Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers
Abstract
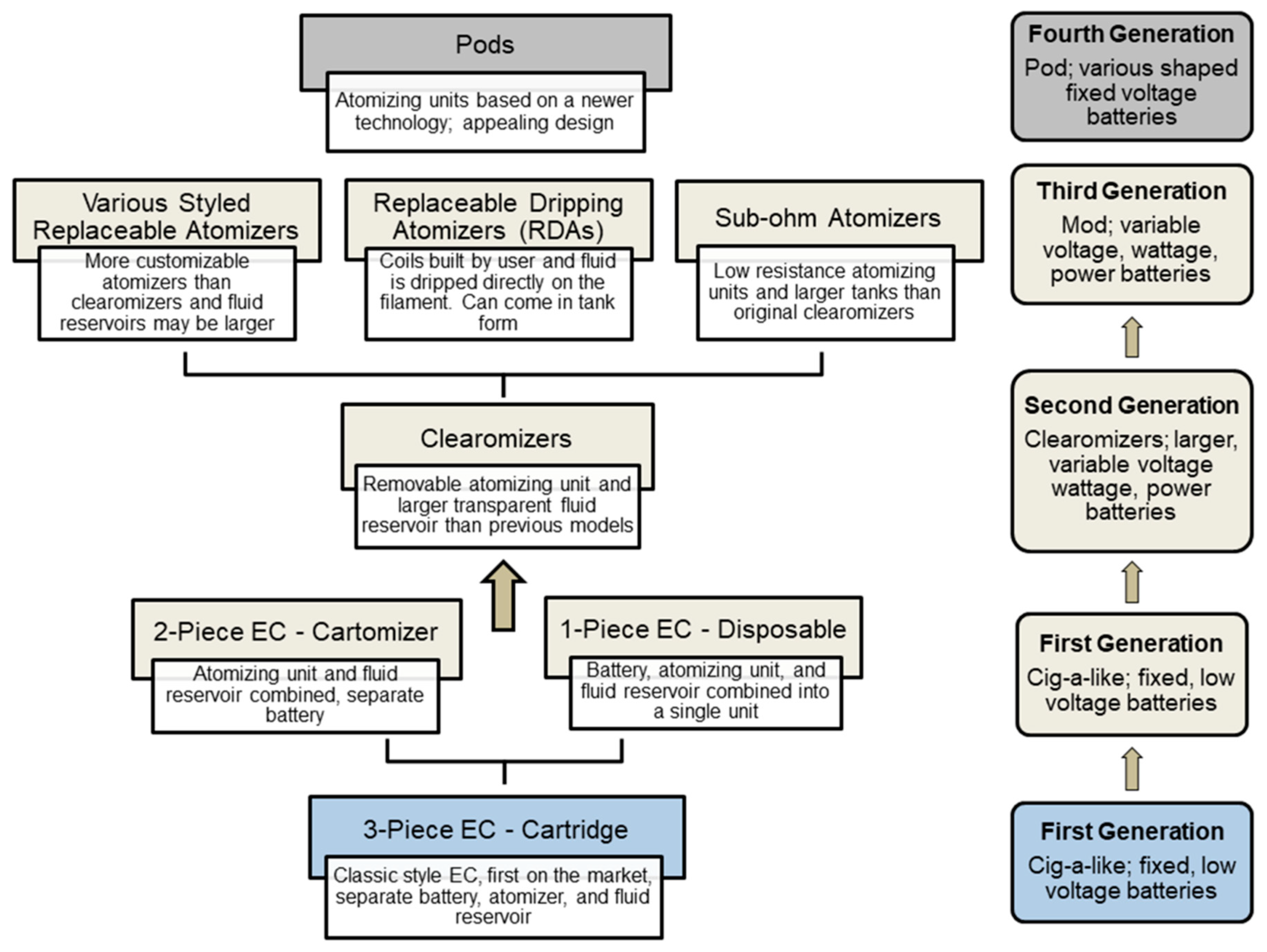
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electronic Cigarette Selection
2.2. Dissections of EC Atomizer Components
3. Results
3.1. Design and Anatomy of Cig-a-Like Style ECs
3.2. Evaluation of Atomizing Unit Design across Cartomizer Generations
3.3. Design and Anatomy of Second Generation Clearomizer and Third Generation Mod-Style ECs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banga, B. Global E-Cigarette and T-Vapor Market to Reach $86.43 Billion by 2025, Reports BIS Research. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-e-cigarette-and-t-vapor-market-to-reach-8643-billion-by-2025-reports-bis-research-675808803.html (accessed on 7 February 2019).
- Breland, A.; Soule, E.; Lopez, A.; Ram, C.; El-hellani, A.; Eissenberg, T. Electronic cigarettes: What are they and what do they do? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1394, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T. 4 Facts You Need to Know About E-Cigarettes. Available online: https://www.verywellmind.com/facts-about-e-cigarettes-2825261 (accessed on 23 January 2019).
