Evidencing the Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Lockdown Measures on Fitness Status in Adolescents: A Preliminary Report
Abstract
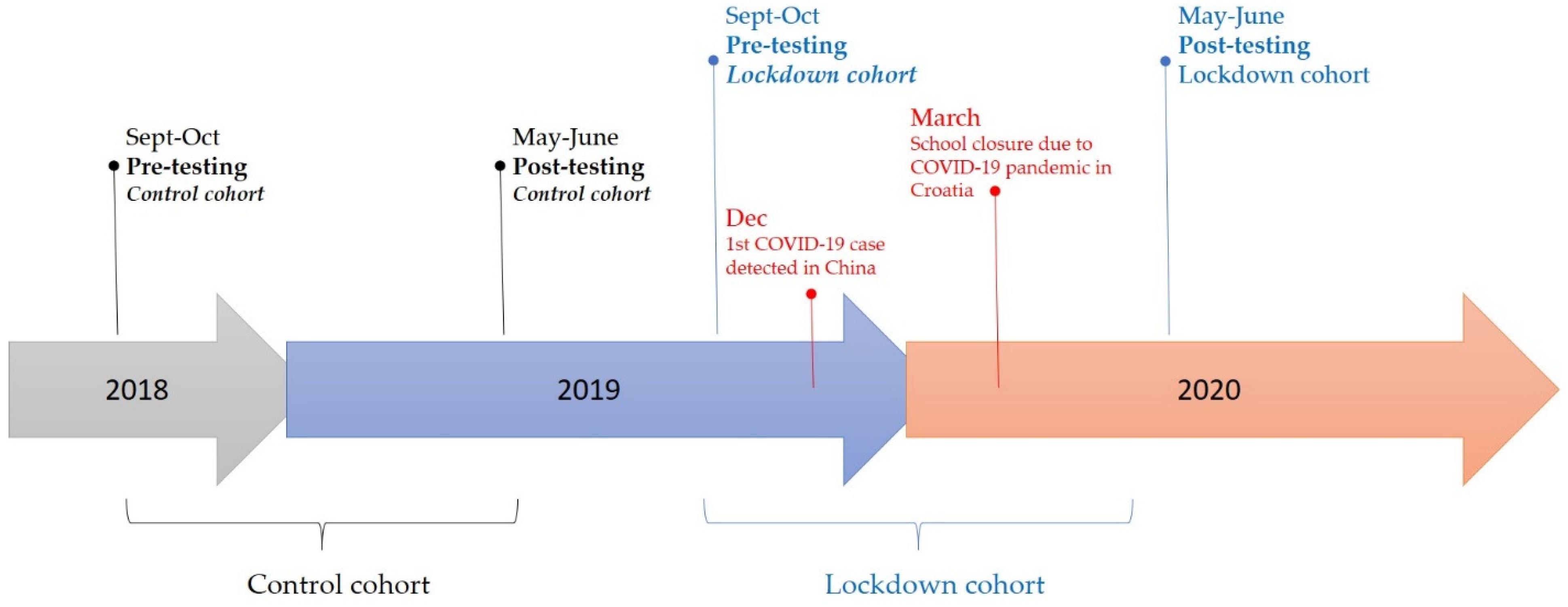
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Variables
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, J.; Enria, D.; Giesecke, J.; Heymann, D.L.; Ihekweazu, C.; Kobinger, G.; Lane, H.C.; Memish, Z.; Oh, M.D.; Sall, A.A.; et al. COVID-19: Towards controlling of a pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, E.L.; Reichert, F.F. Studies of Physical Activity and COVID-19 During the Pandemic: A Scoping Review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustino, V.; Parroco, A.M.; Gennaro, A.; Musumeci, G.; Palma, A.; Battaglia, G. Physical Activity Levels and Related Energy Expenditure during COVID-19 Quarantine among the Sicilian Active Population: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Cooper, J.; McHale, F.; Clifford, J.; Woods, C. Barriers and facilitators to changes in adolescent physical activity during COVID-19. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Larrad, A.; Mañas, A.; Labayen, I.; González-Gross, M.; Espin, A.; Aznar, S.; Serrano-Sánchez, J.A.; Vera-Garcia, F.J.; González-Lamuño, D.; Ara, I.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 Confinement on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in Spanish University Students: Role of Gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, L.A.; Gallo, T.F.; Young, S.L.; Moritz, K.M.; Akison, L.K. The Impact of Isolation Measures Due to COVID-19 on Energy Intake and Physical Activity Levels in Australian University Students. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe, S.; Sperandei, S.; Freebairn, L.; Conroy, E.; Jani, H.; Marjanovic, S.; Page, A. The Impact of Physical Distancing Policies During the COVID-19 Pandemic on Health and Well-Being Among Australian Adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 67, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.A.; Faulkner, G.; Rhodes, R.E.; Brussoni, M.; Chulak-Bozzer, T.; Ferguson, L.J.; Mitra, R.; O’Reilly, N.; Spence, J.C.; Vanderloo, L.M.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 virus outbreak on movement and play behaviours of Canadian children and youth: A national survey. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bueno, R.; López-Sánchez, G.F.; Casajús, J.A.; Calatayud, J.; Gil-Salmerón, A.; Grabovac, I.; Tully, M.A.; Smith, L. Health-Related Behaviors Among School-Aged Children and Adolescents During the Spanish Covid-19 Confinement. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.C.E.; Anedda, B.; Burchartz, A.; Eichsteller, A.; Kolb, S.; Nigg, C.; Niessner, C.; Oriwol, D.; Worth, A.; Woll, A. Physical activity and screen time of children and adolescents before and during the COVID-19 lockdown in Germany: A natural experiment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilic, B.; Zenic, N.; Separovic, V.; Jurcev Savicevic, A.; Sekulic, D. Evidencing the influence of pre-pandemic sports participation and substance misuse on physical activity during the COVID-19 lockdown: A prospective analysis among older adolescents. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuc, J.; Sorić, M.; Radman, I.; Mišigoj-Duraković, M. Moderators of Change in Physical Activity Levels during Restrictions Due to COVID-19 Pandemic in Young Urban Adults. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulic, D.; Blazevic, M.; Gilic, B.; Kvesic, I.; Zenic, N. Prospective Analysis of Levels and Correlates of Physical Activity During COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Rules of Social Distancing; Gender Specific Study Among Adolescents from Southern Croatia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenic, N.; Taiar, R.; Gilic, B.; Blazevic, M.; Maric, D.; Pojskic, H.; Sekulic, D. Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilic, B.; Ostojic, L.; Corluka, M.; Volaric, T.; Sekulic, D. Contextualizing Parental/Familial Influence on Physical Activity in Adolescents before and during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Prospective Analysis. Children 2020, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo-Garzón, M.J.