The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Need for a Biomarker
1.2. Endometriosis: A Systemic Disease
1.3. MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
1.4. Biogenesis of miRNAs
1.5. miRNAs as Candidate Biomarkers
1.6. Various Techniques of miRNA Profiling
1.7. miRNA Profiling Studies in Endometriosis
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. miRNAs with Differential Expression in Endometriosis
3.2. Factors Influencing miRNA Expression
3.3. Candidate Circulating miRNAs in Endometriosis and Their Putative Role
3.3.1. miR-17-5p/20a
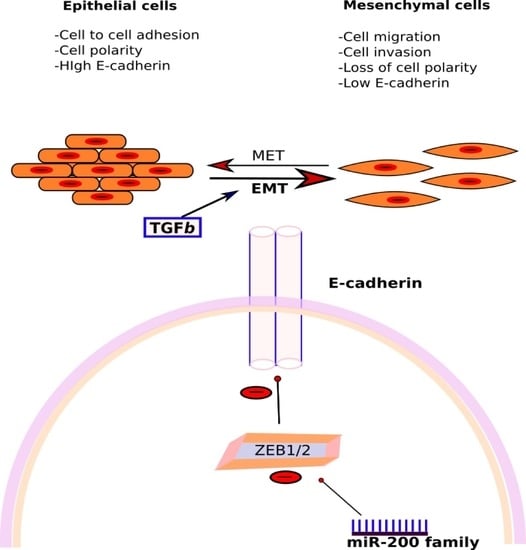
3.3.2. miR-200 Family
3.3.3. miR-199a
3.3.4. miR-143 and 145
3.4. Limitations of the Review
3.5. Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Quality Assessment
4.4. Data Extraction
4.5. Ranking
4.6. Publication Bias
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J.; Beecham, C.; Carrington, E. Endometriosis. Obstet. Gynecol. 1975, 8, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, P.A.W.; D’Hooghe, T.M.; Fazleabas, A.; Gargett, C.E.; Giudice, L.C.; Montgomery, G.W.; Rombauts, L.; Salamonsen, L.A.; Zondervan, K.T. Priorities for endometriosis research: Recommendations from an international consensus workshop. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 16, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, G.D.; Kennedy, S.; Hummelshoj, L. Creating solutions in endometriosis: Global collaboration through the World Endometriosis Research Foundation. J. Endometr. 2010, 2, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Giudice, L.C.; Kao, L.C. Endometriosis. Lancet 2004, 364, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-W.; Wang, Y. The prevalence of endometriosis in women with chronic pelvic pain. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2006, 62, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuleman, C.; Vandenabeele, B.; Fieuws, S.; Spiessens, C.; Timmerman, D.; D’Hooghe, T. High prevalence of endometriosis in infertile women with normal ovulation and normospermic partners. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 92, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercellini, P.; Fedele, L.; Aimi, G.; Pietropaolo, G.; Consonni, D.; Crosignani, P.G. Association between endometriosis stage, lesion type, patient characteristics and severity of pelvic pain symptoms: A multivariate analysis of over 1000 patients. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoens, S.; Dunselman, G.; Dirksen, C.; Hummelshoj, L.; Bokor, A.; Brandes, I.; Brodszky, V.; Canis, M.; Colombo, G.L.; DeLeire, T.; et al. The burden of endometriosis: Costs and quality of life of women with endometriosis and treated in referral centres. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, R.; Mardon, H.; Barlow, D.; Kennedy, S. Delay in the diagnosis of endometriosis: A survey of women from the USA and the UK. Hum. Reprod. 1996, 11, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, S.; Bergqvist, A.; Chapron, C.; D’Hooghe, T.; Dunselman, G.; Greb, R.; Hummelshoj, L.; Prentice, A.; Saridogan, E. ESHRE guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2005, 20, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nnoaham, K.E.; Hummelshoj, L.; Webster, P.; d’Hooghe, T.; de Cicco Nardone, F.; de Cicco Nardone, C.; Kennedy, S.H.; Zondervan, K.T.; d’Hooghe, T.; de Nardone, F.; et al. Impact of endometriosis on quality of life and work productivity: A multicenter study across ten countries. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 366.e8–373.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, S.; Canis, M.; Pouly, J.-L.; Rabischong, B.; Botchorishvili, R.; Mage, G. Relationship between delay of surgical diagnosis and severity of disease in patients with symptomatic deep infiltrating endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 86, 1314–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans Evers, J.L.H. Is Adolescent Endometriosis a Progressive Disease that Needs to Be Diagnosed and Treated? Human Reproduction: Oxford, UK, 2013; p. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- May, K.E.; Conduit-Hulbert, S.A.; Villar, J.; Kirtley, S.; Kennedy, S.H.; Becker, C.M. Peripheral biomarkers of endometriosis: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2010, 16, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James Lind Alliance Priority Setting Partnerships. 2017. Available online: http://www.jla.nihr.ac.uk/about-the-james-lind-alliance/about-psps.htm (accessed on 5 February 2018).
