Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Recognising Fatigue as a Clinical Outcome
3. The Role of Disease Activity
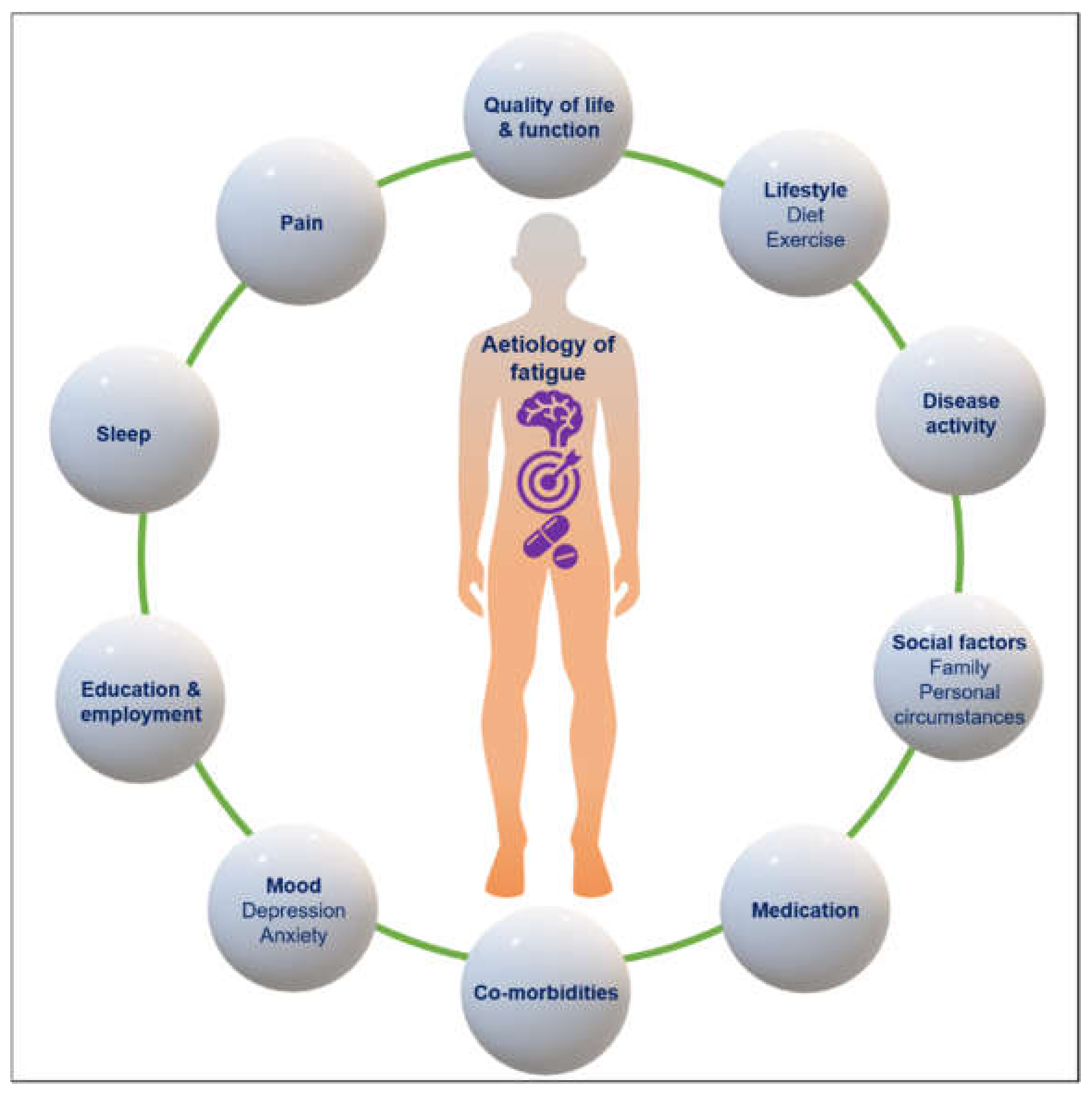
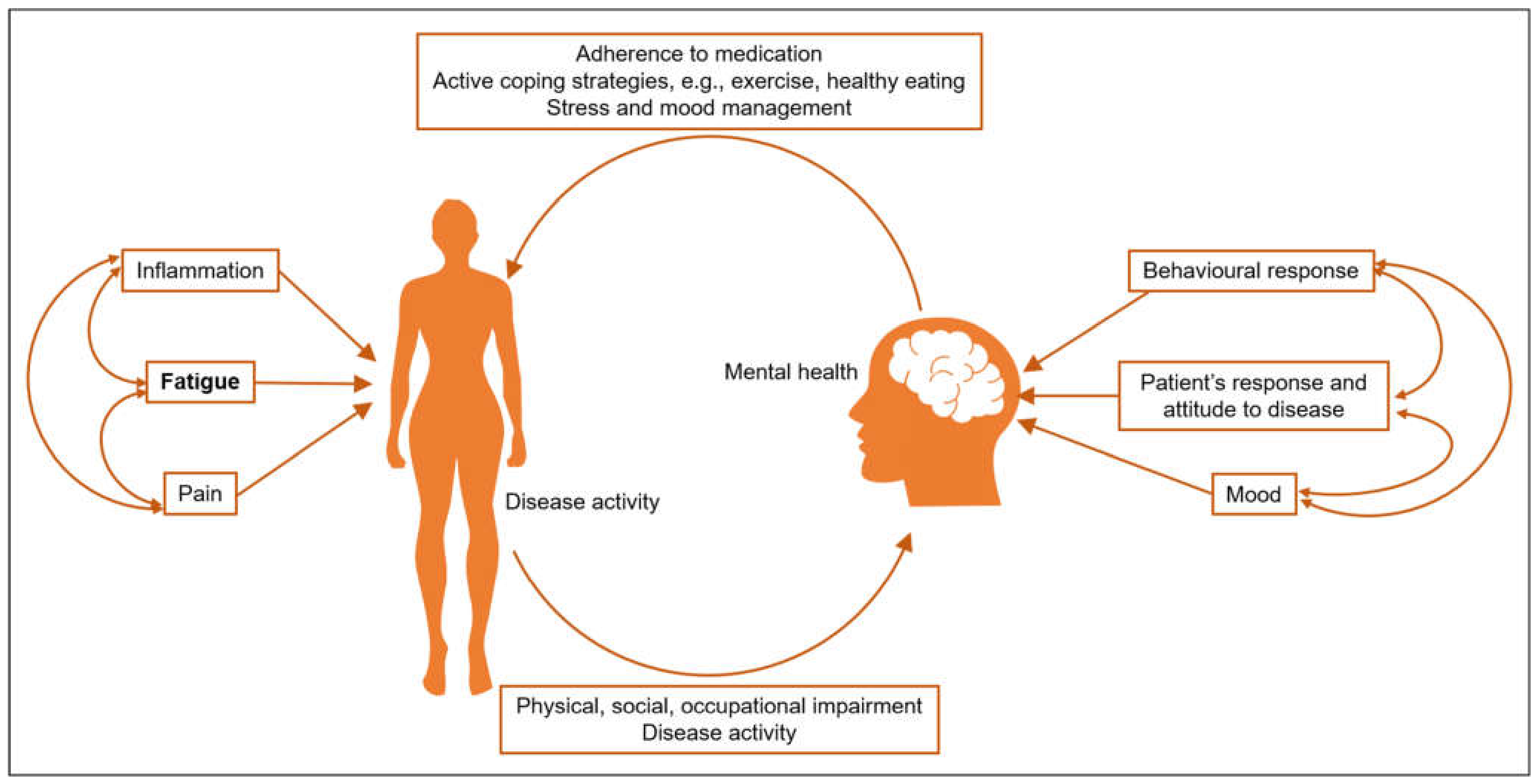
4. Mechanisms of Fatigue and Association with Other Symptoms
5. Measures of Fatigue
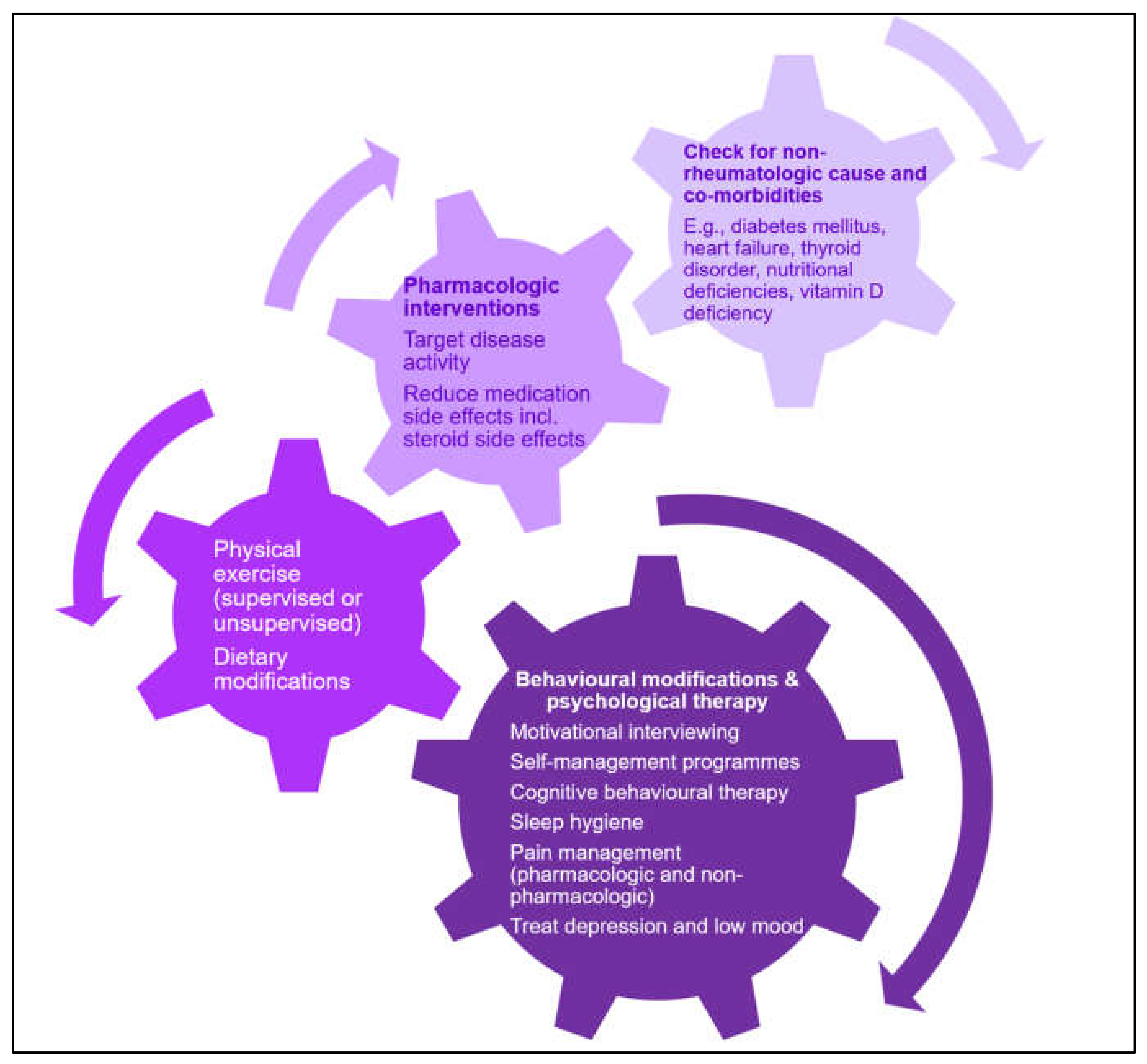
6. Management of Fatigue
7. Conclusions and Future Research Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharpe, M.; Wilks, D. Fatigue. BMJ 2002, 325, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevalence|Background Information|Tiredness/Fatigue in Adults|CKS|NICE. Available online: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/tiredness-fatigue-in-adults/background-information/prevalence/ (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- McAteer, A.; Elliott, A.M.; Hannaford, P.C. Ascertaining the size of the symptom iceberg in a UK-wide community-based survey. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2011, 61, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, F.; Hawley, D.J.; Wilson, K. The prevalence and meaning of fatigue in rheumatic disease. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Mertz, P.; Schlencker, A.; Schneider, M.; Gavand, P.E.; Martin, T.; Arnaud, L. Towards a practical management of fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2020, 7, e000441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleanthous, S.; Tyagi, M.; Isenberg, D.A.; Newman, S.P. What do we know about self-reported fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus? Lupus 2012, 21, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Gavand, P.E.; Voll, R.; Schwarting, A.; Maurier, F.; Blaison, G.; Magy-Bertrand, N.; Pennaforte, J.L.; Peter, H.H.; Kieffer, P.; et al. Predictors of fatigue and severe fatigue in a large international cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and a systematic review of the literature. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, I.K.; Raselli, C.; Stöcklin, M.; Opwis, K.; Kappos, L.; Calabrese, P. The Fatigue Scale for Motor and Cognitive Functions (FSMC): Validation of a new instrument to assess multiple sclerosis-related fatigue. Mult. Scler. J. 2009, 15, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druce, K.L.; Basu, N. Predictors of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, v29–v34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horisberger, A.; Courvoisier, D.; Ribi, C. The Fatigue Assessment Scale as a simple and reliable tool in systemic lupus erythematosus: A cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, P. Causes and consequences of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.J.; Vielhauer, V. Renal co-morbidity in patients with rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziade, N.; El Khoury, B.; Zoghbi, M.; Merheb, G.; Abi Karam, G.; Mroue, K.; Missaykeh, J. Prevalence and pattern of comorbidities in chronic rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: The COMORD study. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.H.; Dures, E. Fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, v1–v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.; Heiberg, T.; Hewlett, S.; Hughes, R.; Kvien, T.; Ahlmèn, M.; Boers, M.; Minnock, P.; Saag, K.; Shea, B.; et al. Outcomes from the Patient Perspective Workshop at OMERACT 6. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, J.R.; Fries, J.F.; Hewlett, S.; Osborne, R.H. Patient perspective: Choosing or developing instruments. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 1716–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, S.; Cockshott, Z.; Byron, M.; Kitchen, K.; Tipler, S.; Pope, D.; Hehir, M. Patients’ perceptions of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: Overwhelming, uncontrollable, ignored. Arthritis Care Res. 2005, 53, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaus, S.; Bode, C.; Taal, E.; van de Laar, M.A.F.J. New insights into the experience of fatigue among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A qualitative study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, R.; Sagez, F.; Gavand, P.-E.; Martin, T.; Korganow, A.-S.; Sordet, C.; Javier, R.M.; Soulas-Sprauel, P.; Rivière, M.; Scher, F.; et al. 10 most important contemporary challenges in the management of S.L.E. Lupus Sci. Med. 2019, 6, e000303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, P. Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2017, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazmino, S.; Lovik, A.; Boonen, A.; de Cock, D.; Stouten, V.; Joly, J.; Bertrand, D.; Van Der Elst, K.; Westhovens, R.; Verschueren, P. Does including pain, fatigue, and physical function when assessing patients with early rheumatoid arthritis provide a comprehensive picture of disease burden? J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Radner, H.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Desthieux, C.; Zabalan, C.; van Eijk-Hustings, Y.; Dixon, W.G.; Hyrich, K.L.; Askling, J.; Gossec, L. Patient global assessment in measuring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: A review of the literature. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norden, D.M.; Bicer, S.; Clark, Y.; Jing, R.; Henry, C.J.; Wold, L.E.; Reiser, P.J.; Godbout, J.P.; McCarthy, D.O. Tumor growth increases neuroinflammation, fatigue and depressive-like behavior prior to alterations in muscle function. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 43, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bluthé, R.M.; Beaudu, C.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. Differential effects of IL-1ra on sickness behavior and weight loss induced by IL-1 in rats. Brain Res. 1995, 677, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, K.; Berenbaum, F. Fatigue in chronic inflammation-a link to pain pathways. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergman, M.J.; Shahouri, S.S.; Shaver, T.S.; Anderson, J.D.; Weidensaul, D.N.; Busch, R.E.; Wang, S.; Wolfe, F. Is fatigue an inflammatory variable in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Analyses of fatigue in ra, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2788–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groth Madsen, S.; Danneskiold-Samsøe, B.; Stockmarr, A.; Bartels, E.M. Correlations between fatigue and disease duration, disease activity, and pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Steenbergen, H.W.; Tsonaka, R.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Boonen, A.; Van Der Helm-Van Mil, A.H.M. Fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis; A persistent problem: A large longitudinal study. RMD Open 2015, 1, e000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matthijssen, X.M.E.; Wouters, F.; Sidhu, N.; Van Der Helm-Van Mil, A.H.M. Value of imaging detected joint inflammation in explaining fatigue in RA at diagnosis and during the disease course: A large MRI study. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, P.I.; Alarcón, G.S.; McGwin, G.; Crews, K.Q.; Reveille, J.D.; Vilá, L.M. Disease activity and damage are not associated with increased levels of fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus patients from a multiethnic cohort: LXVII. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azizoddin, D.R.; Gandhi, N.; Weinberg, S.; Sengupta, M.; Nicassio, P.M.; Jolly, M. Fatigue in systemic lupus: The role of disease activity and its correlates. Lupus 2019, 28, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, V.; Levy, R.A.; Cervera, R.; Petri, M.A.; Birch, H.; Freimuth, W.W.; Zhong, Z.J.; Clarke, A.E. Improvements in health-related quality of life with belimumab, a B-lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, in patients with autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus from the randomised controlled BLISS trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Sjöwall, C.; Jönsen, A.; Ramsköld, D.; Zickert, A.; Frodlund, M.; Sohrabian, A.; Arnaud, L.; Rönnelid, J.; Malmström, V.; et al. Smoking and pre-existing organ damage reduce the efficacy of belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parodis, I.; Benavides, A.L.; Zickert, A.; Pettersson, S.; Möller, S.; Henriksson, E.W.; Voss, A.; Gunnarsson, I. The Impact of Belimumab and Rituximab on Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Qiu, V.; Cederlund, A.; Borg, A.; Lindblom, J.; Emamikia, S.; Enman, Y.; Lampa, J.; Parodis, I. Adverse Health-Related Quality of Life Outcome Despite Adequate Clinical Response to Treatment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 651249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzami, M.; Strand, V.; Su, J.; Touma, Z. Dual trajectories of fatigue and disease activity in an inception cohort of adults with systemic lupus erythematosus over 10 years. Lupus 2021, 30, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, F.H.A.; Freitas, M.V.C.; de Bruin, V.M.S.; de Bruin, P.F.C. Depressive symptoms are associated with impaired sleep, fatigue, and disease activity in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Rheumatol. 