Effects of Low-Immersive vs. High-Immersive Exercise Environment on Postural Stability and Reaction and Motor Time of Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
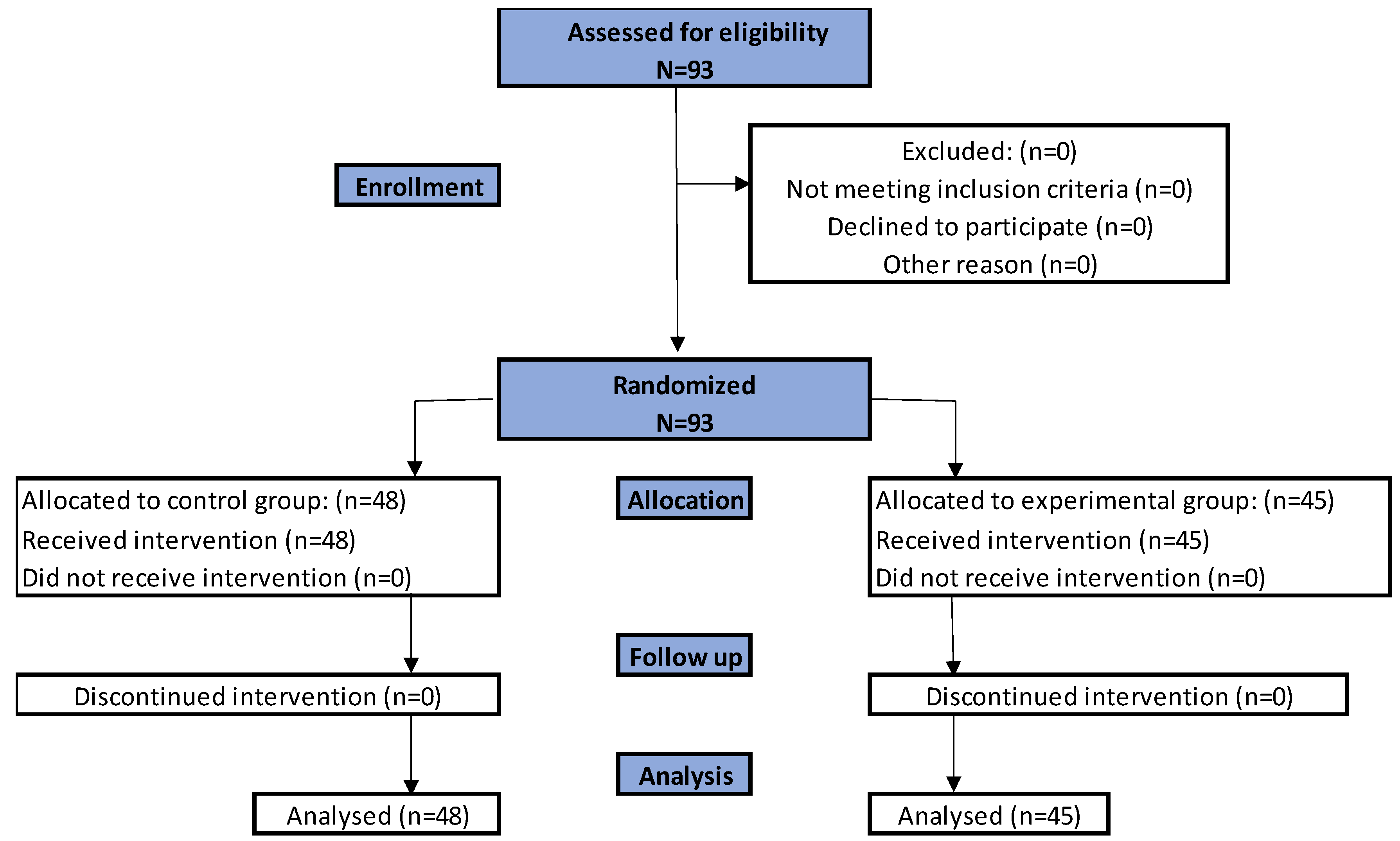
2.1. Participants and Study Design
- >18.5—1 participant
- 18.5–24.9—31 participants
- 25.0–29.9—13 participants
- >18.5—1 participant
- 18.5–24.9—37 participants
- 25.0–29.9—10 participants
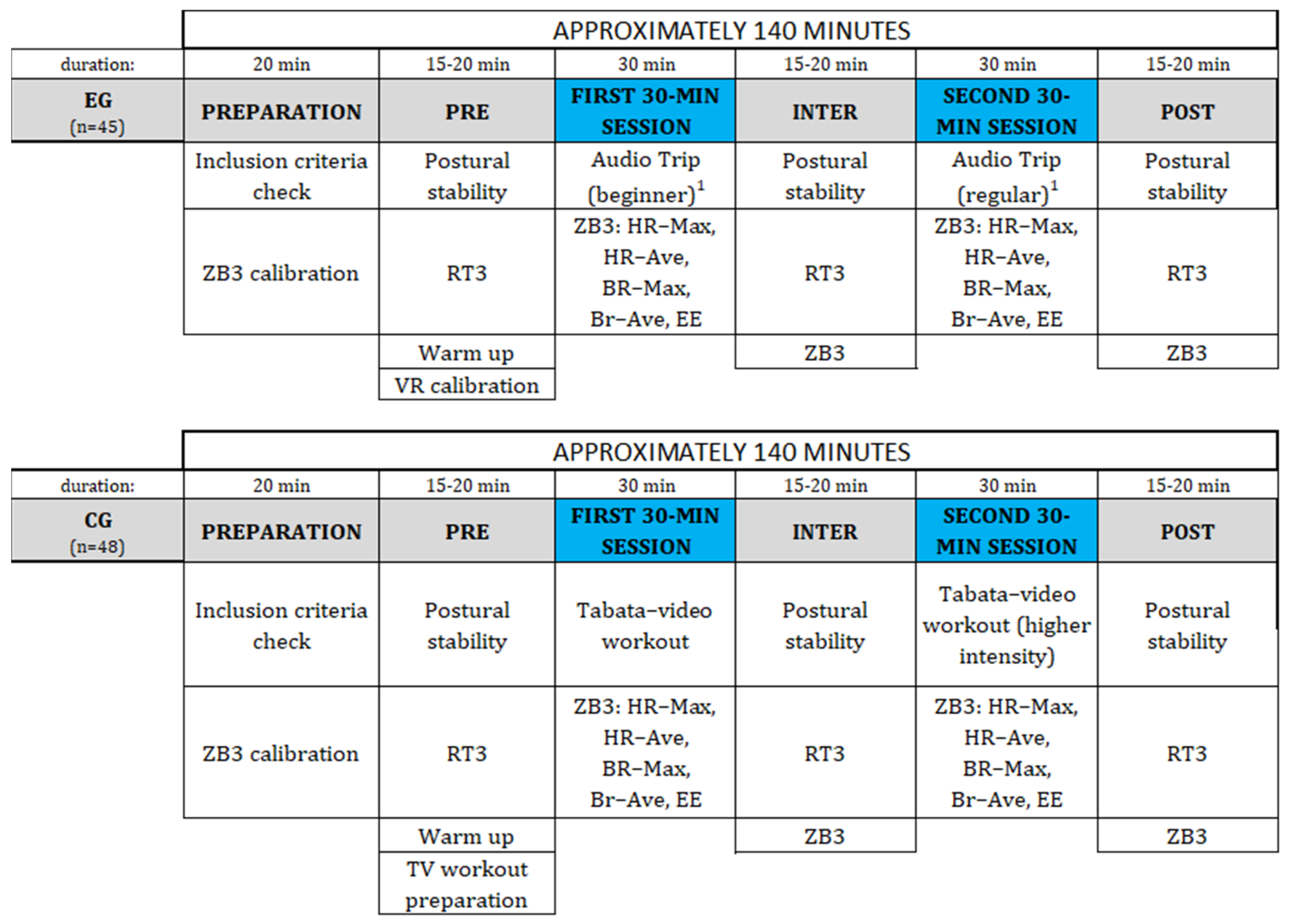
2.2. Hardware and Software
2.3. Measure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
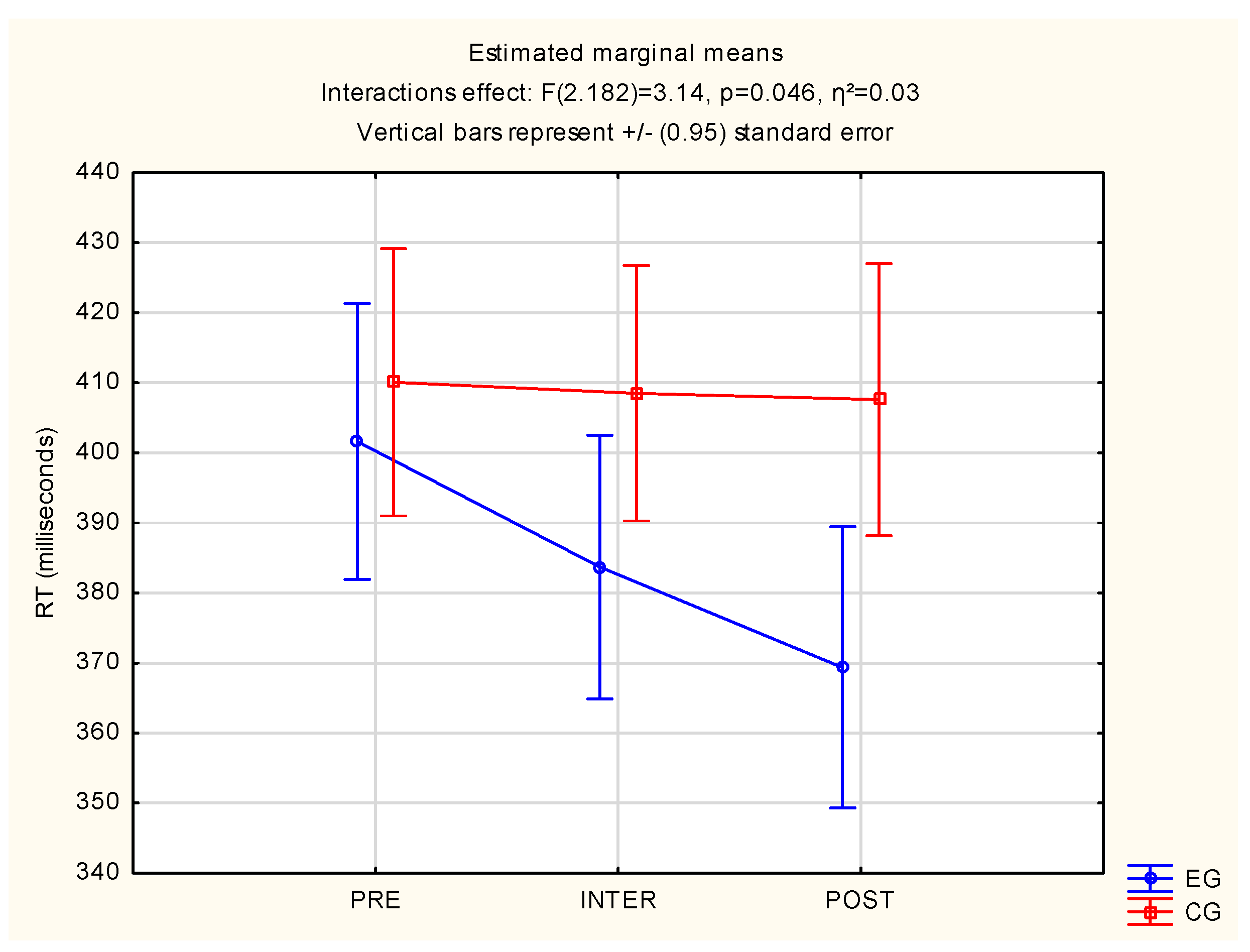
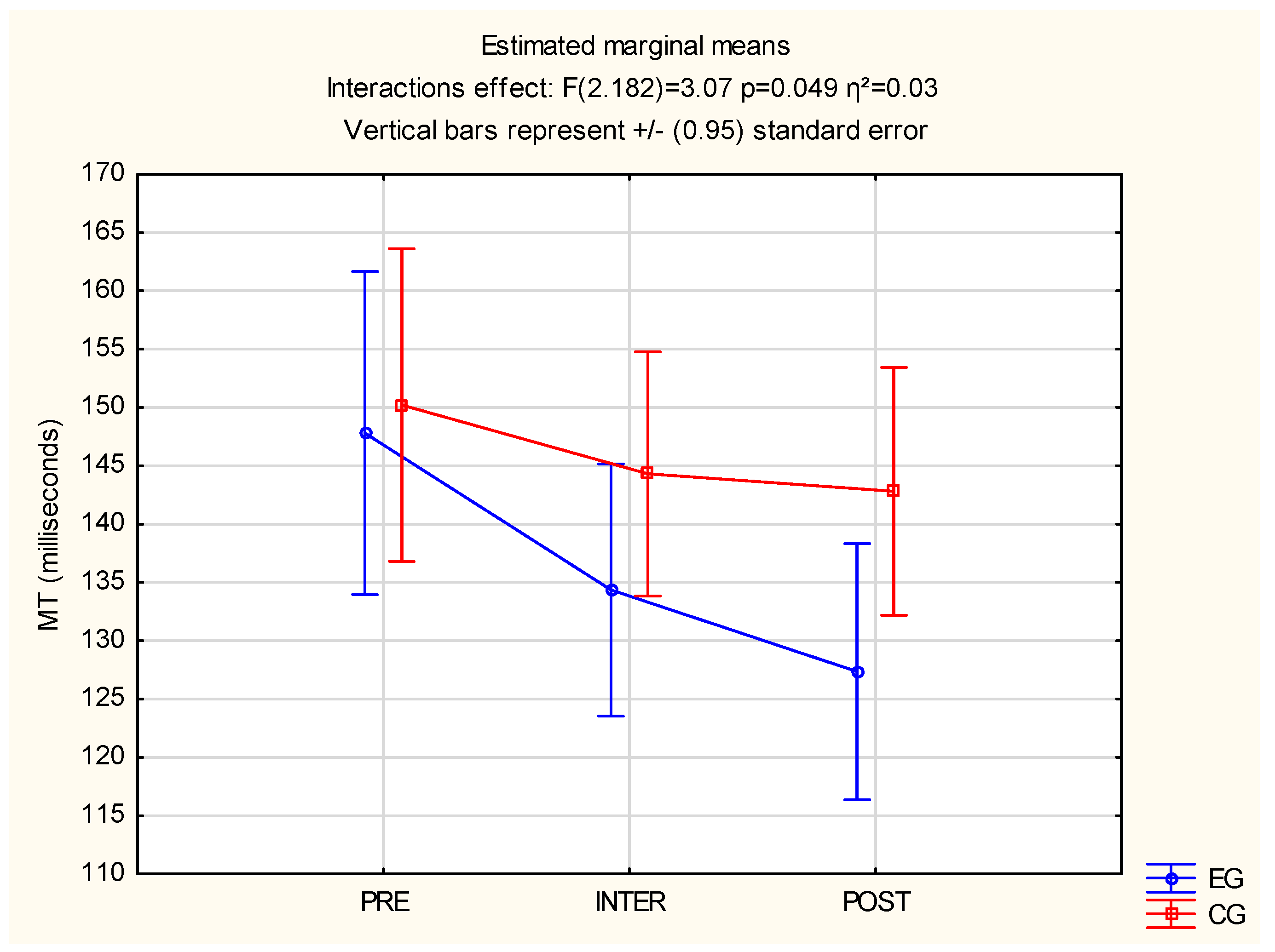
3.1. Reaction Time and Motor Time
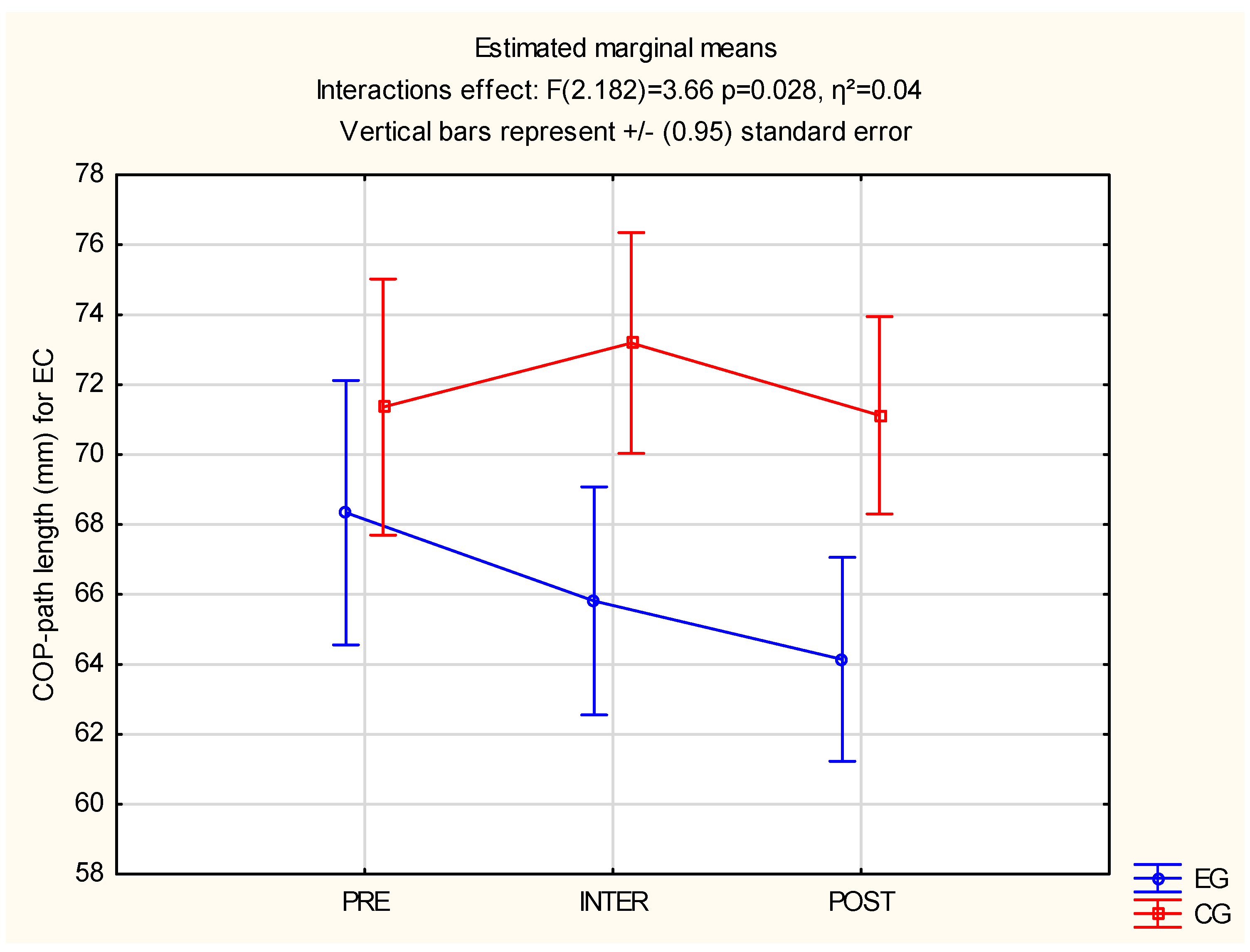
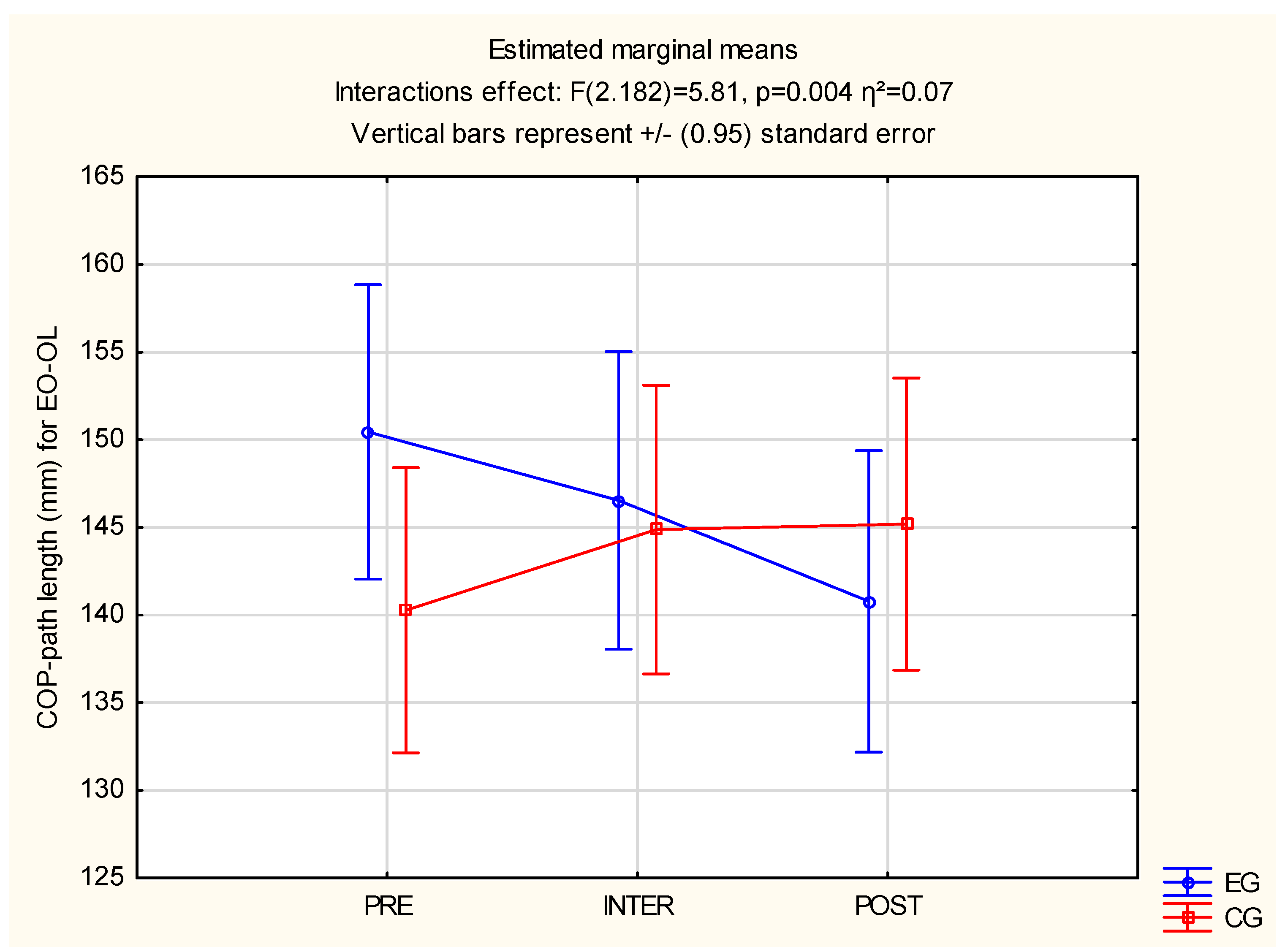
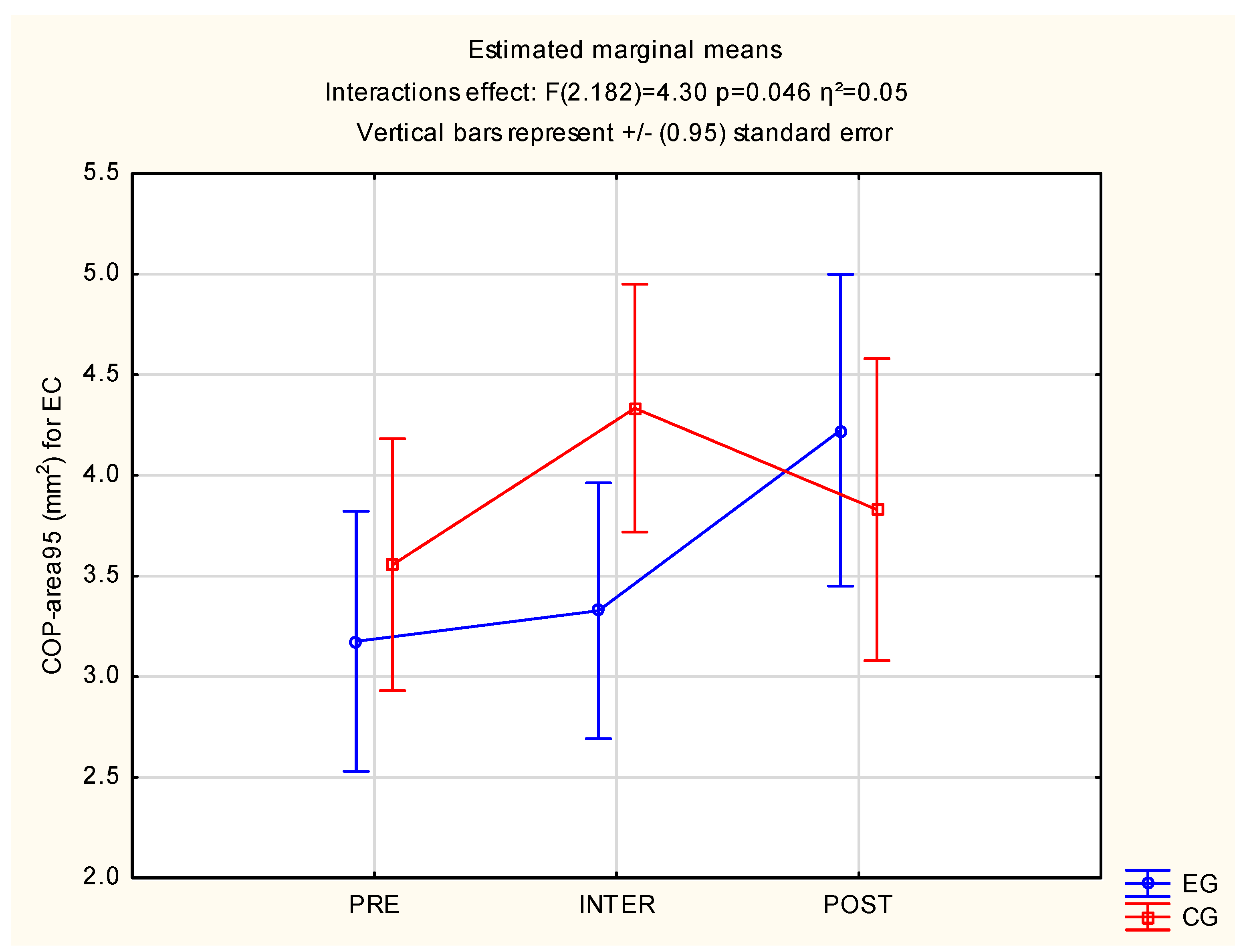
3.2. Postural Stability
3.3. Zephyr Measurement
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blaszczyk, J.W.; Hansen, P.D.; Lowe, D.L. Postural Sway and Perception of the Upright Stance Stability Borders. Perception 1993, 22, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Howard, B.; Healy, G.N.; Owen, N. Too Much Sitting—A Health Hazard. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrysomallis, C. Balance Ability and Athletic Performance. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, K.; Roy, A. A Novel Theoretical Framework for the Dynamic Stability Analysis, Movement Control, and Trajectory Generation in a Multisegment Biomechanical Model. