Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease
Abstract
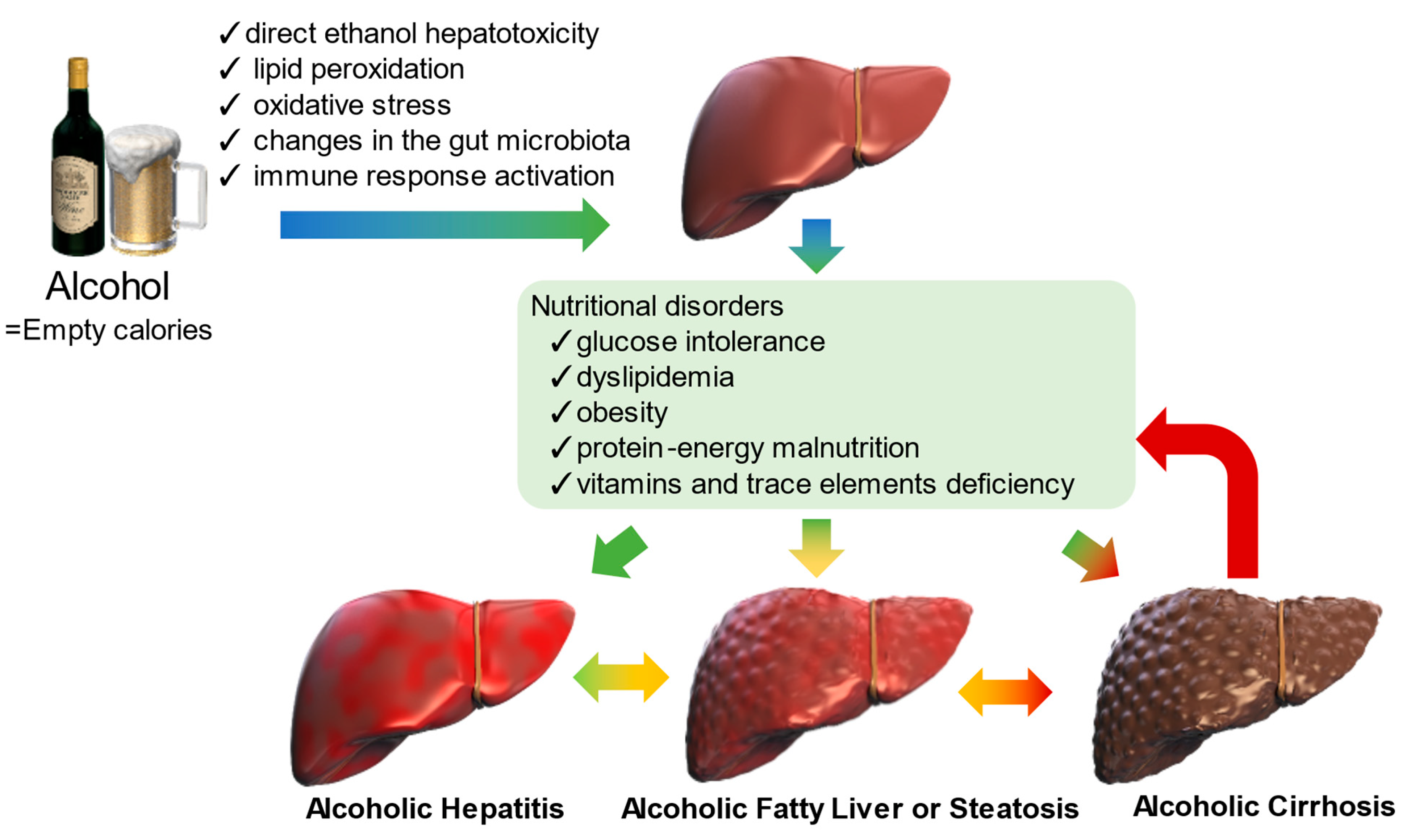
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Alcohol-Induced Metabolic Abnormalities
3.1. Glucose Intolerance
3.2. Dyslipidemia
3.3. Obesity
3.4. Protein–energy Malnutrition
4. Nutritional Therapy for ALD
4.1. Total Calories, Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Recommended for ALD
4.1.1. Total Calories and Nutritional Support Route Recommended for ALD
4.1.2. Carbohydrates Recommended for ALD
4.1.3. Fats Recommended for ALD
4.1.4. Proteins Recommended for ALD
4.1.5. Alcoholic Hepatitis
4.1.6. Alcoholic Fatty Liver or Steatosis
4.1.7. Alcoholic Cirrhosis
4.2. Vitamins and Trace Elements Recommended for ALD
4.2.1. Overview
| Nutrients | ALD | Signs/Symptoms in Deficiency/Excess | Supplementation | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A/Retinol | ↓ | Night blindness | It may be considered in case of deficiency | [90] |
| Immune system disorders | [90,91] | |||
| Severe liver damage | [91] | |||
| Vitamin D | ↓ | Bone diseases (including rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults) | Can be considered | [92] |
| Risk of respiratory illness | [93] | |||
| Altered gut barrier/immune function | [94,95,96] | |||
| Vitamin E | →-↓ | Related to oxidative stress | Can be considered | [97] |
| Vitamin B1/Thiamine | ↓ | Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome | Can be considered | [98] |
| Neurologic symptoms | [98] | |||
| Cardiovascular abnormalities | [98] | |||
| Folate | ↓ | Anemia | Can be considered | [99] |
| Altered methylation | [100] | |||
| Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma | [101,102] | |||
| Zinc | ↓ | Immune abnormalities | It may be considered in case of deficiency | [103] |
| Insulin resistance | [104] | |||
| Hepatic encephalopathy | [105,106] | |||
| Magnesium | ↓ | Insulin resistance | Can be considered | [107] |
| Hypocalcemia or hypokalemia | [108] | |||
| Muscle cramps | [109] | |||
| Iron | ↓-↑ | Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (surplus) | It may be considered in case of deficiency | [110,111] |
| Liver fibrosis (surplus) | [112] | |||
| Insulin resistance (surplus) | [113] | |||
| Manganese | ↑ | Hepatic encephalopathy | No evidence | [114,115] |
| Copper | ↓-↑ | Central nervous system dysfunction (deficiency) | No evidence | [68] |
| Selenium | ↓ | Ballooning of hepatocytes | Can be considered | [116] |
4.2.2. Vitamin A (Retinol)
4.2.3. Vitamin D
4.2.4. Vitamin E
4.2.5. Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
4.2.6. Folate
4.2.7. Zinc
4.2.8. Magnesium
4.2.9. Iron
4.2.10. Manganese
4.2.11. Copper
4.2.12. Selenium
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADH | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| AFL | alcoholic fatty liver |
| AH | alcoholic hepatitis |
| ALD | alcoholic liver disease |
| ALDH | aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| BCAA | branched-chain amino acid |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BTR | BCAA-to-tyrosine ratio |
| CYP2E1 | cytochrome P450 2E1 |
| FFA | free fatty acids |
| Ile | isoleucine |
| Leu | leucine |
| MAFLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease |
| NASH | nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| PEM | protein–energy malnutrition |
| REE | resting energy expenditure |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TG | triglycerides |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| Val | valine |
| Zn | zinc |
References
