Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Resveratrol and HE
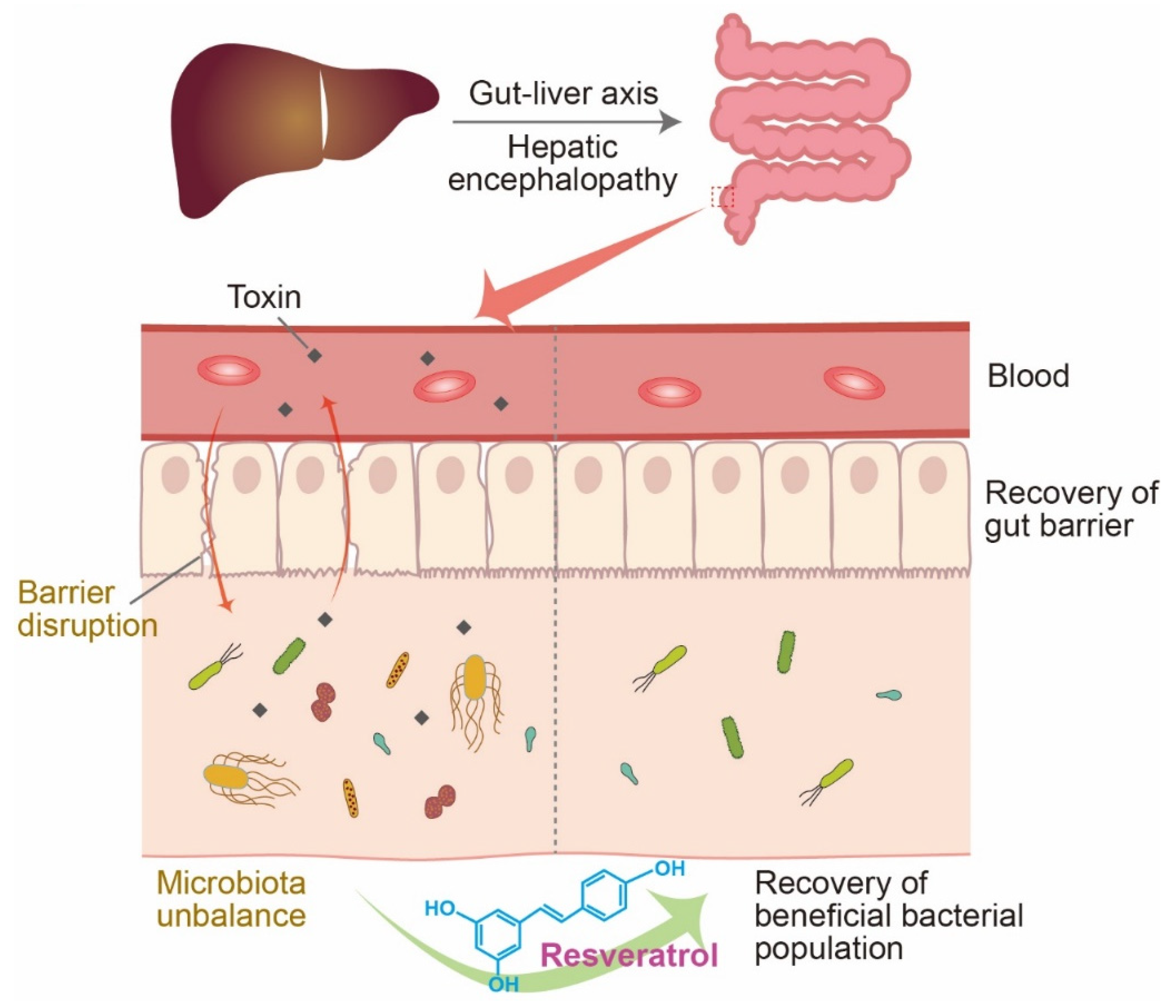
3. Resveratrol and the Microbiome in HE
4. Resveratrol and Brain Edema in HE
5. Resveratrol and Ammonia-Induced Neuroinflammation in HE
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajaj, J.S. Hepatic encephalopathy: Classification and treatment. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 838–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, K.R.; Bajaj, J.S. Covert and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy: Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elsaid, M.I.; Rustgi, V.K. Epidemiology of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, S.; Russo, F.P.; Amodio, P.; Burra, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Loguercio, C.; Marchesini, G.; Merli, M.; Ponziani, F.R.; Riggio, O.; et al. Hepatic encephalopathy 2018: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanny, B.; Winters, A.; Boutros, S.; Saab, S. Hepatic Encephalopathy Challenges, Burden, and Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheis, G.; Wettstein, M.; Timmermann, L.; Schnitzler, A.; Häussinger, D. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2002, 35, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Butz, M.; Baumgarten, T.J.; Füllenbach, N.-D.; Jördens, M.S.; Häussinger, D.; Schnitzler, A.; Lange, J. Impaired Tactile Temporal Discrimination in Patients With Hepatic Encephalopathy. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Wartchow, K.M.; Flores, M.P.; Leite, M.C.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Gonçalves, C.-A. Ammonia-induced oxidative damage in neurons is prevented by resveratrol and lipoic acid with participation of heme oxygenase 1. NeuroToxicology 2015, 49, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussinger, D.; Butz, M.; Schnitzler, A.; Görg, B. Pathomechanisms in hepatic encephalopathy. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S. Review article: The modern management of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O.; Ridola, L.; Pasquale, C.; Pentassuglio, I.; Nardelli, S.; Moscucci, F.; Merli, M.; Montagnese, S.; Amodio, P.; Merkel, C. A Simplified Psychometric Evaluation for the Diagnosis of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 613–616.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.; Sinclair, D. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizzo, A.; Forte, M.; Damato, A.; Trimarco, V.; Salzano, F.; Bartolo, M.; Maciag, A.; Puca, A.A.; Vecchione, C. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in cardiovascular, cerebral and metabolic diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Švajger, U.; Jeras, M. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Resveratrol and Its Potential Use in Therapy of Immune-mediated Diseases. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 31, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Bertino, G.; Gagliano, C.; Malaguarnera, M.; Bella, R.; Borzì, A.M.; Madeddu, R.; Drago, F.; Malaguarnera, G. Resveratrol in Hepatitis C Patients Treated with Pegylated-Interferon-α-2b and Ribavirin Reduces Sleep Disturbance. Nutrients 2017, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Truong, V.-L.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.-S. Role of resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against oxidative stress. BioFactors 2017, 44, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, M.T.; Smith, B.; Denu, J.M. Mechanism of Human SIRT1 Activation by Resveratrol. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17187–17195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, V.; Nestler, E.J. The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 2008, 455, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Gan, L.; Vosler, P.S.; Gao, Y.; Zigmond, M.J.; Chen, J. Protective effects and mechanisms of sirtuins in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 95, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denissova, N.G.; Nasello, C.M.; Yeung, P.L.; Tischfield, J.; Brenneman, M.A. Resveratrol protects mouse embryonic stem cells from ionizing radiation by accelerating recovery from DNA strand breakage. Carcinogenesis 2011, 33, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agbele, A.T.; Fasoro, O.J.; Fabamise, O.M.; Oluyide, O.O.; Idolor, O.R.; Bamise, E.A. Protection Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Normal Tissue Damage by Resveratrol: A Systematic Review. Eurasian J. Med. 2020, 52, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Pinzon, M.A.; Koronowski, K. Sirt1 in cerebral ischemia. Brain Circ. 2015, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramadori, G.; Lee, C.E.; Bookout, A.L.; Lee, S.; Williams, K.; Anderson, J.; Elmquist, J.K.; Coppari, R. Brain SIRT1: Anatomical Distribution and Regulation by Energy Availability. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9989–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, G.; Gatfield, D.; Stratmann, M.; Reinke, H.; Dibner, C.; Kreppel, F.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Alt, F.W.; Schibler, U. SIRT1 Regulates Circadian Clock Gene Expression through PER2 Deacetylation. Cell 2008, 134, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, A.; Anamika; Chakraborty, S.; Tripathi, S.J.; Acharjee, A.; Bs, S.R.; Trigun, S.K. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol reverses atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons and neurobehavioral impairments in moderate grade hepatic encephalopathy rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 106, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.W.; Li, S. Resveratrol, pterostilbene, and dementia. Biofactors 2018, 44, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Beidler, J.; Hong, M.Y. Resveratrol and Depression in Animal Models: A Systematic Review of the Biological Mechanisms. Molecules 2018, 23, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virgili, M.; Contestabile, A. Partial neuroprotection of in vivo excitotoxic brain damage by chronic administration of the red wine antioxidant agent, trans-resveratrol in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 281, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Simonyi, A.; Lubahn, D.; Sun, G.Y.; Sun, A.Y. Resveratrol protects against global cerebral ischemic injury in gerbils. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Han, H.; Cao, P.; Yu, W.; Yang, C.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, W. Resveratrol improves neuron protection and functional recovery through enhancement of autophagy after spinal cord injury in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 4607–4616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michán, S.; Li, Y.; Chou, M.M.-H.; Parrella, E.; Ge, H.; Long, J.M.; Allard, J.S.; Lewis, K.; Miller, M.; Xu, W.; et al. SIRT1 Is Essential for Normal Cognitive Function and Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9695–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G. SIRT1 Regulates Cognitive Performance and Ability of Learning and Memory in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Models. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Rahimi, R.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M. Effect of resveratrol on cognitive and memory performance and mood: A meta-analysis of 225 patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, W.; Kelly, J.; Marshall, S.; Cutajar, J.; Annois, B.; Pipingas, A.; Tierney, A.; Itsiopoulos, C. Effect of resveratrol supplementation on cognitive performance and mood in adults: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, F.; Poljak, A.; Liu, Y.; Lo, J.W.; Crawford, J.D.; Sachdev, P.S. Resveratrol: A “miracle” drug in neuropsychiatry or a cognitive enhancer for mice only? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 65, 101199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P. Hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 5, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijdicks, E.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Jalan, R.; Thabut, M. Understanding hepatic encephalopathy. Intensiv. Care Med. 2017, 44, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poordad, F.F. Review article: The burden of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.Y.; Bajaj, J.S. Advances in the Evaluation and Management of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 13, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipo, V.; Urios, A.; Montesinos, E.; Molina, I.; Garcia-Torres, M.L.; Civera, M.; Olmo, J.A.D.; Ortega, J.; Martinez-Valls, J.; Serra, M.A.; et al. Contribution of hyperammonemia and inflammatory factors to cognitive impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2011, 27, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawcross, D.L.; Shabbir, S.S.; Taylor, N.J.; Hughes, R.D. Ammonia and the neutrophil in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawhney, R.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Rosselli, M.; Mookerjee, R.; Agarwal, B.; Jalan, R. Role of ammonia, inflammation, and cerebral oxygenation in brain dysfunction of acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Liver Transplant. 2016, 22, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albrecht, J.; Jones, E. Hepatic encephalopathy: Molecular mechanisms underlying the clinical syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 170, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón, I.D.; Angulo-Cruz, I.; Sánchez-Abdon, L.; Patricio-Martínez, A. Disturbance of the Glutamate-Glutamine Cycle, Secondary to Hepatic Damage, Compromises Memory Function. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 578922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.G.; Córdoba, J. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: The brain. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2011, 17, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Faff, L. Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions in Hyperammonemia and Hepatic Encephalopathy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1994, 368, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. Neuron-Astrocyte Interactions: Partnership for Normal Function and Disease in the Central Nervous System. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, J.H.; Yamamoto, S.; Steers, J.; Sevlever, D.; Lin, W.; Shimojima, N.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Genco, P.; Golde, T.; Richelson, E.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to brain extravasation and edema in fulminant hepatic failure mice. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauli, O.; López–Larrubia, P.; Rodrigo, R.; Agusti, A.; Boix, J.; Nieto–Charques, L.; Cerdán, S.; Felipo, V. Brain Region-Selective Mechanisms Contribute to the Progression of Cerebral Alterations in Acute Liver Failure in Rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Song, H.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.-X.; Cui, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Tumour necrosis factor-α affects blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction-associated occludin in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godichaud, S.; Krisa, S.; Couronné, B.; Dubuisson, L.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Desmoulière, A.; Rosenbaum, J. Deactivation of cultured human liver myofibroblasts byTrans-resveratrol, a grapevine-derived polyphenol. Hepatology 2000, 31, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, J.; Chen, L.-L.; Xiao, F.-X.; Sun, H.; Ding, H.-C.; Xiao, H. Resveratrol improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, I.C.; Martins, L.A.M.; Coelho, B.P.; Grivicich, I.; Guaragna, R.M.; Gottfried, C.; Borojevic, R.; Guma, F.C.R. Resveratrol inhibits cell growth by inducing cell cycle arrest in activated hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 315, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Chong, S.A.; Nam, M.J. Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human SK-HEP-1 hepatic cancer cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2009, 6, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.-H.; Ootsuki, Y.; Fujita, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Yie, Q.; Tsutsui, K.; Sano, K.; Masuoka, N.; Ogino, K. Resveratrol Inhibited Hydroquinone-Induced Cytotoxicity in Mouse Primary Hepatocytes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiolo, J.A.; Mithieux, G.; Vega, F.V. Resveratrol protects primary rat hepatocytes against oxidative stress damage: Activation of the Nrf2 transcription factor and augmented activities of antioxidant enzymes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallis, J.-L.; Serhan, N.; Gin, H.; Couzigou, P.; Beauvieux, M.-C. Resveratrol plus ethanol counteract the ethanol-induced impairment of energy metabolism: 31P NMR study of ATP and sn-glycerol-3-phosphate on isolated and perfused rat liver. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-L.; Yu, L.; Pan, C.-E.; Jiao, X.-Y.; Lv, Y.; Fu, J.; Meng, K.-W. Apoptosis of lymphocytes in allograft in a rat liver transplantation model induced by resveratrol. Pharmacol. Res. 2006, 54, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.A.; Robich, M.P.; Chu, L.M.; Bianchi, C.; Sellke, F.W. Improving glucose metabolism with resveratrol in a swine model of metabolic syndrome through alteration of signaling pathways in the liver and skeletal muscle. Arch. Surg. 2011, 146, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farghali, H.; Černý, D.; Kameníková, L.; Martínek, J.; Horinek, A.; Kmoníčková, E.; Zídek, Z. Resveratrol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatitis in d-galactosamine sensitized rats: Role of nitric oxide synthase 2 and heme oxygenase-1. Nitric Oxide 2009, 21, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-C.; Cheng, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Lee, F.-Y. The protective role of natural phytoalexin resveratrol on inflammation, fibrosis and regeneration in cholestatic liver injury. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebai, H.; Sani, M.; Yacoubi, M.T.; Aouani, E.; Ghanem-Boughanmi, N.; Ben-Attia, M. Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in rat liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacPherson, A.J.; Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D. Immune responses that adapt the intestinal mucosa to commensal intestinal bacteria. Immunology 2005, 115, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Are We Really Vastly Outnumbered? Revisiting the Ratio of Bacterial to Host Cells in Humans. Cell 2016, 164, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suk, K.T.; Kim, D.J. Gut microbiota: Novel therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C.; Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; et al. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.-J.; Wu, E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ubeda, C.; Djukovic, A.; Isaac, S. Roles of the intestinal microbiota in pathogen protection. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, W. The Molecular and Mechanistic Insights Based on Gut–Liver Axis: Nutritional Target for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, N.; Guo, J.; Qian, G.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Xu, M.; Yang, F.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; et al. Functional gene arrays-based analysis of fecal microbiomes in patients with liver cirrhosis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukui, H. Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Martin-Mateos, R.; Shah, V.H. Gut–liver axis, cirrhosis and portal hypertension: The chicken and the egg. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 12, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Berberine protects acute liver failure in mice through inhibiting inflammation and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 819, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J.; Plummer, N.T. Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Integr. Med. Encinitas Calif. 2014, 13, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, H. Role of Gut Dysbiosis in Liver Diseases: What Have We Learned So Far? Diseases 2019, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quigley, E.M.; Stanton, C.; Murphy, E.F. The gut microbiota and the liver. Pathophysiological and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2012, 58, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tandon, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Bacterial Infections, Sepsis, and Multiorgan Failure in Cirrhosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 026–042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Ridlon, J.M.; Heuman, D.M.; Daita, K.; White, M.B.; Monteith, P.; Noble, N.A.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Colonic mucosal microbiome differs from stool microbiome in cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy and is linked to cognition and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G675–G685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lei, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, L. Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Salzman, N.H.; Acharya, C.; Sterling, R.K.; White, M.B.; Gavis, E.A.; Fagan, A.; Hayward, M.; Holtz, M.L.; Matherly, S.; et al. Fecal Microbial Transplant Capsules Are Safe in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Phase 1, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessione, E. Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: Lights and shadows. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhiman, R.K.; Rana, B.; Agrawal, S.; Garg, A.; Chopra, M.; Thumburu, K.K.; Khattri, A.; Malhotra, S.; Duseja, A.; Chawla, Y.K. Probiotic VSL#3 Reduces Liver Disease Severity and Hospitalization in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1327–1337.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sanyal, A.J.; Puri, P.; Sterling, R.K.; Luketic, V.; Stravitz, R.T.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Fuchs, M.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Lactobacillus GG modulates gut microbiome, metabolome and endotoxemia in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ling, Z. Role of probiotics in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with HBV-induced liver cirrhosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidot, H.; Cvejic, E.; Finegan, L.J.; Shores, E.A.; Bowen, D.G.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; Carey, S.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Shackel, N.A. Supplementation with Synbiotics and/or Branched Chain Amino Acids in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Pilot Randomised Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poh, Z.; Chang, P.E. A Current Review of the Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Wade, J.B.; Heuman, D.M.; Hammeke, T.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Stravitz, R.T.; Luketic, V.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Puri, P.; et al. Enhancement of functional connectivity, working memory and inhibitory control on multi-modal brain MR imaging with Rifaximin in Cirrhosis: Implications for the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Duan, Z.P.; Ha, D.K.; Bengmark, S.; Kurtovic, J.; Riordan, S.M. Synbiotic modulation of gut flora: Effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.-T.; Ye, X.-L.; Li, R.-R.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yong, H.-J.; Pan, M.-L.