Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SDOs Preparation
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Hypotensive Effect of SDOs
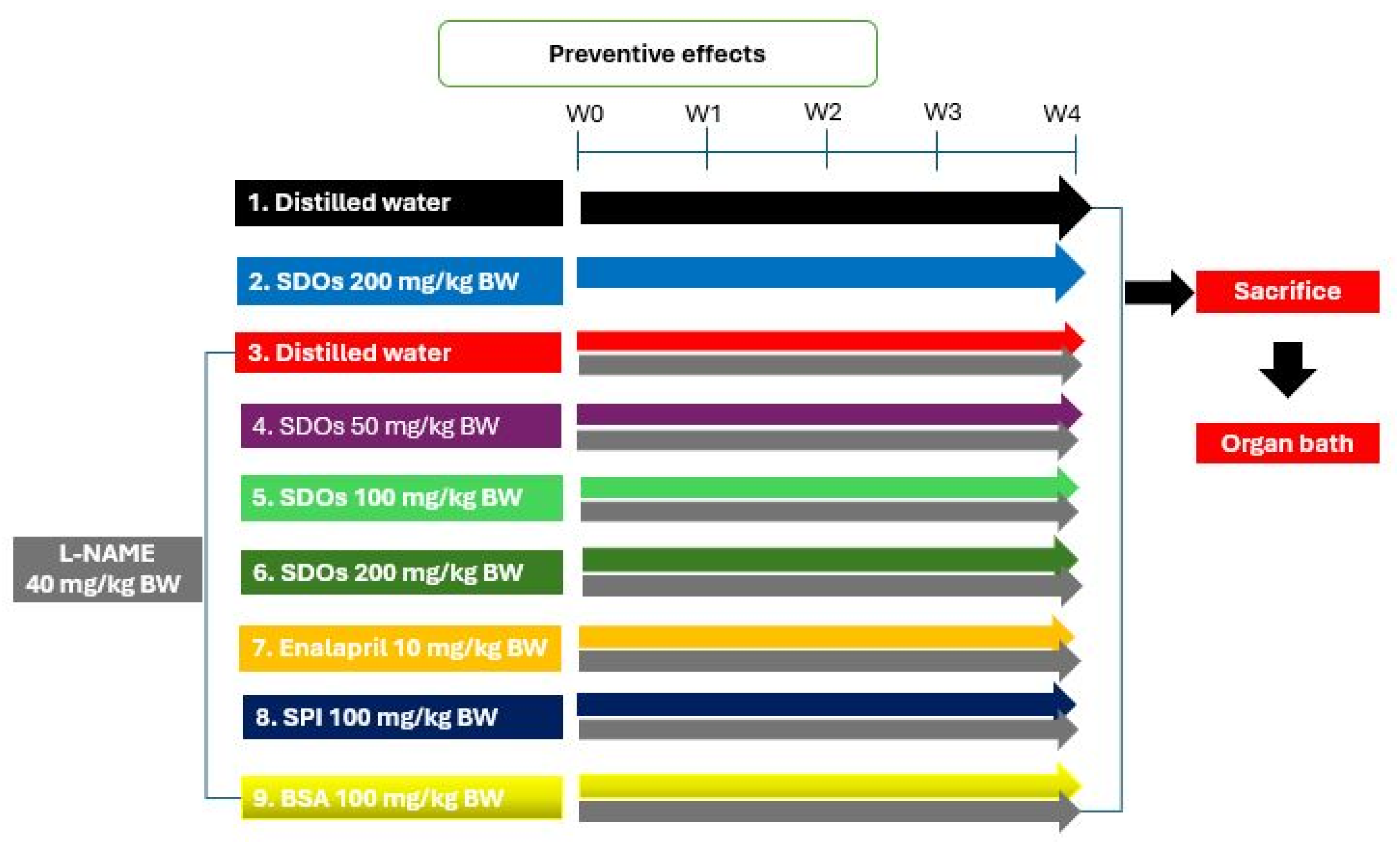
2.3.1. Preventive Effects of SDOs on the Development of Hypertension
2.3.2. Therapeutic Effects of SDOs After Hypertension Induction
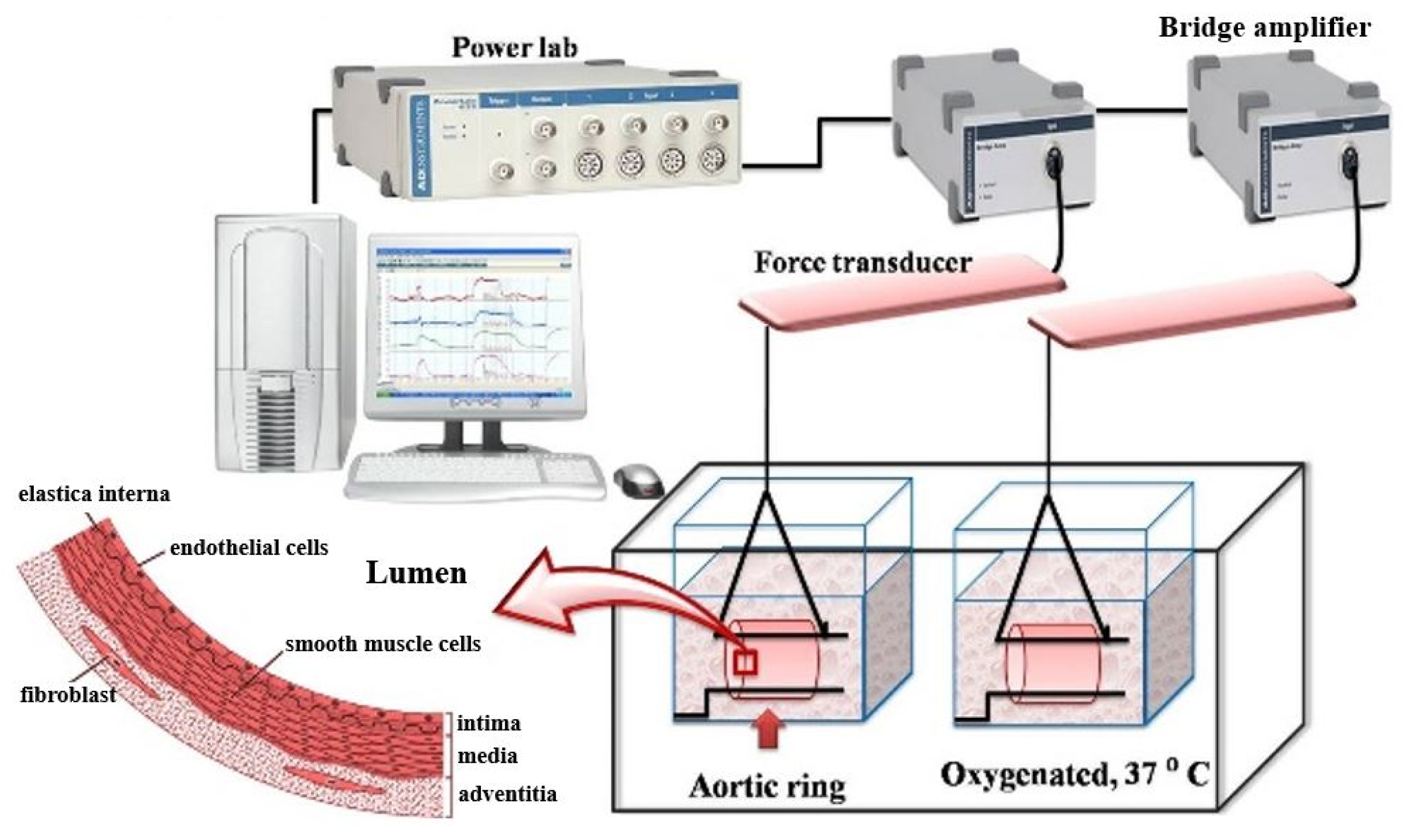
2.4. Functional Vascular Study
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preventive Effects of SDOs During Induced Hypertension
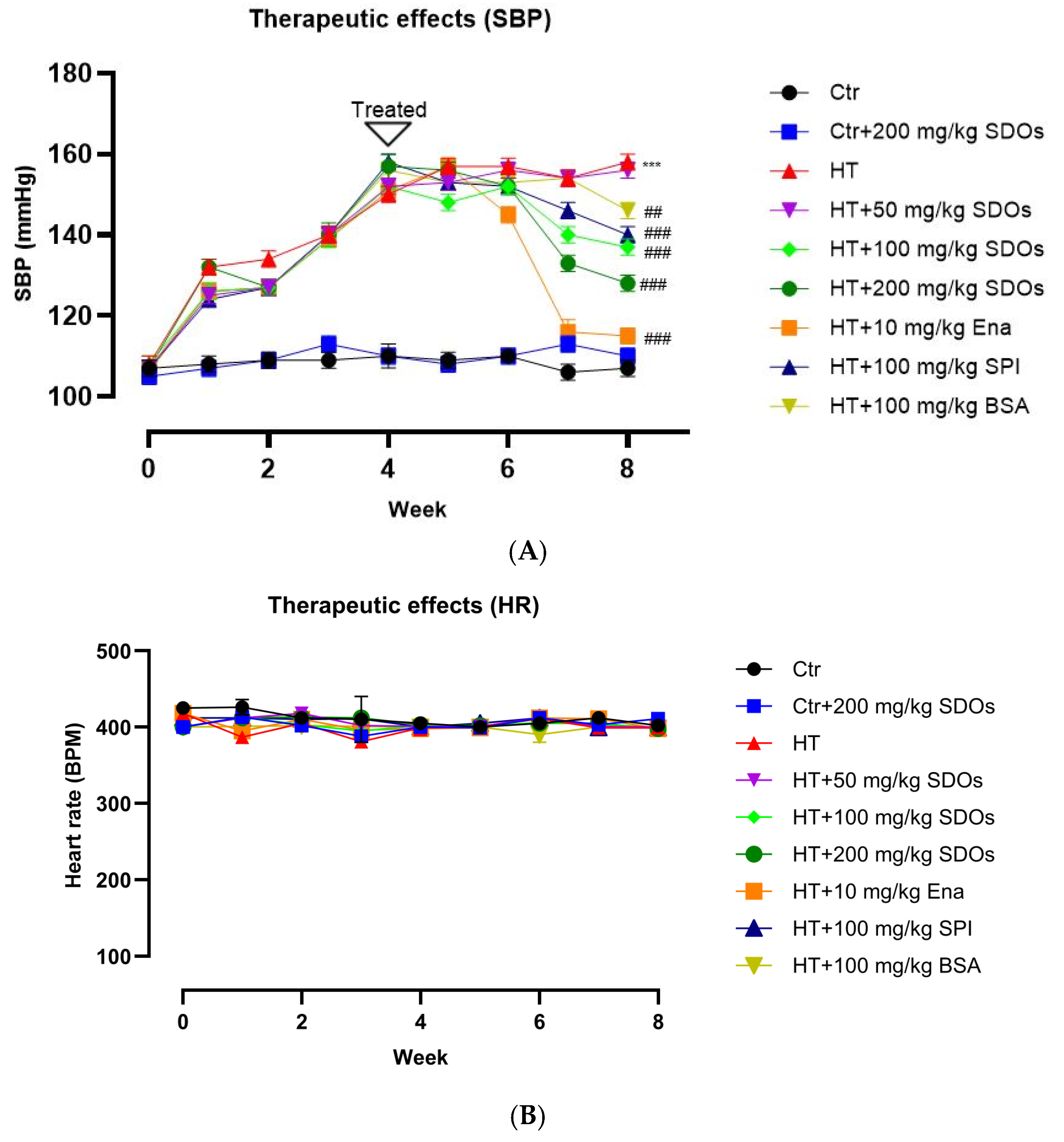
3.2. Therapeutic Effects of SDOs After Hypertension Induction
3.3. Effects of Blood Vessel Function
3.3.1. Preventive Groups
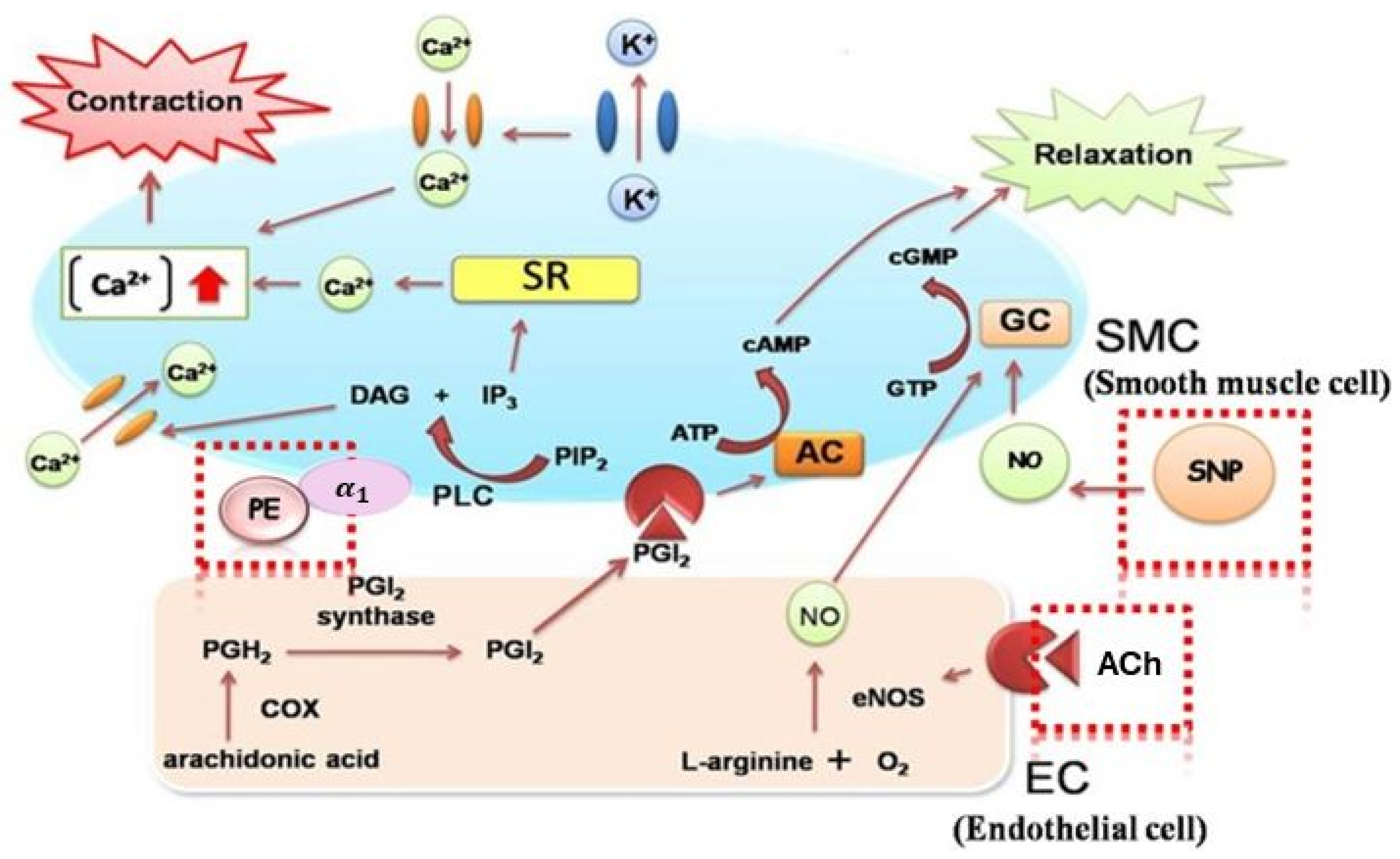
Effect of SDOs on Vascular Function by Acetylcholine (ACh)-Induced Relaxation
Effect of SDOs on Vascular Function by SNP-Induced Relaxation
Effect of SDOs on Vascular Function by PE-Induced Contraction
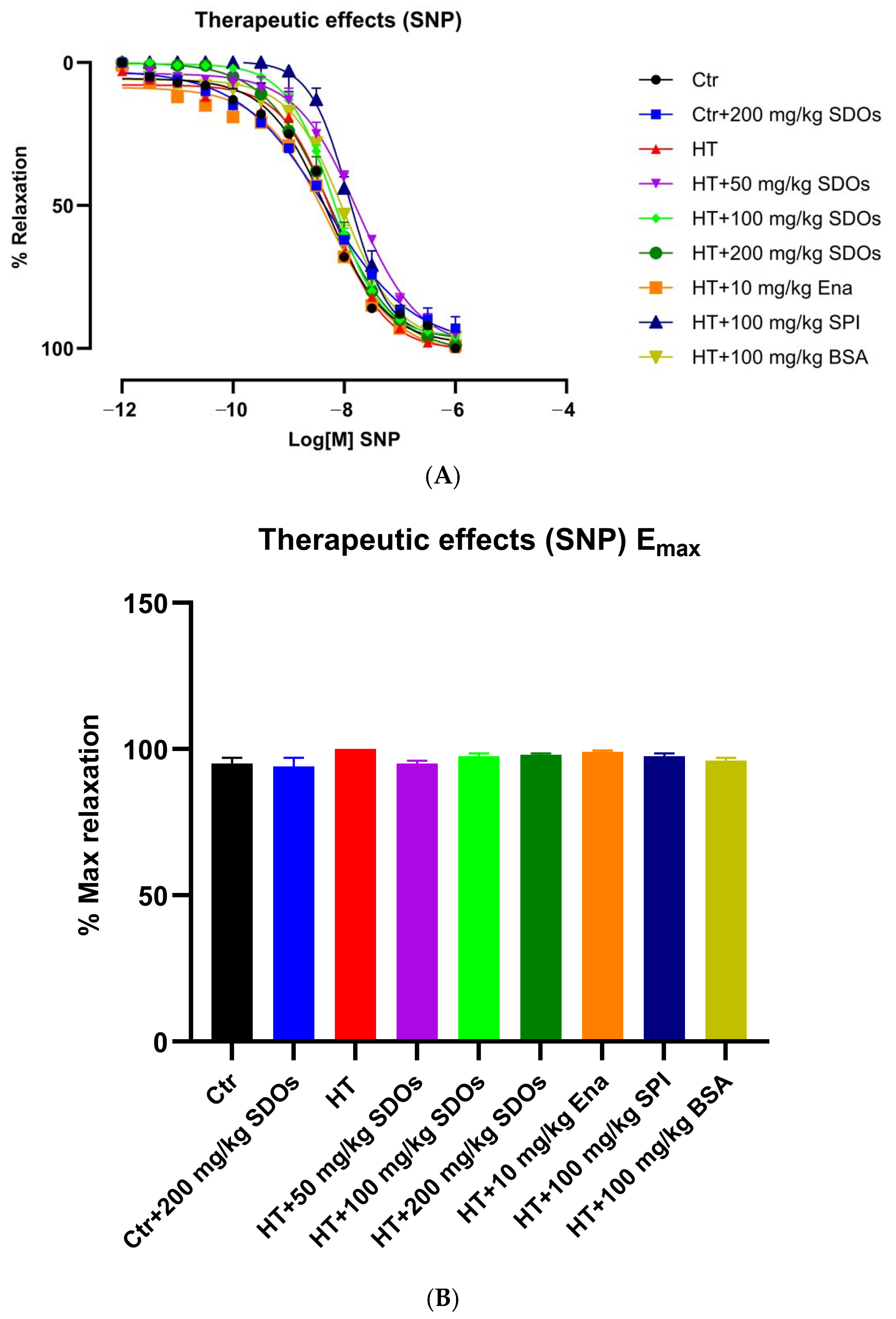
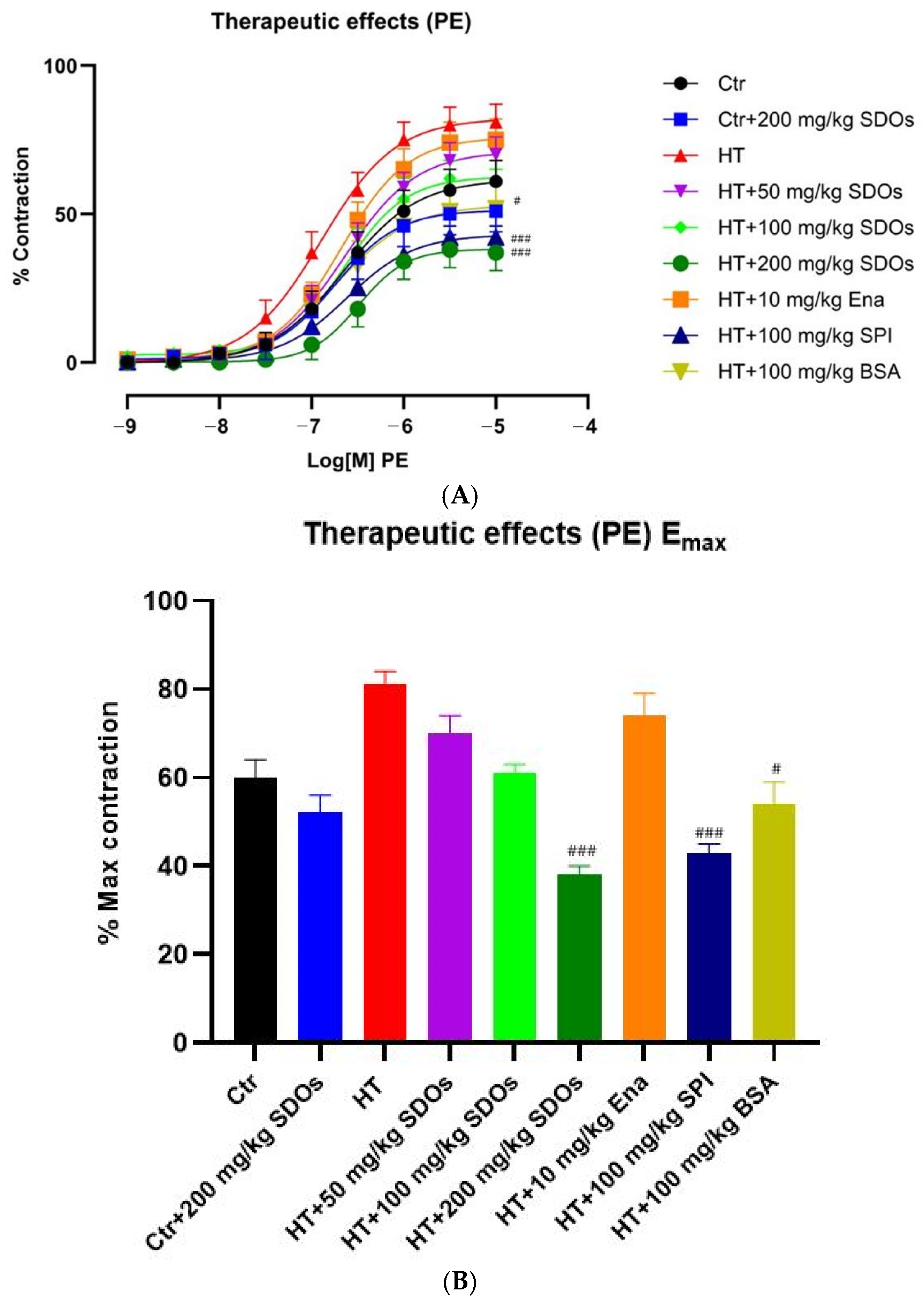
3.3.2. Therapeutic Groups
Effect of SDOs on Vascular Function by ACh-Induced Relaxation
Effect of SDOs on Vascular Function by SNP Relaxation
Effect of SDOs on Vascular Function by PE-Induced Contraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kjeldsen, S.E. Hypertension and cardiovascular risk: General aspects. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Schumacher, H.; Redon, J.; Verdecchia, P.; Schmieder, R.; Jennings, G.; Yusoff, K.; Ryden, L.; Liu, G.L.; Teo, K.; et al. Blood Pressure Targets Recommended by Guidelines and Incidence of Cardiovascular and Renal Events in the Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination With Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial (ONTARGET). Circulation 2011, 124, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muntner, P.; Carey, R.M.; Gidding, S.; Jones, D.W.; Taler, S.J.; Wright, J.T., Jr.; Whelton, P.K. Potential US Population Impact of the 2017 ACC/AHA High Blood Pressure Guideline. Circulation 2018, 137, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goit, L.; Yang, S. Treatment of Hypertension: A Review. Yangtze Med. 2019, 3, 101–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tian, T.; Xu, Y. Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of food-derived bioactive peptides in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 8200–8210. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Sun, G.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Xia, H.; Wang, S. The Blood-Pressure-Lowering Effect of Food-Protein-Derived Peptides: A Meta-Analysis of Recent Clinical Trials. Foods 2021, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, E.B.-M.; Ofosu, F.K.; Chelliah, R.; Lee, B.H.; An, H.; Elahi, F.; Barathikannan, K.; Kim, J.-H.; Oh, D.