geoffrey S. Rachor, Blake A. E. Boehme, Braeden Hysuick-Weik and Gordon J. G. Asmundson
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030114 - 16 Sep 2025
Abstract
Depression is a major global health issue that significantly contributes to the burden of disease. Despite the wealth of existing research on depression, several key aspects remain underexplored, including factors that predict the onset, severity, and recurrence of depressive symptoms. The purpose of
[...] Read more.
Depression is a major global health issue that significantly contributes to the burden of disease. Despite the wealth of existing research on depression, several key aspects remain underexplored, including factors that predict the onset, severity, and recurrence of depressive symptoms. The purpose of the current study was to assess the sociodemographic correlates and risk and protective factors of depression using a representative sample of the Canadian population. The data were drawn from the 2017–2018 Canadian Community Health Survey (CCHS), a cross-sectional survey with a sample size greater than 113,000. Results from regression analyses identified sleep quality, social support, and perceived life satisfaction as protective factors for depression severity, while a current, self-reported diagnosis of an anxiety- or mood-related disorder was identified as a risk factor. Being younger emerged as the only pertinent sociodemographic risk factor for depression. Contrary to expectations, vigorous physical activity and sedentary behaviour did not significantly predict depression severity. Taken together, the results underscore the importance of identifying modifiable risk and protective factors to inform population-level mental health strategies (e.g., campaigns seeking to raise awareness regarding the importance of sleep, social support) to guide the development of targeted, evidence-based interventions.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Nomophobia, Attachment Styles, and Loneliness: A Study Among Adults in Cyprus
by
Erietta Constantinidou, Marilena Mousoulidou, Andri Christodoulou and Michailina Siakalli
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 113; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030113 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
The rapid increase in global smartphone usage and the range of capabilities they offer have resulted in an overdependence on them, leading to the term nomophobia. Nomophobia refers to the psychological discomfort or anxiety experienced when an individual is unable to use or
[...] Read more.
The rapid increase in global smartphone usage and the range of capabilities they offer have resulted in an overdependence on them, leading to the term nomophobia. Nomophobia refers to the psychological discomfort or anxiety experienced when an individual is unable to use or does not have access to their mobile phone, and it is a phenomenon that warrants research attention due to its psychological and social implications. The aim of the current study was to examine the relationship between nomophobia and the time spent on mobile usage, attachment in close romantic relationships, and loneliness. Participants included 300 adults from Cyprus who were recruited through convenience and snowball sampling methods. Data were gathered using an internet-based questionnaire that assessed participants’ time spent on mobile usage, their attachment styles in close relationships, and their level and type of loneliness. The results suggest that (a) anxiety dimension and time spent on mobile phone are significant predictors of nomophobia, (b) higher levels of nomophobia are associated with an insecure attachment style, (c) more severe levels of nomophobia are associated with higher levels of loneliness, and (d) increased time spent on mobile usage is linked to higher levels of nomophobia. The findings suggest that the widespread emergence of nomophobia raises important concerns, highlighting the need for the development of educational programs that promote balanced mobile usage and encourage direct social interaction. The significance of targeted interventions that address mobile phone regulation and attachment-related vulnerabilities is emphasized.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
College Students’ Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Raihan K. Khan, Md Towfiqul Alam, Sojib Bin Zaman and Tony Jehi
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 112; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030112 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted multiple aspects of human life, including the psychological and physical health of college students. This study explores how students in Virginia’s Shenandoah Valley, a region within the larger Appalachian area, experienced anxiety, depression, and fear of COVID-19. An
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted multiple aspects of human life, including the psychological and physical health of college students. This study explores how students in Virginia’s Shenandoah Valley, a region within the larger Appalachian area, experienced anxiety, depression, and fear of COVID-19. An online survey was conducted at a large public university in the US, yielding responses from 680 undergraduate and graduate students. Linear regression was applied to continuous outcomes, specifically the Fear of COVID-19 Scale (FCV-19S) and depression scores. For dichotomous outcomes such as anxiety and depression (when categorized), separate logistic regression models were employed. The majority of respondents were female (78.0%), White (81.9%), and undergraduates (80.4%), with approximately 41.4% majoring in health-related disciplines. Results indicated that female students reported higher levels of anxiety, depression, and fear of infection compared to their male counterparts. Additionally, undergraduate students exhibited greater depressive symptoms than graduate students. Students who perceived less institutional support from their university during the pandemic also reported significantly higher psychological distress. These findings underscore the pressing need for universities and policymakers to collaborate in enhancing mental health resources and communication strategies for students during times of crisis.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
by
Stanley Wong, Nicholas Fabiano, Carl Zhou, Brandon Luu, Risa Shorr, Sarah Slassi, Marco Solmi, Ishrat Husain and Michael S. B. Mak
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 111; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030111 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: To review and synthesize the current literature of clinical trials that investigated the efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) in people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Method: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and PsycINFO were searched for randomized controlled trials
[...] Read more.