- Naqvi, H.; Mamillapalli, R.; Krikun, G.; Taylor, H.S. Endometriosis Located Proximal to or Remote From the Uterus Differentially Affects Uterine Gene Expression. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 23, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinaii, N.; Cleary, S.D.; Ballweg, M.L.; Nieman, L.K.; Stratton, P. High rates of autoimmune and endocrine disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome and atopic diseases among women with endometriosis: A survey analysis. Hum. Reprod. 2002, 17, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gorp, T.; Amant, F.; Neven, P.; Vergote, I.; Moerman, P. Endometriosis and the development of malignant tumours of the pelvis. A review of literature. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2004, 18, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somigliana, E.; Vigano’, P.; Parazzini, F.; Stoppelli, S.; Giambattista, E.; Vercellini, P. Association between endometriosis and cancer: A comprehensive review and a critical analysis of clinical and epidemiological evidence. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 101, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezhat, F.; Datta, M.S.; Hanson, V.; Pejovic, T.; Nezhat, C.; Nezhat, C. The relationship of endometriosis and ovarian malignancy: A review. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 90, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiersz, L.M. Role of endometriosis in cancer and tumor development. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 955, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemmill, J.A.L.; Stratton, P.; Cleary, S.D.; Ballweg, M.L.; Sinaii, N. Cancers, infections, and endocrine diseases in women with endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olovsson, M. Immunological aspects of endometriosis: An update. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 66, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Králíčková, M.; Vetvicka, V. Immunological aspects of endometriosis: A review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.H.; Monsanto, S.P.; Miller, C.; Singh, S.S.; Thomas, R.; Tayade, C. Pathophysiology and Immune Dysfunction in Endometriosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 795976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Agarwal, A.; Sekhon, L.; Krajcir, N.; Cocuzza, M.; Falcone, T. Serum and peritoneal abnormalities in endometriosis: Potential use as diagnostic markers. Minerva Ginecol. 2006, 58, 527–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agic, A.; Xu, H.; Finas, D.; Banz, C.; Diedrich, K.; Hornung, D. Is endometriosis associated with systemic subclinical inflammation? Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2006, 62, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvaskoff, M.; Mu, F.; Terry, K.L.; Harris, H.R.; Poole, E.M.; Farland, L.; Missmer, S.A. Endometriosis: A high-risk population for major chronic diseases? Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2015, 21, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppe, K.; Glinoer, D.; van Steirteghem, A.; Tournaye, H.; Devroey, P.; Schiettecatte, J.; Velkeniers, B. Thyroid dysfunction and autoimmunity in infertile women. Thyroid 2002, 12, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, H.R.; Costenbader, K.H.; Mu, F.; Kvaskoff, M.; Malspeis, S.; Karlson, E.W.; Missmer, S.A. Endometriosis and the risks of systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis in the Nurses’ Health Study II. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawanshi, S.; Vlad, A.M.; Lin, H.-M.; Mantia-Smaldone, G.; Laskey, R.; Lee, M.; Lin, Y.; Donnellan, N.; Klein-Patel, M.; Lee, T.; et al. Plasma MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for endometriosis and endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Ren, C.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, X.; Fang, X.; Xia, X. Analysis of Serum microRNA Profile by Solexa Sequencing in Women with Endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 23, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyholt, D.R.; Low, S.-K.; Anderson, C.A.; Painter, J.N.; Uno, S.; Morris, A.P.; MacGregor, S.; Gordon, S.D.; Henders, A.K.; Martin, N.G.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies new endometriosis risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahmioglu, N.; Nyholt, D.R.; Morris, A.P.; Missmer, S.A.; Montgomery, G.W.; Zondervan, K.T. Genetic variants underlying risk of endometriosis: Insights from meta-analysis of eight genome-wide association and replication datasets. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2014, 20, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P.; Lee, R.; Feinbaum, R. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S. The microRNA Registry. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D109–D111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: MicroRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Saini, H.K.; van Dongen, S.