Chronic Facial Pain: Trigeminal Neuralgia, Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain, and Myofascial Pain Syndrome—An Evidence-Based Narrative Review and Etiological Hypothesis
Abstract
:1. Foreword
Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Discussion
3.1. Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias
Cluster Headache
3.2. Trigeminal Neuralgia
Diagnosis of Trigeminal Neuralgia
3.3. Management of Trigeminal Neuralgia
3.3.1. Pharmacologic Treatment
3.3.2. Botulinum Toxin Type A (BTxA)
3.3.3. Interventional Approaches
Percutaneous
Gamma Knife
Microvascular Decompression
3.4. Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain (PIFP)
3.4.1. Diagnosis of PIFP
3.4.2. Differential Diagnosis between PIFP and TN
3.4.3. Differential Diagnosis of Facial Pain
3.4.4. Treatment of PFIP
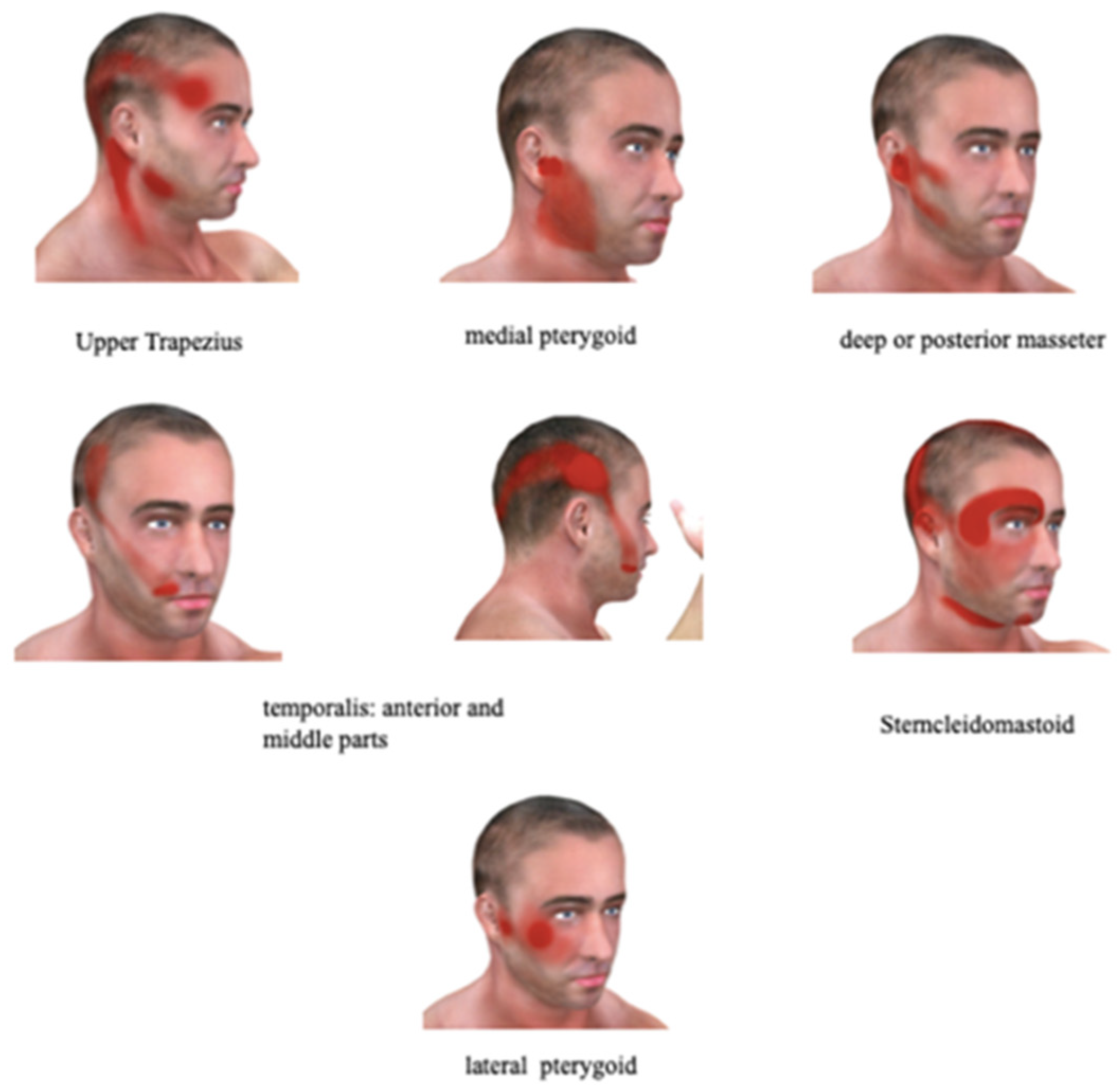
3.5. Myofascial Pain as a Potential Etiology of PIFP
Myofascial Pain Syndrome Definition and Diagnosis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarkson, E.; Jung, E. Atypical Facial Pain. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 64, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renton, T. Tooth-Related Pain or Not? Headache 2020, 60, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska, J.M.; Jensen, T.S. History of facial pain diagnosis. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegeler, C.; May, A. Facial presentations of migraine, TACs, and other paroxysmal facial pain syndromes. Neurology 2019, 93, e1138–e1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddaway, A.P.; Wood, A.M.; Hedges, L.V. How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-Syntheses. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 747–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.; Stovner, L.J. Epidemiology and comorbidity of headache. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- De Toledo, I.P.; Conti Réus, J.; Fernandes, M.; Porporatti, A.L.; Peres, M.A.; Takaschima, A.; Linhares, M.N.; Guerra, E.N.S.; Canto, G.D.L. Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2016, 147, 570–576.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burish, M. Cluster headache and other trigeminal autonomic cephalagias. Continuum 2018, 24, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, A.; Josefsson, P.; Alexanderson, K.; Sjöstrand, C. Cluster headache: Prevalence, sickness absence, and disability pension in working ages in Sweden. Neurology 2019, 93, e404–e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischera, M.; Marziniak, M.; Gralow, I.; Evers, S. The incidence and prevalence of cluster headache: A meta-analysis of population-based studies. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, A.; Andreou, A. Primary Headaches during lifespan. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bang, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Park, U.; Kim, T.K.; Choi, Y. Prevalence of common causes of neuropathic pain in Korea: Population-based observational study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519888102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buono, N.; Thulesius, H.; Petrazzuoli, F.; Castelli, E.; Cambielli, M. Postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and trigeminal neuralgia—Chronic peripheral neuropathic pain in 58,480 rural Italian primary care patients. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2017, 6, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tallawy, H.N.; Farghaly, W.M.; Rageh, T.A.; Shehata, G.A.; Badry, R.; Kandil, M.R. Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia in Al-Quseir city (Red sea Governorate), Egypt. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 1792–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 1907, Erratum in Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Fuh, J.L.; Wang, S.J. Increased risk of trigeminal neuralgia in patients with migraine: A nationwide population-based study. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, S.M.; Hekali, O.; Kurdo, G.; Martola, J.; Sairanen, T.; Atula, S. Trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis: Prevalence and association with demyelination. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 142, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, D.; Annovazzi, P.; Moccia, M.; Laanzillo, R.; De Luca, G.; Nociti, V.; Fantozzi, R.; Paolicelli, D.; Ragonese, P.; Gajofatto, A.; et al. Rising Researchers in Multiple Sclerosis. Characteristics and treat-ment of Multiple Sclerosis-related trigeminal neuralgia: An Italian multi-centre study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 37, 101461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, G.; Maarbjerg, S.; Truini, A. Trigeminal neuralgia secondary to multiple sclerosis: From the clinical picture to the treatment options. J. Headache Pain 2019, 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozhenko, M.; Bozhenko, N.; Nehrych, T. Features of trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 405, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, D.; Obermann, M.; Yoon, M.-S.; Poitz, F.; Hansen, N.; Slomke, M.A.; Dommes, P.; Gizeewski, E.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain: A population-based study. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, M. Recent advances in understanding/managing trigeminal neuralgia. F1000Resarch 2019, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.R.; Urits, I.; Ehrhardt, K.P.; Cefalu, J.N.; Kendrick, J.B.; Park, D.J.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D.; Viswanath, O. A Comprehensive Review of Trigeminal Neuralgia. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2019, 23, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.; Mortini, P.; Alemanno, F.; Houdayer, E.; Iannaccone, S. Trigeminal Neuralgia: Toward a Multimodal Approach. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, P.R.; Hermier, M.; Souza, M.A.; Cristino-Filho, G.; Froment, J.C.; Sindou, M. Visualization of vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve with high-resolution 3T MRI: A prospective study comparing preoperative imaging analysis to surgical findings in 40 consecutive patients who underwent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, A.X.; Nayar, V.V. Update on trigeminal neuralgia. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2019, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godazandeh, K.; Martinez Sosa, S.; Wu, J.; Zakrzewska, J.M. Trigeminal neuralgia: Comparison of characteristics and impact in patients with or without multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 34, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truini, A.; Prosperini, L.; Calistri, V.; Fiorelli, M.; Pozzilli, C.; Millefiorini, E.; Frontoni, M.; Cortese, A.; Caramia, F.; Cruccu, G. A dual concurrent mechanism explains trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2016, 86, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuboori, Z.; Nauta, H.J. Multiple recurrences of trigeminal neuralgia caused by deformation of the trigeminal nerve. Cureus 2019, 20, e6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amighi-Allisan, A.E.; Delman, B.N.; Yao AAlper, J.; Huang, K.H.; Bachandani, P.; Shrivastava, R.K. Neuroanatomical determinants of secondary trigeminal neuralgia: Applicaton of 7T ultra-high-field multimodal magnetic resonance imaging. World Neurosurg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohyama, S.; Hung, P.S.; Cheng, J.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Halawani, A.; Mikulis, D.J.; Oh, J.; Hodaie, M. Trigeminal neuralgia associated with a solitary pontine lesion: Clinical and neuroimaging definition of a new syndrome. Pain 2020, 161, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cruse, R.P.; Conomy, J.P.; Wilbourn, A.J.; Hanson, M.R. Hereditary hypertrophic neuropathy combining features of tic douloureux, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and deafness. Clevel. Clin. Q. 1977, 44, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Rodríguez, B.; Simonet, C.; Cerdán, D.M.; Morollón, N.; Guerrero, P.; Tabernero, C.; Duarte, J. Familial classic trigeminal neuralgia. Neuralgia del trigémino clásica familiar. Neurologia 2019, 34, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Caress, J.B.; Lewis, J.A.; Pinyan, C.W.; Lawson, V.H. A charcot-marie-tooth type 1B kindred associated with hemifacial spasm and trigeminal neuralgia. Muscle Nerve 2019, 60, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar]