Objective: To review and synthesize the current literature of clinical trials that investigated the efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) in people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Method: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and PsycINFO were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in which GLP-1RAs were used to treat people diagnosed with OSA. This systematic review and meta-analysis complied with PRISMA 2020 guidelines and was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42024537280). A random effects model was used for meta-analysis to assess changes in OSA as measured by the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) compared to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or placebo controls. The standardized mean difference (SMD) and risk ratio (RR) were computed for continuous and binary outcomes. Variability between studies, risk of bias, subgroup analysis, and leave-one-out analysis were completed. Results: Five studies were included (N = 1023; 511 GLP-1RA and 512 control). Two trials used tirzepatide and four studies used liraglutide as the GLP-1RA. Six studies showed a decrease in AHI with an SMD of −14.5 events per hour (95%CI = −24.73 to −4.21; I2 = 96.3%). When compared to placebo, GLP-1RA treatment had a significant reduction in AHI (SMD = −0.69; 95%CI = −1.10 to −0.26; p = 0.001; I2 = 88.0%). When compared to CPAP, no significant difference in the reduction of AHI was found. No evidence of publication bias was found. Compared to control, there was no significant difference in serious adverse events (RR = 0.89; 95%CI = 0.50 to 1.57; p = 0.68; I2 = 20.93%). Conclusions: People with psychiatric disorders may also experience comorbid OSA that can impact their quality of life, which may perpetuate psychiatric symptoms of depression. GLP-1RAs may provide therapeutic potential in the treatment of OSA in addition to their cardioprotective effects. Current studies are limited by small sample sizes, lack of blinding, and short duration. Future studies will require further investigation in long-term efficacy and safety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Patient Satisfaction in Person-Centered Physical Rehabilitation for Patients with Schizophrenia: A Scoping Review
by
Ryuichi Tanioka, Krishan Soriano, Feni Betriana, Allan Paulo Blaquera, Leah Anne Christine L. Bollos, Sato Mai, Reiko Kamoi, Yoshihiro Mifune, Kazushi Mifune, Savina Schoenhofer and Tetsuya Tanioka
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 110; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030110 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Person-centered care emphasizes shared decision-making and a holistic approach to support patient autonomy. This scoping review aimed to clarify the definitions and approaches of person-centered physical rehabilitation (PCPR) that satisfy patients with schizophrenia and to identify specific methods to increase their satisfaction. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Person-centered care emphasizes shared decision-making and a holistic approach to support patient autonomy. This scoping review aimed to clarify the definitions and approaches of person-centered physical rehabilitation (PCPR) that satisfy patients with schizophrenia and to identify specific methods to increase their satisfaction. Methods: This scoping review was conducted in accordance with the recommendations of the Joanna Briggs Institute and adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews checklist. The studies were screened, the data were extracted, and the findings were charted. Results: PCPR is an individually optimized rehabilitation approach that is centered around the “person” and is aimed at supporting the entire life of the individual, while respecting their values and wishes. This approach emphasizes the importance of patients actively participating in their own treatment and enhancing their self-management abilities rather than relying solely on medical techniques. PCPR involves empowering patients, particularly patients with schizophrenia; establishing comprehensive rehabilitation plans; and adopting flexible responses. Conclusions: Effective PCPR enhances healthcare providers’ moral sensitivity and ability to manage complex needs, thereby improving patient satisfaction and motivation to join physical rehabilitation. Furthermore, to conduct PCPR for patients with schizophrenia effectively, it is crucial to provide not only physical rehabilitation, but also appropriate psychosocial support, and to promote the establishment and maintenance of healthy lifestyle habits.