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D154–D158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, C.M.; Calin, G.A. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 2005, 122, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, S.M. RNAi, microRNAs, and human disease. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58 (Suppl. 1), S63–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T. microRNAs in vertebrate physiology and human disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2007, 8, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhayani, M.K.; Calin, G.A.; Lai, S.Y. Functional relevance of miRNA sequences in human disease. Mutat. Res. 2012, 731, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, R.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and protein that promote tumor growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, S.; Tong, Y.; Steitz, J.A. Switching from repression to activation: MicroRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 2007, 318, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grun, D.; Wang, Y.-L.; Langenberger, D.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Rajewsky, N. microRNA target predictions across seven Drosophila species and comparison to mammalian targets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Ashurst, J.L.; Bradley, A. Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskerville, S.; Bartel, D.P. Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 2005, 11, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4051–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Cullen, B.R. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 2004, 10, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Han, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Yim, J.; Lee, J.; Provost, P.; Radmark, O.; Kim, S.; et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 2003, 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Yan, K.-P.; Amuthan, G.; Chendrimada, T.; Doratotaj, B.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denli, A.M.; Tops, B.B.J.; Plasterk, R.H.A.; Ketting, R.F.; Hannon, G.J. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 2004, 432, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, R.; Qin, Y.; Macara, I.G.; Cullen, B.R. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, E.; Guttinger, S.; Calado, A.; Dahlberg, J.E.; Kutay, U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 2004, 303, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, E.; Caudy, A.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Hannon, G.J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 2001, 409, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chendrimada, T.P.; Gregory, R.I.; Kumaraswamy, E.; Norman, J.; Cooch, N.; Nishikura, K.; Shiekhattar, R. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature 2005, 436, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-E.; Heo, I.; Tian, Y.; Simanshu, D.K.; Chang, H.; Jee, D.; Patel, D.J.; Kim, V.N. Dicer recognizes the 5′ end of RNA for efficient and accurate processing. Nature 2011, 475, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Chendrimada, T.P.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 2005, 123, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamore, P.D.; Tuschl, T.; Sharp, P.A.; Bartel, D.P. RNAi: Double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 2000, 101, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheridge, A.; Lee, I.; Hood, L.; Galas, D.; Wang, K. Extracellular microRNA: A new source of biomarkers. Mutat. Res. 2011, 717, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.J. MicroRNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer diagnostics. Biomark. Res. 2014, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA as Biomarkers and Diagnostics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, N.; Aharonov, R.; Meiri, E.; Rosenwald, S.; Spector, Y.; Zepeniuk, M.; Benjamin, H.; Shabes, N.; Tabak, S.; Levy, A.; et al. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Maki, M.; Ding, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, L. Genome-wide survey of tissue-specific microRNA and transcription factor regulatory networks in 12 tissues. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Drug Discovery, Development and Translation. Emerging Safety Science: Workshop Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondal, T.; Jensby Nielsen, S.; Baker, A.; Andreasen, D.; Mouritzen, P.; Wrang Teilum, M.; Dahlsveen, I.K. Assessing sample and miRNA profile quality in serum and plasma or other biofluids. Methods 2013, 59, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Lee, E.J.; Jiang, J.; Sarkar, A.; Yang, L.; Elton, T.S.; Chen, C. Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods 2008, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’haene, B.; Vandesompele, J.; Hellemans, J. Accurate and objective copy number profiling using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods 2010, 50, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ’t Hoen, P.A.C.; Ariyurek, Y.; Thygesen, H.H.