Orchestrating Resilience: How Neuropilin-2 and Macrophages Contribute to Cardiothoracic Disease
Abstract
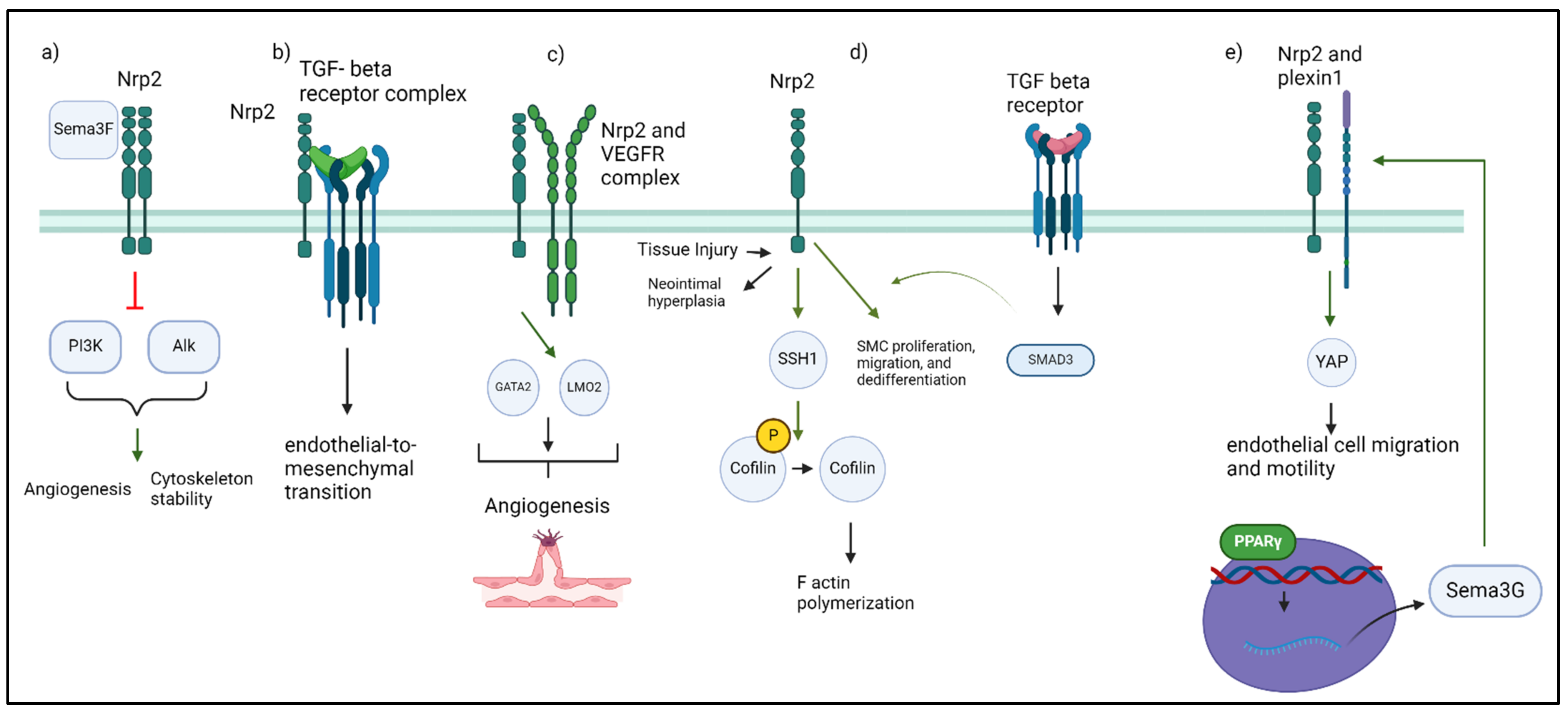
:1. An Introduction to Neuropilins
2. Neuropilin Structure and Variants
3. Neuropilin Signaling
4. Neuropilin-2 in Immunity
5. Neuropilin-2 in Macrophages
6. Neuropilin-2 in Benign and Malignant Lung Processes
6.1. Respiratory Infections
6.2. Asthma
6.3. Lung Cancer
6.4. Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Neuropilin-2
7. Cardiac Disease
7.1. Neuropilin-2 in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis
7.2. Neuropilin-2 in Cardiovascular Disease
7.3. Neuropilin-2 in Heart Failure
8. Therapeutic Targeting of Nrp2
9. Conclusions
10. Methods
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soker, S.; Takashima, S.; Miao, H.Q.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 1998, 92, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, F.; Goshima, Y. Structural and functional relation of neuropilins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2002, 515, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol, M.; Gagnon, M.L.; Klagsbrun, M. Genomic organization of human neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 genes: Identification and distribution of splice variants and soluble isoforms. Genomics 2000, 70, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodkin, A.L.; Levengood, D.V.; Rowe, E.G.; Tai, Y.T.; Giger, R.J.; Ginty, D.D. Neuropilin Is a Semaphorin III Receptor. Cell 1997, 90, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chédotal, A.; He, Z.; Goodman, C.S.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Neuropilin-2, a novel member of the neuropilin family, is a high affinity receptor for the semaphorins Sema E and Sema IV but not Sema III. Neuron 1997, 19, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Hirata, T.; Agata, K.; Mochii, M.; Eguchi, G.; Fujisawa, H. The A5 antigen, a candidate for the neuronal recognition molecule, has homologies to complement components and coagulation factors. Neuron 1991, 7, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, R.; Mishra, J.; Bodas, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Batra, S.K.; Dutta, S.; Datta, K. Role of Neuropilin-2-mediated signaling axis in cancer progression and therapy resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022, 41, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, J.L.; Sayers, J.; Chapman, C.; Pellet-Many, C. Emerging Roles for Neuropilin-2 in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Bag, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Talmadge, J.E.; Batra, S.K.; Datta, K. Multifaceted role of neuropilins in the immune system: Potential targets for immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuckran, C.A.; Liu, C.; Bruno, T.C.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Neuropilin-1: A checkpoint target with unique implications for cancer immunology and immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niland, S.; Eble, J.A. Neuropilin: Handyman and Power Broker in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1223, 31–67. [Google Scholar]
- Broz, M.; Kolarič, A.; Jukič, M.; Bren, U. Neuropilin (NRPs) Related Pathological Conditions and Their Modulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-J.; Chen, X.; Qin, J.; Hong, Y.-K.; Tsai, M.-J.; Tsai, S.Y. Direct transcriptional regulation of neuropilin-2 by COUP-TFII modulates multiple steps in murine lymphatic vessel development. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Moyon, D.; Pardanaud, L.; Breant, C.; Karkkainen, M.J.; Alitalo, K.; Eichmann, A. Abnormal lymphatic vessel development in neuropilin 2 mutant mice. Development 2002, 129, 4797–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, S.; Kitakaze, M.; Asakura, M.; Asanuma, H.; Sanada, S.; Tashiro, F.; Niwa, H.; Miyazaki, J.; Hirota, S.; Kitamura, Y.; et al. Targeting of both mouse neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 genes severely impairs developmental yolk sac and embryonic angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kitsukawa, T.; Bekku, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Sanbo, M.; Yagi, T.; Fujisawa, H. A requirement for neuropilin-1 in embryonic vessel formation. Development 1999, 126, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsukawa, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sanbo, M.; Hirata, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Bekku, Y.; Yagi, T.; Fujisawa, H. Neuropilin-semaphorin III/D-mediated chemorepulsive signals play a crucial role in peripheral nerve projection in mice. Neuron 1997, 19, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werneburg, S.; Buettner, F.F.R.; Erben, L.; Mathews, M.; Neumann, H.; Mühlenhoff, M.; Hildebrandt, H. Polysialylation and lipopolysaccharide-induced shedding of E-selectin ligand-1 and neuropilin-2 by microglia and THP-1 macrophages. Glia 2016, 64, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issitt, T.; Bosseboeuf, E.; Winter, N.D.; Dufton, N.; Gestri, G.; Senatore, V.; Chikh, A.; Randi, A.M.; Raimondi, C. Neuropilin-1 Controls Endothelial Homeostasis by Regulating Mitochondrial Function and Iron-Dependent Oxidative Stress. iScience 2019, 11, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, L.; Nasarre, C.; Dirrig-Grosh, S.; Aunis, D.; Cremel, G.; Hubert, P.; Bagnard, D. Transmembrane domain interactions control biological functions of neuropilin-1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geretti, E.; Shimizu, A.