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ołpińska-Lischka, M.; Kujawa, K.; Maciaszek, J. Differences in the Effect of Sleep Deprivation on the Postural Stability among Men and Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, E.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. United States Adolescents’ Television, Computer, Videogame, Smartphone, and Tablet Use: Associations with Sugary Drinks, Sleep, Physical Activity, and Obesity. J. Pediatr. 2017, 182, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallavicini, F.; Ferrari, A.; Mantovani, F. Video Games for Well-Being: A Systematic Review on the Application of Computer Games for Cognitive and Emotional Training in the Adult Population. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okubo, Y.; Schoene, D.; Lord, S.R. Step Training Improves Reaction Time, Gait and Balance and Reduces Falls in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 51, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Menhas, R.; Dai, J.; Saqib, Z.A.; Peng, X. Fitness Apps, Live Streaming Workout Classes, and Virtual Reality Fitness for Physical Activity during the COVID-19 Lockdown: An Empirical Study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 852311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, D.J.; Helgeson, M.A.; Liu, W.; Gao, Z. Effects of a Remote, YouTube-Delivered Exercise Intervention on Young Adults’ Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep during the Covid-19 Pandemic: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Sport Health Sci. 2022, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeas, T.; More-chevalier, B.; Charbonneau, M.; Bieuzen, F. Virtual-Reality Training of Elite Boxers Preparing for the Tokyo 2020 Olympics During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study. Case Stud. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2022, 6, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyo, E.; Nyamandi, C. Application of Virtual Reality Technologies in the Comrades’ Marathon as a Response to Covid-19 Pandemic. Dev. S. Afr. 2021, 39, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martirosov, S.; Bureš, M.; Zítka, T. Cyber Sickness in Low-Immersive, Semi-Immersive, and Fully Immersive Virtual Reality. Virtual Real. 2021, 26, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, N.C.; Nordahl, R.; Serafin, S. Immersion Revisited: A Review of Existing Definitions of Immersion and Their Relation to Different Theories of Presence. Hum. Technol. 2016, 12, 108–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.; Chang, M.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, S.; Lee, K. The Effect of Immersion on Emotional Responses to Film Viewing in a Virtual Environment. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Reutlingen, Germany, 18–22 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Visch, V.T.; Tan, E.S.; Molenaar, D. The Emotional and Cognitive Effect of Immersion in Film Viewing. Cogn. Emot. 2010, 24, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Garrett, B.; Taverner, T.; Cordingley, E.; Sun, C. Immersive Virtual Reality & Health Games: A Narrative Review of Game Design. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Eknoyan, G. Adolphe Quetelet (1796 1874) the Average Man and Indices of Obesity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 23, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witmer, B.G.; Singer, M.J. Measuring Presence in Virtual Environments: A Presence Questionnaire. Presence Teleoperat. Virtual Environ. 1998, 7, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagymáté, G.; Orlovits, Z.; Kiss, R.M. Reliability Analysis of a Sensitive and Independent Stabilometry Parameter Set. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asseman, F.; Caron, O.; Crémieux, J. Effects of the Removal of Vision on Body Sway during Different Postures in Elite Gymnasts. Int. J. Sports Med. 2005, 26, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjernström, F.; Björklund, M.; Malmström, E.-M. Romberg Ratio in Quiet Stance Posturography—Test to Retest Reliability. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soffel, F.; Zank, M.; Kunz, A. Postural Stability Analysis in Virtual Reality Using the HTC Vive. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Munich, Germany, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cyma-Wejchenig, M.; Tarnas, J.; Marciniak, K.; Stemplewski, R. The Influence of Proprioceptive Training with the Use of Virtual Reality on Postural Stability of Workers Working at Height. Sensors 2020, 20, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamborini, R.; Grizzard, M.; David Bowman, N.; Reinecke, L.; Lewis, R.J.; Eden, A. Media Enjoyment as Need Satisfaction: The Contribution of Hedonic and Nonhedonic Needs. J. Commun. 2011, 61, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Mao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, M. The Influence of Academic Emotions on Learning Effects: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersin, A.; Tezeren, H.C.; Pekyavas, N.O.; Asal, B.; Atabey, A.; Diri, A.; Gonen, İ. The Relationship between Reaction Time and Gaming Time in E-SPORTS Players. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/ojs/index.php/kinesiology/article/view/19294 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Wilms, I.L.; Petersen, A.; Vangkilde, S. Intensive Video Gaming Improves Encoding Speed to Visual Short-Term Memory in Young Male Adults. Acta Psychol. 2013, 142, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, K.; Audiffren, M.; Denjean, A. A Distributional Analysis of the Effect of Physical Exercise on a Choice Reaction Time Task. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audiffren, M.; Tomporowski, P.D.; Zagrodnik, J. Acute Aerobic Exercise and Information Processing: Energizing Motor Processes during a Choice Reaction Time Task. Acta Psychol. 2008, 129, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavicini, F.; Pepe, A. Virtual Reality Games and the Role of Body Involvement in Enhancing Positive Emotions and Decreasing Anxiety: Within-Subjects Pilot Study. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8, e15635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glueck, A.C.; Han, D.Y. Improvement Potentials in Balance and Visuo-Motor Reaction Time after Mixed Reality Action Game Play: A Pilot Study. Virtual Real. 2019, 24, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumaa, M.; Khaireldin, A.; Rehan Youssef, A. Validity and Reliability of Interactive Virtual Reality in Assessing the Musculoskeletal System: A Systematic Review. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2021, 14, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Participants Characteristics | EG (95% CI) | CG (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 21.69 ± 2.76 (22.14) | 22.25 ± 1.66 (21.77) |
| Body weight (kg) | 71.03 ± 13.07 (74.96) | 68.39 ± 12.96 (64.62) |
| Body height (cm) | 173.98 ± 8.09 (176.41) | 173.83 ± 8.63 (176.33) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.3 ± 3.23 (24.31) | 22.5 ± 2.80 (23.28) |
| F/M (number) | 22/23 | 26/22 |
| RI (Ruffier index)1 | 6.5 | 6.8 |
| Title (Chronological) | Duration (min:s) | BPM (Beats per Minute) |
|---|---|---|
| Dance monkey | 03:28 | 98 |
| Bangarang | 03:32 | 110 |
| Just Dance | 03:38 | 118 |
| Krishna | 02:39 | 128 |
| Red | 07:31 | 136 |
| Satisfaction | 04:44 | 136 |
| Mandala | 04:39 | 143 |