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Vossen, R.H.A.M.; de Menezes, R.X.; Boer, J.M.; van Ommen, G.B.; den Dunnen, J.T. Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestdagh, P.; Hartmann, N.; Baeriswyl, L.; Andreasen, D.; Bernard, N.; Chen, C.; Cheo, D.; D’Andrade, P.; DeMayo, M.; Dennis, L.; et al. Evaluation of quantitative miRNA expression platforms in the microRNA quality control (miRQC) study. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson Teague, E.M.C.; Print, C.G.; Hull, M.L. The role of microRNAs in endometriosis and associated reproductive conditions. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2009, 16, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Yuasa, Y. Multiple-to-multiple relationships between microRNAs and target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson Teague, E.M.C.; van der Hoek, K.H.; Van der Hoek, M.B.; Perry, N.; Wagaarachchi, P.; Robertson, S.A.; Print, C.G.; Hull, L.M. MicroRNA-Regulated Pathways Associated with Endometriosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Takahashi, R.; Hiura, Y.; Hirokawa, G.; Fukushima, Y.; Iwai, N. Plasma miR-208 as a biomarker of myocardial injury. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Samatov, T.R.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Burwinkel, B. Circulating miRNAs: Cell-cell communication function? Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Tominaga, N.; Ochiya, T. Functional analysis of exosomal microRNA in cell-cell communication research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuokkanen, S.; Chen, B.; Ojalvo, L.; Benard, L.; Santoro, N.; Pollard, J.W. Genomic profiling of microRNAs and messenger RNAs reveals hormonal regulation in microRNA expression in human endometrium. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 82, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, A.-G.; Liu, J.-L.; Jiang, X.-M.; Ren, J.-Z.; Ma, C.-H.; Lei, W.; Su, R.W.; Yang, Z.M. Genome-wide identification of micro-ribonucleic acids associated with human endometrial receptivity in natural and stimulated cycles by deep sequencing. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 150.e5–155.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braza-Boils, A.; Mari-Alexandre, J.; Gilabert, J.; Sanchez-Izquierdo, D.; Espana, F.; Estelles, A.; ilabert-Estelles, J. MicroRNA expression profile in endometriosis: Its relation to angiogenesis and fibrinolytic factors. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burney, R.O.; Hamilton, A.E.; Aghajanova, L.; Vo, K.C.; Nezhat, C.N.; Lessey, B.A.; Giudice, L.C. MicroRNA expression profiling of eutopic secretory endometrium in women with versus without endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petracco, R.; Grechukhina, O.; Popkhadze, S.; Massasa, E.; Zhou, Y.; Taylor, H.S. MicroRNA135 regulates HOXA10 expression in endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1925–E1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudanski, P.; Charkiewicz, R.; Kuzmicki, M.; Szamatowicz, J.; Charkiewicz, A.; Niklinski, J. MicroRNAs expression profiling of eutopic proliferative endometrium in women with ovarian endometriosis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, W. Down regulation of MiR-93 contributes to endometriosis through targeting MMP3 and VEGFA. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Mutlu, L.; Grechukhina, O.; Taylor, H.S. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 1252.e1–1260.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekker, K.; Saare, M.; Roost, A.M.; Kaart, T.; Soritsa, D.; Karro, H.; Soritsa, A.; Simon, C.; Salumets, A.; Peters, M. R. K.; et al. Circulating miR-200-family micro-RNAs have altered plasma levels in patients with endometriosis and vary with blood collection time. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 938.e2–946.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-T.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Han, B.-W.; Hong, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-Q. Circulating microRNAs identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression analysis as noninvasive biomarkers for endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosar, E.; Mamillapalli, R.; Ersoy, G.S.; Cho, S.; Seifer, B.; Taylor, H.S. Serum microRNAs as diagnostic markers of endometriosis: A comprehensive array-based analysis. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.-Z.; Yang, Y.; Lang, J.; Sun, P.; Leng, J. Plasma miR-17-5p, miR-20a and miR-22 are down-regulated in women with endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Tsai, C.-F.; Tsai, H.-P.; Chen, H.-S.; Chang, Y.; Chuang, H.Y.; Lee, J.N.; Hsu, Y.L.; Tsai, E.M. MiRNA-199a-5p regulates VEGFA in endometrial mesenchymal stem cells and contributes to the pathogenesis of endometriosis. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashti, O.; Noruzinia, M.; Garshasbi, M.; Abtahi, M. miR-31 and miR-145 as Potential Non-Invasive Regulatory Biomarkers in Patients with Endometriosis. Cell J. 2018, 20, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ASRM. Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil. Steril. 1997, 67, 817–821. [Google Scholar]