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin structure governs VEGF and semaphorin binding and regulates angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, B.; Pellet-Many, C.; Britton, G.; Hartzoulakis, B.; Zachary, I.C. VEGF binding to NRP1 is essential for VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell migration, complex formation between NRP1 and VEGFR2, and signaling via FAK Tyr407 phosphorylation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 2766–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giger, R.J.; Urquhart, E.R.; Gillespie, S.K.; Levengood, D.V.; Ginty, D.D.; Kolodkin, A.L. Neuropilin-2 is a receptor for semaphorin IV: Insight into the structural basis of receptor function and specificity. Neuron 1998, 21, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giger, R.J.; Cloutier, J.F.; Sahay, A.; Prinjha, R.K.; Levengood, D.V.; Moore, S.E.; Pickering, S.; Simmons, D.; Rastan, S.; Walsh, F.S.; et al. Neuropilin-2 is required in vivo for selective axon guidance responses to secreted semaphorins. Neuron 2000, 25, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Reed, R.R. Cloning and characterization of neuropilin-1-interacting protein: A PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1 domain-containing protein that interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of neuropilin-1. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6519–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Zheng, J.J. PDZ domains and their binding partners: Structure, specificity, and modification. Cell Commun. Signal 2010, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.; Hor, C.H.H.; Chew, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, Z.; Ryu, J.R.; Goh, E.L. Neuropilin 2 Signaling Is Involved in Cell Positioning of Adult-born Neurons through Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β (GSK3β). J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25088–25095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, A.A.A.; Benwell, C.J.; Atkinson, S.J.; Lambert, J.; Johnson, R.T.; Robinson, S.D. NRP2 as an Emerging Angiogenic Player; Promoting Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Migration by Regulating Recycling of α5 Integrin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, B.; Ala, A.; Barron, P.; Bonnin, J.; Laboudie, P.; Fons, P.; Mandron, M.; Herault, J.; Neufeld, G.; Savi, P.; et al. Neuropilin-2 interacts with VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 and promotes human endothelial cell survival and migration. Blood 2006, 108, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.W.; Linkugel, A.D.; Goel, H.L.; Gonzalez, T.W.; Mercurio, A.M.; Vander Kooi, C.W. Structural basis for VEGF-C binding to neuropilin-2 and sequestration by a soluble splice form. Structure 2015, 23, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttmann-Raviv, N.; Shraga-Heled, N.; Varshavsky, A.; Guimaraes-Sternberg, C.; Kessler, O.; Nuefeld, G. Semaphorin-3A and semaphorin-3F work together to repel endothelial cells and to inhibit their survival by induction of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26294–26305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellet-Many, C.; Mehta, V.; Fields, L.; Mahmoud, M.; Lowe, V.; Evans, I.; Ruivo, J.; Zachary, I. Neuropilins 1 and 2 mediate neointimal hyperplasia and re-endothelialization following arterial injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 108, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Y.; Cho, J.G.; Park, J.; Oh, S.; Park, D.; Yoo, K.H.; Lee, M.-S.; Kwon, B.S.; Kim, J.; Yang, Y. MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells. Genes 2020, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, P.; Grubinger, M.; Groger, C.; Huber, H.; Sieghart, W.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Mikulits, W. Neuropilin-2 induced by transforming growth factor-β augments migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulpice, E.; Plouet, J.; Berge, M.; Allanic, D.; Tobelem, G.; Merkulova-Rainon, T. Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 act as coreceptors, potentiating proangiogenic activity. Blood 2008, 111, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, D.C.; Rees, C.G.; Duchesne, L.; Patey, S.J.; Terry, C.J.; Turnbull, J.E.; Delehedde, M.; Heegaard, C.W.; Allain, F.; Vanpouille, C.; et al. Interactions of multiple heparin binding growth factors with neuropilin-1 and potentiation of the activity of fibroblast growth factor-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13457–13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdembri, D.; Caswell, P.T.; Anderson, K.I.; Schwarz, J.P.; Konig, I.; Astanina, E.; Caccavari, F.; Norman, J.C.; Humprhries, M.J.; Bussolino, F.; et al. Neuropilin-1/GIPC1 signaling regulates alpha5beta1 integrin traffic and function in endothelial cells. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqoob, U.; Cao, S.; Shergill, U.; Jagavelu, K.; Geng, Z.; Yin, M.; de Assuncao, T.M.; Cao, Y.; Szabolcs, A.; Thorgeirsson, S.; et al. Neuropilin-1 stimulates tumor growth by increasing fibronectin fibril assembly in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4047–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, H.L.; Pursell, B.; Chang, C.; Shaw, L.M.; Mao, J.; Simin, K.; Kumar, P.; Vander Kooi, C.W.; Shultz, L.D.; Greiner, D.L.; et al. GLI1 regulates a novel neuropilin-2/α6β1 integrin based autocrine pathway that contributes to breast cancer initiation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Okon, I.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Song, P.; Zou, M.-H. A novel role for myeloid cell-specific neuropilin 1 in mitigating sepsis. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellenburg, S.; Schulz, A.; Poitz, D.M.M.; Muders, M.H.H. Role of neuropilin-2 in the immune system. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 90, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, A.A.; Eisenberg, S.H.; Jones, K.E.; Stabile, L.P.; Lotze, M.T.; Dhupar, R.; Soloff, A.C. Cellular Indoctrination: How the Tumor Microenvironment Reeducates Macrophages Towards Nefarious Ends. In Comprehensive Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 552–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.B.; Yeh, E.S.; Soloff, A.C. Tumor-associated macrophages: Unwitting accomplices in breast cancer malignancy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immormino, R.M.; Lauzier, D.C.; Nakano, H.; Hernandez, M.L.; Alexis, N.E.; Ghio, A.J.; Tilley, S.L.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Peden, D.B.; Cook, D.N.; et al. Neuropilin-2 regulates airway inflammatory responses to inhaled lipopolysaccharide. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L202–L211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.Y.; Ohe, R.; Meng, H.; Kabasaw, T.; Yang, S.; Kato, T.; Yamakawa, M. Specific Neuropilins Expression in Alveolar Macrophages among Tissue-Specific Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhupar, R.; Jones, K.E.; Powers, A.A.; Eisenberg, S.H.; Ding, K.; Chen, F.; Nasarre, C.; Cen, Z.; Gong, Y.; LaRue, A.C.; et al. Isoforms of Neuropilin-2 Denote Unique Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ran, J.; Miao, Z.; Yang, M.; Mou, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xie, Q.; Jin, K. Deficiency of inflammation-sensing protein neuropilin-2 in myeloid-derived macrophages exacerbates colitis via NF-κB activation. J. Pathol. 2023, 262, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucka, P.; Levonyak, N.; Geretti, E.; Zwaans, B.M.M.; Li, X.; Adini, I.; Klagsbrun, M.; Adam, R.M.; Bielenberg, D.R. Inflammation and Lymphedema Are Exacerbated and Prolonged by Neuropilin 2 Deficiency. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Su, J.; Xu, J.; Liang, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, L.; et al. IKKβ increases neuropilin-2 and promotes the inhibitory function of CD9+ Bregs to control allergic diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 185, 106517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werneburg, S.; Mühlenhoff, M.; Stangel, M.; Hildebrandt, H. Polysialic acid on SynCAM 1 in NG2 cells and on neuropilin-2 in microglia is confined to intracellular pools that are rapidly depleted upon stimulation. Glia 2015, 63, 1240–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotzer, V.L.; Glosson, N.; Zhou, D.; Nishino, I.; Blum, J.S. LAMP-2-deficient human B cells exhibit altered MHC class II presentation of exogenous antigens. Immunology 2010, 131, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.-Q.; Wang, S.; Lei, C.-Q.; Sun, M.-S.; Shu, H.-B.; Liu, Y. WDFY1 mediates TLR3/4 signaling by recruiting TRIF. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curreli, S.; Wong, B.S.; Latinovic, O.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Stamatos, N.M. Class 3 semaphorins induce F-actin reorganization in human dendritic cells: Role in cell migration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Cabello, T.M.; Gutiérrez-Valenzuela, L.D.; Salinas-Marín, R.; López-Guerrero, D.V.; Martínez-Duncker, I. Polysialic Acid in the Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 823637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Johnson, C.B.; Olsson, A.; Slaughter, A.; May, M.; Weinhaus, B.; D’Alessandro, A.; Engel, J.D.; Jiang, J.X.; et al. Spatial Mapping of Myelopoiesis Reveals the Bone Marrow Niche for Monocyte Dendritic Cell Progenitors. Blood 2019, 134, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Gallardo, A.; Escribano, C.; Delgado-Martin, C.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, J.L.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Rutishauser, U.; Corbi, A.L.; Vega, M.A. Polysialylated neuropilin-2 enhances human dendritic cell migration through the basic C-terminal region of CCL21. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Gallardo, A.; Delgado-Martín, C.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Rodríguez-Fernández, J.L.; Vega, M.A. Polysialic acid is required for neuropilin-2a/b-mediated control of CCL21-driven chemotaxis of mature dendritic cells and for their migration in vivo. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahraz, A.; Kopatz, J.; Mathy, R.; Kappler, J.; Winter, D.; Kapoor, S.; Schutza, V.; Scheper, T.; Gieselman, V.; Neumann, H. Anti-inflammatory activity of low molecular weight polysialic acid on human macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatos, N.M.; Xhang, L.; Jokilammi, A.; Finne, J.; Chen, W.H.; El-Maarouf, A.; Cross, A.S.; Hankey, K.G. Changes in polysialic acid expression on myeloid cells during differentiation and recruitment to sites of inflammation: Role in phagocytosis. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, S.T. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mallampalli, R.K. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: From Mechanism to Translation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, T.A.; Panzica, L.; Kalathil, S.G.; Thanavala, Y. Transatlantic Airway Conference Immune Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.D.; Serhan, C.N. Resolution of Acute Inflammation in the Lung. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, W.; Qiu, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wu, C.; Lai, X.; Feng, X. Alveolar macrophage-derived NRP2 curtails lung injury while boosting host defense in bacterial pneumonia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 112, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; van der Meer, F.; Kallio, K.; Kaya, T.; Anastasina, M.; et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science 2020, 370, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghez, D.; Lepelletier, Y.; Lambert, S.; Fourneau, J.-M.; Blot, V.; Janvier, S.; Arnulf, B.; van Endert, P.M.; Heveker, N.; Pique, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is involved in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 entry. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6844–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.-P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Feng, G.-K.; Du, Y.; Xiong, D.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, W.-L.; et al. Neuropilin 1 is an entry factor that promotes EBV infection of nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Martin, N.; Marcandalli, J.; Huang, C.S.; Arthur, C.P.; Perotti, M.; Foglierini, M.; Ho, H.; Dosey, A.M.; Shriver, S.; Payandeh, J.; et al. An Unbiased Screen for Human Cytomegalovirus Identifies Neuropilin-2 as a Central Viral Receptor. Cell 2018, 174, 1158–1171.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, J.V. Type 2 inflammation in asthma-present in most, absent in many. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötvall, J.; Akdis, C.A.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bjermer, L.; Casale, T.B.; Custovic, A.; Lemanske, R.F.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Wenzel, S.E.; Greenberger, P.A. Asthma endotypes: A new approach to classification of disease entities within the asthma syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Raundhal, M.; Oriss, T.B.; Ray, P.; Wenzel, S.E. Current concepts of severe asthma. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, E.; Reddel, H.K. Severe and Difficult-to-Treat Asthma in Adults. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Kolls, J.K. Neutrophilic Inflammation in Asthma and Association with Disease Severity Epidemiology of Neutrophilic Asthma. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadebe, S.; Kirstein, F.; Fierens, K.; Chen, K.; Drummond, R.A.; Vautier, S.; Sajaniemi, S.; Murray, G.; Williams, D.L.; Redelinghuys, P.; et al. Microbial Ligand Costimulation Drives Neutrophilic Steroid-Refractory Asthma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 134219. [Google Scholar]
- Immormino, R.M.; Jania, C.M.; Tilley, S.L.; Moran, T.P. Neuropilin-2 regulates airway inflammation in a neutrophilic asthma model. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, N.; Douda, D.N.; Bruggemann, T.R.; Ricklefs, I.; Duvall, M.G.; Abdulnour, R.E.; Martinod, K.; Tavares, L.; Wang, X.; Cernadas, M.; et al. Neutrophil cytoplasts induce Th17 differentiation and skew inflammation toward neutrophilia in severe asthma. HHS Public Access. 2018, 3, eaao4747. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.H.; Whitehead, G.S.; Nakano, H.; Free, M.E.; Kolls, J.K.; Cook, D.N. Allergic Sensitization through the Airway Primes Th17-dependent Neutrophilia and Airway Hyperresponsiveness. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, T.; Nakano, K.; Whitehead, G.S.; Thomas, S.Y.; Cook, D.N.; Nakano, H. Inhaled house dust programs pulmonary dendritic cells to promote type 2 T-cell responses by an indirect mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrinos, G.; Cristofaro, V.; Pelton, K.; Bigger-Allen, A.; Doyle, C.; Vasquez, E.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Sullivan, M.P.; Adam, R.M. Neuropilin 2 Is a Novel Regulator of Distal Colon Contractility. Am. J. Pathol. 2022, 192, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Reutershan, J.; Morris, M.A.; Solga, M.; Rose, C.E., Jr.; Ley, K. CAM-1 and LFA-1 play critical roles in LPS-induced neutrophil recruitment into the alveolar space. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.L.; Gibson, P.G.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.; James, A.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; AMAZES Study Research Group. Impaired macrophage phagocytosis in non-eosinophilic asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabiec, A.M.; Hussell, T. The role of airway macrophages in apoptotic cell clearance following acute and chronic lung inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Boyanapalli, R.; Goleva, E.; Kolakowski, C.; Min, E.; Day, B.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Riches, D.W.H.; Bratton, D.L.; Sutherland, E.R. Obesity impairs apoptotic cell clearance in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 131, 1041–1047.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.L.; Malcolm, K.C.; Kotaru, C.; Tilstra, J.A.; Westcott, J.Y.; Fadok, V.A.; Wenzel, S.E. Defective Apoptotic Cell Phagocytosis Attenuates Prostaglandin E2 and 15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid in Severe Asthma Alveolar Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 172, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bag, A.K.; Dutta, S.; Polavaram, N.S.; Islam, R.; Schellenburg, S.; Banwait, J.; Guda, C.; Ran, S.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; et al. Macrophage-Derived Neuropilin-2 Exhibits Novel Tumor-Promoting Functions. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5600–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadok, V.A.; Bratton, D.L.; Konowal, A.; Freed, P.W.; Westcott, J.Y.; Henson, P.M. Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabkin, H.A.; Starkova, J.; Gemmill, R.M. A triad of NRP2, DLX and p53 proteins in lung cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 96464–96465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, A.; Nasarre, C.; Peterson, Y.K.; Pagano, R.; Gooz, M.; Nasarre, P.; Drabkin, H.A.; Armeson, K.E.; Gibney, B.C.; Gemmill, R.M.; et al. Europilin-2b facilitates resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 162, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmill, R.M.; Nasarre, P.; Nair-Menon, J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Landi, L.; D’Incecco, A.; Uramoto, H.; Yoshida, T.; Haura, E.B.; Armeson, K.; et al. The neuropilin 2 isoform NRP2b uniquely supports TGFβ-mediated progression in lung cancer. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaag0528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasarre, P.; Gemmill, R.M.; Potiron, V.A.; Roche, J.; Lu, X.; Barón, A.E.; Korch, C.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Lagana, A.; Howe, P.H.; et al. Neuropilin-2 Is Upregulated in Lung Cancer Cells during TGF-β1–Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 7111–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasarre, P.; Gemmill, R.M.; Drabkin, H.A. The emerging role of class-3 semaphorins and their neuropilin receptors in oncology. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 1663–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Caunt, M.; Mak, J.; Liang, W.C.; Stawicki, S.; Pan, Q.; Tong, R.K.; Kowalski, J.; Ho, C.; Reslan, H.B.; Ross, J.; et al. Blocking neuropilin-2 function inhibits tumor cell metastasis. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, N.A.; Gray, M.J.; Xia, L.; Fan, F.; van Buren, G., II; Gaur, P.; Samuel, S.; Lim, S.J.; Arumugam, T.; Ramachandran, V.; et al. Neuropilin-2-mediated tumor growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 8052–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Hoeppner, L.H.; Bach, S.; Guangqi, E.; Guo, Y.; Wang, E.; Wu, J.; Cowley, M.J.; Chang, D.K.; Waddell, N.; et al. Neuropilin-2 promotes extravasation and metastasis by interacting with endothelial α5 integrin. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4579–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Hatanaka, H.; Kijima, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Abe, Y.; Osamura, Y.; Inoue, H.; Ueyama, Y.; Nakamura, M. Neuropilin 1 and neuropilin 2 co-expression is significantly correlated with increased vascularity and poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Roy, S.; Polavaram, N.S.; Stanton, M.J.; Zhang, H.; Bhola, T.; Hönscheid, P.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Band, H.; Batra, S.K.; et al. Neuropilin-2 Regulates Endosome Maturation and EGFR Trafficking to Support Cancer Cell Pathobiology. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, M.J.; Dutta, S.; Polavaram, N.S.; Roy, S.; Muders, M.H.; Datta, K. Angiogenic growth factor axis in autophagy regulation. Autophagy 2013, 9, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandclement, C.; Pallandre, J.R.; Degano, S.V.; Viel, E.; Bouard, A.; Balland, J.; Remy-Martin, J.-P.; Simon, B.; Rouleau, A.; Boireau, W.; et al. Neuropilin-2 expression promotes TGF-β1-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowetz, A.; Froehner, M.; Rauner, M.; Conrad, S.; Erdmann, K.; Mayr, T.; Datta, K.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Baretton, G.B.; Wirth, M.; et al. Neuropilin-2 is an independent prognostic factor for shorter cancer-specific survival in patients with acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Chen, Z.; Chang, R.; Yuan, T.; Li, G.; Zhu, C.; Wen, J.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ding, Z.; et al. CENPA functions as a transcriptional regulator to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression via cooperating with YY1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 5218–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, H.; Kadoma, R.; Tsujimoto, M.; Yoshidome, K.; Akamatsu, H.; Nakahara, M.; Inagaki, M.; Sanke, T.; Nakamura, Y. Neuropilin-2 expression in breast cancer: Correlation with lymph node metastasis, poor prognosis, and regulation of CXCR4 expression. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenberg, C.D.; Livingston, S.; Chen, R.; Kruk, P.A.; Nicosia, S.V. Expression of Semaphorin 3F and Its Receptors in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer, Fallopian Tubes, and Secondary Müllerian Tissues. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2009, 2009, 730739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, D.G.; Oh, K.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Hong, S.D.; Lee, J.I.; Shin, J.A.; et al. Neuropilin-2 acts a critical determinant for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and aggressive behaviors of human head and neck cancer. Cell Oncol. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Roy, S.; Polavaram, N.S.; Baretton, G.B.; Muders, M.H.; Batra, S.; Datta, K. NRP2 transcriptionally regulates its downstream effector WDFY1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, M.J.; Stanton, M.J.; Dutta, S.; Zhang, H.; Polavaram, N.S.; Leontovich, A.A.; Hönscheid, P.; Sinicrope, F.A.; Tindall, D.J.; Muders, M.H.; et al. Autophagy control by the VEGF-C/NRP-2 axis in cancer and its implication for treatment resistance. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muders, M.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, E.; Tindall, D.J.; Datta, K. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C protects prostate cancer cells from oxidative stress by the activation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex-2 and AKT-1. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6042–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.; Lu, S.; Taglienti, C.A.; Mercurio, A.M. Metabolic stress induces the lysosomal degradation of neuropilin-1 but not neuropilin-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 28074–28080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, A.M.; Parker, M.W.; Vander Kooi, C.W. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a novel benzamidine-based inhibitor of VEGF-C binding to Neuropilin-2. Bioorg Chem. 2020, 100, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wisniewski, C.A.; Xiong, C.; Chhoy, P.; Goel, H.L.; Kumar, A.; Zhu, L.J.; Li, R.; St Louis, P.A.; Ferreira, L.M.; et al. Therapeutic blocking of VEGF binding to neuropilin-2 diminishes PD-L1 expression to activate antitumor immunity in prostate cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eade5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaimy, A.L.; Guru, S.; Chang, C.; Ou, J.; Amante, J.J.; Zhu, L.J.; Goel, H.L.; Mercurio, A.M. VEGF-neuropilin-2 signaling promotes stem-like traits in breast cancer cells by TAZ-mediated repression of the Rac GAP β2-chimaerin. Sci. Signal 2018, 11, eaao6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzolio, S.; Battistini, C.; Cagnoni, G.; Apicella, M.; Vella, V.; Giordano, S.; Tamagnone, L. Downregulating Neuropilin-2 Triggers a Novel Mechanism Enabling EGFR-Dependent Resistance to Oncogene-Targeted Therapies. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.J.; Wei, X.; Peng, Y.; Zha, L.; Zhou, R.B.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, H.J. Neuropilin-2 mediates lymphangiogenesis of colorectal carcinoma via a VEGFC/VEGFR3 independent signaling. Cancer Lett. 2015, 358, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, H.L.; Chang, C.; Pursell, B.; Leav, I.; Lyle, S.; Xi, H.S.; Hsieh, C.C.; Adisetiyo, H.; Roy-Burman, P.; Coleman, I.M.; et al. VEGF/neuropilin-2 regulation of Bmi-1 and consequent repression of IGF-IR define a novel mechanism of aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, A.; Silvano, M.; Miele, E.; Capalbo, C.; Eramo, A.; Salvati, V.; Todaro, M.; Besharat, Z.M.; Catanzaro, G.; Cucchi, D.; et al. Noncanonical GLI1 signaling promotes stemness features and in vivo growth in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4641–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Polavaram, N.S.; Islam, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bodas, S.; Mayr, T.; Roy, S.; Albala, S.A.Y.; Toma, M.I.; Darehshouri, A.; et al. Neuropilin-2 regulates androgen-receptor transcriptional activity in advanced prostate cancer. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3747–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercurio, A.M. VEGF/neuropilin signaling in cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; He, J.Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.Y.; Mo, B.H.; Shu, Q.X.; Chen, C.; Gong, Y.Z.; Zhao, X.L.; Xie, G.F.; et al. Vascular NRP2 triggers PNET angiogenesis by activating the SSH1-cofilin axis. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benwell, C.J.; Johnson, R.T.; Taylor, J.A.G.E.; Price, C.A.; Robinson, S.D. Endothelial VEGFR Coreceptors Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 Are Essential for Tumor Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 1626–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coma, S.; Shimizu, A.; Klagsbrun, M. Hypoxia induces tumor and endothelial cell migration in a semaphorin 3F- and VEGF-dependent manner via transcriptional repression of their common receptor neuropilin 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2011, 5, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, H.L.; Pursell, B.; Standley, C.; Fogarty, K.; Mercurio, A.M. Neuropilin-2 regulates α6β1 integrin in the formation of focal adhesions and signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, R.T.; Feng, B.Y.; Ni, J.; Woo, W.M.; Milenkovic, L.; Hayden Gephart, M.G.; Teruel, M.N.; Oro, A.E.; Chen, J.K.; Scott, M.P. Neuropilins are positive regulators of Hedgehog signal transduction. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, A.J.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Dai, R.; Heyman, B.; Hsu, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Hedgehog signaling promotes tumor-associated macrophage polarization to suppress intratumoral CD8+ T cell recruitment. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 5151–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Peng, B.; Ye, R. FOXM1 accelerates wound healing in diabetic foot ulcer by inducing M2 macrophage polarization through a mechanism involving SEMA3C/NRP2/Hedgehog signaling. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 184, 109121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, S.; Allard-Ratick, M.; Akino, T.; van Meeteren, L.A.; Mammoto, A.; Klagsbrun, M. GATA2 and Lmo2 control angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis via direct transcriptional regulation of neuropilin-2. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.M.; Lund, A.W. Afferent Lymphatic Transport and Peripheral Tissue Immunity. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, S.; Cervero, P.; Eddy, R.; Condeelis, J. Mechanisms and roles of podosomes and invadopodia. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benwell, C.J.; Taylor, J.A.G.E.; Robinson, S.D. Endothelial neuropilin-2 influences angiogenesis by regulating actin pattern development and α5-integrin-p-FAK complex recruitment to assembling adhesion sites. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamalice, L.; Le Boeuf, F.; Huot, J. Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, F.; Luo, J.Y.; Chen, A.F. Sema3G activates YAP and promotes VSMCs proliferation and migration via Nrp2/PlexinA1. Cell Signal 2023, 105, 110613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N. PPAR-γ promotes endothelial cell migration by inducing the expression of Sema3g. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Gao, N.; Dike, M.; Shkilnyy, O.; Me, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F.X. Opposing Effects of Neuropilin-1 and -2 on Sensory Nerve Regeneration in Wounded Corneas: Role of Sema3C in Ameliorating Diabetic Neurotrophic Keratopathy. Diabetes 2019, 68, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, A.; Ma, T.; Menon, D.; Deshpande, M.; Jee, K.; Dinabandhu, A.; Vancel, J.; Lu, D.; Montaner, S. Angiopoietin-like 4 binds neuropilins and cooperates with VEGF to induce diabetic macular edema. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 4593–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Uemura, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Hirashima, M. Semaphorin 3G Provides a Repulsive Guidance Cue to Lymphatic Endothelial Cells via Neuropilin-2/PlexinD1. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielenberg, D.; Doyle, C.; Vasquez, E.; Pelton, K.; Cristofaro, V.; Sullivan, M.; Adam, R. Altered Gut Motility in Mice Lacking Neuropilin 2 in Smooth Muscle. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 496.31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Urabe, G.; Marcho, L.; Williams, C.; Guo, L.W.; Kent, K.C. Smad3 Regulates Neuropilin 2 Transcription by Binding to its 5’ Untranslated Region. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutschera, S.; Weber, H.; Weick, A.; De Smet, F.; Genove, G.; Takemoto, M.; Prahst, C.; Riedel, M.; Mikelis, C.; Baulande, S.; et al. Differential endothelial transcriptomics identifies semaphorin 3G as a vascular class 3 semaphorin. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Bruneau, S.; Kochupurakkal, N.; Coma, S.; Briscoe, D.M.; Klagsbrun, M. Regulation of mTOR Signaling by Semaphorin 3F-Neuropilin 2 Interactions In Vitro and In Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Kong, X.; Zuo, G.; Zhou, W.; Gu, Y.; et al. NRP2 promotes atherosclerosis by upregulating PARP1 expression and enhancing low shear stress-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Sun, N.H.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.J.; Yuan, S.T.; Hu, Z.Z.; Lu, N.N.; Körbelin, J.; Fukunaga, K.; Liu, Q.H.; et al. Endothelium-derived semaphorin 3G attenuates ischemic retinopathy by coordinating β-catenin–dependent vascular remodeling. J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 131, e135296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, S.; Scheid, S.; Roth, T.; Herkel, M.; Petrova, D.; Linden, A.; Weberbauer, M.; Esser, J.; Diehl, P.; Grundmann, S.; et al. Semaphorin 3F Promotes Transendothelial Migration of Leukocytes in the Inflammatory Response After Survived Cardiac Arrest. Inflammation 2019, 42, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.D.; Nishi, H.; Poles, J.; Niu, X.; Mccauley, C.; Rahman, K.; Brown, E.J.; Yeung, S.T.; Vozhilla, N.; Weinstock, A.; et al. Single-cell analysis of fate-mapped macrophages reveals heterogeneity, including stem-like properties, during atherosclerosis progression and regression. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e124574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochain, C.; Vafadarnejad, E.; Arampatzi, P.; Pelisek, J.; Winkels, H.; Ley, K.; Wolf, D.; Saliba, A.-E.; Zernecke, A. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the transcriptional landscape and heterogeneity of aortic macrophages in murine atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1661–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid–induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, E.M.; Pearce, S.W.A.; Xiao, Q. Foam cell formation: A new target for fighting atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2019, 112, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Hudis, C.A.; Dannenberg, A.J. Obesity and Cancer: Local and Systemic Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, L.S.; Gomez, D.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Salmon, M.; Alencar, G.F.; Haskins, R.M.; Swiatlowska, P.; Newman, A.A.; Greene, E.S.; Straub, A.C.; et al. KLF4-dependent phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells has a key role in atherosclerotic plaque pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, Y.; Kalcheim, C.; Kahane, N.; Reshef, R.; Neufeld, G. Differential expression of neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 in arteries and veins. Mech. Dev. 2001, 109, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Fu, X.; Tan, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Ding, S. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in tumor-associated macrophages on lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, H.E.; Hoelscher, G.L.; Bethea, S.; Hanley, E.N.J. Interleukin 1-beta upregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin 3 and neuropilin 2 gene expression and NGF production in annulus cells. Biotech. Histochem. 