Is Being Physically Active Enough or Do People with Parkinson’s Disease Need Structured Supervised Exercise? Lessons Learned from COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Sampling and Recruitment
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analyses
2.5. Ethics and Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Exercise’s Habits/Lifestyle Behaviour
3.3. Non-Motor Symptoms (MDS-UPDRS Part I)
3.4. Motor Symptoms (MDS-UPDRS Part II)
3.5. Quality of Life
3.6. Disability and Independence in Activities of Daily Living (ADL)
3.7. Sleep Assessment
3.8. Falls
3.9. Patient’s Clinical Global Impression Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woods, J.A.; Hutchinson, N.T.; Powers, S.K.; Roberts, W.O.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Radak, Z.; Berkes, I.; Boros, A.; Boldogh, I.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; et al. The COVID-19 pandemic and physical activity. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2020, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghrir, M.H.; Akbarialiabad, H.; Ahmadi Marzaleh, M. Efficacy of Mass Quarantine as Leverage of Health System Governance During COVID-19 Outbreak: A Mini Policy Review. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020, 23, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmich, R.C.; Bloem, B.R. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Parkinson’s Disease: Hidden Sorrows and Emerging Opportunities. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2020, 10, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schootemeijer, S.; van der Kolk, N.M.; Bloem, B.R.; de Vries, N.M. Current Perspectives on Aerobic Exercise in People with Parkinson’s Disease. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTherap. 2020, 17, 1418–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keus, S.; Munneke, M.; Graziano, M.; Paltamaa, J.; Pelosin, E.; Domingos, J.; Bruhlmann, S.; Ramaswamy, B.; Prins, J.; Struiksma, C.; et al. European Physiotherapy Guideline for Parkinson’s Disease; KNGF/ParkinsonNet: Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bloem, B.R.; de Vries, N.M.; Ebersbach, G. Nonpharmacological treatments for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2015, 30, 1504–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradsson, D.; Lofgren, N.; Nero, H.; Hagstromer, M.; Stahle, A.; Lokk, J.; Franzen, E. The Effects of Highly Challenging Balance Training in Elderly With Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, J.; Dean, J.; Cruickshank, T.M.; Smilowska, K.; Fernandes, J.B.; Godinho, C. A Novel Boot Camp Program to Help Guide Personalized Exercise in People with Parkinson Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouca-Machado, R.; Rosario, A.; Caldeira, D.; Castro Caldas, A.; Guerreiro, D.; Venturelli, M.; Tinazzi, M.; Schena, F.; Ferreira, J.J. Physical Activity, Exercise, and Physiotherapy in Parkinson’s Disease: Defining the Concepts. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.; Boudreau, J.K.; DeAngelis, T.R.; Brown, L.E.; Cavanaugh, J.T.; Earhart, G.M.; Ford, M.P.; Foreman, K.B.; Dibble, L.E. Barriers to exercise in people with Parkinson disease. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, L.D.; Zaman, A.; Stegemoller, E.L. Sedentary Behavior and Quality of Life in Individuals With Parkinson’s Disease. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2019, 33, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, I.A.; Nienhuis, C.P. The Impact of COVID-19 on Physical Activity Behavior and Well-Being of Canadians. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukkonen-Harjula, K.; Hiilloskorpi, H.; Manttari, A.; Pasanen, M.; Parkkari, J.; Suni, J.; Fogelholm, M.; Laukkanen, R. Self-guided brisk walking training with or without poles: A randomized-controlled trial in middle-aged women. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2007, 17, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, M.K.Y.; Wong-Yu, I.S.K. Six-Month Community-Based Brisk Walking and Balance Exercise Alleviates Motor Symptoms and Promotes Functions in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2021, 11, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkman, M.; Moore, C.G.; Kohrt, W.M.; Hall, D.A.; Delitto, A.; Comella, C.L.; Josbeno, D.A.; Christiansen, C.L.; Berman, B.D.; Kluger, B.M.; et al. Effect of High-Intensity Treadmill Exercise on Motor Symptoms in Patients With De Novo Parkinson Disease: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nimwegen, M.; Speelman, A.D.; Smulders, K.; Overeem, S.; Borm, G.F.; Backx, F.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Munneke, M.; ParkFit Study, G. Design and baseline characteristics of the ParkFit study, a randomized controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of a multifaceted behavioral program to increase physical activity in Parkinson patients. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, C.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Peto, V.; Greenhall, R.; Hyman, N. The PDQ-8: Development and validation of a short-form parkinson’s disease questionnaire. Psychol. Health 1997, 12, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, M.L.; Benes, H.; Sixel-Doring, F.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Suzuki, K.; Hirata, K.; Zimmermann, J.; Trenkwalder, C. Clinically relevant cut-off values for the Parkinson’s Disease Sleep Scale-2 (PDSS-2): A validation study. Sleep Med. 2016, 24, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Rodriguez-Blazquez, C.; Alvarez-Sanchez, M.; Arakaki, T.; Bergareche-Yarza, A.; Chade, A.; Garretto, N.; Gershanik, O.; Kurtis, M.M.; Martinez-Castrillo, J.C.; et al. Expanded and independent validation of the Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS). J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology; U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration, National Institute of Mental Health, Psychopharmacology Research Branch, Division of Extramural Research Programs: Rockville, MD, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, R.S.; England, A.C. Projection Technique for Evaluating Surgery in Parkinson’s Disease; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shachar, M.; Lüdecke, D.; Makowski, D. effectsize: Estimation of Effect Size Indices and Standardized Parameters. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, K.; Rey, K. ggResidpanel: Panels and Interactive Versions of Diagnostic Plots using ‘ggplot2′. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggResidpanel (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Lachman, M.E.; Lipsitz, L.; Lubben, J.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C.; Jette, A.M. When Adults Don’t Exercise: Behavioral Strategies to Increase Physical Activity in Sedentary Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Innov. Aging 2018, 2, igy007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.B.; Fernandes, S.B.; Almeida, A.S.; Vareta, D.A.; Miller, C.A. Older Adults’ Perceived Barriers to Participation in a Falls Prevention Strategy. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lai, B.; Mehta, T.; Thirumalai, M.; Padalabalanarayanan, S.; Rimmer, J.H.; Motl, R.W. Exercise Training Guidelines for Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke, and Parkinson Disease: Rapid Review and Synthesis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 98, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Mao, L.; Nassis, G.P.; Harmer, P.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Li, F. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): The need to maintain regular physical activity while taking precautions. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leritz, E.; Loftis, C.; Crucian, G.; Friedman, W.; Bowers, D. Self-awareness of deficits in Parkinson disease. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2004, 18, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudlicka, A.; Clare, L.; Hindle, J.V. Awareness of executive deficits in people with Parkinson’s disease. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. JINS 2013, 19, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brajot, F.X.; Shiller, D.M.; Gracco, V.L. Autophonic loudness perception in Parkinson’s disease. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Rochester, L.; Birleson, A.; Hetherington, V.; Nieuwboer, A.; Willems, A.M.; Van Wegen, E.; Kwakkel, G. Everyday walking with Parkinson’s disease: Understanding personal challenges and strategies. Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deck, B.L.; Xie, S.X.; Choi, G.; Rick, J.; Siderowf, A.; Rudovsky, S.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Duda, J.E.; Morley, J.F.; Dahodwala, N.; et al. Cognitive Functional Abilities in Parkinson’s Disease: Agreement Between Patients and Informants. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, M.E.; Earhart, G.M. Health-related quality of life and alternative forms of exercise in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcos, D.M.; Robichaud, J.A.; David, F.J.; Leurgans, S.E.; Vaillancourt, D.E.; Poon, C.; Rafferty, M.R.; Kohrt, W.M.; Comella, C.L. A two-year randomized controlled trial of progressive resistance exercise for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2013, 28, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodoehl, J.; Rafferty, M.R.; David, F.J.; Poon, C.; Vaillancourt, D.E.; Comella, C.L.; Leurgans, S.E.; Kohrt, W.M.; Corcos, D.M.; Robichaud, J.A. Two-year exercise program improves physical function in Parkinson’s disease: The PRET-PD randomized clinical trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G.; Stebbins, G.T.; Luo, S. Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Use in the COVID-19 Era. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2020, 35, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, D.; Tobin, V. A Modification to the Behavioural Regulation in Exercise Questionnaire to Include an Assessment of Amotivation. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2004, 26, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.; Latham, N.K.; DeAngelis, T.R.; Thomas, C.A.; Saint-Hilaire, M.; Bickmore, T.W. Feasibility of a virtual exercise coach to promote walking in community-dwelling persons with Parkinson disease. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 472–481, quiz 482–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient’s Exercise | Overall (N = 27) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maintained (N = 17) | Interrupted (N = 10) | ||