| Title (Chronological) | Duration (min:s) | Movement Type 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Dance monkey 2 | 03:28 | 00:30 dumbbell fly’s ×3 2 00:30 boxing run ×4 2 |
| Bangarang 3 | 03:32 | 00:30 jabs left/right hand ×3 3 00:30 biceps drop down ×2 3 00:30 diagonally jabs ×2 3 |
| Just Dance 4 | 03:38 | 00:30 marking “X” ×2 4 00:30 knee up ×2 4 00:30 jumps left to right ×2 4 00:30 marking “square” ×1 4 |
| Krishna 5 | 02:39 | 00:30 CrossFit rope ×3 5 00:30 marking “u” in a squat ×2 5 |
| Red 6 | 07:31 | 00:30 jabs side to side ×3 6 00:30 dumbbell fly’s ×2 6 00:30 V-step ×3 6 00:30 marking “circle” ×2 6 00:30 squat wrists supination ×3 6 00:30 torso twists ×2 6 |
| Satisfaction 7 | 04:44 | 00:30 marking “wave” ×2 7 00:30 diagonally jabs side to side ×2 7 00:30 marking “wave” ×2 7 00:30 drums ×2 7 00:30 extra step ×2 7 |
| Mandala 8 | 04:39 | 00:30 squat dumbbell fly’s ×3 8 00:30 arms circling ×3 8 00:30 knee up to hand ×3 8 00:10 EXTRA: deep breath |
| Path Length | CG | EG | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| EO 1 (mm) | 61.42 | 60.17 | F(2.182) = 1.29, p = 0.28, η2 = 0.01 |
| EO 2 (mm) | 64.97 | 62.60 | |
| EO 3 (mm) | 66.19 | 62.81 | |
| EC 1 (mm) | 71.36 | 68.16 | F(2, 182) = 3.66, p = 0.028 *, η2 = 0.04 |
| EC 2 (mm) | 72.49 | 66.55 | |
| EC 3 (mm) | 70.63 | 65.45 | |
| Romberg 1 | 0.87 | 0.90 | |
| Romberg 2 | 0.90 | 0.95 | |
| Romberg 3 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| EO-OL 1 (mm) | 140.28 | 150.45 | F(2, 182) = 5.81, p = 0.004 *, η2 = 0.07 |
| EO-OL 2 (mm) | 144.88 | 146.54 | |
| EO-OL 3 (mm) | 145.20 | 140.78 |