2021, 61, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, B.A.; Stallknecht, S.E.; Madsen, M.E.; Hagelund, L.; Pilgaard, T. Correlations of fatigue in Danish patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgeon, J.A.; Finan, P.H.; Zautra, A.J. Affective disturbance in rheumatoid arthritis: Psychological and disease-related pathways. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dietz, B.; Katz, P.; Dall’Era, M.; Murphy, L.B.; Lanata, C.; Trupin, L.; Criswell, L.A.; Yazdany, J. Major Depression and Adverse Patient-Reported Outcomes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results From a Prospective Longitudinal Cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HQIP. National Early Inflammatory Arthritis Audit (NEIAA) 1st Annual Report; HQIP: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Harrold, L.R.; Shan, Y.; Rebello, S.; Kramer, N.; Connolly, S.E.; Alemao, E.; Kelly, S.; Kremer, J.M.; Rosenstein, E.D. Prevalence of Sjögren’s syndrome associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the USA: An observational study from the Corrona registry. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasoto, S.G.; de Oliveira Martins, V.A.; Bonfa, E. Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: Links and risks. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2019, 11, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, L.H.; Miyamoto, S.T.; Giovelli, R.A.; de Magalhães, C.I.M.; Valim, V. Pain and fatigue are predictors of quality of life in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Adv. Rheumatol. 2021, 61, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carsons, S.E.; Vivino, F.B.; Parke, A.; Carteron, N.; Sankar, V.; Brasington, R.; Brennan, M.T.; Ehlers, W.; Fox, R.; Scofield, H.; et al. Treatment Guidelines for Rheumatologic Manifestations of Sjögren’s Syndrome: Use of Biologic Agents, Management of Fatigue, and Inflammatory Musculoskeletal Pain. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsokos, G.C. Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Nixon, D.G.D.; Palmer, J.; Lightfoot, C.J.; Smith, A.C. Differences in physical symptoms between those with and without kidney disease: A comparative study across disease stages in a UK population. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, L.P.; Jain, N.; Carmody, T.; Minhajuddin, A.T.; Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Hedayati, S.S. Fatigue in Nondialysis Chronic Kidney Disease: Correlates and Association with Kidney Outcomes. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Carrara, G.; Sakellariou, G.; Caporali, R.; Hmamouchi, I.; Dougados, M.; Montecucco, C. Cardiovascular comorbidities relate more than others with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofat, N.; Malik, O.; Higgens, C.S. Neurological involvement in patients with rheumatic disease. QJM 2006, 99, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atzeni, F.; Talotta, R.; Masala, I.F.; Gerardi, M.C.; Casale, R.