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B.; Gutiérrez, A. Anti-aging therapy through fitness enhancement. Clin. Interv. Aging 2006, 1, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M. Physical activity and fitness: Pathways from childhood to adulthood. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2001, 13, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, K.F.; Dawson, J.D.; Mahoney, L.T. Increases in physical fitness during childhood improve cardiovascular health during adolescence: The Muscatine Study. Int. J. Sports Med. 2002, 23, S15–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Jiang, Y. The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Physical Fitness among Chinese University Students: Results of a Longitudinal Study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júdice, P.B.; Silva, A.M.; Berria, J.; Petroski, E.L.; Ekelund, U.; Sardinha, L.B. Sedentary patterns, physical activity and health-related physical fitness in youth: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seljebotn, P.H.; Skage, I.; Riskedal, A.; Olsen, M.; Kvalø, S.E.; Dyrstad, S.M. Physically active academic lessons and effect on physical activity and aerobic fitness. The Active School study: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Prev. Med. Rep. 2019, 13, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Song, H.H.; Kim, S. Effects of School-Based Exercise Program on Obesity and Physical Fitness of Urban Youth: A Quasi-Experiment. Healthcare 2021, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, C.S.; Caria, A.C.I.; Aras Júnior, R.; Pitanga, F.J.G. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on levels of physical fitness. Rev. Assoc. Méd. Bras. 2020, 66, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.A.; Hutchinson, N.T.; Powers, S.K.; Roberts, W.O.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Radak, Z.; Berkes, I.; Boros, A.; Boldogh, I.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; et al. The COVID-19 pandemic and physical activity. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2020, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigilis, N.; Douda, H.; Tokmakidis, S.P. Test-Retest Reliability of the Eurofit Test Battery Administered to University Students. Percept. Motor Skills 2002, 95, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neljak, B.; Novak, D.; Sporis, G.; Viskovic, S.; Markus, D. Metodologija Vrednovanja Kinantropoloskih Obiljezja Ucenika u Tjelesnoj i Zdravstvenoj Kulturi (Methodology of Evaluating the Kinantropological Characteristics of Students in Physical Education: CROFIT Norms); Crofit Norme; Kinezioloski Fakultet: Zagreb, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bakeman, R. Recommended effect size statistics for repeated measures designs. Behav. Res. Methods 2005, 37, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.; Brach, M.; Trabelsi, K.; Chtourou, H.; Boukhris, O.; Masmoudi, L.; Bouaziz, B.; Bentlage, E.; How, D.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Effects of COVID-19 Home Confinement on Eating Behaviour and Physical Activity: Results of the ECLB-COVID19 International Online Survey. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Iemitsu, M. Exercise and sex steroid hormones in skeletal muscle. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hymer, W.C.; Nindl, B.C.; Fragala, M.S. Growth Hormone(s), Testosterone, Insulin-Like Growth Factors, and Cortisol: Roles and Integration for Cellular Development and Growth with Exercise. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.M.; Jones, D.A.; Honour, J.W.; Nevill, A.M. Hormonal factors in the development of differences in strength between boys and girls during adolescence: A longitudinal study. Ann. Human Biol. 1999, 26, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyenhuis, S.M.; Greiwe, J.; Zeiger, J.S.; Nanda, A.; Cooke, A. Exercise and Fitness in the Age of Social Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2152–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogol, A.D.; Roemmich, J.N.; Clark, P.A. Growth at puberty. J. Adolesc. Health 2002, 31, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pišot, S.; Milovanović, I.; Šimunič, B.; Gentile, A.; Bosnar, K.; Prot, F.; Bianco, A.; Lo Coco, G.; Bartoluci, S.; Katović, D.; et al. Maintaining everyday life praxis in the time of COVID-19 pandemic measures (ELP-COVID-19 survey). Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 30, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Group (Lockdown vs. Control) | Measurement (Pre- vs. Post) | Interaction (Cohort x× Measurement) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Test | p | ES | F Test | p | ES | F Test | p | ES | |
