An Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm for the Prediction and Localization of Angiography-Proven Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Populations
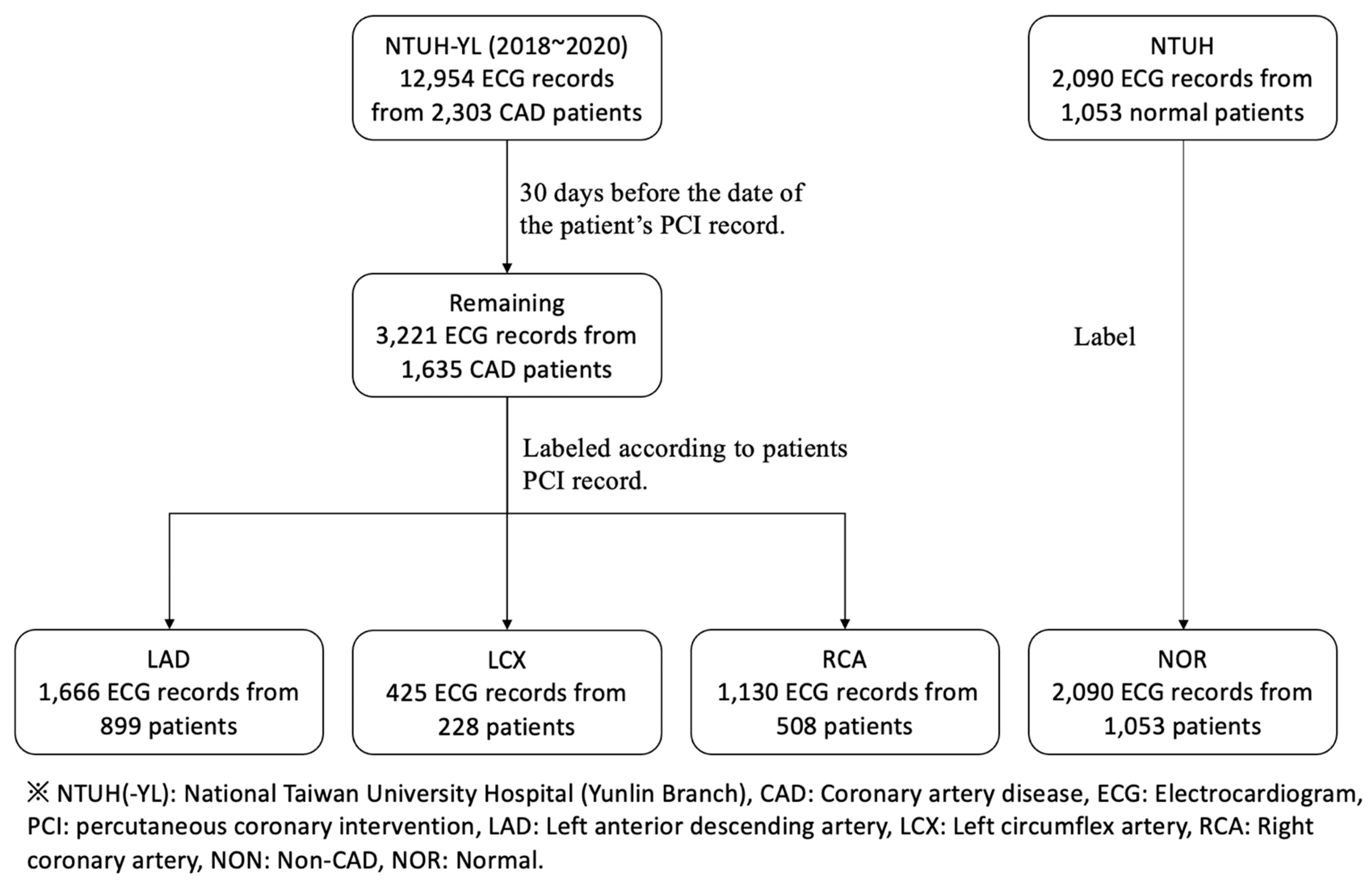
2.2. Data Collection and Parsing
2.3. Dataset Preparation and Data Analysis
2.4. Data Type and Preprocessing
2.5. Model Build-Up
2.6. Training Process
2.7. Evaluation Metrics
- (1)
- AUC < 0.5 (no discrimination)
- (2)
- 0.7 ≤ AUC < 0.8 (acceptable discrimination)
- (3)
- 0.8 ≤ AUC < 0.9 (excellent discrimination)
- (4)
- 0.9 ≤ AUC ≤ 1.0 (outstanding discrimination)
3. Results
3.1. Image Input Model Architecture Optimization
3.2. Detection of CAD and Prediction of the Obstructed Coronary Vessel
3.2.1. Random Selection Dataset
3.2.2. Subgroup Datasets
4. Discussion
4.1. Importance of Model Optimization
4.2. AI in Significant CAD Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malakar, A.K.; Choudhury, D.; Halder, B.; Paul, P.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. A review on coronary artery disease, its risk factors, and therapeutics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 16812–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neglia, D.; Rovai, D.; Caselli, C.; Pietila, M.; Teresinska, A.; Aguadé-Bruix, S.; Pizzi, M.N.; Todiere, G.; Gimelli, A.; Schroeder, S.; et al. Detection of Significant Coronary Artery Disease by Noninvasive Anatomical and Functional Imaging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, e002179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haraphongse, M.; Kappagoda, T.; Rossall, R.E. Localization of coronary artery disease with exercise induced ST segment depression: Coronary angiographic correlation. Can. J. Cardiol. 1985, 1, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, S.; Uzu, T.; Inenaga, T.; Kimura, G. Prediction of coronary artery disease and cardiac events using electrocardiographic changes during hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Kwon, J.-M.; Kim, K.-H.; Medina-Inojosa, J.R.; Jeon, K.-H.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.; Oh, B.-H. Artificial intelligence algorithm for detecting myocardial infarction using six-lead electrocardiography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.S.; Jadhav, S.M. Deep convolutional neural network based medical image classification for disease diagnosis. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M.; Qayyum, A.; Awais, M.; Alnowami, M.; Khan, M.K. Medical Image Analysis using Convolutional Neural Networks: A Review. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faust, O.; Hagiwara, Y.; Hong, T.J.; Lih, O.S.; Acharya, U.R. Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: A review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.; A Noseworthy, P.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Gersh, B.J.; E Carter, R.; Yao, X.; A Rabinstein, A.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: A retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet 2019, 394, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedinsewo, D.; Carter, R.E.; Attia, Z.; Johnson, P.; Kashou, A.H.; Dugan, J.L.; Albus, M.; Sheele, J.M.; Bellolio, F.; Friedman, P.A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm to Identify Patients With Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Ghose, A.; Mandana, K.M. A Hybrid CNN-LSTM Architecture for Detection of Coronary Artery Disease from ECG. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qassim, H.; Verma, A.; Feinzimer, D. Compressed residual-VGG16 CNN model for big data places image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–10 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, D.; Lu, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, G. Synthetic Medical Images Using F&BGAN for Improved Lung Nodules Classification by Multi-Scale VGG16. Symmetry 2018, 10, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, K.; Garg, L.; Datta, D.; Alaboudi, A.A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Agarwal, R.; Thomas, A.G. Performance Comparison of Deep CNN Models for Detecting Driver’s Distraction. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 4109–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, T.; Palivela, H.; Tiwari, S. Optimization and Fine-Tuning of DenseNet model for classification of Covid-19 cases in Medical Imaging. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Benz, P.; Argaw, D.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Rameau, F.; Bazin, J.-C.; Kweon, I.S. Resnet or densenet? Introducing dense shortcuts to ResNet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikola, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3550–3559. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Bisong, E. Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Obuchowski, N.A. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves and Their Use in Radiology. Radiology 2003, 229, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, C.; Torreton, E.; Briere, J.-B.; Evers, T.; Fagnani, F. Economic burden of coronary artery disease or peripheral artery disease in patients at high risk of ischemic events in the French setting: A claims database analysis. J. Med. Econ. 2020, 23, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danad, I.; Raijmakers, P.G.; Driessen, R.S.; Leipsic, J.; Raju, R.; Naoum, C.; Knuuti, J.; Mäki, M.; Underwood, R.S.; Min, J.K.; et al. Comparison of Coronary CT Angiography, SPECT, PET, and Hybrid Imaging for Diagnosis of Ischemic Heart Disease Determined by Fractional Flow Reserve. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; He, L.; Gao, Z. Feature extraction from a novel ECG model for arrhythmia diagnosis. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 2883–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butun, E.; Yildirim, O.; Talo, M.; Tan, R.S.; Rajendra Acharya, U. 1D-CADCapsNet: One dimensional deep capsule networks for coronary artery disease detection using ECG signals. Phys Med. 2020, 70, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lih, O.S.; Jahmunah, V.; San, T.R.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Yamakawa, T.; Tanabe, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Faust, O.; Acharya, U.R. Comprehensive electrocardiographic diagnosis based on deep learning. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 103, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.; Hagiwara, Y.; Pang, W.; Lim, I.; Oh, S.L.; Adam, M.; Tan, R.S.; Chen, M.; Acharya, U.R. Application of stacked convolutional and long short-term memory network for accurate identification of CAD ECG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 94, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| w/ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Acc. | AUC | Precision | Recall | |||
| NOR | LAD | LCX | RCA | ||||
| VGG16 | 0.670 ± 0.030 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.873 ± 0.036 | 0.807 ± 0.064 | 0.913 ± 0.024 | 0.720 ± 0.039 | 0.674 ± 0.020 |
| ResNet50V2 | 0.827 ± 0.007 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.927 ± 0.026 | 0.903 ± 0.024 | 0.950 ± 0.000 | 0.836 ± 0.012 | 0.831 ± 0.12 |