2012, 87, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xing, B.; Xuan, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Tang, J. NRP-2 in tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 418, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioschi, M.; Gianazza, E.; Agostoni, P.; Zoanni, B.; Mallia, A.; Banfi, C. Multiplexed MRM-Based Proteomics Identified Multiple Biomarkers of Disease Severity in Human Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, J.; Khan, M.A.; Klip, I.T.; Meyer, S.; de Boer, R.A.; Jaarsma, T.; Hillege, H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; van der Meer, P.; Voors, A.A. Biomarker Profiles in Heart Failure Patients with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e003989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chong, Y.; Crampton, S.; Adams, R.; Rauch, K.; Paz, S.; Chu, D.; Zhai, L.; Burman, L.; Ampudia, J.; et al. ATYR1923 Specifically Binds to Neuropilin-2, a Novel Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Diseases. ATS 2020 International Conference American Thoracic Society International Conference Meetings Abstracts. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, A3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.S.; Gardiner, E.; Xu, Z.; Lau, C.F.; Wang, F.; Zhou, J.J.; Mendlein, J.D.; Nangle, L.A.; Chiang, K.P.; Yang, X.L.; et al. Human tRNA synthetase catalytic nulls with diverse functions. Science 2014, 345, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.A.; Aryal, S.; Barney, J.; Hsia, C.C.W.; James, W.E.; Maier, L.A.; Marts, L.T.; Obi, O.N.; Sporn, P.H.S.; Sweiss, N.J.; et al. Efzofitimod for the Treatment of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Chest 2023, 163, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Niranjan, V.; Walker, G.; Burkart, C.; Paz, S.; Chong, Y.; Siefker, D.; Sun, E.; Nangle, L.; Forster, S.; et al. Efzofitimod: A novel anti-inflammatory agent for sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023, 40, e2023011. [Google Scholar]
- Burkart, C.; Seikkula, M.; Eide, L.; Paz, S.; Chu, D.; Polizzi, C.; King, D.; Rosengren, S.; Ogilvie, K. ATYR1923 Modulates the Inflammatory Response in Experimental Models of Interstitial Lung Disease. American Thoracic Society International Conference Meetings Abstracts American Thoracic Society International Conference Meetings Abstracts. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, A2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Costabel, U.; Dai, H. The Role of Diverse Immune Cells in Sarcoidosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 788502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, S.; Chong, Y.E.; Siefker, D.; Becker, Y.; Bao, R.; Escobedo, E.; Qing, Y.; Rauch, K.; Burman, L.; Burkart, C.; et al. Development and Characterization of a Novel Neuropilin-2 Antibody for Immunohistochemical Staining of Cancer and Sarcoidosis Tissue Samples. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2023, 42, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, P.; Luo, X.; Wu, T.; Luo, F.; Yan, J. N2E4, a Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Neuropilin-2, Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma via Suppressing FAK/Erk/HIF-1α Signaling. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 657008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Goel, H.L.; Burkart, C.; Burman, L.; Chong, Y.E.; Barber, A.G.; Geng, Y.; Zhai, L.; Wang, M.; Kumar, A.; et al. Inhibition of VEGF binding to neuropilin-2 enhances chemosensitivity and inhibits metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadf1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Disease | Target Pathway | Endpoint | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcoidosis | Targets macrophages in pulmonary granulomas to potentially downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF alpha and IL-6 | Weaning of steroid dose and duration Symptomatic quality of life improvement | Currently phase 3 trial taking place using efzofitimod |
| Systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related interstitial lung disease | Innate immune system Downregulation of inflammatory cytokines | Change and improvement of Pulmonary function tests Symptomatic quality of life improvement | Ongoing phase 2 trial using efzofitimod |
| Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor | F-acting-mediated motility via SSH1-cofilin signaling | Tumor vascularity and growth | Preclinical studies |
| Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | FAK/Erk/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling | Tumor growth and metastasis | Preclinical studies |
| Prostate cancer | PD-L1 expression due to VEGF/Nrp2 signaling | Decreased PD-L1 expression, increase in immune mediated tumor killing | Preclinical studies |
| Breast cancer | Nrp2/VEGF-C pathway | Decreased tumor lymphangiogenesis | Preclinical studies |
| Vascular occlusive disease | VEGF-C/NRP2 pathway | Decrease in vascular inflammation | Preclinical studies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhupar, R.; Powers, A.A.; Eisenberg, S.H.; Gemmill, R.M.; Bardawil, C.E.; Udoh, H.M.; Cubitt, A.; Nangle, L.A.; Soloff, A.C. Orchestrating Resilience: How Neuropilin-2 and Macrophages Contribute to Cardiothoracic Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051446
Dhupar R, Powers AA, Eisenberg SH, Gemmill RM, Bardawil CE, Udoh HM, Cubitt A, Nangle LA, Soloff AC. Orchestrating Resilience: How Neuropilin-2 and Macrophages Contribute to Cardiothoracic Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051446
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhupar, Rajeev, Amy A. Powers, Seth H. Eisenberg, Robert M. Gemmill, Charles E. Bardawil, Hannah M. Udoh, Andrea Cubitt, Leslie A. Nangle, and Adam C. Soloff. 2024. "Orchestrating Resilience: How Neuropilin-2 and Macrophages Contribute to Cardiothoracic Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051446