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Central nervous system involvement in rheumatoid arthritis patients and the potential implications of using biological agents. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraclough, M.; McKie, S.; Parker, B.; Jackson, A.; Pemberton, P.; Elliott, R.; Bruce, I.N. Altered cognitive function in systemic lupus erythematosus and associations with inflammation and functional and structural brain changes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.S.; Hutcheson, J.; Mohan, C. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackay, M. Lupus brain fog: A biologic perspective on cognitive impairment, depression, and fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2015, 63, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harboe, E.; Greve, O.J.; Beyer, M.; Gøransson, L.G.; Tjensvoll, A.B.; Maroni, S.; Omdal, R. Fatigue is associated with cerebral white matter hyperintensities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, B.; Boneschi, F.M.; Rossi, P.; Rovaris, M.; Maderna, L.; Filippi, M.; Comi, G. MRI and motor evoked potential findings in nondisabled multiple sclerosis patients with and without symptoms of fatigue. J. Neurol. 2000, 247, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Barberà, I.; Salman-Monte, T.C.; Castell, S.; Castro, F.; Ojeda, F.; Carbonell, J. Prevalence and factors associated with fatigue in female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Med. Clin. 2018, 151, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøn, K.L.; Ørnbjerg, L.M.; Hetland, M.L.; Aslam, F.; Khan, N.A.; Jacobs, J.W.G. The association of fatigue, comorbidity burden, disease activity, disability and gross domestic product in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results from 34 countries participating in the Quest-RA programme. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Butrus, F.H.; Johansson, P.; Åkerström, E.; Soukka, S.; Emamikia, S.; Enman, Y.; Pettersson, S.; Parodis, I. Impact of overweight and obesity on patient-reported health-related quality of life in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Landewe, R.; Karonitsch, T.; Bathon, J.; Boers, M.; Bombardier, C.; Choi, H.; Combe, B.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P. Reporting disease activity in clinical trials of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: EULAR/ACR collaborative recommendations. Arthritis Care Res. 2008, 59, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, S.; Hehir, M.; Kirwan, J.R. Measuring fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review of scales in use. Arthritis Care Res. 2007, 57, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, J.E. Management of Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.O.; Gutierrez, A.K.; Butanis, A.; Bykerk, V.P.; Curtis, J.R.; Leong, A.; Lyddiatt, A.; Nowell, W.B.; Orbai, A.M.; Bartlett, S.J. PROMIS Fatigue short forms are reliable and valid in adults with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Patient Rep. Outcomes 2019, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bingham, C.O.; Butanis, A.L.; Orbai, A.M.; Jones, M.; Ruffing, V.; Lyddiatt, A.; Schrandt, M.S.