Circulating miR-99a-5p Expression in Plasma: A Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
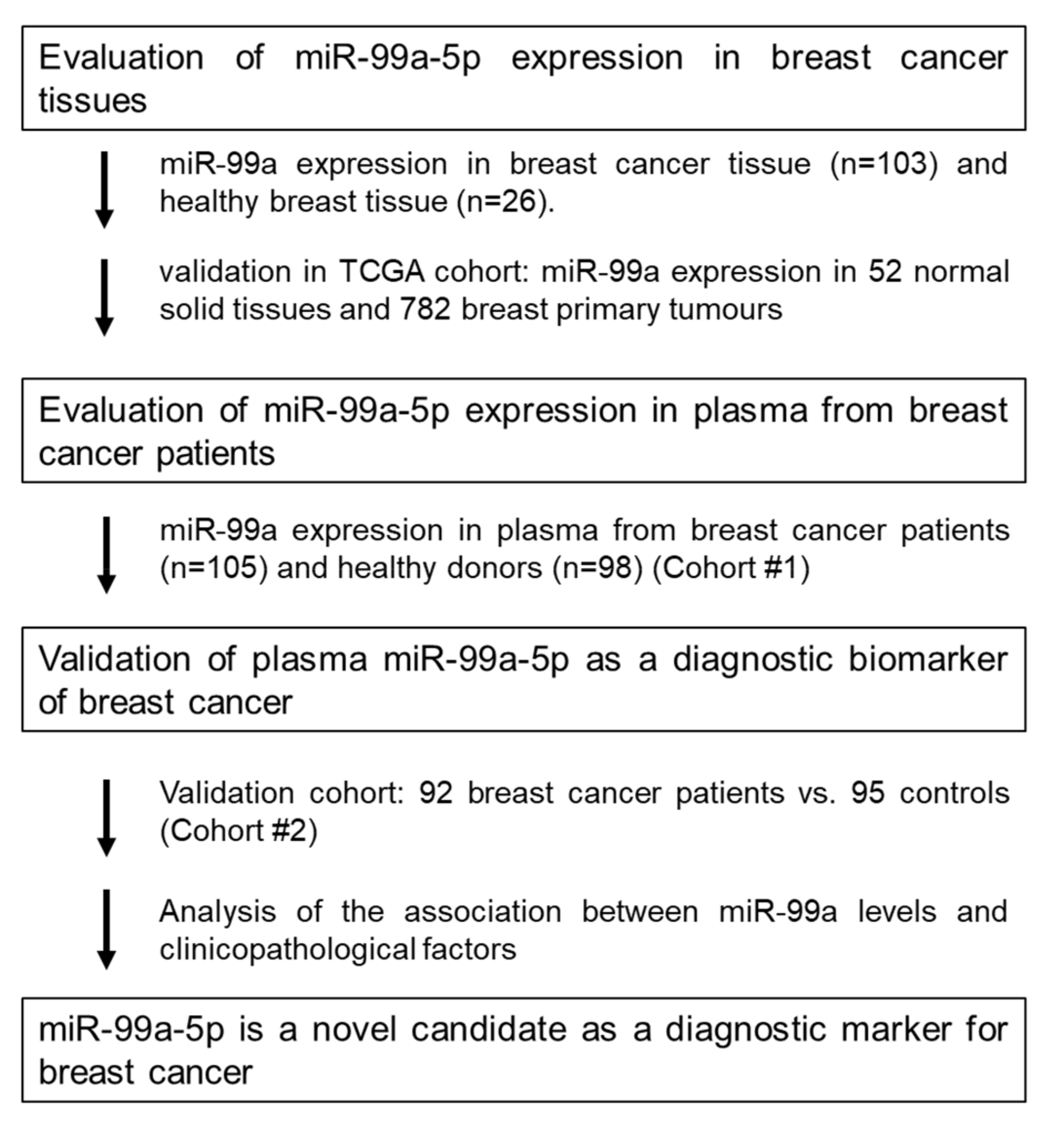
2.1. Study Design to Develop a Novel miRNA Biomarker
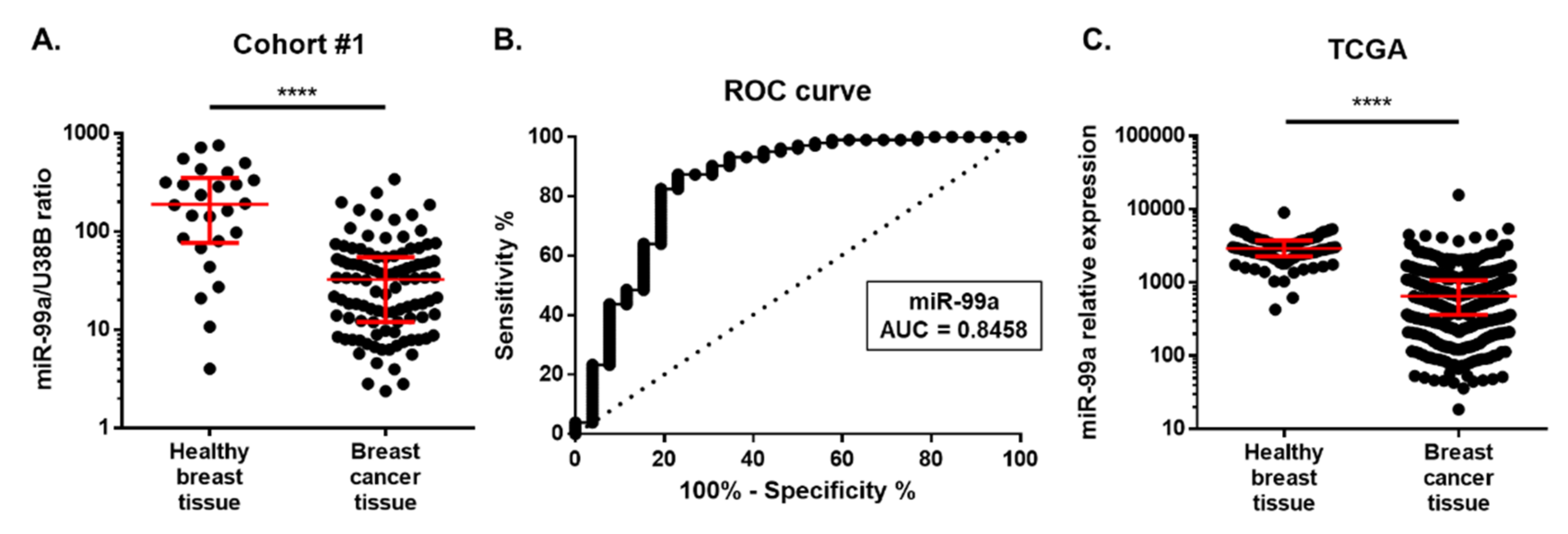
2.2. MiR-99a-5p Expression in Tissue
Cohort #1: Discovery Cohort
2.3. MiR-99a-5p Expression in Plasma
2.3.1. Cohort #2: Testing Cohort
2.3.2. Cohort #3: Validation Cohort
2.4. miR-99a-5p as a Biomarker for Early BC Detection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Samples
4.2. RNA Extraction from Tissue and Plasma
4.3. cDNA Synthesis
4.4. miRNA Expression Analysis
4.5. TCGA Database Validation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Mariotto, A.B.; Rowland, J.H.; Yabroff, K.R.; Alfano, C.M.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.L.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jafari, S.H.; Saadatpour, Z.; Salmaninejad, A.; Momeni, F.; Mokhtari, M.; Nahand, J.S.; Rahmati, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Kianmehr, M. Breast cancer diagnosis: Imaging techniques and biochemical markers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5200–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Kaur, H. Cell-free miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers in breast cancer: Significance in early diagnosis and metastasis prediction. Life Sci. 2020, 246, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.K.O.; Li, R.; Shin, V.Y.; Jin, H.C.; Leung, C.P.H.; Ma, E.S.K.; Pang, R.; Chua, D.; Chu, K.M.; Law, W.L.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Specific Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Detection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamam, R.; Hamam, D.; Alsaleh, K.A.; Kassem, M.; Zaher, W.; Alfayez, M.; Aldahmash, A.; Alajez, N.M. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer: Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottani, M.; Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G. Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Common Solid Tumors: Focus on Lung, Breast, Prostate Cancers, and Osteosarcoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loh, H.Y.; Norman, B.P.; Lai, K.S.; Rahman, N.M.A.N.A.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Osman, M.A. The regulatory role of microRNAs in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortez, M.A.; Welsh, J.J.; Calin, G.A. Circulating MicroRNAs as Noninvasive Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2012, 195, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tormo, E.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Ballester, S.; Pineda, B.; Zazo, S.; González-Alonso, P.; Albanell, J.; Rovira, A.; Rojo, F.; Lluch, A.; et al. The role of miR-26a and miR-30b in HER2+ breast cancer trastuzumab resistance and regulation of the CCNE2 gene. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tormo, E.; Ballester, S.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Burgués, O.; Alonso, E.; Bermejo, B.; Menéndez, S.; Zazo, S.; Madoz-Gúrpide, J.; Rovira, A.; et al. The miRNA-449 family mediates doxorubicin resistance in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating cell cycle factors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; Briant, K.C.O.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, E.K.O.; Chong, W.W.S.; Jin, H.; Lam, E.K.Y.; Shin, V.Y.; Yu, J.; Poon, T.C.W.; Ng, S.S.M.; Sung, J.J.Y. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 2009, 58, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidarra, D.; Constâncio, V.; Barros-Silva, D.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Antunes, L.; Maurício, J.; Oliveira, J.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Detection and Metastasis Development Prediction. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estevão-Pereira, H.; Lobo, J.; Salta, S.; Amorim, M.; Lopes, P.; Cantante, M.; Reis, B.; Antunes, L.; Castro, F.; Palma De Sousa, S.; et al. Overexpression of circulating MiR-30b-5p identifies advanced breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Schooneveld, E.; Wouters, M.C.A.; Van der Auwera, I.; Peeters, D.J.; Wildiers, H.; Van Dam, P.A.; Vergote, I.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y.; Van Laere, S.J. Expression profiling of cancerous and normal breast tissues identifies microRNAs that are differentially expressed in serum from patients with (metastatic) breast cancer and healthy volunteers. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matamala, N.; Vargas, M.T.; González-Cámpora, R.; Miñambres, R.; Arias, J.; Menéndez, P.; Andrés-León, E.; Mez-López, G.G.; Yanowsky, K.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; et al. Tumor MicroRNA expression profiling identifies circulating MicroRNAs for early breast cancer detection. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Kang, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Yang, P.; Yu, Z. MicroRNA-99a acts as a tumor suppressor and is down-regulated in bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, B.; Ishinaga, H.; Midorikawa, K.; Shah, S.A.; Nakamura, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Murata, M.; Takeuchi, K. Circulating microRNAs as novel prognosis biomarkers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Tang, L. MiR-99a Antitumor Activity in Human Breast Cancer Cells through Targeting of mTOR Expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhang, N.; Sun, M.; Huo, Q.; Cai, C.; Lv, S.; Yang, Q. MicroRNA-99a inhibits tumor aggressive phenotypes through regulating HOXA1 in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32737–32747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, H.; Liu, W. MicroRNA-99a-5p suppresses breast cancer progression and cell-cycle pathway through downregulating CDC25A. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, H.; Seki, N.; Kurozumi, S.; Shinden, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Nohata, N.; Moriya, S.; Idichi, T.; Maemura, K.; Fujii, T.; et al. RNA-sequence-based microRNA expression signature in breast cancer: Tumor-suppressive miR-101-5p regulates molecular pathogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, M.; Li, H.; Wang, J.-J.; Zeng, H.-J.; Wang, S.-H. MiR-99a suppress proliferation, migration and invasion through regulating insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Turcatel, G.; Rubin, N.; El-Hashash, A.; Warburton, D. MIR-99a and MIR-99b Modulate TGF-β Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Plasticity in Normal Murine Mammary Gland Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Shi, Y.; Ye, P.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, Y. MicroRNA-99a Suppresses Breast Cancer Progression by Targeting FGFR3. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, S.; Liu, H.; Gao, B.; Wei, W.; Yang, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. MiR-155, miR-96 and miR-99a as potential diagnostic and prognostic tools for the clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Tong, D.; Zhang, S.; Cai, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L.; Chang, S.; Guo, B.; Song, T.; et al. miRNA-99b-3p functions as a potential tumor suppressor by targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3β in oral squamous cell carcinoma Tca-8113 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Torres, K.; Pesci, A.; Ceccaroni, M.; Paszkowski, T.; Cassandrini, P.; Zamboni, G.; Maciejewski, R. Deregulation of miR-100, miR-99a and miR-199b in tissues and plasma coexists with increased expression of mTOR kinase in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Y. miR-99a suppresses the metastasis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting AKT1 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-G.; Luo, X.; Wu, S.; Jian, B. MiR-99a inhibits cell proliferation and tumorigenesis through targeting mTOR in human anaplastic thyroid cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2015, 16, 4937–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Liu, X.; Lin, L.; Hou, J.