-H. Influence of fermented soy protein consumption on hypertension and gut microbial modulation in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2020, 39, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Lv, M.; Zhou, M.; Huang, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, M. Soybean-Derived Antihypertensive Peptide LSW (Leu–Ser–Trp) Antagonizes the Damage of Angiotensin II to Vascular Endothelial Cells through the Trans-vesicular Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10536–10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Soy protein isolates: A review of their composition, aggregation, and gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar]
- Ramdath, D.D.; Padhi, E.M.; Sarfaraz, S.; Renwick, S.; Duncan, A.M. Beyond the Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Soy Protein: A Review of the Effects of Dietary Soy and Its Constituents on Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, C.; Gleddie, S.; Xiao, C.W. Soybean Bioactive Peptides and Their Functional Properties. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosallanezhad, Z.; Mahmoodi, M.; Ranjbar, S.; Hosseini, R.; Clark, C.C.T.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Norouzi, Z.; Abbasian, A.; Sohrabi, Z.; Jalali, M. Soy intake is associated with lowering blood pressure in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2021, 59, 102692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, S.; Burke, G.L.; Morgan, T.; Anthony, M. Effect of soy protein supplementation on serum lipoproteins, blood pressure, and menopausal symptoms in perimenopausal women. Menopause 1999, 6, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, B.; Cui, C.; Zhang, X.; Sugiyama, D.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Sekikawa, A. The effect of soy isoflavones on arterial stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Shu, X.O.; Jin, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.L.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y.T.; Zheng, W. Longitudinal study of soy food intake and blood pressure among middle-aged and elderly Chinese women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Tabibiazar, M.; Amarowicz, R. Recent developments in the detection of bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, O.; Szota, M.; Rakowski, K.; Prochownik, M.; Doveiko, D.; Chen, Y.; Jachimska, B. Bovine Serum Albumin as a Platform for Designing Biologically Active Nanocarriers—Experimental and Computational Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andishmand, H.; Roufegari-nejad, L.; Tabibiazar, M. Nanostructure characterization of bovine serum albumin-resveratrol complex. Res. Innov. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ampawong, S.; Isarangkul, D.; Aramwit, P. Sericin improves heart and liver mitochondrial architecture in hypercholesterolaemic rats and maintains pancreatic and adrenal cell biosynthesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bunarsa, S.; Promphet, P.; Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Kunthalert, D. Hematological assessments of sericin-derived oligopeptides in BALB/c mice. Sci. Res. Essays 2013, 8, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jantaruk, P.; Promphet, P.; Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Kunthalert, D. Augmentation of natural killer cell activity in vitro and in vivo by sericin-derived oligopeptides. J. Appl. Biomed. 2015, 13, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewkorn, W.; Limpeanchob, N.; Tiyaboonchai, W.; Pongcharoen, S.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Effects of silk sericin on the proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewkon, W.; Aonsri, C.; Tiyaboonchai, W.; Pongcharoen, S.; Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Limpeanchob, N. Sericin consumption suppresses development and progression of colon tumorigenesis in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-treated rats. Biologia 2012, 67, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Limpeanchob, N.; Trisat, K.; Duangjai, A.; Tiyaboonchai, W.; Pongcharoen, S.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Sericin reduces serum cholesterol in rats and cholesterol uptake into Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12519–12522. [Google Scholar]
- Tocharus, C.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Hypoglycemic Ability of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Bombyx mori Yellow Silk Cocoons and Their Physiological Effects on Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Diabetic Rats. Foods 2024, 13, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsawad, P.; Katemala, S.; Pao, D.; Suwanangul, S.; Jeencham, R.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Integrated Evaluation of Dual-Functional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effects of Peptides Derived from Sericin Hydrolysis and Their Stabilities during In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal and Plasmin Digestions. Foods 2022, 11, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangsawad, P.; Chumee, S.; Laosam, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Katemala, S.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Pilot-scale production of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons: Peptide Characterization and Specifications. Foods 2025, 14, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsa-Ard, A.; Shimbhu, D.; Tocharus, J.; Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Pantan, R.; Tocharus, C. Hypotensive and vasorelaxant effects of sericin-derived oligopeptides in rats. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013, 2013, 717529. [Google Scholar]