Full article
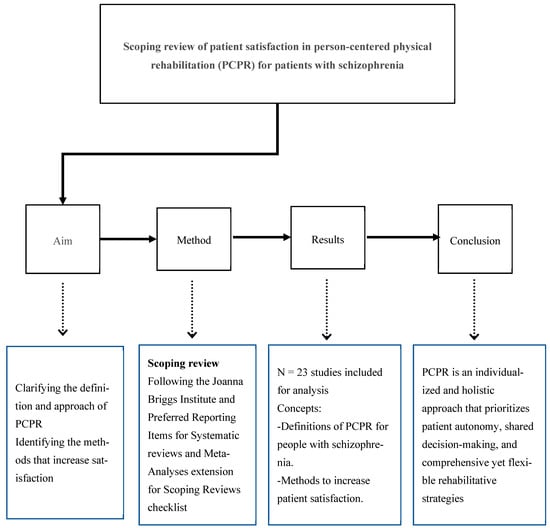
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Mental Health in Europe After COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Adult Primary Health Care Users
by
Sara Diogo Gonçalves, Ana Luísa Santos, Clara Ramos, Fábio Valente, Lisete Jesus, José Pereira Alexandre and Fabiana Chyczij
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 109; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030109 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on mental health globally, especially among users of primary health care (PHC) services. This systematic review aims to synthesize the current evidence on the prevalence and associated factors of depression, anxiety, and stress among adult
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on mental health globally, especially among users of primary health care (PHC) services. This systematic review aims to synthesize the current evidence on the prevalence and associated factors of depression, anxiety, and stress among adult PHC users in Europe during the post-pandemic period. The review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines and was registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251033455). We searched Web of Science, PubMed, b-on, and Scopus up to April 2025. Eligible studies included peer-reviewed, quantitative observational studies conducted in Europe from 2022 onward, provided they addressed the post-pandemic context and assessed depression, anxiety, and/or stress using validated tools. Two reviewers independently screened the studies and performed data extraction. The risk of bias was assessed using the ROBINS-I tool. A narrative synthesis of the findings was subsequently conducted. A total of 11 studies involving 8958 participants were included in this analysis. Most studies were cross-sectional and employed tools such as the DASS-21, PHQ-9, and HADS. The prevalence of depressive symptoms reached up to 63%, and anxiety affected over 40% of participants in several studies. Vulnerable groups included women, individuals with chronic illnesses, those unemployed, and persons living alone or facing financial hardship. The risk of bias was moderate to serious in most studies. The evidence highlights significant post-pandemic psychological distress, conceptualized as symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress measured through validated psychometric instruments, in PHC settings, with underdiagnosis remaining a key issue. Limitations include heterogeneity in assessment tools and designs, as well as reliance on self-report measures. Results underscore the need for routine mental health screening and integrated care in PHC. This review received no specific funding.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Validity and Reliability of the Chinese Version of the Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder
by
Hui Zhou, Yu Chang, Chaiyun Sakulsriprasert, Tinakon Wongpakaran, Nahathai Wongpakaran, Chawisa Suradom, Ronald O’Donnell and Nan Jia
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 108; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030108 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Borderline personality disorder (BPD), a significant personality trait frequently observed in young adults, is associated with challenges in mental health and academic performance. Screening for BPD symptoms is essential. The Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder (SI-Bord) is widely used to assess
[...] Read more.
Background: Borderline personality disorder (BPD), a significant personality trait frequently observed in young adults, is associated with challenges in mental health and academic performance. Screening for BPD symptoms is essential. The Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder (SI-Bord) is widely used to assess general BPD symptoms. However, despite being translated and culturally adapted, the psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the SI-Bord have not been thoroughly investigated in a Chinese population. Objectives: The aim of the study was to evaluate the psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder (SI-Bord) among university students using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Methods: Participants completed the SI-Bord along with the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), the Meaning in Life Questionnaire (MLQ), the Experiences in Close Relationships–Revised (ECR-R), and the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES). Results: A total of 715 Chinese university students (mean age = 20.33 years; age range = 18–25), including 385 males (54.2%) and 325 females (45.5%), participated in this study. The unidimensional model demonstrated adequate fit indices. The SI-Bord showed significant correlations with the PSS and ECR-R (attachment anxiety), alongside smaller correlations with the MLQ, supporting its convergent and discriminant validity. The Chinese version of the SI-Bord exhibited good reliability. Invariance testing confirmed at least metric invariance across various groups. Conclusions: The Chinese version of the SI-Bord demonstrates strong validity and reliability as a tool for screening for core BPD symptoms among Chinese university students. Further studies are encouraged to evaluate the validity of the SI-Bord across diverse groups, including age, socioeconomic status, and geographic regions. Applying it in clinical BPD samples will further enhance its utility across Chinese populations.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
An Altered Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis in Fragile X Syndrome May Explain Autistic Traits in Some Patients
by
Yolanda de Diego-Otero, Ana Bodoque-García, Carolina Quintero-Navarro, Rocío Calvo-Medina and José María Salgado-Cacho
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030107 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The gut microbiota plays an essential role in human health, influencing gut–brain communication. Imbalances in this microbial ecosystem, termed dysbiosis, have been associated with increased gut permeability and gastrointestinal symptoms commonly reported in autism spectrum disorder (ASD), without implying a direct causal role
[...] Read more.