- Debta, P.; Sarode, G.; Sarode, S.; Gadbail, A.; Debta, F.M.; Swain, S.K.; Mishra, E.; Sahu, M.C. Natural history of trigeminal neuralgia-A hospital-based retrospective study. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 647–655. [Google Scholar]
- Defrin, R.; Brill, S.; Goor-Arieh, I.; Wood, I.; Devor, M. “Shooting pain” in lumbar radiculopathy and trigeminal neuralgia, and ideas concerning its neural substrates. Pain 2020, 161, 308–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, L.; Zakrzewska, J.M.; Abbott, J.; Braschinsky, M.; di Stefano, G.; Donnet, A.; Eide, P.K.; Leal, P.R.L.; Maarbjerg, S.; May, A.; et al. European Academy of Neurology guideline on trigeminal neuralgia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 831–849. [Google Scholar]
- Nova, C.V.; Zakrzewska, J.M.; Baker, S.R.; Riordain, R.N. Treatment outcomes in Trigeminal neuralgia—A systematic review of domains, dimensions, and measures. World Neurosurg. X 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambeta, E.; Chichorro, J.G.; Zamponi, G.W. Trigeminal neuralgia: An overview from pathophysiology to pharmacological treatments. Mol. Pain 2020, 16, 1744806920901890. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, N.; Chen, Y. CGRP Plasma Levels Decrease in Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia Patients Treated with Botulinum Toxin Type A: A Pilot Study. Pain Med. 2020, 21, pnaa028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zou, L.; Qi, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Mao, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Subcutaneous botulinum toxin-A injection for treating postherpetic neuralgia. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, H.J. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Toxins 2017, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puentes Gutiérrez, A.B.; García Bascones, M.; Puentes Gutiérrez, R.; Díaz Jiménez, M. Toxina botulínica subcutánea en el tratamiento del dolor neuropático periférico [Subcutaneous botulinum toxin in the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain]. Rehabilitacion 2019, 53, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sousa, E.J.S.; Sousa, G.C.; Baia, V.F.; Somensi, D.N.; Xavier, M.B. Botulinum toxin type A in chronic neuropathic pain in refractory leprosy. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2019, 77, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwin, R.D. Botulinum Toxin as Successful Treatment of Refractory Erythromelalgia Pain. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, I.; Bölcskei, K.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Helyes, Z. Mechanisms of botulinum toxin type A action on pain. Toxins 2019, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micheli, F.; Scorticati, M.C.; Raina, G. Beneficial effects of botulinum toxin type a for patients with painful tic convulsif. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2002, 25, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Lian, Y.J.; Zheng, Y.K.; Zhang, H.-F.; Chen, Y.; Xie, N.-C.; Wang, L.-J. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, M.E.; Elgebaly, A.; Elmaraezy, A.; Khalil, A.M.; Altibi, A.M.; Vu, T.L.-H.; Mostafa, M.R.; Huy, N.T.; Hirayama, K. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of Botulinum Toxin A Therapy in Trigeminal Neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shackleton, T.; Ram, S.; Black, M.; Ryder, J.; Clark, G.T.; Enciso, R. The efficacy of botulinum toxin for the treatment of trigeminal and postherpetic neuralgia: A systematic review with meta-analyses. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türk Börü, Ü.; Duman, A.; Bölük, C.; Coşkun Duman, S.; Taşdemir, M. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: 6-Month follow-up. Medicine 2017, 96, e8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K. Sphenopalatine ganglion block with botulinum neurotoxin for treating trigeminal neuralgia using CAD/CAM-derived injection guide. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2020, 34, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, J.; Bratbak, D.; Dodick, D.W.; Matharu, M.; Jamtøy, K.A.; Tronvik, E. Pilot Study of Injection of Onabotu-linumtoxinA Toward the Sphenopalatine Ganglion for the Treatment of Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia. Headache 2019, 59, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Missios, S.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Barnett, G.H. Percutaneous treatments for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Chang, J.W. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery on the Trigeminal Root Entry Zone for Idiopathic Trigeminal Neuralgia: Results and a Review of the Literature. Yonsei Med. J. 2020, 61, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Quliti, K.W. Update on neuropathic pain treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. The pharmacological and surgical options. Neurosciences 2015, 20, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Texakalidis, P.; Xenos, D.; Tora, M.S.; Wetzel, J.S.; Boulis, N.M. Comparative safety and efficacy of percutaneous approaches for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 182, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elawamy, A.; Abdalla, E.E.M.; Shehata, G.A. Effects of Pulsed Versus Conventional Versus Combined Radiofrequency for the Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Prospective Study. Pain Physician 2017, 20, E873–E881. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, B.T.; Pun, C.D.; Lake, W.B.; Resnick, D.K. Computed Tomography Guidance for Percutaneous Glycerol Rhizotomy for Trigeminal Neuralgia. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 19, opz400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Kotecha, R.; Modugula, S.; Murphy, E.S.; Jones, M.; Kotecha, R.; Reddy, C.A.; Sut, J.H.; Barnett, G.H.; Neyman, F.; et al. Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated With Stereotactic Radiosurgery: The Effect of Dose Escalation on Pain Control and Treatment Outcomes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.; DIng, Y.; Yao, P. Long-term efficacy and complications of radiofrequency thermocoagulation at different temperatures for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Biochem. Res. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajali, Y.; Ward, M.; Abraham, M.; Hillen, M.; Mahmoud, O.; Herschman, Y.; Mammis, A.; Paskhover, B. Minimally invasive trigeminal ablation in patients with refractory trigeminal neuralgia who are ineligible for intracranial intervention. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 70, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansai, V.; Mmowar, A.; Dubey, P.; Gupta, S. Role of cryotherapy in trigeminal neuralgia with certain modification: A long-term prospective study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichida, M.C.; Zemuner, M.; Hosomi, J.; Pai, H.J.; Teixeira, M.J.; de Siqueira, J.T.T.; de Siqueira, S.R.D.T. Acupuncture treatment for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: A longitudinal case-control double blinded study. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 23, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, A.; Lunsford, L.D. Radiosurgery for the management of refractory trigeminal neuralgia. Neurol. India 2016, 64, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, R.W.; Palsma, R.S.; Weinand, M.E.; Kasoff, W.S. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for Refractory Trigeminal Pain: Recent Single-Institution Case Series with Long-Term Follow-Up and Review of the Literature. Neuromodulation 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuleasca, C.; Régis, J.; Sahgal, A.; De Salles, A.; Hayashi, M.; Ma, L.; Martiniez-Álvarez, R.; Paddick, I.; Ryu, S.; Slotman, B.J.