Management of the Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Current Guidance, Controversies, and Recent Advances
Abstract
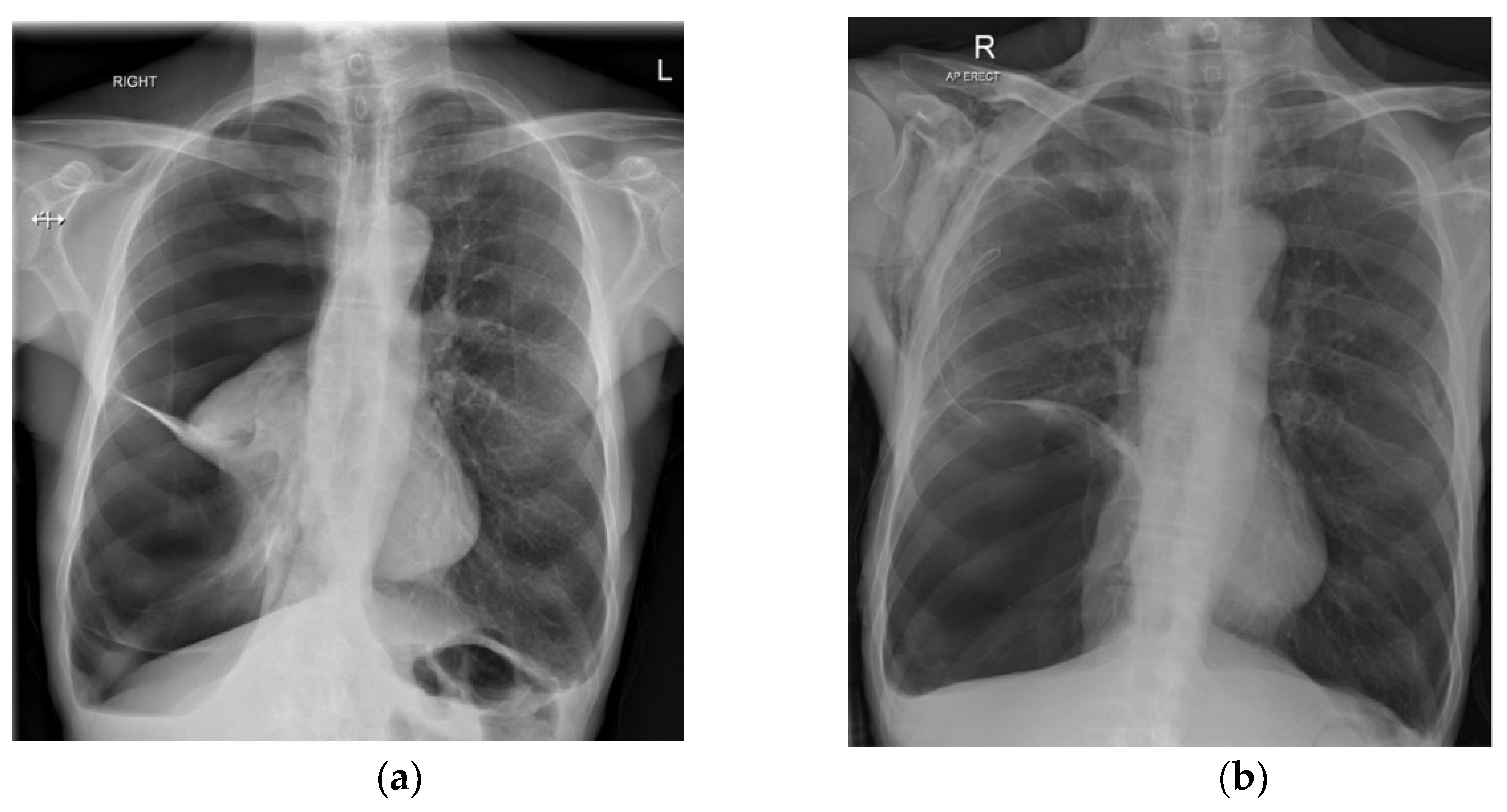
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Management of Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax
2.1. Current Management Guidelines
- Conservative inpatient management if the SSP is <1 cm at the hilum.
- 14–16 gauge needle aspiration (NA) and admission for observation if the SSP is 1–2 cm at the hilum.
- <14-French chest tube drainage (CTD) if the patient is unstable, breathless, if the pneumothorax is >2 cm at the hilum, or >1 cm at the hilum after an attempted aspiration.
2.2. Initial Management: Needle Aspiration [NA] vs. Chest Tube Drainage [CTD]
2.3. Conservative Management
2.4. Ambulatory Management
2.5. Management Options for Persistent Air Leaks (PALs)
- Persistence with CTD
- The application of suction
- Chemical pleurodesis
- Autologous blood patch (ABP)
- Endobronchial/intrabronchial valves.