- Wren, J.D.; Wu, Y.; Guo, S.-W. A system-wide analysis of differentially expressed genes in ectopic and eutopic endometrium. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yuan, Y.; Cho, J.-H.; McClarty, S.; Baxter, D.; Galas, D.J. Comparing the MicroRNA spectrum between serum and plasma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Shen, B.; Li, J.; Lv, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, J. Serum microRNA-499 and microRNA-208a as biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fichtlscherer, S.; De Rosa, S.; Fox, H.; Schwietz, T.; Fischer, A.; Liebetrau, C.; Weber, M.; Hamm, C.W.; Roxe, T.; Muller-Ardogan, M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heegaard, N.H.H.; Schetter, A.J.; Welsh, J.A.; Yoneda, M.; Bowman, E.D.; Harris, C.C. Circulating micro-RNA expression profiles in early stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.S.; Milosevic, D.; Reddi, H.V.; Grebe, S.K.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A. Analysis of circulating microRNA: Preanalytical and analytical challenges. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Chen, C.-L.; Ting, T.-T.; Tseng, T.-C.; Chen, P.-J.; Kao, J.-H.; Chen, D.-S. Serum microRNA-122 level correlates with virologic responses to pegylated interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7844–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Shen, Y.; Tian, F.; Lu, J.; Bai, Y.; Lu, Z. Profiling circulating microRNAs in maternal serum and plasma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3323–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, M.B.; Kao, S.C.; Edelman, J.J.; Armstrong, N.J.; Vallely, M.P.; van Zandwijk, N.; Reid, G. Haemolysis during sample preparation alters microRNA content of plasma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saal, S.; Harvey, S.J. MicroRNAs and the kidney: Coming of age. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredni, S.T.; Gadd, S.; Jafari, N.; Huang, C.-C. A Parallel Study of mRNA and microRNA Profiling of Peripheral Blood in Young Adult Women. Front. Genet. 2011, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.S.; Gamazon, E.R.; Ziliak, D.; Wen, Y.; Im, H.K.; Zhang, W.; Wing, C.; Duan, S.; Bleibel, W.K.; Cox, N.J.; et al. Population differences in microRNA expression and biological implications. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, R.; Strulovici-Barel, Y.; Salit, J.; Staudt, M.R.; Ahmed, J.; Tilley, A.E.; Yee-Levin, J.; Hollmann, C.; Harvey, B.; et al. Persistence of smoking-induced dysregulation of miRNA expression in the small airway epithelium despite smoking cessation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameling, S.; Kacprowski, T.; Chilukoti, R.K.; Malsch, C.; Liebscher, V.; Suhre, K.; Pietzner, M.; Friedrich, N.; Homuth, G.; Hammer, E.; et al. Associations of circulating plasma microRNAs with age, body mass index and sex in a population-based study. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyaeva, L.F.; Kushlinskiy, N.E. Regulatory mechanisms of microRNA expression. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Suliman, H.B.; Hollingsworth, J.W.; Piantadosi, C.A. Differential regulation of the PGC family of genes in a mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus sepsis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Faria, O.; Moore, C.S.; Kennedy, T.E.; Antel, J.P.; Bar-Or, A.; Dhaunchak, A.S. MicroRNA dysregulation in multiple sclerosis. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Nerurkar, V.R. Integrated analysis of microRNAs and their disease related targets in the brain of mice infected with West Nile virus. Virology 2014, 452, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.H.; Duroux, M.; Gazerani, P. MicroRNAs as modulators and biomarkers of inflammatory and neuropathic pain conditions. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 71, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. Advances in microRNAs: Implications for immunity and inflammatory diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zondervan, K.T.; Cardon, L.R.; Kennedy, S.H. What makes a good case-control study? Design issues for complex traits such as endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2002, 17, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmae, S.; Martinez-Conejero, J.A.; Esteban, F.J.; Ruiz-Alonso, M.; Stavreus-Evers, A.; Horcajadas, J.A.; et al. MicroRNAs miR-30b, miR-30d, and miR-494 regulate human endometrial receptivity. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 20, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekker, K.; Saare, M.; Roost, A.M.; Salumets, A.; Peters, M. Circulating microRNA Profile throughout the menstrual cycle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabita, F.; de Candia, P.; Torri, A.; Tegnér, J.; Abrignani, S.; Rossi, R.L. Normalization of circulating microRNA expression data obtained by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, M.G.M.; Halliani, A.; Moerland, P.D.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Creemers, E.E.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J. Normalization panels for the reliable quantification of circulating microRNAs by RT-qPCR. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3853–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroh, E.M.; Parkin, R.K.; Mitchell, P.S.; Tewari, M. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods 2010, 50, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltier, H.J.; Latham, G.J. Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: Identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. Rna 2008, 14, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoren, P.A.; McNeill, R.E.; Lowery, A.J.; Kerin, M.J.; Miller, N. Identification of suitable endogenous control genes for microRNA gene expression analysis in human breast cancer. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, R.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, J.; Xie, H.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, X. U6 is not a suitable endogenous control for the quantification of circulating microRNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Torres, K.; Wdowiak, P.; Paszkowski, T.; Maciejewski, R.A.T. Selection and validation of endogenous controls for microRNA expression studies in endometrioid endometrial cancer tissues. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 130, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonini, P.; Plebani, M.; Ceriotti, F.; Rubboli, F. Errors in laboratory medicine. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, N.; Lockwood, C.M. Pre-analytical variables in miRNA analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramon, L.A.; Braza-Boils, A.; Gilabert-Estelles, J.; Gilabert, J.; Espana, F.; Chirivella, M.; Estelles, A. MicroRNAs expression in endometriosis and their relation to angiogenic factors. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, K.-Y.; Lin, S.-C.; Wu, M.-H.; Tsai, S.-J. Pathological functions of hypoxia in endometriosis. Front. Biosci. 2015, 7, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; McGough, R.; Aswad, B.; Block, J.A.; Terek, R. Hypoxia induces HIF-1α and VEGF expression in chondrosarcoma cells and chondrocytes. J. Orthop. Res. 2004, 22, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-H.; Chen, K.-F.; Lin, S.-C.; Lgu, C.-W.; Tsai, S.-J. Aberrant expression of leptin in human endometriotic stromal cells is induced by elevated levels of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.M.; Rohwer, N.; Funakoshi, T.; Cramer, T.; Bernhardt, W.; Birsner, A.; Folkman, J.; D’Amato, R.J. 2-methoxyestradiol inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and suppresses growth of lesions in a mouse model of endometriosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Zou, J.; Li, Y. Effect of oxygen tensions on the proliferation and angiogenesis of endometriosis heterograft in severe combined immunodeficiency mice. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 101, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, D.E.; Berardo, P.T.; Palmero, C.Y.; Nasciutti, L.E. Higher expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor VEGFR-2 (Flk-1) and metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in a rat model of peritoneal endometriosis is similar to cancer diseases. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnez, J.; Smoes, P.; Gillerot, S.; Casanas-Roux, F.; Nisolle, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Wu, M.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Tsai, S.-J. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-20a expression increases ERK phosphorylation and angiogenic gene expression in endometriotic stromal cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1515–E1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosperi, J.R.; Robertson, F.M. Cyclooxygenase-2 directly regulates gene expression of P450 Cyp19 aromatase promoter regions pII, pI.3 and pI.7 and estradiol production in human breast tumor cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2006, 81, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Agarwal, V.R.; Mendelson, C.R.; Simpson, E.R. Estrogen biosynthesis proximal to a breast tumor is stimulated by PGE2 via cyclic AMP, leading to activation of promoter II of the CYP19 (aromatase) gene. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5739–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Tang, Q.; Wu, W.; Xia, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X. miR-20a contributes to endometriosis by regulating NTN4 expression. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5793–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.-X.; Zhou, T. miR20a is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer and is involved in cell metastasis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Nie, Y.; Mi, Q.; Zhao, S. Ovarian tumor-associated microRNA-20a decreases natural killer cell cytotoxicity by downregulating MICA/B expression. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Yao, D.; Chen, J.; Ding, N.; Ren, F. MiR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ding, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, W.; et al. MiR-20a Induces Cell Radioresistance by Activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backes, C.; Meese, E.; Keller, A. Specific miRNA Disease Biomarkers in Blood, Serum and Plasma: Challenges and Prospects. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, S.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Matzuk, M.M. Functional MicroRNA Involved in Endometriosis Results Clinical demographics Endometriomas have dysregulated microRNA expression. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 5, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, S.; Darcha, C. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition-like and mesenchymal to epithelial transition-like processes might be involved in the pathogenesis of pelvic endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetje, R.; Kotzian, S.; Herrmann, G.; Baumann, R.; Starzinski-Powitz, A. Nonmalignant epithelial cells, potentially invasive in human endometriosis, lack the tumor suppressor molecule E-cadherin. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeitvogel, A.; Baumann, R.; Starzinski-Powitz, A. Identification of an invasive, N-cadherin-expressing epithelial cell type in endometriosis using a new cell culture model. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1839–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpal, M.; Lee, E.S.; Hu, G.; Kang, Y. The miR-200 Family Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Cell Migration by Direct Targeting of E-cadherin Transcriptional Repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14910–14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Gu, L.; Di, W. MiR-199a attenuates endometrial stromal cell invasiveness through suppression of the IKKβ/nf-κb pathway and reduced interleukin-8 expression. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 18, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Xue, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.-Y.; Duan, P. The differential expression of microRNA-143,145 in endometriosis. Iran J. Reprod. Med. 2014, 12, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, T.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Sun, S. Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin expression. Hepatology 2009, 50, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.M.; Laufer, M.R.; Stratton, P.; Hummelshoj, L. Foundation Endometriosis Phenome and Biobanking Harmonisation Project: I. Surgical phenotype data collection in endometriosis research. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassbender, A.; Vodolazkaia, A.; Saunders, P.; Lebovic, D.; Waelkens, E.; de Moor, B.; D’Hooghe, T. Biomarkers of endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 99, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmioglu, N.; Fassbender, A.; Vitonis, A.F.; Tworoger, S.S.; Hummelshoj, L.; D’Hooghe, T.M.; Adamson, G.D.; Giudice, L.C.; Becker, C.M.; Zondervan, K.T.; et al. World Endometriosis Research Foundation Endometriosis Phenome and Biobanking Harmonization Project: III. Fluid biospecimen collection, processing, and storage in endometriosis research. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitonis, A.F.; Vincent, K.; Rahmioglu, N.; Fassbender, A.; Buck Louis, G.M.; Hummelshoj, L.; Giudice, L.C.; Stratton, P.; Adamson, G.D.; Becker, C.M.; et al. World Endometriosis Research Foundation Endometriosis Phenome and Biobanking Harmonization Project: II. Clinical and covariate phenotype data collection in endometriosis research. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, O.L.; Melck, A.; Jones, S.J.M.; Wiseman, S.M. Meta-analysis and meta-review of thyroid cancer gene expression profiling studies identifies important diagnostic biomarkers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5043–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interven-Tions; Cochrane Collab John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]






| S. No | Author | Country | Sample Size | Sample Type | Mean Age (Years) | Stage of Endometriosis * in Cases | Characteristics of Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Controls | |||||||
| 1 | Suryavanshi et al. 2013 [31] | USA | Cases-33 Control-20 | Plasma | NA | NA | NA | Healthy women |