The gut microbiota plays an essential role in human health, influencing gut–brain communication. Imbalances in this microbial ecosystem, termed dysbiosis, have been associated with increased gut permeability and gastrointestinal symptoms commonly reported in autism spectrum disorder (ASD), without implying a direct causal role in ASD itself. This study aimed to determine whether alterations in gut microbiota exist in individuals with Fragile X Syndrome (FXS), with or without ASD, compared to ASD patients and neurotypical controls, and to identify microbiota biomarkers associated with these disorders. Stool samples from Caucasian individuals aged 3–18 years belonging to four groups (ASD, FXS, FXS + ASD, and controls) were analysed by amplifying the V3–V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene to characterize microbiota composition. Significant differences were found among patient groups compared to neurotypical controls, with notable similarities between the ASD and FXS + ASD groups. Additionally, specific microbiota biomarkers were identified for each patient group. These findings suggest that distinct microbiota alterations are associated with FXS and ASD, which may contribute to a more accurate characterization of symptoms in these disorders and could serve as potential biomarkers for assessing neurodevelopmental risk.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Wellness Needs of Saudi University Students: Mental Health as a Key Determinant of Lifestyle and Quality of Life
by
Faris Alzahrani, Abdulmajid Zarbah, Abdullah Asiri, Ashwag Asiri, Sarah Alzahrani, Aram Alqathradi, Hasan Korairi, Ali Alshahrani and Mohamed Aliessa
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 106; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030106 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The transition to university is a critical period for establishing lifelong health habits, particularly in Saudi Arabia, where non-communicable diseases linked to lifestyle are increasingly prevalent. To address this, our study sought to comprehensively assess lifestyle behaviors, mental health status, and their combined
[...] Read more.
The transition to university is a critical period for establishing lifelong health habits, particularly in Saudi Arabia, where non-communicable diseases linked to lifestyle are increasingly prevalent. To address this, our study sought to comprehensively assess lifestyle behaviors, mental health status, and their combined impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among students at King Khalid University. We conducted a cross-sectional study between September 2024 and February 2025, recruiting 865 undergraduates via a two-stage stratified random sampling technique. Data were collected using a validated online questionnaire that included the FANTASTIC lifestyle and EuroQol 5-Dimension 3-Level (EQ-5D-3L) instruments. Our study population exhibited a significant health burden; 37.6% were overweight or obese, 55.9% reported anxiety or depression, and 36.1% experienced pain or discomfort. Although the mean lifestyle score was generally positive, regression analysis revealed that anxiety/depression was the strongest predictor of a poorer lifestyle (OR = 2.94, 95% CI: 2.02–4.28). This study concludes that a profound negative association exists between mental health, lifestyle, and overall HRQoL, highlighting the urgent need for integrated wellness policies and support systems within the university setting to address these interconnected challenges.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Psychological Factors Influencing Climate Anxiety in Young Adults: Exploring the Impact of Age, Trait Anxiety, Flexible Goal Adjustment and Tenacious Goal Pursuit
by
Kévin Nadarajah, Tivizio Pavic, Laurent Brun, Stéphanie Bordel and Alain Somat
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 105; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030105 - 3 Sep 2025
Abstract
Climate change and its consequences for human beings are considered to be a major mental health problem, commonly referred to as ‘climate anxiety’. This particular form of anxiety is currently the subject of extensive research. Research is investigating its relationship to more general
[...] Read more.