- Tocharus, C.; Prum, V.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Oral Toxicity and Hypotensive Influence of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons of Bombyx mori in Rodent Studies. Foods 2024, 13, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapphanichayakool, P.; Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Limpeanchob, N. Hypocholesterolemic effect of sericin-derived oligopeptides in high-cholesterol fed rats. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Limpeanchob, N.; Tocharus, C.; Tiyaboonchai, W.; Kanthalert, D.; Taepavarapruk, P.; Tocharus, J.; Khotcharrat, R.; Pannarunothai, S. Silk-Based Bioactive Oligopeptide Compositions and Manufacturing Process Therefor. WO2013032411A1, 3 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, M.A.; Younis, W.; Malik, M.N.H.; Alsahli, T.G.; Alamgeer; Jahan, S.; Ehsan, R.; Gasparotto Junior, A.; Bashir, A. Pulegone Prevents Hypertension through Activation of Muscarinic Receptors and Cyclooxygenase Pathway in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2023, 2023, 8166840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanthlal, S.K.; Joseph, J.; Paul, B.; M, V.; P, U.D. Antioxidant and vasorelaxant effects of aqueous extract of large cardamom in L-NAME induced hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2020, 42, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, L.R.; Campos, H.O.; de Andrade Lima, P.M.; da Fonseca, C.G.; Kunstetter, A.C.; Rodrigues, Q.T.; Szawka, R.E.; Natali, A.J.; Prímola-Gomes, T.N.; Wanner, S.P. Impaired thermoregulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats during physical exercise is related to reduced hypothalamic neuronal activation. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Panthiya, L.; Tocharus, J.; Onsa-ard, A.; Chaichompoo, W.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, C. Hexahydrocurcumin ameliorates hypertensive and vascular remodeling in L-NAME-induced rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechanova, O.; Vrankova, S.; Cebova, M. Chronic L-Name-Treatment Produces Hypertension by Different Mechanisms in Peripheral Tissues and Brain: Role of Central eNOS. Pathophysiology 2020, 27, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greish, S.M.; Abdel-Hady, Z.; Mohammed, S.S.; Abdel-Hamed, A.R.; Masoud, R.E.; Eltamany, D.A.; Abogresha, N.M. Protective potential of curcumin in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rat model: AT1R, mitochondrial DNA synergy. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 12, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Blum-Johnston, C.; Thorpe, R.B.; Wee, C.; Romero, M.; Brunelle, A.; Blood, Q.; Wilson, R.; Blood, A.B.; Francis, M.; Taylor, M.S.; et al. Developmental acceleration of bradykinin-dependent relaxation by prenatal chronic hypoxia impedes normal development after birth. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L271–L286. [Google Scholar]