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Miao, H.; et al. Resveratrol Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Protect Against Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. Targeting the gut microbiota with resveratrol: A demonstration of novel evidence for the management of hepatic steatosis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 81, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Shu, L.; Xing, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, C.; Song, G. Effect of resveratrol on intestinal tight junction proteins and the gut microbiome in high-fat diet-fed insulin resistant mice. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hou, P.; Zhou, M.; Ren, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Hui, S.; Yi, L.; Mi, M. Resveratrol attenuates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by maintaining gut barrier integrity and inhibiting gut inflammation through regulation of the endocannabinoid system. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 39, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Liang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Resveratrol-induced gut microbiota reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 44, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bémeur, C.; Cudalbu, C.; Dam, G.; Thrane, A.S.; Cooper, A.J.L.; Rose, C.F. Brain edema: A valid endpoint for measuring hepatic encephalopathy? Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C. Brain edema in acute liver failure and chronic liver disease: Similarities and differences. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norenberg, M.D.; Rao, K.V.R.; Jayakumar, A.R. Mechanisms of Ammonia-Induced Astrocyte Swelling. Metab. Brain Dis. 2005, 20, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francesca, B.; Rezzani, R. Aquaporin and Blood Brain Barrier. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin water channels in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thrane, A.S.; Thrane, V.R.; Nedergaard, M. Drowning stars: Reassessing the role of astrocytes in brain edema. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Aquaporin-4 in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007, 22, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Rao, K.R.; Murthy, C.; Norenberg, M. Glutamine in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solenov, E.; Watanabe, H.; Manley, G.T.; Verkman, A.S. Sevenfold-reduced osmotic water permeability in primary astrocyte cultures from AQP-4-deficient mice, measured by a fluorescence quenching method. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2004, 286, C426–C432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 Gene Disruption in Mice Reduces Brain Swelling and Mortality in Pneumococcal Meningitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13906–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, T.R.; Kronsten, V.T.; Hughes, R.D.; Shawcross, D.L. Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 9240–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Brain edema in acute liver failure: Mechanisms and concepts. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Verkman, A.; Curtis, K.; Norenberg, M.D. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces encephalopathy and brain edema in experimental acute liver failure. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 63, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayakumar, A.; Bethea, J.; Tong, X.; Gomez, J.; Norenberg, M. NF-κB in the mechanism of brain edema in acute liver failure: Studies in transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Changlin, H.; Tan, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Gui, Y.; Qin, L.; Deng, F.; Yuejiang, G.; Hu, C.; et al. Resveratrol ameliorates oxidative stress and inhibits aquaporin 4 expression following rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7756–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgos, I.M.A.; Ortiz-Plata, A.; Franco-Pérez, J.; Millán, A.; Aguilera, P. Resveratrol reduces cerebral edema through inhibition of de novo SUR1 expression induced after focal ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 330, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Jin, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Mo, H.; Chen, G. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol reduces brain edema and neuronal apoptosis in an experimental rat subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9627–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, D.; Li, X.; Ding, D.; Xu, H. Reperfusion combined with intraarterial administration of resveratrol-loaded nanoparticles improved cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 28, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherian, M.; Norenberg, M.D.; Panickar, K.S.; Shamaladevi, N.; Ahmad, A.; Rahman, P.; Jayakumar, A.R. Additive Effect of Resveratrol on Astrocyte Swelling Post-exposure to Ammonia, Ischemia and Trauma In Vitro. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, G.F.; Liebetrau, M.; Martens, H.; Burggraf, D.; Kloss, C.U.A.; Bültemeier, G.; Wunderlich, N.; Jäger, G.; Pfefferkorn, T. Microvascular Basal Lamina Injury after Experimental Focal Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion in the Rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 22, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagaoka, I.; Hirota, S. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in neutrophils in glycogen-induced peritoneal inflammation of guinea pigs. Inflamm. Res. 2000, 49, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Patnaik, R.; Bhattacharya, P.; Shukla, S.C.; Paul, S. Resveratrol inhibits matrix metalloproteinases to attenuate neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia: A molecular docking study exploring possible neuroprotection. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, S.; Zhen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lei, X.; Lv, J.; Xiong, L.; Xue, R. Resveratrol Attenuates the Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Regulation of the MMP-9/TIMP-1 Balance after Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion in Rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 55, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Z.; Rong, X.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Neuroprotection of Resveratrol Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice Through a Mechanism Targeting Gut-Brain Axis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Gao, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Li, F. New insights into mechanism for the effect of resveratrol preconditioning against cerebral ischemic stroke: Possible role of matrix metalloprotease-9. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Peng, Y.; Huang, W.; Cheng, G.; Song, L. Resveratrol reduces the elevated level of MMP-9 induced by cerebral ischemia–reperfusion in mice. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2564–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.; Yan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, J.; Tong, F.; Ma, Q. Combined Ischemic Preconditioning and Resveratrol Improved Bloodbrain Barrier Breakdown via Hippo/YAP/TAZ Signaling Pathway. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 18, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, T. Resveratrol decreases the insoluble Aβ1–42 level in hippocampus and protects the integrity of the blood–brain barrier in AD rats. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairappan, B.; Sundhar, M.; Srinivas, B.H. Resveratrol Restores Neuronal Tight Junction Proteins Through Correction of Ammonia and Inflammation in CCl4-Induced Cirrhotic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 4718–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.S.; Norenberg, M.D. Effect of ammonia on GABA uptake and release in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 36, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Rao, K.R.; Murthy, C.; Panickar, K.; Jayakumar, A.; Norenberg, M. Ammonia induces the mitochondrial permeability transition in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 66, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.M.; Rao, K.V.R.; Brahmbhatt, M.; Norenberg, M.D. Interaction between cytokines and ammonia in the mitochondrial permeability transition in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Kafitz, K.W.; Roderigo, C.; Rose, C.R. Ammonium-evoked alterations in intracellular sodium and pH reduce glial glutamate transport activity. Glia 2009, 57, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Guerra, M.C.; Leite, M.C.; Souza, D.O.; Gonçalves, C.-A.; Gottfried, C. Resveratrol Prevents Ammonia Toxicity in Astroglial Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skowrońska, M.; Albrecht, J. Oxidative and nitrosative stress in ammonia neurotoxicity. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C.F. Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 2008, 24, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northrop, N.A.; Halpin, L.E.; Yamamoto, B.K. Peripheral ammonia and blood brain barrier structure and function after methamphetamine. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Hao, D.; Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T.; Su, Y. Internal ammonium excess induces ROS-mediated reactions and causes carbon scarcity in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klejman, A.; Węgrzynowicz, M.; Szatmari, E.M.; Mioduszewska, B.; Hetman, M.; Albrecht, J. Mechanisms of ammonia-induced cell death in rat cortical neurons: Roles of NMDA receptors and glutathione. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.; Leke, R.; Bak, L.K. Effects of hyperammonemia on brain energy metabolism: Controversial findings in vivo and in vitro. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, K.; Aoyama, M.; Fujita, M.; Sobue, K.; Asai, K. Prolonged exposure to ammonia increases extracellular glutamate in cultured rat astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 462, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görg, B.; Qvartskhava, N.; Keitel, V.; Bidmon, H.J.; Selbach, O.; Schliess, F.; Häussinger, D. Ammonia induces RNA oxidation in cultured astrocytes and brainin vivo. Hepatology 2008, 48, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, R.; Cauli, O.; Gomez–Pinedo, U.; Agusti, A.; Hernandez–Rabaza, V.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Felipo, V. Hyperammonemia Induces Neuroinflammation That Contributes to Cognitive Impairment in Rats With Hepatic Encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenko, E.; Venediktova, N.; Kaminsky, Y.; Montoliu, C.; Felipo, V. Sources of oxygen radicals in brain in acute ammonia intoxication in vivo. Brain Res. 2003, 981, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RamaRao, K.; Jayakumar, A.; Norenberg, M.; Rao, K.R. Role of oxidative stress in the ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability transition in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhosis: Pathology and Pathophysiology. Drugs 2019, 79, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aitbaev, K.A.; Murkamilov, I.T.; Fomin, V.V. Liver diseases: The pathogenetic role of the gut microbiome and the potential of treatment for its modulation. Terapevticheskii 2017, 89, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedik, E.; Girgin, S.; Ozturk, H.; Obay, B.D.; Ozturk, H.; Buyukbayram, H. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress and histological alterations induced by liver ischemia/reperfusion in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 7101–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan-Khabbar, S.; Vamy, M.; Cottart, C.-H.; Wendum, D.; Vibert, F.; Savouret, J.-F.; Thérond, P.; Clot, J.-P.; Waligora, A.-J.; Nivet-Antoine, V. Protective effect of post-ischemic treatment with trans-resveratrol on cytokine production and neutrophil recruitment by rat liver. Biochimie 2010, 92, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Souza, D.; Gonçalves, C.-A.; Quincozes-Santos, A. Resveratrol prevents ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular redox imbalance in C6 astroglial cells. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 21, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Hansel, G.; Scherer, E.B.; Wyse, A.T.; Souza, D.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Gonçalves, C.-A. Ammonia impairs glutamatergic communication in astroglial cells: Protective role of resveratrol. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Andreazza, A.C.; Nardin, P.; Funchal, C.; Gonçalves, C.-A.; Gottfried, C. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative-induced DNA damage in C6 Glioma cells. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, X. Regulators in the DNA damage response. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 594, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaky, A.; Mohammad, B.; Moftah, M.; Kandeel, K.M.; Bassiouny, A.R. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a key modulator of aluminum-induced neuroinflammation. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, N.; Gomes, A.P.; Ling, A.J.; Duarte, F.V.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; North, B.J.; Agarwal, B.; Ye, L.; Ramadori, G.; Teodoro, J.; et al. SIRT1 Is Required for AMPK Activation and the Beneficial Effects of Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Function. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muriel, P.; Espinoza, Y.R. Beneficial drugs for liver diseases. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, L.; Zahn, D.; Gieseler, R.K.; Fingas, C.D.; Marquitan, G.; Jochum, C.; Gerken, G.; Friedman, S.L.; Canbay, A. Resveratrol amplifies profibrogenic effects of free fatty acids on human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodotou, M.; Fokianos, K.; Moniatis, D.; Kadlenic, R.; Chrysikou, A.; Aristotelous, A.; Mouzouridou, A.; Diakides, J.; Stavrou, E. Effect of resveratrol on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malaguarnera, G.; Pennisi, M.; Bertino, G.; Motta, M.; Borzì, A.M.; Vicari, E.; Bella, R.; Drago, F.; Malaguarnera, M. Resveratrol in Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samuel, V.P.; Gupta, G.; Dahiya, R.; Jain, D.A.; Mishra, A.; Dua, K. Current Update on Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Resveratrol, a Naturally Occurring Phenolic Compound. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2019, 29, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-K.; Song, J. Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819
Kim Y-K, Song J. Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Kook, and Juhyun Song. 2021. "Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819
APA StyleKim, Y.-K., & Song, J. (2021). Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819