| Area95 | CG | EG | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| EO 1 (mm2) | 2.43 | 2.39 | F(2, 182) = 0.60, p = 0.57, η2 = 0.01 |
| EO 2 (mm2) | 3.06 | 3.44 | |
| EO 3 (mm2) | 3.17 | 3.57 | |
| EC 1 (mm2) | 3.56 | 3.18 | F(2, 182) = 4.30, p = 0.02 *, η2 = 0.05 |
| EC 2 (mm2) | 4.34 | 3.33 | |
| EC 3 (mm2) | 3.83 | 4.23 | |
| EO-OL 1 (mm2) | 8.25 | 9.24 | F(2, 182) = 0.76, p = 0.47, η2 = 0.01 |
| EO-OL 2 (mm2) | 9.56 | 11.09 | |
| EO-OL 3 (mm2) | 10.67 | 11.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciążyńska, J.; Maciaszek, J. Effects of Low-Immersive vs. High-Immersive Exercise Environment on Postural Stability and Reaction and Motor Time of Healthy Young Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010389
Ciążyńska J, Maciaszek J. Effects of Low-Immersive vs. High-Immersive Exercise Environment on Postural Stability and Reaction and Motor Time of Healthy Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010389
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiążyńska, Julia, and Janusz Maciaszek. 2023. "Effects of Low-Immersive vs. High-Immersive Exercise Environment on Postural Stability and Reaction and Motor Time of Healthy Young Adults" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010389
APA StyleCiążyńska, J., & Maciaszek, J. (2023). Effects of Low-Immersive vs. High-Immersive Exercise Environment on Postural Stability and Reaction and Motor Time of Healthy Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010389