Climate change and its consequences for human beings are considered to be a major mental health problem, commonly referred to as ‘climate anxiety’. This particular form of anxiety is currently the subject of extensive research. Research is investigating its relationship to more general forms of anxiety as well as the coping strategies that can be put in place to manage it. The present study was conducted to examine the role of variables such as age, trait anxiety, tenacious goal pursuit, and flexible goal adjustment on climate-related anxiety. A cross-sectional study was conducted in which 396 participants completed the questionnaire. Hierarchical multiple regression analysis was used to analyze the data. Results from the hierarchical regression model revealed that age, trait anxiety and flexible goal adjustment had a positive and significant effect on climate anxiety scores. In this study, the older the young participants are, the higher their trait anxiety scores, and the higher their levels of flexible goal adjustment, the more climate anxiety they experience. Contrary to our hypotheses, flexible goal adjustment was positively associated with climate anxiety, suggesting that accommodative coping may in some contexts amplify rather than alleviate emotional distress. This study highlights the increased vulnerability to climate anxiety of older participants among the young adults with trait anxiety and higher levels of accommodative coping strategies (i.e., FGA). These findings provide some guidelines for clinical practice, in particular by questioning educational intervention and cognitive flexibility in young adults.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Dysregulated Oxidative Stress Pathways in Schizophrenia: Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Human Biomarker Evidence
by
Mohammad Mohabbulla Mohib, Mohammad Borhan Uddin, Md Majedur Rahman, Munichandra Babu Tirumalasetty, Md. Mamun Al-Amin, Shakila Jahan Shimu, Md. Faruk Alam, Shahida Arbee, Afsana R. Munmun, Asif Akhtar and Mohammad Sarif Mohiuddin
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 104; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030104 - 3 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Schizophrenia is a complex neuropsychiatric disorder whose pathophysiology may involve oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage and inflammation. We conducted a cross-species study to elucidate oxidative stress dysregulation in schizophrenia. Methods: We measured peripheral oxidative stress biomarkers (malondialdehyde [MDA], nitric oxide [NO], reduced glutathione
[...] Read more.
Background: Schizophrenia is a complex neuropsychiatric disorder whose pathophysiology may involve oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage and inflammation. We conducted a cross-species study to elucidate oxidative stress dysregulation in schizophrenia. Methods: We measured peripheral oxidative stress biomarkers (malondialdehyde [MDA], nitric oxide [NO], reduced glutathione [GSH], superoxide dismutase [SOD], catalase [CAT], advanced protein oxidation products [APOP]), and C-reactive protein (CRP) in antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia patients and matched controls. We also assayed liver enzymes (ALP, ALT, AST) as indicators of systemic metabolic stress. In parallel, we re-analyzed published single-cell RNA-sequencing data from a Setd1a^+/–^ mouse model of schizophrenia, focusing on prefrontal cortex (PFC) cell types and oxidative stress-related gene expression. Results: Patients with schizophrenia showed markedly elevated MDA and NO (indicators of lipid and nitrosative stress) and significantly reduced antioxidant defenses (GSH, SOD, CAT) versus controls (p < 0.01 for all comparisons). Notably, urban patients exhibited higher oxidative stress biomarker levels than rural patients, implicating environmental contributions. Liver function tests revealed increased ALT, AST, and ALP in schizophrenia, suggesting hepatic/metabolic dysregulation. Single-cell analysis confirmed dysregulated redox pathways in the schizophrenia model; PFC neurons from Setd1a^+/–^ mice displayed significantly lower expression of key antioxidant genes (e.g., Gpx4, Nfe2l2) compared to wild-type, indicating impaired glutathione metabolism. Conclusions: Our integrative data identify convergent oxidative stress imbalances in schizophrenia across species. These findings advance a mechanistic understanding of schizophrenia as a disorder of redox dysregulation and inflammation. They also have translational implications as augmenting antioxidant defenses (for example, with N-acetylcysteine or vitamins C/E) could mitigate oxidative injury and neuroinflammation in schizophrenia, representing a promising adjunct to antipsychotic therapy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Benefits of Hypnosis Support in Stress Management for First-Year Students at the Higher Institute of Nursing and Health Techniques, Rabat
by
Ilham Benarfa, Dia Eddine Oudghiri, Nadia Mountaj, Aboubaker El Hessni, Abdelhalim Mesfioui and Hasna Ahyayauch
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 103; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030103 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The transition from secondary to higher education presents numerous academic, social, and psychological challenges that can negatively impact students’ well-being, particularly during the first year. This randomized controlled trial aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of hypnosis as a non-pharmacological intervention for managing perceived
[...] Read more.
