Lack of Correlation between Accelerometers and Heart-Rate Monitorization during Exercise Session in Older Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Instruments
2.3.1. Heart-Rate Monitoring
2.3.2. Accelerometers
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
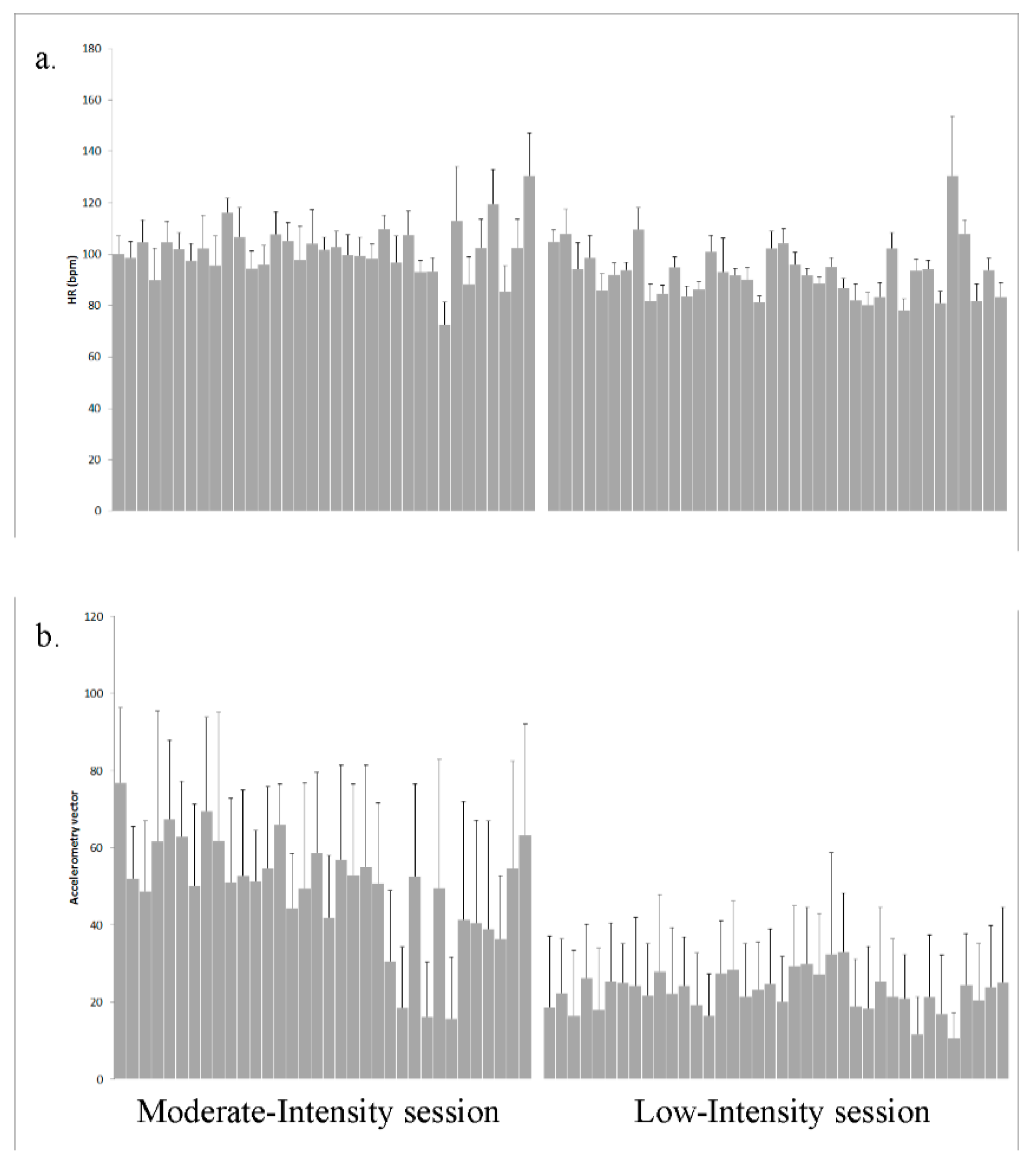
3.1. Heart Rate and Accelerometry Correlations in Different Sessions
3.2. Heart Rate and Energy Expenditure Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Fehlings, M.G.; Tetreault, L.; Nater, A.; Choma, T.; Harrop, J.; Mroz, T.; Santaguida, C.; Smith, J.S. The aging of the global population: The changing epidemiology of disease and spinal disorders. Neurosurgery 2015, 77, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.R.; Scheuerlein, A.; Salguero-Gomez, R.; Camarda, C.G.; Schaible, R.; Casper, B.B.; Dahlgren, J.P.; Ehrlen, J.; Garcia, M.B.; Menges, E.S.; et al. Diversity of ageing across the tree of life. Nature 2014, 505, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.C.; Yeo, S.G. Aging. Korean J. Audiol. 2013, 17, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontology Ser. Abiological Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souto Barreto, P. Time to challenge public health guidelines on physical activity. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, W.; Struder, H.K.; Tagarakis, C.V.; King, G. Physical activity and the elderly. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2007, 14, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.N.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.R.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1510–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P.; American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, G.; Blazevich, A.J.; Boreham, C.; Cooper, A.R.; Crank, H.; Ekelund, U.; Fox, K.R.; Gately, P.; Giles-Corti, B.; Gill, J.M.; et al. The ABC of physical activity for health: A consensus statement from the British Association of Sport and Exercise Sciences. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borresen, J.; Lambert, M.I. The quantification of training load, the training response and the effect on performance. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, T.W.; Roberts, M.D.; Church, T.S. Toward exercise as personalized medicine. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorman, E.; Hanson, H.M.; Yang, P.H.; Khan, K.M.; Liu-Ambrose, T.; Ashe, M.C. Accelerometry analysis of physical activity and sedentary behavior in older adults: A systematic review and data analysis. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. Off. J. Eur. Group Res. Into Elder Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.J.; Fan, X.; Moe, S.T. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: A meta-analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2002, 20, 873–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Carrillo, V.; Sierra, V.; Jimenez-Loaisa, A.; Gonzalez-Cutre, D.; Martinez-Galindo, C.; Cervello, E. Diferencias según género en el tiempo empleado por adolescentes en actividad sedentaria y actividad física en diferentes segmentos horarios del día. [Gender differences in time spent by adolescents in sedentary and physical activity in different day segments]. Retos: Nuevas Tend. En Educ. Físicadeporte Y Recreación 2017, 31, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Evenson, K.R.; Wen, F.; Herring, A.H. Associations of accelerometry-assessed and self-reported physical activity and sedentary behavior with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among US adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 184, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, M.P.; Chui, K.K.; White, D.K.; Reid, K.F.; Kirn, D.; Nelson, M.E.; Sacheck, J.M.; Folta, S.C.; Fielding, R.A. Accelerometer assessment of physical activity and its association with physical function in older adults residing at assisted care facilities. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.P.; Fairclough, S.J.; Savory, L.A.; Denton, S.J.; Pang, D.; Deane, C.S.; Kerr, C.J. Accelerometry-assessed sedentary behaviour and physical activity levels during the segmented school day in 10–14-year-old children: The HAPPY study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calahorro Canada, F.; Torres-Luque, G.; Lopez Fernandez, I.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Garatachea, N.; Alvarez Carnero, E. Physical activity and accelerometer; methodological training, recommendations and movement patterns in school. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 31, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, S.J.; Beighle, A.; Erwin, H.; Ridgers, N.D. School day segmented physical activity patterns of high and low active children. BMC Pub. Health 2012, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laguna, M.; Ruiz, J.R.; Gallardo, C.; Garcia-Pastor, T.; Lara, M.T.; Aznar, S. Obesity and physical activity patterns in children and adolescents. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2013, 49, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos-Lozano, A.; Santin-Medeiros, F.; Cardon, G.; Torres-Luque, G.; Bailon, R.; Bergmeir, C.; Ruiz, J.R.; Lucia, A.; Garatachea, N. Actigraph GT3X: Validation and determination of physical activity intensity cut points. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaka, M. A Guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Schrack, J.A.; Leroux, A.; Fleg, J.L.; Zipunnikov, V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Studenski, S.A.; Crainiceanu, C.; Ferrucci, L. Using heart rate and accelerometry to define quantity and intensity of physical activity in older adults. J. Gerontology Ser. Abiological Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar-Farias, N.; Peeters, G.; Brychta, R.J.; Chen, K.Y.; Brown, W.J. Comparing ActiGraph equations for estimating energy expenditure in older adults. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
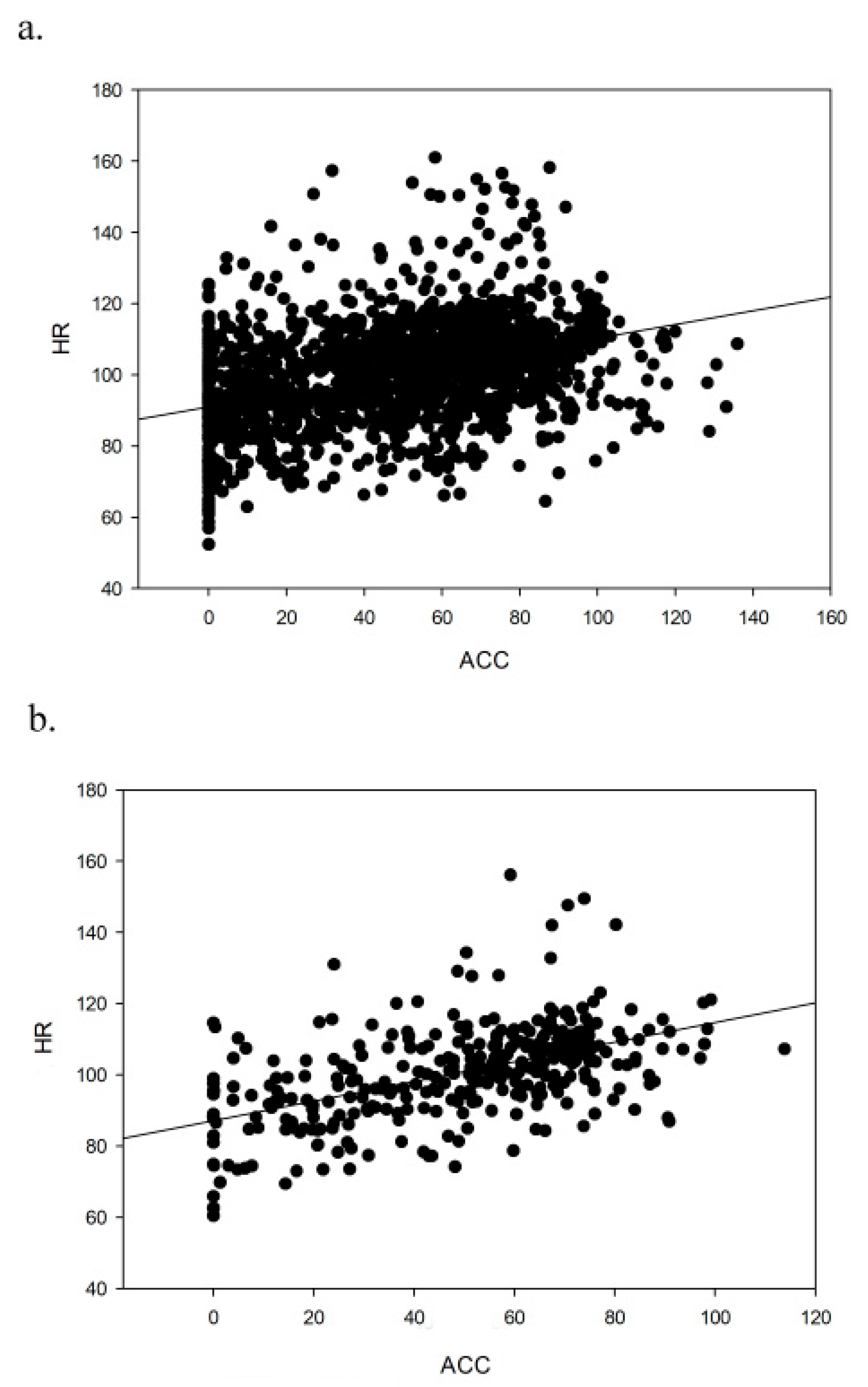
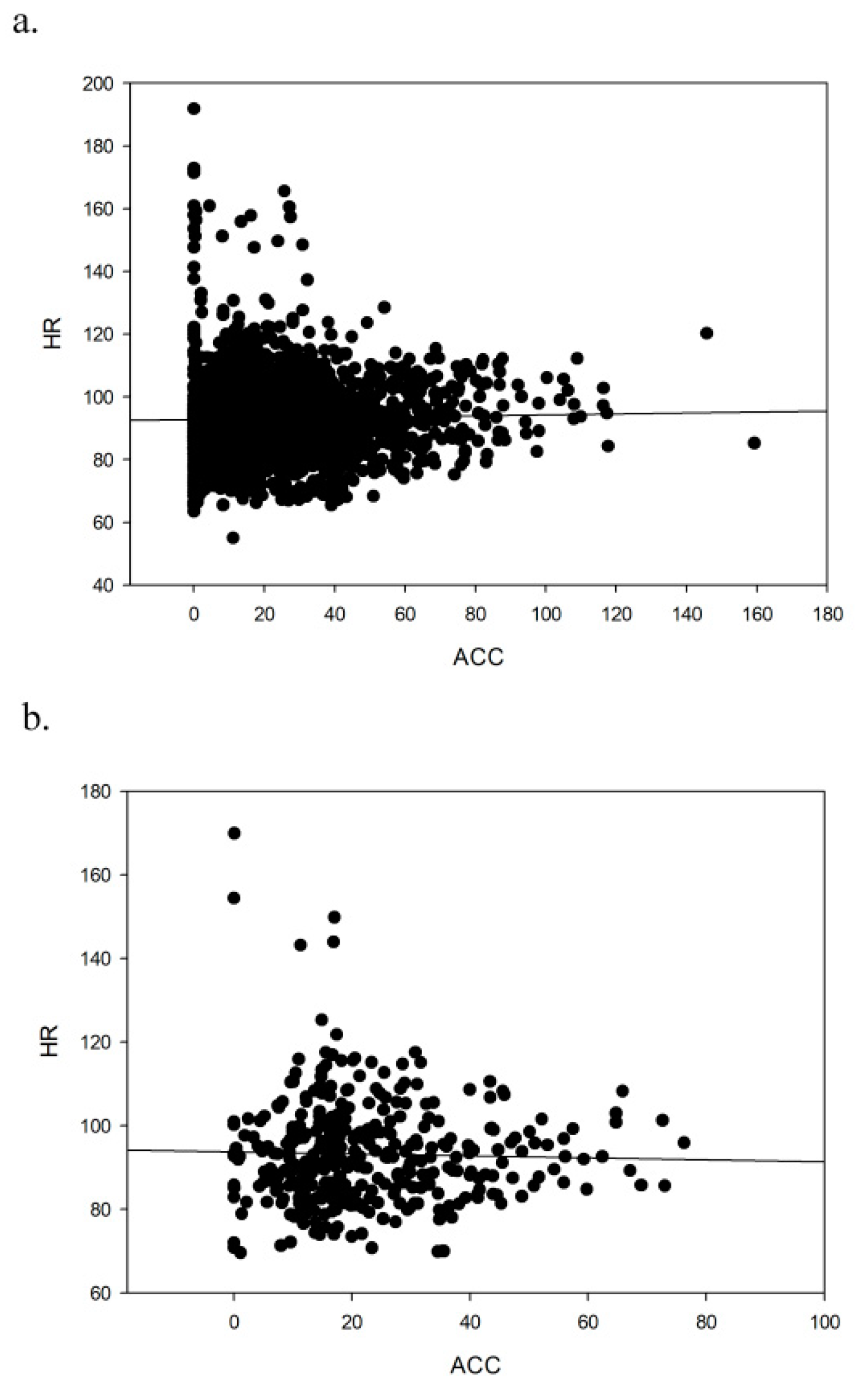
| Minute-by-Minute | 5-Minute Intervals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOD | LOW | MOD | LOW | |