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, W.; et al. MicroRNA-99a Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Correlates with Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36677–36685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Oikawa, K.; Takanashi, M.; Kudo, M.; Ohyashiki, J.; Ohyashiki, K.; Kuroda, M. Down-regulation of miR-92 in human plasma is a novel marker for acute leukemia patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuk, K.; Zucknick, M.; Heil, J.; Madhavan, D.; Schott, S.; Turchinovich, A.; Arlt, D.; Rath, M.; Sohn, C.; Benner, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Liaw, C.S.; Ji, S.M.; Tan, H.H.; Wong, C.Y.; Thike, A.A.; Tan, P.H.; Ho, G.H.; Lee, A.S.G. Identification of circulating microRNA signatures for breast cancer detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4477–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pigati, L.; Yaddanapudi, S.C.S.; Iyengar, R.; Kim, D.J.; Hearn, S.A.; Danforth, D.; Hastings, M.L.; Duelli, D.M. Selective release of MicroRNA species from normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Z.J.J.; Wang, Y.Y.Y.; Yin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Nan, X. Low levels of serum miR-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Liang, J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Xing, S.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Huang, L.; et al. Identification and validation of circulating microRNA signatures for breascancer early detection based on large scale tissue-derived data. J. Breast Cancer 2018, 21, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heegaard, N.H.H.; Schetter, A.J.; Welsh, J.A.; Yoneda, M.; Bowman, E.D.; Harris, C.C. Circulating microRNA expression profiles in early stage non- small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, T.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W.; Ding, Q.; Wang, S. Circulating microRNAs from the miR-106a–363 cluster on chromosome X as novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schisterman, E.F.; Perkins, N.J.; Liu, A.; Bondell, H. Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden index to discriminate individuals using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Tissue Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer Patients | Controls | ||
| Number | 103 | 26 | |
| Median age, years (range) | 59.7 (57–62) | 54.6 (47–63) | |
| Molecular subtype, n (%) | |||
| Luminal | 59 (57.3%) | n.a. | |
| TNBC | 30 (29.1%) | ||
| Her 2 | 14 (13.6%) | ||
| Grade group, n (%) | |||
| 1 | 9 (8.7%) | n.a. | |
| 2 | 36 (35%) | ||
| 3 | 46 (44.7%) | ||
| Unknown | 12 (11.6%) | ||
| Stage, n (%) | |||
| I | 12 (11.7%) | n.a. | |
| II | 63 (61.2%) | ||
| III | 13 (12.6%) | ||
| Unknown | 15 (14.6%) | ||