| Age | |||
| Mean (SD) | 68.9 (6.37) | 77.0 (7.29) | 71.9 (7.69) |
| Median [Min, Max] | 69.0 (57.0, 80.0) | 77.5 (66.0, 92.0) | 70.0 (57.0, 92.0) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 4 (23.5%) | 1 (10.0%) | 5 (18.5%) |
| Male | 13 (76.5%) | 9 (90.0%) | 22 (81.5%) |
| Hoehn & Yahr | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2.50 (0.866) | 3.00 (0.471) | 2.69 (0.774) |
| Median [Min, Max] | 2.50 (1.00, 4.00) | 3.00 (2.00, 4.00) | 3.00 (1.00, 4.00) |
| Pre-Social Isolation | Post-Social Isolation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Maintained (N = 17) | Exercise Interrupted (N = 10) | Exercise Maintained (N = 17) | Exercise Interrupted (N = 10) | |
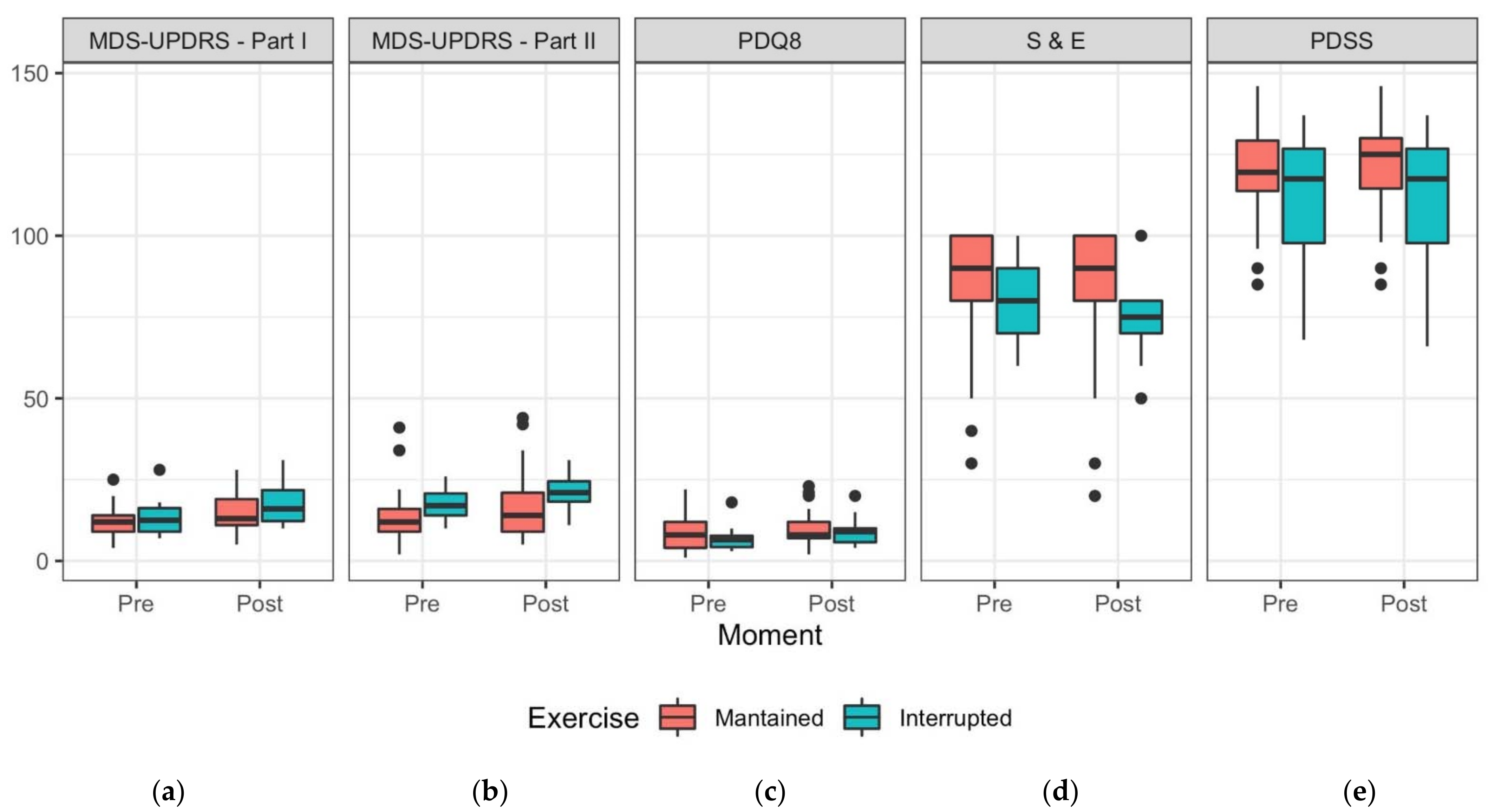
| MDS-UPDRS Part I | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 12.1 (5.26) | 13.4 (6.45) | 15.1 (6.24) | 17.6 (7.00) |
| Median (Min, Max) | 12.0 (4.00, 25.0) | 12.5 (7.00, 28.0) | 13.0 (5.00, 28.0) | 16.0 (10.0, 31.0) |
| MDS-UPDRS Part II | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 15.4 (11.0) | 17.7 (5.54) | 17.9 (11.9) | 21.3 (5.46) |
| Median (Min, Max) | 12.0 (2.00, 41.0) | 17.0 (10.0, 26.0) | 14.0 (5.00, 44.0) | 21.0 (11.0, 31.0) |
| PDQ8 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 16.8 (6.71) | 15.2 (4.34) | 18.1 (6.41) | 17.5 (4.88) |
| Median (Min, Max) | 16.0 (9.00, 30.0) | 14.5 (11.0, 26.0) | 16.0 (10.0, 31.0) | 17.0 (12.0, 28.0) |
| S & E | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 84.1 (22.4) | 80.0 (12.5) | 81.8 (25.3) | 74.0 (13.5) |
| Median (Min, Max) | 90.0 (30.0, 100) | 80.0 (60.0, 100) | 90.0 (20.0, 100) | 75.0 (50.0, 100) |
| PDSS | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 119 (17.3) | 111 (23.9) | 120 (17.4) | 111 (24.3) |
| Median (Min, Max) | 120 (85.0, 146) | 118 (68.0, 137) | 125 (85.0, 146) | 118 (66.0, 137) |
| Missing | 1 (5.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0 (0%) |
| CGIC | ||||
| Mean (SD) | NA | NA | 5.41 (0.618) | 5.80 (0.422) |
| Median (Min, Max) | NA | NA | 5.00 (5.00, 7.00) | 6.00 (5.00, 6.00) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domingos, J.; Família, C.; Fernandes, J.B.; Dean, J.; Godinho, C. Is Being Physically Active Enough or Do People with Parkinson’s Disease Need Structured Supervised Exercise? Lessons Learned from COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042396
Domingos J, Família C, Fernandes JB, Dean J, Godinho C. Is Being Physically Active Enough or Do People with Parkinson’s Disease Need Structured Supervised Exercise? Lessons Learned from COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(4):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042396
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomingos, Josefa, Carlos Família, Júlio Belo Fernandes, John Dean, and Catarina Godinho. 2022. "Is Being Physically Active Enough or Do People with Parkinson’s Disease Need Structured Supervised Exercise? Lessons Learned from COVID-19" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 4: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042396
APA StyleDomingos, J., Família, C., Fernandes, J. B., Dean, J., & Godinho, C. (2022). Is Being Physically Active Enough or Do People with Parkinson’s Disease Need Structured Supervised Exercise? Lessons Learned from COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042396