| Body height | 0.22 | 0.64 | 0.001 | 3.27 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 4.35 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Body mass | 0.12 | 0.73 | 0.001 | 4.37 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.001 |
| Body mass index | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.002 | 0.16 | 0.69 | 0.001 | 0.91 | 0.34 | 0.001 |
| Sit-ups | 2.39 | 0.13 | 0.001 | 0.35 | 0.55 | 0.001 | 67.11 | 0.001 | 0.38 |
| Run-600 m | 0.08 | 0.77 | 0.001 | 40.68 | 0.001 | 0.28 | 61.97 | 0.001 | 0.37 |
| Variables | Baseline | Follow-up | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Lockdown | Control | Lockdown | |
| Body height (cm) | 173.67 ± 9.58 | 173.14 ± 8.68 | 174.19 ± 9.66 | 173.27 ± 8.53 |
| Body mass (kg) | 64.69 ± 15.46 | 64.16 ± 12.15 | 65.99 ± 15.06 | 64.91 ± 12.16 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.16 ± 3.73 | 22.44 ± 10.71 | 21.68 ± 3.81 | 21.53 ± 2.95 |
| Sit-ups (rep) | 36.52 ± 6.65 | 42.83 ± 11.33 ¥ | 44.04 ± 9.73 £ | 33.89 ± 7.59 £, ¥ |
| Run-600 m (s) | 173.18 ± 48.16 | 148.24 ± 21.38 ¥ | 168.78 ± 34.16 | 191.44 ± 36.38 £, ¥ |
| Variables | Group (Males vs. Females) | Measurement (Pre- vs. Post) | Interaction (Group × Measurement) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Test | p | ES | F Test | p | ES | F Test | p | ES | |
| Body height | 83.02 | 0.001 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.96 | 0.001 |
| Body mass | 12.22 | 0.001 | 0.16 | 4.23 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 8.05 | 0.01 | 0.11 |
| Body mass index | 0.18 | 0.67 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.28 | 0.02 |
| Sit-ups | 16.05 | 0.001 | 0.21 | 45.44 | 0.001 | 0.43 | 11.08 | 0.01 | 0.15 |
| Run-600 m | 12.58 | 0.001 | 0.18 | 105.11 | 0.001 | 0.64 | 1.83 | 0.18 | 0.03 |
| Variables | Baseline | Follow-up | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | |
| Body height (cm) | 182.75 ± 5.38 | 168.87 ± 6.04 | 182.76 ± 4.94 | 168.84 ± 5.77 |
| Body mass (kg) | 70.10 ± 11.84 | 61.52 ± 11.46 | 73.19 ± 9.78 | 61.04 ± 11.46 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.01 ± 3.31 | 23.08 ± 12.68 | 21.94 ± 2.64 | 21.34 ± 12.68 |
| Sit-ups (rep) | 51.25 ± 14.60 | 39.00 ± 6.76 ¥ | 35.33 ± 8.06 £ | 33.22 ± 6.76 £ |
| Run-600 m (s) | 129.17 ± 20.65 | 156.42 ± 15.91 | 179.41 ± 42.40 | 197.06 ± 15.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunda, M.; Gilic, B.; Peric, I.; Jurcev Savicevic, A.; Sekulic, D. Evidencing the Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Lockdown Measures on Fitness Status in Adolescents: A Preliminary Report. Healthcare 2021, 9, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060681
Sunda M, Gilic B, Peric I, Jurcev Savicevic A, Sekulic D. Evidencing the Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Lockdown Measures on Fitness Status in Adolescents: A Preliminary Report. Healthcare. 2021; 9(6):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060681
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunda, Mirela, Barbara Gilic, Ivan Peric, Anamarija Jurcev Savicevic, and Damir Sekulic. 2021. "Evidencing the Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Lockdown Measures on Fitness Status in Adolescents: A Preliminary Report" Healthcare 9, no. 6: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060681
APA StyleSunda, M., Gilic, B., Peric, I., Jurcev Savicevic, A., & Sekulic, D. (2021). Evidencing the Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Lockdown Measures on Fitness Status in Adolescents: A Preliminary Report. Healthcare, 9(6), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060681