- Stratton, K.; Kwan, L.Y.; Eaton, D.L.; Health, P.; Practice, P.H.; Division, M. Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-309-46834-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, S.; Agnihotri, R. Health Effects of Trace Metals in Electronic Cigarette Aerosols—A Systematic Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 188, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peace, M.R.; Mulder, H.A.; Baird, T.R.; Butler, K.E. Evaluation of Nicotine and the Components of e-Liquids Generated from e-Cigarette Aerosols. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, M.; Bozhilov, K.; Ghai, S.; Talbot, P. Elements including metals in the atomizer and aerosol of disposable electronic cigarettes and electronic hookahs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.P.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F.; Strongin, R.M.; Peyton, D. Hidden Formaldehyde in E-Cigarette Aerosols. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talih, S.; Balhas, Z.; Eissenberg, T.; Salman, R.; Karaoghlanian, N.; Hellani, A.E.; Baalbaki, R.; Saliba, N.; Shihadeh, A. Effects of user puff topography, device voltage, and liquid nicotine concentration on electronic cigarette nicotine yield: Measurements and model predictions. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2015, 17, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talih, S.; Balhas, Z.; Salman, R.; Karaoghlanian, N.; Shihadeh, A. “Direct dripping”: A high-temperature, high- formaldehyde emission electronic cigarette use method. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2016, 18, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, V.; Lin, S.; Xu, N.; Davis, B.; Wang, Y.; Talbot, P. Comparison of electronic cigarette refill fluid cytotoxicity using embryonic and adult models. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behar, R.Z.; Davis, B.; Wang, Y.; Bahl, V.; Lin, S.; Talbot, P. Toxicology in Vitro Identification of toxicants in cinnamon-flavored electronic cigarette refill fluids. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, R.Z.; Luo, W.; McWhirter, K.J.; Pankow, J.F.; Talbot, P. Analytical and toxicological evaluation of flavor chemicals in electronic cigarette refill fluids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behar, R.Z.; Wang, Y.; Talbot, P. Comparing the cytotoxicity of electronic cigarette fluids, aerosols and solvents. Tob. Control 2017, 27, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, P.W.; Pawlak, E.A.; Lackey, J.T.; Keating, J.E.; Reeber, S.L.; Glish, G.L.; Jaspers, I. Flavored e-cigarette liquids and cinnamaldehyde impair respiratory innate immune cell function. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L278–L292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, I.G.; Kistler, K.A.; Stewart, E.W.; Paolantonio, A.R. Effect of variable power levels on the yield of total aerosol mass and formation of aldehydes in e-cigarette aerosols. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 75, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farsalinos, K.E.; Spyrou, A.; Tsimopoulou, K.; Stefopoulos, C.; Romagna, G.; Voudris, V. Nicotine absorption from electronic cigarette use: Comparison between first and new-generation devices. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, R.Z.; Hua, M.; Talbot, P. Puffing Topography and Nicotine Intake of Electronic Cigarette Users. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.J.; Hensel, E.C.; Morabito, P.N.; Roundtree, K.A. Electronic Cigarette Topography in the Natural Environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; To, A.; Bozhilov, K.; Talbot, P. Strategies to Reduce Tin and Other Metals in Electronic Cigarette Aerosol. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Bozhilov, K.N.; Talbot, P. Analysis of the elements and metals in multiple generations of electronic cigarette atomizers. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrell, P.T.; Eissenberg, T. Automated dripping devices for vapers: RDTAs, bottomfeeders, squonk mods and dripboxes. Tob. Control 2018, 27, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protano, C.; Avino, P.; Manigrasso, M.; Vivaldi, V.; Perna, F.; Valeriani, F.; Vitali, M. Environmental Electronic Vape Exposure from Four Different Generations of Electronic Cigarettes: Airborne Particulate Matter Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Duan, Z.; Kwok, J.; Binns, S.; Vera, L.E.; Kim, Y.; Szczypka, G.; Emery, S.L. Vaping versus JUULing: How the extraordinary growth and marketing of JUUL transformed the US retail e-cigarette market. Tob. Control 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trtchounian, A.; Talbot, P. Electronic nicotine delivery systems: Is there a need for regulation? Tob. Control 2011, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Ghai, S.; Talbot, P. Disposable Electronic Cigarettes and Electronic Hookahs: Evaluation of Performance. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grana, R.; Benowitz, N.; Glantz, S. A E-cigarettes: A scientific review. Circulation 2014, 129, 1972–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Omaiye, E.; Luo, W.; McWhirter, K.; Pankow, J.F.; Talbot, P. Identification of Cytotoxic Flavor Chemicals in Top-Selling Electronic Cigarette Refill Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Disposable Electronic Cigarette. US Patent 2014/0311506 A1, 21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grana, R.; Benowitz, N.L.; Glantz, S. A Background Paper on E-Cigarettes (Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems); World Health Organization Tobacco Free Initiative: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/13p2b72n (accessed on 19 April 2019).