2.5.1. Persistence with CTD
2.5.2. Suction
2.5.3. Chemical Pleurodesis
2.5.4. Autologous Blood Patch (ABP)
2.5.5. Endobronchial Valves (EBVs)
2.6. Surgical Management for PAL
2.7. Recurrence Prevention
2.8. Phenotyping SP: Can We Risk Stratify Better?
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinelli, A.W.; Ingle, T.; Newman, J.; Nadeem, I.; Jackson, K.; Lane, N.D.; Melhorn, J.; Davies, H.E.; Rostron, A.J.; Adeni, A.; et al. COVID-19 and pneumothorax: A multicentre retrospective case series. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulutas, H.; Celik, M.R.; Gulcek, I.; Kalkan, M.; Agar, M.; Kilic, T.; Gulcek, E. Management of spontaneous pneumothorax in patients with COVID-19. Interact. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2021, ivab280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallifax, R.J.; Goldacre, R.; Landray, M.J.; Rahman, N.M.; Goldacre, M.J. Trends in the Incidence and Recurrence of Inpatient-Treated Spontaneous Pneumothorax, 1968–2016. JAMA 2018, 320, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobbio, A.; Dechartres, A.; Bouam, S.; Damotte, D.; Rabbat, A.; Régnard, J.F.; Roche, N.; Alifano, M. Epidemiology of spontaneous pneumothorax: Gender-related differences. Thorax 2015, 70, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onuki, T.; Ueda, S.; Yamaoka, M.; Sekiya, Y.; Yamada, H.; Kawakami, N.; Araki, Y.; Wakai, Y.; Saito, K.; Inagaki, M.; et al. Primary and Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Prevalence, Clinical Features, and In-Hospital Mortality. Can. Respir. J. 2017, 2017, 6014967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.G.A.; Ball, E.L.; Macdonald, S.P.J.; Wright, C.; Taylor, D.M. Spontaneous pneumothorax; a multicentre retrospective analysis of emergency treatment, complications and outcomes. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenenberger, R.A.; Haefeli, W.E.; Weiss, P.; Ritz, R.F. Timing of invasive procedures in therapy for primary and secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. Arch. Surg. 1991, 126, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, C.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Light, R.W. Factors related to recurrence of spontaneous pneumothorax. Respirology 2005, 10, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDuff, A.; Arnold, A.; Harvey, J. Management of spontaneous pneumothorax: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65 (Suppl. 2), ii18–ii31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, M.H.; Strange, C.; Heffner, J.E.; Light, R.; Kirby, T.J.; Klein, J.; Luketich, J.D.; Panacek, E.A.; Sahn, S.A. Management of spontaneous pneumothorax: An American College of Chest Physicians Delphi consensus statement. Chest 2001, 119, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northfield, T.C. Oxygen Therapy for Spontaneous Pneumothorax. Br. Med. J. 1971, 4, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chadha, T.S.; Cohn, M.A. Noninvasive treatment of pneumothorax with oxygen inhalation. Respiration 1983, 44, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson-Chahhoud, K.V.; Wakai, A.; van Agteren, J.E.; Smith, B.J.; McCabe, G.; Brinn, M.P.; O’Sullivan, R. Simple aspiration versus intercostal tube drainage for primary spontaneous pneumothorax in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 9, CD004479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, G.J.; Hamilton, A.A.; Upadhyay, R.; Finlay, M.; Grace, P.M. Results of simple aspiration of pneumothoraces. Br. J. Dis. Chest 1985, 79, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.W.; Chan, K.W.; Lee, S.K. Simple aspiration of pneumothorax. Singap. Med. J. 1994, 35, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Thelle, A.; Gjerdevik, M.; Suechu, M.; Hagen, O.M.; Bakke, P. Randomised comparison of needle aspiration and chest tube drainage in spontaneous pneumothorax. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, W.-K.; Chen, W.; Lee, J.-C.; Cheng, W.-E.; Chen, C.-H.; Hsu, W.-H.; Shih, C.M. Pigtail catheters vs large-bore chest tubes for management of secondary spontaneous pneumothoraces in adults. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 24, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.M.; Elshahat, H.M.; Shaker, A.; Hashem, A.Z.A. Study of pigtail catheter and chest tube in management of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2017, 66, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.G.; Ball, E.L.; Perrin, K.; Asha, S.E.; Braithwaite, I.; Egerton-Warburton, D.; Jones, P.G.; Keijzers, G.; Kinnear, F.B.; Kwan, B.C.; et al. Conservative versus Interventional Treatment for Spontaneous Pneumothorax. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Telles, A.; Ortíz-Farias, D.L.; Perez-Hernandez, F.; Rodriguez-Morejon, D. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: A time to re-evaluate management. Respirol. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e00749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardy, B.C.; Simpson, G. Conservative versus invasive management of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: A retrospective cohort study. Acute Med. Surg. 2021, 8, e663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röggla, M.; Wagner, A.; Brunner, C.; Röggla, G. The management of pneumothorax with the thoracic vent versus conventional intercostal tube drainage. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 1996, 108, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.K.; Ong, M.E.; Koh, M.S.; Wong, E.; Raghuram, J. A randomized controlled trial comparing minichest tube and needle aspiration in outpatient management of primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 29, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallifax, R.J.; McKeown, E.; Sivakumar, P.; Fairbairn, I.; Peter, C.; Leitch, A.; Rahman, N.M. Ambulatory management of primary spontaneous pneumothorax: An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brims, F.J.H.; Maskell, N.A. Ambulatory treatment in the management of pneumothorax: A systematic review of the literature. Thorax 2013, 68, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, S.P.; Keenan, E.; Bintcliffe, O.; Stanton, A.E.; Roberts, M.; Pepperell, J.; Maskell, N.A. Ambulatory management of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, C.; Abisheganaden, J.; Yeo, J.; Lee, P.; Huan, P.; Poh, S.; Wang, Y. Persistent air-leak in spontaneous pneumothorax—Clinical course and outcome. Respir. Med. 1998, 92, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- So, S.Y.; Yu, D.Y. Catheter drainage of spontaneous pneumothorax: Suction or no suction, early or late removal? Thorax 1982, 37, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.M.; Ray, A.; Dale, M.; Morgan, H.; Dimmock, P.; Carolan-Rees, G. Thopaz+ Portable Digital System for Managing Chest Drains: A NICE Medical Technology Guidance. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2019, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallifax, R.J.; Laskawiec-Szkonter, M.; Rahman, N.M. Predicting outcomes in primary spontaneous pneumothorax using air leak measurements. Thorax 2019, 74, 410–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Ng, K.Y.; Poh, S.C. Intrapleural tetracycline for spontaneous pneumothorax with persistent air leak. Singap. Med. J. 1988, 29, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Light, R.W.; O’Hara, V.S.; Moritz, T.E.; McElhinney, A.J.; Butz, R.; Haakenson, C.M.; Read, R.C.; Sassoon, C.S.; Eastridge, C.E.; Berger, R. Intrapleural Tetracycline for the Prevention of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Results of a Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. JAMA 1990, 264, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Fukai, I.; Okuda, K.; Moriyama, S.; Haneda, H.; Kawano, O.; Yokota, K.; Shitara, M.; Tatematsu, T.; Sakane, T.; et al. Talc pleurodesis for secondary pneumothorax in elderly patients with persistent air leak. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallifax, R.J.; Yousuf, A.; Jones, H.; Corcoran, J.P.; Psallidas, I.; Rahman, N.M. Effectiveness of chemical pleurodesis in spontaneous pneumothorax recurrence prevention: A systematic review. Thorax 2017, 72, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shackcloth, M.; Poullis, M.; Jackson, M.; Soorae, A.; Page, R.D. Intrapleural Instillation of Autologous Blood in the Treatment of Prolonged Air Leak After Lobectomy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kitagawa, C.; Kumazawa, A.; Sato, M.; Shima, K.; Watanabe, A.; Shimokata, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Autologous blood-patch pleurodesis for secondary spontaneous pneumothorax with persistent air leak. Respir. Med. 1999, 93, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumire, R.; Crabbe, M.M.; Mappin, F.G.; Fontenelle, L.J. Autologous “blood patch” pleurodesis for persistent pulmonary air leak. Chest 1992, 101, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cagirici, U.; Sahin, B.; Cakan, A.; Kayabas, H.; Buduneli, T. Autologous blood patch pleurodesis in spontaneous pneumothorax with persistent air leak. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 1998, 32, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Escobar, S.; Ruiz-Bailén, M.; Lorente-Acosta, M.J.; Vicente-Rull, J.R.; Martínez-Coronel, J.F.; Rodríguez-Cuartero, A. Pleurodesis using autologous blood: A new concept in the management of persistent air leak in acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Crit. Care 2006, 21, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.; Routledge, T.; Billè, A.; Scarci, M. Is blood pleurodesis effective for determining the cessation of persistent air leak? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 11, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, I.; Elaziz, M.E.A.; El-Hag-Aly, M.A. Early Autologous Blood-Patch Pleurodesis versus Conservative Management for Treatment of Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 67, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.Q.; Kang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, H. Intrapleural instillation of autologous blood for persistent air leak in spontaneous pneumothorax in patients with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 93, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criner, G.J.; Sue, R.; Wright, S.; Dransfield, M.; Rivas-Perez, H.; Wiese, T.; Sciurba, F.C.; Shah, P.; Wahidi, M.M.; De Oliveira, H.G.; et al. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of Zephyr Endobronchial Valve Treatment in Heterogeneous Emphysema [LIBERATE]. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.C.; Yu, E.L.; Kwok, H.C.; She, H.L.; Kwong, K.K.; Chan, Y.H.; Tsang, Y.L.; Yeung, Y.C. Endobronchial valve for treatment of persistent air leak complicating spontaneous pneumothorax. Hong Kong Med. J. 2018, 24, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bermea, R.S.; Miller, J.; Wilson, W.W.; Dugan, K.; Frye, L.; Murgu, S.; Hogarth, D.K. One-Way Endobronchial Valves as Management for Persistent Air Leaks: A Preview of What’s to Come? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, D.; McConnell, S.; Rajesh, P. Delayed referral reduces the success of video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for spontaneous pneumothorax. Respir. Med. 1998, 92, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.T.; Xie, Y.H.; Gu, X.; Li, W.P.; Zeng, Y.M.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Wang, H.W.; Bai, C.; Jin, F.G. Management of Persistent Air Leaks Using Endobronchial Autologous Blood Patch and Spigot Occlusion: A Multicentre Randomized Controlled Trial in China. Respiration 2019, 97, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.M.; Lee, P. Thoracoscopy for Spontaneous Pneumothorax. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, J.; Takamoto, S.; Murakawa, T.; Fukami, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Kusakabe, M. Outcomes of thoracoscopic management of secondary pneumothorax in patients with COPD and interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 23, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Chen, C.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Z. Surgical management of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Retrospective study of 107 cases. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 57, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Asai, K.; Urabe, N. Surgery for secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: Risk factors for recurrence and morbidity. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 17, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichinose, J.; Nagayama, K.; Hino, H.; Nitadori, J.-I.; Anraku, M.; Murakawa, T.; Nakajima, J. Results of surgical treatment for secondary spontaneous pneumothorax according to underlying diseases. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 49, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, H.H.; Hassaballa, A.; Ahmed, T. Is video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery talc pleurodesis superior to talc pleurodesis via tube thoracostomy in patients with secondary spontaneous pneumothorax? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 23, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Abougergi, M.S.; Li, S.; Kazmierski, D.; Patel, P.; Sharma, N.; Ochieng, P. Recurrence Prophylaxis in Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Nationwide Readmission Database Analysis. Chest 2020, 158, 2474–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppen, M.; Alexander, P.; Driesen, P.; Slabbynck, H.; Verstraeten, A. Manual aspiration versus chest tube drainage in first episodes of primary spontaneous pneumothorax: A multicenter, prospective, randomized pilot study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1240–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, A.K.; Chandrasekaran, C.; Sukumar, M. Aspiration versus tube drainage in primary spontaneous pneumothorax: A randomised study. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramouz, A.; Lashkari, M.H.; Fakour, S.; Rasihashemi, S.Z. Randomized controlled trial on the comparison of chest tube drainage and needle aspiration in the treatment of primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Kang, D.K.; Min, H.-K.; Hwang, Y.-H. A Prospective Randomized Trial Comparing Manual Needle Aspiration to Closed Thoracostomy as an Initial Treatment for the First Episode of Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax. Korean, J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 52, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Takihara, T.; Nakamura, N.; Horio, Y.; Enokida, K.; Hayama, N.; Oguma, T.; Aoki, T.; Masayuki, I.; Asano, K. Etiology and prognosis of spontaneous pneumothorax in the elderly. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.P.; Bibby, A.C.; Halford, P.; Stadon, L.; White, P.; Maskell, N.A. Recurrence rates in primary spontaneous pneumothorax: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bintcliffe, O.J.; Edey, A.J.; Armstrong, L.; Negus, I.S.; Maskell, N.A. Lung Parenchymal Assessment in Primary and Secondary Pneumothorax. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nava, G.W.; Walker, S.P. Management of the Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Current Guidance, Controversies, and Recent Advances. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051173
Nava GW, Walker SP. Management of the Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Current Guidance, Controversies, and Recent Advances. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(5):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051173
Chicago/Turabian StyleNava, George William, and Steven Philip Walker. 2022. "Management of the Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Current Guidance, Controversies, and Recent Advances" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 5: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051173
APA StyleNava, G. W., & Walker, S. P. (2022). Management of the Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Current Guidance, Controversies, and Recent Advances. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(5), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051173