The transition from secondary to higher education presents numerous academic, social, and psychological challenges that can negatively impact students’ well-being, particularly during the first year. This randomized controlled trial aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of hypnosis as a non-pharmacological intervention for managing perceived stress among first-year nursing students at the Higher Institute of Nursing and Health Techniques (ISPITS) in Rabat, Morocco. A total of 166 students from five academic tracks were randomly assigned to intervention and control groups with comparable baseline characteristics. Their perceived stress levels were assessed using two validated instruments, the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and the 14-item Perceived Stress Scale (PSS-14), administered before and after a five-session hypnosis program conducted over 10 weeks. The results showed a marked and statistically significant reduction in stress among the intervention group, with the mean VAS scores decreasing from 7.82 ± 2.05 to 3.00 ± 1.71 compared to a smaller reduction in the control group (from 7.65 ± 1.78 to 5.80 ± 1.72; between-group difference = 2.8, p < 0.0001). Similarly, the PSS-14 scores in the intervention group declined significantly from 26.42 ± 7.54 (moderate stress) to 24.32 ± 8.20 (still moderate), with a mean difference of 2.09 ± 7.70 (t = 2.21, p = 0.0307, 95% CI [0.20; 3.98]). These findings indicate that hypnosis is an effective mind–body approach for alleviating perceived stress, improving emotional regulation, and could be incorporated into academic support programs to enhance student well-being.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unseen Wounds: PTSD Among Search and Rescue Teams Responding to the February 6, 2023 Earthquake in Türkiye
by
Okan Ozbakir
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 102; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030102 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In terms of occupational health and safety, psychosocial risks in the workplace can lead to temporary or permanent harm. Search and rescue workers assisting earthquake victims may develop PTSD due to the trauma they experience and witness. This study estimates the prevalence of
[...] Read more.
In terms of occupational health and safety, psychosocial risks in the workplace can lead to temporary or permanent harm. Search and rescue workers assisting earthquake victims may develop PTSD due to the trauma they experience and witness. This study estimates the prevalence of PTSD among search and rescue workers involved in the February 6, 2023, earthquake in Türkiye. This study utilized the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5) to assess 619 individuals. The results showed that the earthquake significantly affected post-traumatic stress symptoms across all demographic groups. Female participants (x̄ = 2.43) exhibited higher stress levels than male participants (x̄ = 2.24), showing an 8.48% difference. Participants with higher education levels (x̄ = 2.34) showed more stress than those with lower education (x̄ = 1.67). Individuals with over a decade of experience (x̄ = 3.28) experienced more distress compared to those with less than three years of experience (x̄ = 2.83). Participants under 30 (x̄ = 2.30) were more affected than those over 50 (x̄ = 2.25). Firsthand experience of the earthquake (x̄ = 2.49) resulted in greater distress compared to learning about it through communication channels (x̄ = 2.01). Concerning PTSD symptoms, 191 participants (30.86%) scored 33 or higher, which indicates clinically significant PTSD. Among the participants, 22 experienced severe to extremely severe symptoms, with 19 showing extremely severe symptoms on at least one subscale, 3 displaying extremely severe symptoms across all four subscales, and 9 demonstrating extremely severe symptoms in three subscales.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predictors of Emotional Exhaustion and Depersonalization in Teachers After the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications for Mental Health and Psychiatric Support in Spanish-Speaking Countries
by
Sofia Catalina Arango-Lasprilla, Natalia Albaladejo-Blázquez, Bryan R. Christ, Oswaldo A. Moreno, Maria Camila Gomez Posada, Paul B. Perrin and Rosario Ferrer-Cascales
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 101; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030101 - 21 Aug 2025
Abstract
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion and depersonalization, is increasingly recognized as a significant mental health concern with psychiatric implications. This cross-sectional study explored variables associated with current burnout levels among 2004 teachers in 19 Latin American countries and Spain, drawing on retrospective perceptions