| Pathological T stage, n (%) | |||
| pT1 | 24 (23.3%) | n.a. | |
| pT2 | 57 (55.3%) | ||
| pT3 | 6 (5.8%) | ||
| pT4 | 1 (1%) | ||
| Unknown | 15 (14.6%) | ||
| Regional lymph node metastasis, n (%) | |||
| No | 39 (37.9%) | n.a. | |
| Yes | 50 (48.5%) | ||
| Unknown | 14 (13.6) | ||
| Distant metastasis, n (%) | |||
| No | 89 (86.4%) | n.a. | |
| Yes | 0 (0%) | ||
| Unknown | 14 (13.6%) | ||
| TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; n.a., not applicable | |||
| Number (%) | Median (95% CI) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histological subtype, n (%) | ||||
| Luminal | 59 (57.3%) | 27.00 (31.25–55.26) | 0.9783 | |
| TNBC | 30 (29.1%) | 33.65 (25.62–44.83) | ||
| Her 2-enriched | 14 (13.6%) | 18.51 (8.64–93.79) | ||
| Unknown | n.a. | |||
| Grade group, n (%) | ||||
| 1 | 9 (8.7%) | 38.76 (9.45–110.10) | 0.7869 | |
| 2 | 36 (35.0%) | 18.18 (25.27–56.10) | ||
| 3 | 46 (44.7%) | 32.33 (25.31–57.65) | ||
| Unknown | 12 (11.6%) | |||
| Stage | ||||
| Early (I and II) | 75 (72.8%) | 21.38 (29.78–54.31) | 0.8250 | |
| Late (III and IV) | 13 (12.6%) | 35.87 (19.85–43.36) | ||
| Unknown | 15 (14.6%) | |||
| Pathological T stage, n (%) | ||||
| pT1 | 24 (23.3%) | 23.40 (18.43–52.7) | 0.687 | |
| pT2 | 57 (55.3%) | 23.05 (28.32–48.89) | ||
| pT3 | 6 (5.8%) | 24.57 (-61.25–213.1) | ||
| pT4 | 1 (1%) | 54.97 | ||
| Unknown | 15 (14.6%) | |||
| Regional lymph node metastasis, n (%) | ||||
| No | 39 (37.9%) | 18.51 (23.08–64.21) | 0.6279 | |
| Yes | 50 (48.5%) | 33.90 (28.52–49.03) | ||
| Unknown | 14 (13.6) | |||
| TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; n.a., not applicable | ||||
| Plasma Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort #2 | Cohort #3 | |||
| Breast Cancer Patients | Controls | Breast Cancer Patients | Controls | |
| Number | 105 | 98 | 89 | 85 |
| Median age, years (range) | 52 (29–82) | 50 (40–64) | 54.1(32–92) | 55 (32–90) |
| Histological subtype, n (%) | ||||
| Luminal | 92 (87.6%) | n.a. | 54 (60.7%) | n.a. |
| TNBC | 7 (6.7%) | 15 (16.9%) | ||
| Her 2-enriched | 5 (4.8%) | 18 (20.2%) | ||
| Unknown | 1 (1%) | 2 (2.2%) | ||
| Grade group, n (%) | ||||
| 1 | 8 (7.6%) | n.a. | 19 (21.3%) | n.a. |
| 2 | 54 (51.4%) | 44 (49.4%) | ||
| 3 | 39 (37.1%) | 25 (28.1%) | ||
| Unknown | 4 (3.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | ||
| Stage, n (%) | ||||
| I | 42 (40%) | n.a. | 24 (27.0%) | n.a. |
| II | 18 (17.1%) | 41 (46.1%) | ||
| III | 32 (30.5%) | 15 (16.3%) | ||
| IV | 13 (12.4%) | 5 (5.4%) | ||
| Unknown | 4 (4.3%) | |||
| Pathological T stage, n (%) | ||||
| pT1 | 46 (43.8%) | n.a. | 36 (40.4%) | n.a. |
| pT2 | 29 (27.6%) | 37 (41.6%) | ||
| pT3 | 18 (17.1%) | 9 (10.1%) | ||