| r | 0.407 | 0.024 | 0.519 | 0.106 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.297 | <0.001 | 0.583 |
| n | 1789 | 1891 | 343 | 357 |
| HR | <3 METs | 3–6 METs | 6+ METs |
|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.324 | 0.167 | 0.097 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.160 | 0.416 |
| n | 72 | 72 | 72 |
| HR | <3 METs | 3–6 METs | 6+ METs |
|---|---|---|---|
| r | 0.057 | −0.107 | 0.029 |
| p | 0.747 | 0.549 | 0.870 |
| n | 34 | 34 | 34 |
| HR | <3 METs | 3–6 METs | 6+ METs |
|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.497 | −0.089 | 0.018 |
| p | 0.002 | 0.592 | 0.911 |
| n | 38 | 38 | 38 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbonell-Hernández, L.; Pastor, D.; Jiménez-Loaisa, A.; Ballester-Ferrer, J.A.; Montero-Carretero, C.; Cervelló, E. Lack of Correlation between Accelerometers and Heart-Rate Monitorization during Exercise Session in Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155518
Carbonell-Hernández L, Pastor D, Jiménez-Loaisa A, Ballester-Ferrer JA, Montero-Carretero C, Cervelló E. Lack of Correlation between Accelerometers and Heart-Rate Monitorization during Exercise Session in Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(15):5518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155518
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbonell-Hernández, Laura, Diego Pastor, Alejandro Jiménez-Loaisa, Juan Arturo Ballester-Ferrer, Carlos Montero-Carretero, and Eduardo Cervelló. 2020. "Lack of Correlation between Accelerometers and Heart-Rate Monitorization during Exercise Session in Older Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 15: 5518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155518
APA StyleCarbonell-Hernández, L., Pastor, D., Jiménez-Loaisa, A., Ballester-Ferrer, J. A., Montero-Carretero, C., & Cervelló, E. (2020). Lack of Correlation between Accelerometers and Heart-Rate Monitorization during Exercise Session in Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(15), 5518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155518