[...] Read more.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion and depersonalization, is increasingly recognized as a significant mental health concern with psychiatric implications. This cross-sectional study explored variables associated with current burnout levels among 2004 teachers in 19 Latin American countries and Spain, drawing on retrospective perceptions of COVID-19 pandemic-related changes in work conditions and student behavior. Using a comprehensive survey, researchers gathered demographic information, work-related characteristics, and burnout levels measured by the Maslach Burnout Inventory. Participants were recruited through social media platforms and teacher groups. Participants reported high emotional exhaustion, with 45.9% exceeding the clinical threshold. Moderate depersonalization levels were observed, with 30.2% scoring above the clinical cutoff. Hierarchical regressions indicated that emotional exhaustion was significantly predicted by individual (e.g., gender, age, socioeconomic status, pre-existing mental and chronic illnesses), school (e.g., school level, sector, and workload), and student factors (e.g., behavior and social adjustment problems), accounting for 17.4% of the variance. Depersonalization was similarly associated with individual (e.g., gender, age, education, and pre-existing mental illness), school (e.g., workload and school level), and student characteristics (e.g., educational, behavioral, and family adjustment problems), explaining 6.5% of the variance. These findings contribute to psychiatric and psychological research by identifying specific risk profiles for chronic stress syndromes in educators—an occupational group facing long-term psychological impacts from the COVID-19 crisis. This study underscores the need for interdisciplinary psychiatric approaches to diagnose and prevent burnout and promote teacher well-being through clinical and policy-level interventions.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Vicarious Trauma and Burnout Among Mental Health Professionals in Greece: The Role of Core Self-Evaluations, Self-Compassion, and Occupational Factors
by
Kalliope Kounenou, Christos Pezirkianidis, Maria Blantemi, Antonios Kalamatianos, Ntina Kourmousi and Spyridoula G. Kostara
Psychiatry Int. 2025, 6(3), 100; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint6030100 - 13 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mental health professionals are often confronted with clients’ traumatic narratives, which may lead to increased levels of vicarious trauma and burnout, especially when work-related risk factors are present. This study aims to investigate the relationship between vicarious trauma and burnout among mental health
[...] Read more.
Mental health professionals are often confronted with clients’ traumatic narratives, which may lead to increased levels of vicarious trauma and burnout, especially when work-related risk factors are present. This study aims to investigate the relationship between vicarious trauma and burnout among mental health professionals in Greece while taking into account work-related and intrapersonal factors using a sample of 266 mental health professionals, who completed the Core Self-Evaluations Scale, Self-Compassion Scale, Vicarious Trauma Scale, and Counselor Burnout Inventory, and provided information about work-related variables, such as caseload, clinical supervision, clinical training, and therapeutic experience. The findings showed that Greek mental health professionals’ burnout positively associated with vicarious trauma and caseload, while negatively associated with intrapersonal factors and work-related factors, namely, years of clinical supervision, clinical training and therapeutic experience. Vicarious trauma negatively correlated with core self-evaluations, self-compassion, and clinical experience. Finally, low core self-evaluations and self-compassion were found to explain greater burnout levels together with higher vicarious trauma and work overload per week, while core self-evaluations were the only variable that moderated the relationship between vicarious trauma and burnout of Greek mental health professionals. These findings indicate that in order to address the interplay between vicarious trauma and burnout, targeted interventions that focus on personal attributes, coping strategies, and systemic organizational support are needed.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Behavioral Sciences, Healthcare, Psychiatry International, Adolescents, Social Sciences, Children
Behavioral Addictions and Risk-Taking in the Digital Age: Gambling, Sports Betting, and Emerging Challenges
Topic Editors: André Luiz Monezi Andrade, Denise De MicheliDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
Education Sciences, Youth, Behavioral Sciences, Psychiatry International, EJIHPE
Addictive Behaviors and Mental Disorders Among Youth and Adolescents
Topic Editors: Wenchao Wang, Chao SongDeadline: 30 November 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Psychiatry International
Precision Psychiatry and Advances in Patient Care: Innovations Transforming the Diagnosis and Treatment of Mental Disorders
Guest Editors: Antonio Del Casale, Paolo Girardi, Carlo Lai, Maurizio Simmaco, Marina BorroDeadline: 7 April 2026
Special Issue in
Psychiatry International
Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders
Guest Editor: Rekha JagadapillaiDeadline: 31 December 2026