| Xception | 0.850 ± 0.023 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.940 ± 0.023 | 0.907 ± 0.033 | 0.963 ± 0.007 | 0.855 ± 0.009 | 0.851 ± 0.011 |
| Inception ResNetV2 | 0.857 ± 0.035 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.957 ± 0.013 | 0.943 ± 0.017 | 0.96 ± 0.011 | 0.847 ± 0.012 | 0.840 ± 0.012 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.843 ± 0.007 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.953 ± 0.007 | 0.920 ± 0.023 | 0.953 ± 0.007 | 0.851 ± 0.014 | 0.831 ± 0.012 |
| InceptionV3 | 0.876 ± 0.025 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.958 ± 0.019 | 0.944 ± 0.024 | 0.970 ± 0.011 | 0879 ± 0.020 | 0.873 ± 0.025 |
| w/o | |||||||
| VGG16 | 0.250 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 0.085 ± 0.043 | 0.252 ± 0.004 |
| ResNet50V2 | 0.854 ± 0.013 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.952 ± 0.004 | 0.908 ± 0.010 | 0.966 ± 0.005 | 0.856 ± 0.017 | 0.852 ± 0.015 |
| Xception | 0.856 ± 0.005 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.954 ± 0.021 | 0.928 ± 0.016 | 0.968 ± 0.004 | 0.857 ± 0.006 | 0.855 ± 0.005 |
| Inception ResNetV2 | 0.872 ± 0.010 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.950 ± 0.015 | 0.924 ± 0.017 | 0.976 ± 0.010 | 0.875 ± 0.009 | 0.872 ± 0.010 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.890 ± 0.014 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.978 ± 0.007 | 0.936 ± 0.025 | 0.966 ± 0.012 | 0.893 ± 0.010 | 0.889 ± 0.013 |
| InceptionV3 | 0.900 ± 0.012 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.966 ± 0.010 | 0.948 ± 0.014 | 0.978 ± 0.010 | 0.903 ± 0.011 | 0.899 ± 0.012 |
| Image Input Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | Accuracy | AUC | Precision | Recall | |||
| NOR | LAD | LCX | RCA | ||||
| 1 | 0.973 ± 0.012 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 0.966 ± 0.010 | 0.948 ± 0.014 | 0.978 ± 0.010 | 0.903 ± 0.011 | 0.899 ± 0.012 |
| 2 | 0.566 ± 0.008 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 0.710 ± 0.040 | 0.672 ± 0.029 | 0.704 ± 0.040 | 0.553 ± 0.045 | 0.563 ± 0.006 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.-S.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-F.; Chen, J.-J.; Yang, S.-C.; Chiu, F.-C.; Chen, Z.-W.; Hwang, J.-J.; Chuang, E.Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm for the Prediction and Localization of Angiography-Proven Coronary Artery Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020394
Huang P-S, Tseng Y-H, Tsai C-F, Chen J-J, Yang S-C, Chiu F-C, Chen Z-W, Hwang J-J, Chuang EY, Wang Y-C, et al. An Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm for the Prediction and Localization of Angiography-Proven Coronary Artery Disease. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020394
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Pang-Shuo, Yu-Heng Tseng, Chin-Feng Tsai, Jien-Jiun Chen, Shao-Chi Yang, Fu-Chun Chiu, Zheng-Wei Chen, Juey-Jen Hwang, Eric Y. Chuang, Yi-Chih Wang, and et al. 2022. "An Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm for the Prediction and Localization of Angiography-Proven Coronary Artery Disease" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020394
APA StyleHuang, P.-S., Tseng, Y.-H., Tsai, C.-F., Chen, J.-J., Yang, S.-C., Chiu, F.-C., Chen, Z.-W., Hwang, J.-J., Chuang, E. Y., Wang, Y.-C., & Tsai, C.-T. (2022). An Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm for the Prediction and Localization of Angiography-Proven Coronary Artery Disease. Biomedicines, 10(2), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020394