- Hess, C.A.; Olmedo, P.; Navas-Acien, A.; Goessler, W.; Cohen, J.E.; Rule, A.M. E-cigarettes as a source of toxic and potentially carcinogenic metals. Environ. Res. 2017, 152, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, P.; Goessler, W.; Tanda, S.; Grau-Perez, M.; Jarmul, S.; Aherrera, A.; Chen, R.; Hilpert, M.; Cohen, J.E.; Navas-Acien, A.; et al. Metal Concentrations in e-Cigarette Liquid and Aerosol Samples: The Contribution of Metallic Coils. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 027010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L. The Basics of Vaping—Types of E-Cig Atomizers and Vape Tanks. Available online: https://ecigarettereviewed.com/types-of-atomizer (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- Omaiye, E.E.; Mcwhirter, K.J.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F.; Talbot, P. High-Nicotine Electronic Cigarette Products: Toxicity of JUUL Fluids and Aerosols Correlates Strongly with Nicotine and Some Flavor Chemical Concentrations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavuluru, R.; Han, S.; Hahn, E.J. On the popularity of the USB flash drive-shaped electronic cigarette Juul. Tob. Control 2019, 28, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Villarreal, A.; Bozhilov, K.; Lin, S.; Talbot, P. Metal and silicate particles including nanoparticles are present in electronic cigarette cartomizer fluid and aerosol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Talbot, P. Variability among electronic cigarettes in the pressure drop, airflow rate, and aerosol production. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2011, 13, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Villarreal, A.; Davis, B.; Talbot, P. Comparison of the performance of cartomizer style electronic cigarettes from major tobacco and independent manufacturers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Knysak, J.; Gawron, M.; Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Kurek, J.; Prokopowicz, A.; Jablonska-Czapla, M.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Havel, C.; et al. Levels of selected carcinogens and toxicants in vapour from electronic cigarettes. Tob. Control 2014, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyarah, R.; Long, G.A. Comparison of select analytes in aerosol from e-cigarettes with smoke from conventional cigarettes and with ambient air. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Kuma, T.; Gawron, M.; Knysak, J.; Kosmider, L. Nicotine levels in electronic cigarettes. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2013, 15, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Helen, G.; Ross, K.; Dempsey, D.; Havel, C.; Jacob, P., III; Benowitz, N.L. Nicotine Delivery and Vaping Behavior During ad Libitum E- cigarette Access Gideon. Tob. Regul. Sci. 2016, 2, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, P.; Przulj, D.; Phillips, A.; Anderson, R.; Mcrobbie, H. Nicotine delivery to users from cigarettes and from different types of e-cigarettes. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2017, 234, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnan-sarin, S.; Morean, M.; Kong, G.; Bold, K.W. E-Cigarettes and “Dripping” Among High-School Youth NIH. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poklis, J.L.; Mulder, H.A.; Halquist, M.S.; Wolf, C.E.; Poklis, A.; Peace, M.R. The Blue Lotus Flower (Nymphea caerulea) Resin Used in a New Type of Electronic Cigarette, the Re-Buildable Dripping Atomizer. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2018, 49, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Llados, F.; Diamond, G.; Chappell, L.L. Toxicological Profile for Tin and Tin Compounds; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005; p. 302.
- Abadin, H.; Ashizawa, A.; Stevens, Y.-W.; Llados, F.; Diamond, G.; Sage, G.; Citra, M.; Quinones, A.; Bosch, S.J.; Swarts, S.G. Toxicological Profile for Lead; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007.
- Dunworth, J. Electronic Cigarette Batteries: The Ultimate Beginners Guide. Available online: https://www.ecigarettedirect.co.uk/ashtray-blog/2014/04/electronic-cigarette-batteries-guide.html#comments (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Fik, M.; Knysak, J.; Zaciera, M.; Kurek, J.; Goniewicz, M.L. Carbonyl compounds in electronic cigarette vapors: Effects of nicotine solvent and battery output voltage. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 16, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, P.A.; Karpinski, C.D.; Brown, J.E.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F. Flavour chemicals in electronic cigarette fluids. Tob. Control 2016, 25, e10–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlet, V.; Farsalinos, K.; Augsburger, M.; Thomas, A.; Etter, J.F. Toxicity assessment of refill liquids for electronic cigarettes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4796–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, M.; Talbot, P. Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904
Williams M, Talbot P. Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(16):2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Monique, and Prue Talbot. 2019. "Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 16: 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904
APA StyleWilliams, M., & Talbot, P. (2019). Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(16), 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904