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cook, K.F.; Bartlett, S.J. Patients and clinicians define symptom levels and meaningful change for PROMIS pain interference and fatigue in RA using bookmarking. Rheumatology 2021, keab014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, J.L.; Davis, E.S.; Curtis, J.R.; Cella, D.; Yun, H. Meaningful Change Thresholds for Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Fatigue and Pain Interference Scores in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 200990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, S.; Dures, E.; Almeida, C. Measures of fatigue: Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Multi-Dimensional Questionnaire (BRAF MDQ), Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Numerical Rating Scales (BRAF NRS) for Severity, Effect, and Coping, Chalder Fatigue Questionnaire (CFQ), Checklist Individual Strength (CIS20R and CIS8R), Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS), Functional Assessment Chronic Illness Therapy (Fatigue) (FACIT-F), Multi-Dimensional Assessment of Fatigue (MAF), Multi-Dimensional Fatigue Inventory (MFI), Pediatric Quality Of Life (PedsQL) Multi-Dimensional Fatigue Scale, Profile of Fatigue (ProF), Short Form 36 Vitality Subscale (SF-36 VT), and Visual Analog Scales (VAS). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. 11), S263–S286. [Google Scholar]
- Druce, K.L.; Bhattacharya, Y.; Jones, G.T.; Macfarlane, G.J.; Basu, N. Most patients who reach disease remission following anti-TNF therapy continue to report fatigue: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choy, E.H. Effect of biologics and targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs on fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, v51–v55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Choy, E.H.S.; Hewlett, S.; Kirwan, J.R.; Cramp, F.; Chalder, T.; Pollock, J.; Christensen, R. Biologic interventions for fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD008334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keystone, E.C.; Taylor, P.C.; Tanaka, Y.; Gaich, C.; Delozier, A.M.; Dudek, A.; Zamora, J.V.; Cobos, J.A.C.; Rooney, T.; de Bono, S.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a phase 3 study of baricitinib versus placebo or adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis: Secondary analyses from the RA-BEAM study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, P.; Blanco, R.; Maldonado Cocco, J.; Chen, Y.C.; Gaich, C.L.; Delozier, A.M.; de Bono, S.; Liu, J.; Rooney, T.; Chang, C.H.C.