- Blood, A.B.; Terry, M.H.; Merritt, T.A.; Papamatheakis, D.G.; Blood, Q.; Ross, J.M.; Power, G.G.; Longo, L.D.; Wilson, S.M. Effect of chronic perinatal hypoxia on the role of rho-kinase in pulmonary artery contraction in newborn lambs. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R136–R146. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Yang, J.; Santulli, G.; Reiken, S.R.; Wronska, A.; Kim, M.M.; Osborne, B.W.; Lacampagne, A.; Yin, Y.; Marks, A.R. Maintenance of normal blood pressure is dependent on IP3R1-mediated regulation of eNOS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8532–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Zhang, X.; Buckley, C.; Heathcote, H.R.; Lee, M.D.; McCarron, J.G. Increased Vascular Contractility in Hypertension Results From Impaired Endothelial Calcium Signaling. Hypertension 2019, 74, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marconi, K.P.; Bharathi, B.; Venis, A.M.; Raj, R.; Amirtham, S.M.; Subramani, S. Phenylephrine induces relaxation of longitudinal strips from small arteries of goat legs. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227316. [Google Scholar]
- Gada, K.D.; Logothetis, D.E. PKC regulation of ion channels: The involvement of PIP(2). J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102035. [Google Scholar]
- Meerasri, J.; Chollakup, R.; Sothornvit, R. Factors affecting sericin hydrolysis and application of sericin hydrolysate in sericin films. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28441–28450. [Google Scholar]
- Wubulikasimu, A.; Omar, A.; Gao, Y.; Mukhamedov, N.; Arken, A.; Wali, A.; Mirzaakhmedov, S.Y.; Yili, A. Antioxidant Hydrolysate of Sericin from Bombyx mori Cocoons. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 346–349. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, N.J.; Vaughan, D.E. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Circulation 1998, 97, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Del Vecchio, L.; Andrulli, S.; Colzani, S. Role of combination therapy with ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers in renal protection. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2002, 62, S53–S60. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, R.D.; Visentin, J.D.; Bronskill, S.E.; Wang, X.; Gruneir, A.; Giannakeas, V.; Guan, J.; Lam, K.; Luke, M.J.; Read, S.H.; et al. Evaluation of a Common Prescribing Cascade of Calcium Channel Blockers and Diuretics in Older Adults with Hypertension. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, R.A. Rationale for calcium entry-blocking drugs in systemic hypertension complicated by coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1985, 56, H34–H40. [Google Scholar]