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 733–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, N.B.; Amburgy, J.W.; Self, D.M.; Christen, A.M.; Larios, E.A.; Ditty, B.J.; Jacob, R.; Fiveash, J.; Spencer, S.; Markert, J.M.; et al. Repeat gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: A single-center experience and focused review of the literature. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 70, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holste, K.; Chan, A.Y.; Rolston, J.D.; Englot, D.J. Pain Outcomes Following Microvascular Decompression for Drug-Resistant Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Ni, J.; Dou, Z. Microvascular decompression and radiofrequency for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: A meta-analysis. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patra, D.P.; Savardekar, A.R.; Dossani, R.H.; Narayan, V.; Mohammed, N.; Nanda, A. Repeat Gamma Knife radiosurgery versus microvascular decompression following failure of GKRS in trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendelson, Z.S.; Velagala, J.R.; Kohil, G.; Heir, G.M.; Mammis, A.; Liu, J.K. Pain-free outcaomes and durability of surgical intervention for trigeminal neuralgia: A comparison of gamma knife and microvascular decompression. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e732–e746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.M.; Duvall, J.B.; Phan, K.; Jonker, B.P. First treatment and retreatment of medically refractive trigeminal neuralgia by stereotactic radiosurgery versus microvascular decompression: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 32, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Phalak, M.; Katiyar, V.; Borkar, S.; Kale, S.S.; Mahapatra, A.K. Microvascular decompression versus stereotactic radiosurgery as primary treatment modality for trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective comparative trials. Neurol. India 2018, 66, 688–694. [Google Scholar]
- Gubian, A.; Rosahl, S.K. Meta-analysis on safety and efficacy of microsurgical and radiosurgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, S.K.; Eskandar, E.N. Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, L. The long-term clinical outcomes of microvascular decompression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia compressed by the vertebra-basilar artery: A case series review. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jannetta, P.J. Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J. Neurosurg. 1967, 26, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mao, F.; Cheng, F.; Peng, C.; Guo, D.; Wang, B. A meta-analysis of endoscopic microvascular decompression versus microscopic microvascular decompression for the treatment for cranial nerve syndrome caused by vascular compression. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, 647–655.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagzoog, N.; Attar, A.; Takroni, R.; Alotaibi, M.B.; Reddy, K. Endoscopic versus open microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review and comparative meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafree, D.J.; Williams, A.C.; Zakrzewska, J.M. Impact of pain and postoperative complications on patient-reported outcome measures 5 years after microvascular decompression or partial sensory rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maarbjerg, S.; Wolfram, F.; Heinskou, T.B.; Rochat, P.; Gozalov, A.; Brennum, J.; Olesen, J.; Bendtsen, L. Persistent idiopathic facial pain—A prospective systematic study of clinical characteristics and neuroanatomical findings at 3.0 Tesla MRI. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siqueira, S.R.; Siviero, M.; Alvarez, F.K.; Teixeira, M.J.; Siqueira, J.T. Quantitative sensory testing in trigeminal traumatic neuropathic pain and persistent idiopathic facial pain. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2013, 71, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenaga, N.; Matsuki, Y.; Maeda, L.; Nagai, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Takao, Y.; Hirose, M. Neuropathic Characteristics In Patients With Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2801–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, A.L.; Ehrhardt, K.P.; Tolba, R. Atypical facial pain: A comprehensive, evidence-based review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoliel, R.; Gaul, C. Persistent idiopathic facial pain. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Deun, L.; de Witte, M.; Goessens, T.; Halewyck, S.; Ketelaer, M.-C.; Matic, M.; Moens, M.; Vaes, P.; Van Lint, M.; Versijpt, J. Facial Pain: A Comprehensive Review and Proposal for a Pragmatic Diagnostic Approach. Eur. Neurol. 2020, 83, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K.; Sugawara, S.; Watanabe, K.; Hong, C.; Tu, T.T.H.; Watanabe, T.; Sakamoto, J.; Yoshino, N.; Suga, T.; Mikuzuki, L.; et al. Differences in the Clinical Characteristics of Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain (Atypical Odontalgia) Patients with or Without Neurovascular Compression of the Trigeminal Nerve. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwin, R.D. Myofascial Trigger Point Pain Syndromes. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, H.A.; Cappellari, A.M.; Gaffuri, F.; Curone, M.; Tullo, V.; Didier, A.H.; Giannì, A.B.; Bussone, G. Predictive role of gnathological techniques for the treatment of persistent idiopathic facial pain (PIFP). Neurol. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwin, R.D.; Cagnie, B.; Petrovic, M.; Van Dorpe, J.; Calders, P.; De Meulemeester, K. Foci of Segmentally Contracted Sarcomeres in Trapezius Muscle Biopsy Specimens in Myalgic and Nonmyalgic Human Subjects: Preliminary Results. Pain Med. 2020, pnaa019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerwin, R.D. Diagnosis of myofascial pain syndrome. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Dommerholt, J. International Consensus on Diagnostic Criteria and Clinical Considerations of Myofascial Trigger Points: A Delphi Study. Pain Med. 2018, 19, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Huang, Q.M.; Liu, Q.G.; Ye, G.; Bo, C.Z.; Chen, M.J.; Li, P. Effectiveness of dry needling for myofascial trigger points associated with neck and shoulder pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifeh, M.; Mehta, K.; Varguise, N.; Suarez-Durall, P.; Enciso, R. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of head and neck chronic myofascial pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2016, 147, 959–973.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattie, E.; Cleland, J.A.; Snodgrass, S. The Effectiveness of Trigger Point Dry Needling for Musculoskeletal Conditions by Physical Therapists: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meulemeester, K.E.; Castelein, B.; Coppieters, I.; Barbe, T.; Cools, A.; Cagnie, B. Comparing Trigger Point Dry Needling and Manual Pressure Technique for the Management of Myofascial Neck/Shoulder Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2017, 40, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yildirim, M.A.; Öneş, K.; Gökşenoğlu, G. Effectiveness of Ultrasound Therapy on Myofascial Pain Syndrome of the Upper Trapezius: Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Arch. Rheumatol. 2018, 33, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vier, C.; Almeida, M.B.; Neves, M.L.; Santos, A.R.S.D.; Bracht, M.A. The effectiveness of dry needling for patients with orofacial pain associated with temporomandibular dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2019, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, L.A.; Bezerra de Medeiros, A.K.; Campos, M.F.T.P.; Bastos Machado de Resende, C.M.; Barbosa, G.A.S.; de Almeida, E.O. Manual Therapy in the Treatment of Myofascial Pain Related to Temporomandibular Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2020, 34, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| A. | Diagnostic Criteria: |