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a phase III study of baricitinib in patients with conventional synthetic DMARD-refractory rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Kremer, J.M.; Gaich, C.L.; Delozier, A.M.; Schlichting, D.E.; Xie, L.; Stoykov, I.; Rooney, T.; Bird, P.; Bursón, J.M.S.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a randomised phase III study of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to biological agents (RA-BEACON). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Fleischmann, R.; Gaich, C.L.; DeLozier, A.M.; Schlichting, D.; Kuo, W.L.; Won, J.E.; Carmack, T.; Rooney, T.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and no or limited prior disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hope, H.F.; Hyrich, K.L.; Anderson, J.; Bluett, J.; Sergeant, J.C.; Barton, A.; Cordingley, L.; Verstappen, S.M. The predictors of and reasons for non-adherence in an observational cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis commencing methotrexate. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayden, C.; Neame, R.; Tarrant, C. Patients’ adherence-related beliefs about methotrexate: A qualitative study of the role of written patient information. BMJ Open 2015, 5, 6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Santos, E.J.F.; Marques, A.; Böhm, P.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Daien, C.I.; Esbensen, B.A.; Ferreira, R.J.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Holmes, P.; et al. 2021 EULAR recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021. Available online: http://ard.bmj.com/ (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Cramp, F.; Hewlett, S.; Almeida, C.; Kirwan, J.R.; Choy, E.H.S.; Chalder, T.; Pollock, J.; Christensen, R. Non-pharmacological interventions for fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD008322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewlett, S.; Ambler, N.; Almeida, C.; Cliss, A.; Hammond, A.; Kitchen, K.; Knops, B.; Pope, D.; Spears, M.; Swinkels, A.; et al. Self-management of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: A randomised controlled trial of group cognitive-behavioural therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangtham, M.; Kasturi, S.; Bannuru, R.R.; Nash, J.L.; Wang, C. Non-pharmacologic therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2019, 28, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Tektonidou, M.G. Long-term outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus: Trends over time and major contributors. Rheumatology 2020, 59 (Suppl. 5), v29–v38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhoff, G.; Rau, R.; Zink, A. Rheumatoid arthritis patients who smoke have a higher need for DMARDs and feel worse, but they do not have more joint damage than non-smokers of the same serological group. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chasset, F.; Francès, C.; Barete, S.; Amoura, Z.; Arnaud, L. Influence of smoking on the efficacy of antimalarials in cutaneous lupus: A meta-analysis of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.; Baraniuk, M.D. Chronic fatigue syndrome (Myalgic encephalomyelitis)-Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. BMJ Best Pract. 2021, 5, 121. [Google Scholar]