- McKeever, R.G.; Patel, P.; Hamilton, R.J. Calcium channel blockers. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, R.B.; Pfeiffer, M.; Zhang, P.; Shafique, E.; Rayta, B.; Karbasiafshar, C.; Ahsan, N.; Sellke, F.W.; Abid, M.R. Reduction in mitochondrial ROS improves oxidative phosphorylation and provides resilience to coronary endothelium in non-reperfused myocardial infarction. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2023, 118, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Yan, F.; Qin, X.; Zhang, K.; He, W.; Dong, M.; Wu, G. Mitochondrial dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells and its role in atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1084604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zeng, Y.; He, K.; Luo, Y.; Yu, F. Antioxidant peptides from Mytilus Coruscus on H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell stress. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100762. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D.Y.; Jo, K.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Lim, K.; Suh, H.J.; Oh, S. Antioxidant Effect and Functional Properties of Hydrolysates Derived from Egg-White Protein. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noviyanti, E. Effect of germination on free radical scavenging activities and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory of melinjo (Gnetum gnemon L.) seed proteins. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2020, 9, 809–812. [Google Scholar]
- Chataigneau, T.; Félétou, M.; Huang, P.L.; Fishman, M.C.; Duhault, J.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Acetylcholine-induced relaxation in blood vessels from endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 126, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler, A.; Li, J.-H.; Shah, V.; Tsaava, T.; Tynan, A.; Yang, H.; Tamari, Y.; Brines, M.; Tracey, K.J.; Chavan, S.S. Systemic administration of choline acetyltransferase decreases blood pressure in murine hypertension. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.X.; Gauthier, K.M.; Campbell, W.B. Acetylcholine-Induced Relaxation and Hyperpolarization in Small Bovine Adrenal Cortical Arteries: Role of Cytochrome P450 Metabolites. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4532–4539. [Google Scholar]
- Czambel, R.K.; Kharlamov, A.; Jones, S.C. Variations of brain endothelial nitric oxide synthase concentration in rat and mouse cortex. Nitric Oxide 2010, 22, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gooderham, M.H.; Adlercreutz, H.; Ojala, S.T.; Wähälä, K.; Holub, B.J. A soy protein isolate rich in genistein and daidzein and its effects on plasma isoflavone concentrations, platelet aggregation, blood lipids and fatty acid composition of plasma phospholipid in normal men. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, W.W.; Taylor, A.A.; Smith, E.O.; Barnes, S.; Hachey, D.L. Effect of soy isoflavone supplementation on nitric oxide metabolism and blood pressure in menopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, K. Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and Prevent Cardiovascular Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 74, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, C. Antihypertensive effect of soybean bioactive peptides: A review. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaventura, D.; Lunardi, C.N.; Rodrigues, G.J.; Neto, M.A.; Bendhack, L.M. A novel mechanism of vascular relaxation induced by sodium nitroprusside in the isolated rat aorta. Nitric Oxide 2008, 18, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grześk, E.; Stolarek, W.; Wiciński, M.; Szadujkis-Szadurska, K.; Malinowski, B.; Tejza, B.; Kołtan, S.; Gołębiewska, M.; Kołtan, A.; Grześk, G. Effect of acetylcholine on vascular smooth muscle contraction induced by phenylephrine, angiotensin II and mastoparan-7. Med. Res. J. 2014, 2, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yao, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Lou, G.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, S.; et al. Inhibition of eNOS by L-NAME resulting in rat hind limb developmental defects through PFKFB3 mediated angiogenetic pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16754. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.W.; Tovey, S.C. IP(3) receptors: Toward understanding their activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a004010. [Google Scholar]
- Piamsiri, C.; Fefelova, N.; Pamarthi, S.H.; Gwathmey, J.K.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N.; Xie, L.-H. Potential Roles of IP3 Receptors and Calcium in Programmed Cell Death and Implications in Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkban, T.; Boonprom, P.; Bunbupha, S.; Welbat, J.U.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Pakdeechote, P.; Prachaney, P. Ellagic Acid Prevents L-NAME-Induced Hypertension via Restoration of eNOS and p47phox Expression in Rats. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5265–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.; Goto, K.; Chaston, D.J.; Brackenbury, T.D.; Meaney, K.R.; Falck, J.R.; Wojcikiewicz, R.J.; Hill, C.E. Enalapril treatment alters the contribution of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids but not gap junctions to endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor activity in mesenteric arteries of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, E.B.; García-Garibay, M.; Díaz-Ramírez, M.; Cruz Monterrosa, R.; Ruiz-Hernández, R.; Pérez-Ruiz, R.; Jimenez-Guzman, J. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity from bovine serum albumin protein fractions. Agro Product. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Mostaghim, R.; Ramwell, P.W. Albumin does not inhibit endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 138, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keaney, J.; Simon, D.; Stamler, J.; Jaraki, O.; Scharfstein, J.; Vita, J.; Loscalzo, J. NO forms an adduct with serum albumin that has endothelium-derived relaxing factor-like properties. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stamler, J.S.; Simon, D.I.; Osborne, J.A.; Mullins, M.E.; Jaraki, O.; Michel, T.; Singel, D.J.; Loscalzo, J. S-nitrosylation of proteins with nitric oxide: Synthesis and characterization of biologically active compounds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 444–448. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, W.L.; Formanuik, N.L.; Harnpanich, D.; Cheung, M.; Talbot, D.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Sanders, T.A.B. A Meal Enriched with Soy Isoflavones Increases Nitric Oxide-Mediated Vasodilation in Healthy Postmenopausal Women12. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Liu, D. Genistein, a soy phytoestrogen, upregulates the expression of human endothelial nitric oxide synthase and lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Sangiorgio, S.; Vidović, N.; Boschin, G.; Aiello, G.; Arcidiaco, P.; Arnoldi, A.; Morelli, C.F.; Rabuffetti, M.; Recca, T.; Scarabattoli, L.; et al. Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Stability of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptide from Soybean Protein. Foods 2022, 11, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-T.; Cai, Q.-L.; Gu, Z.-Y.; Song, T.-Y. Novel ACE-inhibiting peptides from soybean protein hydrolysates by peptidomics combined with in silico analysis and their inhibitory effects on proliferation and migration of Ang II-induced VSMCs. Food Med. Homol. 2024, 1, 9420023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J. Small Peptides Isolated from Enzymatic Hydrolyzate of Fermented Soybean Meal Promote Endothelium-Independent Vasorelaxation and ACE Inhibition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10844–10850. [Google Scholar]
- Kalita, C.; Mehta, U.; Aayush, K.; Sawant, P.; Chavan, P.; Rasane, P.; Sharma, S.; Singh, G.P.; Nawghare, G.K.; Dhruv; et al. Recent trends in antioxidative peptides derived from soybean and other soy-based products: A comprehensive review. Process Biochem. 2024, 136, 311–323. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Liao, W.; Bai, J.; Wu, W.; Wu, J. Soy protein-derived ACE-inhibitory peptide LSW (Leu-Ser-Trp) shows anti-inflammatory activity on vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 34, 248–253. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tocharus, C.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Foods 2025, 14, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071256
Tocharus C, Sutheerawattananonda M. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071256
Chicago/Turabian StyleTocharus, Chainarong, and Manote Sutheerawattananonda. 2025. "Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats" Foods 14, no. 7: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071256
APA StyleTocharus, C., & Sutheerawattananonda, M. (2025). Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Foods, 14(7), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071256