| 2 | Jia et al. 2013 [99] | China | Cases-20 Controls-20 | Plasma | 34.1 | 32.1 | III–IV | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| 3 | Wang et al. 2013 [97] | China | Cases-60 Controls-25 | Serum | 34.43 | 30.0 | I–IV | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| 4 | Hsu et al. 2014 [100] | China | Cases-40 Controls-25 | Serum | 34.8 | 37.3 | II–IV | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| 5 | Rekker et al. 2015 [96] | Estonia | Cases-61 Controls-65 | Plasma | 32.5 | 29.7 | I–IV | 35: No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy 30: Healthy |
| 6 | Cho et al. 2015 [95] | USA | Cases-24 Controls-24 | Serum | 33.08 | 32.16 | III–IV | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| 7 | Cosar et al. 2016 [98] | USA and Korea | Cases-24 Controls-24 | Serum | 33.08 | 32.16 | III–IV | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| 8 | Wang et al. 2016 [32] | China | Cases-30 Controls-20 | Serum | 34.0 | 32.5 | I–II | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| 9 | Bashti et al. 2018 [101] | Iran | Cases-55 Controls-23 | Plasma | 28 | 28 | I–IV | No evidence of endometriosis on laparoscopy |
| Methodologic Parameter | Number of Studies (Out of 8 Manuscripts Analysed) |
|---|---|
| Kits used for RNA extraction | |
| mirVana | 5 |
| Trizol | 1 |
| miRNeasy | 1 |
| miRCURY | 2 |
| Real-time PCR technique | |
| SYBR Green | 7 |
| TaqMan | 2 |
| Normalisation control in qPCR | |
| Internal reference | 8 |
| External reference | 1 |
| S. No | Author | Method | Normalisation Control Used in qRT-PCR | Dysregulated miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suryavanshi et al. 2013 [31] | Global miRNA profiling using qRT-PCR followed by validation by qRT-PCR | miR-132 | Up → miR-15b, 16, 191, 195, 362-5p, 1973, 1974, 1978, 1979, 4284 |
| 2 | Jia et al. 2013 [99] | Microarray followed by qRT-PCR | miR-16 | Down → miR-17-5p, 20a-5p, 22 |
| 3 | Wang et al. 2013 [97] | Microarray followed by qRT-PCR | U6 snRNA | Up → miR-122, 199a Down → miR-9-3p, 141-5p, 145-3p, 542-3p |
| 4 | Hsu et al. 2014 [100] | Microarray followed by qRT-PCR | 18s RNA | Down → miR-199a-5p |
| 5 | Rekker et al. 2015 [96] | qRT-PCR | miR-30e, 99a | Down → miR-141-3p, 200a-3p |
| 6 | Cho et al. 2015 [95] | qRT-PCR | U6 snRNA | Down → let-7b, miR-135a, let-7d, 7f |
| 7 | Cosar et al. 2016 [98] | Microarray followed by qRT-PCR | U6 snRNA | Up → miR-18a-5p, 125b-5p, 143-3p, 145-5p, 150-5p, 342-3p, 451a, 500a-3p Down → miR-3613-5p, 6755-3p |
| 8 | Wang et al. 2016 [32] | Solexa sequencing followed by qRT-PCR | cel-miR-39 | Up → miR-185-5p, 424-3p Down → miR-15b-5p, 20a-5p, 30c-5p, 99b-5p, 127-3p |
| 9 | Bashti et al. 2018 [101] | qRT-PCR | miR-103-3p | Up→ miR-145 Down→ miR-31 |
| S. No | Author | miRNA | Cut-Off | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suryavanshi et al. 2013 [31] | miR-16 + miR-191 + miR-195 | NA | 0.90 | 88 | 60 |
| 2 | Jia et al. 2013 [99] | miR-17-5p miR-20a miR-22 miR-17-5p + miR-20a + miR-22 | 0.9057 0.6879 0.5647 NA | 0.74 0.79 0.85 0.90 | 60 60 90 NA | 90 90 80 NA |
| 3 | Wang et al. 2013 [97] | miR-9-3p miR-122 miR-141-5p miR-145 miR-199a miR-542-3p miR-122 + miR-145 + miR-199a + miR-542-3p | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | 0.828 0.835 0.849 0.883 0.825 0.854 0.994 | 68.33 80 71.69 70 78.33 79.66 93.22 | 96 76 96 96 76 92 96 |
| 4 | Hsu et al. 2014 [100] | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 5 | Rekker et al. 2015 [96] | miR-141 miR-200a miR-200b miR-141 + miR-200a + miR-200b | NA NA NA NA | 0.71 0.75 0.67 0.76 | 71.9 90.6 90.6 84.4 | 70.8 62.5 70.8 66.7 |
| 6 | Cho et al. 2015 [95] | let-7d | 0.823 | 0.905 | 83.3 | 100 |
| 7 | Cosar et al. 2016 [98] | miR-125b-5p miR-125b-5p + miR-451a + miR-3613-5p | 0.0688 | 0.974 1 | 100 100 | 96 100 |
| 8 | Wang et al. 2016 [32] | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 9 | Bashti et al. 2018 [101] | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Parameters | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Study Design | Prospective or Retrospective Cohort or Case-Control Design with a Well-Defined Study Population |
| Source | Peer-reviewed journals |
| Language | English |
| Disease | Endometriosis |
| Sample type | Blood, serum or plasma |
| Technique | Microarray, qRT-PCR, NGS, ISH |
| Stage of disease | any |
| Type of endometriosis | any |
| Sample size | ≥20 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agrawal, S.; Tapmeier, T.T.; Rahmioglu, N.; Kirtley, S.; Zondervan, K.T.; Becker, C.M. The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020599
Agrawal S, Tapmeier TT, Rahmioglu N, Kirtley S, Zondervan KT, Becker CM. The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020599
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgrawal, Swati, Thomas T. Tapmeier, Nilufer Rahmioglu, Shona Kirtley, Krina T. Zondervan, and Christian M. Becker. 2018. "The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020599
APA StyleAgrawal, S., Tapmeier, T. T., Rahmioglu, N., Kirtley, S., Zondervan, K. T., & Becker, C. M. (2018). The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020599