| SLE and RA | RA Only | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS) | 9-item scale covering psychosocial and cognitive aspects of fatigue. Originally developed for use in multiple sclerosis and SLE. | Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Multi-Dimensional Questionnaire | 20-item scale assessing the experience and impact fatigue, giving an overall score comprising 4 subscale scores (physical fatigue, living with fatigue, cognitive fatigue, emotional fatigue). |
| Multi-dimensional Fatigue Inventory (MFI) | 20-item scale comprising 5 domains: general fatigue, physical fatigue, mental fatigue, reduced motivation, reduced activity. Significant fatigue is defined depending on age and gender. | Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Numeric Rating scales | 3 scales, scored 0–10: severity (no fatigue–totally exhausted), effect (no effect–a great deal of effect), coping (not at all well–very well). |
| Visual analogue scale to evaluate fatigue severity (VAS-F) | 18-item scale based on subjective experience of fatigue, using fatigue and energy subscales | Checklist of Individual Strength (CIS20) | 20-item scale giving overall score comprising 4 sub-scores (subjective fatigue, concentration, motivation, physical activity levels). |
| Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Fatigue (FACIT-Fatigue) | 13-item questionnaire on self-reported aspects of physical, mental and functional fatigue, and effect of these on daily living. | Fatigue Severity Inventory | 11-item scale comprising 2 scores: 6 items rating average fatigue in past week, on days with most and least fatigue, number of days with fatigue, duration of fatigue each day and current fatigue levels; 5-item fatigue interference scale. |
| Multidimensional Assessment of Fatigue (MAF) | 15-item scale comprising 4 aspects of fatigue (severity, distress, ability to undertake activities of daily living, frequency and change during previous week). | ||
| Profile of Mood States (POMS) | 7-item scale, focussing mainly on mood plus cognitive components and overwhelming fatigue. | ||
| SF-36 (36-Item Short Form Survey) | 4-item score, 2 on energy and 2 on fatigue. | ||
| Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Fatigue scales | Scale ranging from subjective feelings of tiredness to overwhelming exhaustion impacting activities of daily living. | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dey, M.; Parodis, I.; Nikiphorou, E. Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163566
Dey M, Parodis I, Nikiphorou E. Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163566
Chicago/Turabian StyleDey, Mrinalini, Ioannis Parodis, and Elena Nikiphorou. 2021. "Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163566
APA StyleDey, M., Parodis, I., & Nikiphorou, E. (2021). Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163566