| pT4 | 10 (9.5%) | 1 (1.1%) | ||
| Unknown | 2 (1.9%) | 6 (6.7%) | ||
| Regional lymph node metastasis, n (%) | ||||
| No | 53 (50.5%) | n.a. | 47 (52.8%) | n.a. |
| Yes | 50 (47.6%) | 36 (40.4%) | ||
| Unknown | 2 (1.9%) | 6 (6.7%) | ||
| Distant metastasis, n (%) | ||||
| No | 92 (87.6%) | n.a. | 80 (89.9%) | n.a. |
| Yes | 13 (12.4%) | 7 (7.9%) | ||
| Unknown | 2 (2.2%) | |||
| TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; n.a., not applicable | ||||
| Number (%) | Median (95% CI) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histological subtype, n (%) | ||||
| Luminal | 146 (75.3%) | 24.42 (16.00–36.14) | 0.0590 | |
| TNBC | 22 (11.3%) | 9.50 (3.46–33.22) | ||
| Her 2-enriched | 23 (11.9%) | 29.93 (13.53–89.41) | ||
| Unknown | 3 (1.5%) | |||
| Grade group, n (%) | ||||
| 1 | 27 (13.9%) | 14.86 (5.61–36.9) | 0.4594 | |
| 2 | 98 (50.5%) | 28.29 (18.05–44.09) | ||
| 3 | 64 (33.0%) | 18.06 (12.88–36.14) | ||
| Unknown | 5 (2.6%) | |||
| Stage | ||||
| Early (I and II) | 125 (64.4%) | 24.26 (15.98–36.90) | 0.2382 | |
| Late (III and IV) | 65 (33.5%) | 21.02 (12.08–35.81) | ||
| Unknown | 4 (2.1%) | |||
| Pathological T stage, n (%) | ||||
| pT1 | 82 (42.3%) | 24.23 (15.98–38.61) | 0.4119 | |
| pT2 | 66 (34.0%) | 27.26 (12.91–44.91) | ||
| pT3 | 27 (13.9%) | 10.99 (3.54–49.49) | ||
| pT4 | 11 (5.6%) | 35.81 (5.34–48.45) | ||
| Unknown | 8 (4.1%) | |||
| Regional lymph node metastasis, n (%) | ||||
| No | 100 (51.5%) | 24.23 (15.98–38.61) | 0.3232 | |
| Yes | 86 (44.3%) | 19.54 (12.91–35.84) | ||
| Unknown | 8 (4.1%) | |||
| Distant metastasis, n (%) | ||||
| No | 172 (88.7%) | 20.03 (15.18–29.70) | 0.1810 | |
| Yes | 20 (10.3%) | 35.82 (16.2–91.99) | ||
| Unknown | 2 (1.0%) | |||
| TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; n.a., not applicable | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrido-Cano, I.; Constâncio, V.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Lameirinhas, A.; Simón, S.; Ortega, B.; Martínez, M.T.; Hernando, C.; Bermejo, B.; Lluch, A.; et al. Circulating miR-99a-5p Expression in Plasma: A Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197427
Garrido-Cano I, Constâncio V, Adam-Artigues A, Lameirinhas A, Simón S, Ortega B, Martínez MT, Hernando C, Bermejo B, Lluch A, et al. Circulating miR-99a-5p Expression in Plasma: A Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197427
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrido-Cano, Iris, Vera Constâncio, Anna Adam-Artigues, Ana Lameirinhas, Soraya Simón, Belen Ortega, María Teresa Martínez, Cristina Hernando, Begoña Bermejo, Ana Lluch, and et al. 2020. "Circulating miR-99a-5p Expression in Plasma: A Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197427