| B. | Recurrent paroxysms of unilateral facial pain in the distribution of one or more ivisions of the trigeminal nerve, with no radiation, and fulling criteria B and C |
| C. | Pain has all of the following characteristics |
| 1. Occurring in one or more trigeminal nerve divisions, without radiation beyond the trigeminal distribution | |
| 2. Paroxysms lasting from a fraction of a second to two minutes | |
| 3. Severe intensity | |
| 4. Electric shock like, shooting, stabbing or sharp | |
| D. | Precipitated by innocuous stimuli within the affected trigeminal distribution |
| E. | No clinically evident neurologic deficit |
| F. | Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis |
| Modality | Assessment | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacologic Therapy | Carbamazepine: moderate level of evidence for long-term benefit, but loss of benefit (failure rate of 50% long term) Other anticonvulsant drugs: oxcarbazepine, lamotrigine, gabapentin—commonly used but low quality or insufficient evidence re: benefit | High degree of adverse effects with carbamazepine |
| Peripheral Nerve Intervention | Percutaneous rhizotomy (glycerol): high level of evidence for long-term benefit Radiofrequency thermocoagulation: high level of evidence for long-term benefit Balloon compression: high level of evidence for long-term benefit | Loss of benefit over time for all three techniques Low incidence of serious adverse effects, but anesthesia dolorosa can be a serious adverse effect No agreement on the optimal temperature for radiofrequency thermocoagulation |
| Botulinum Toxin | High quality of evidence for benefit | Low incidence of transient side effects, but treatment must be repeated to maintain benefit |
| Gamma Knife Radiosurgery | High quality of evidence in favor of long-term benefit. Benefit falls by almost half in 5–10 years, but treatment can be repeated | Onset of improvement is delayed from 2 to 6 months after treatment Low incidence of adverse effects is increased with repeated treatment |
| Microvascular Decompression | High level of evidence for long-term improvement that is maintained over 5 years | Low incidence of adverse effects Endoscopic microvascular decompression has a higher rate of benefit and a lower rate of recurrence with fewer adverse effects than traditional open microvascular decompression |
| A. Facial and/or oral pain fulling criteria B and C |
| B. Recurring daily for >2 h per day for >3 months |
| C. Pain has both of the following characteristics |
| 1. poorly localized, and not following the distribution of a peripheral nerve |
| 2. dull, aching or nagging quality |
| D. Clinical neurological examination is normal |
| E. A dental cause has been excluded by appropriate investigations. |
| F. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis. |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants (amitriptlyline) |
| Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors |
| (duloxetine) |
| (venlefaxine) |
| Antiepileptics (i.e., lamotrigine) |
| Cannabinoids |
| Low-level laser |
| Cognitive behavioral therapy |
| Temporomandibular joint dysfunction and gnathic dysfunction |
| Sphenopalatine ganglion block |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerwin, R. Chronic Facial Pain: Trigeminal Neuralgia, Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain, and Myofascial Pain Syndrome—An Evidence-Based Narrative Review and Etiological Hypothesis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197012
Gerwin R. Chronic Facial Pain: Trigeminal Neuralgia, Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain, and Myofascial Pain Syndrome—An Evidence-Based Narrative Review and Etiological Hypothesis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(19):7012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerwin, Robert. 2020. "Chronic Facial Pain: Trigeminal Neuralgia, Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain, and Myofascial Pain Syndrome—An Evidence-Based Narrative Review and Etiological Hypothesis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 19: 7012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197012