- Patel, P.V.; Flamm, S.L. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Including New Developments. Clin. Liver Dis. 2023, 27, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styskel, B.; Natarajan, Y.; Kanwal, F. Nutrition in Alcoholic Liver Disease: An Update. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.; Roselle, G.A.; Gartside, P.; Moritz, T. Relationship of protein calorie malnutrition to alcoholic liver disease: A reexamination of data from two Veterans Administration Cooperative Studies. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Mueller, M. Alcoholic Liver Disease. In StatPearls; StatsPearl Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, N.; Shor, J.; Szabo, G. Alcoholic Hepatitis: A Review. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.M.; Horiguchi, N.; Jeong, W.I.; Radaeva, S.; Gao, B. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholic liver disease: Innate immunity and cytokines. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grauers Wiktorin, H.; Aydin, E.; Hellstrand, K.; Martner, A. NOX2-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 7095902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montuschi, P.; Barnes, P.J.; Roberts, L.J. 2nd. Isoprostanes: Markers and mediators of oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engen, P.A.; Green, S.J.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Alcohol Effects on the Composition of Intestinal Microbiota. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhao, M.; Ruan, G.; Dai, Z.; Xue, Y.; Shi, D.; Xu, C.; Yu, O.; Wang, F.; et al. Microbial treatment of alcoholic liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1054265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Marcos, M.; Kodys, K.; Csak, T.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. Up-regulation of microRNA-155 in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Mehmood, A.; Yuan, D.; Usman, M.; Murtaza, M.A.; Yaqoob, S.; Wang, C. Protective Mechanism of Edible Food Plants against Alcoholic Liver Disease with Special Mention to Polyphenolic Compounds. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.K.; Charlton, M.R. Nutrition in alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S. Relationships between nutrition, alcohol use, and liver disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Dasarathy, S. Nutrition and Alcoholic Liver Disease: Effects of Alcoholism on Nutrition, Effects of Nutrition on Alcoholic Liver Disease, and Nutritional Therapies for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michelena, J.; Altamirano, J.; Abraldes, J.G.; Affo, S.; Morales-Ibanez, O.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Dominguez, M.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Fernandez, J.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Systemic inflammatory response and serum lipopolysaccharide levels predict multiple organ failure and death in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 2015, 62, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orntoft, N.W.; Sandahl, T.D.; Jepsen, P.; Vilstrup, H. Short-term and long-term causes of death in patients with alcoholic hepatitis in Denmark. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1739–1744.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniai, M.; Hashimoto, E.; Tokushige, K.; Kodama, K.; Kogiso, T.; Torii, N.; Shiratori, K. Roles of gender, obesity, and lifestyle-related diseases in alcoholic liver disease: Obesity does not influence the severity of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliunas, D.O.; Taylor, B.J.; Irving, H.; Roerecke, M.; Patra, J.; Mohapatra, S.; Rehm, J. Alcohol as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes. Care 2009, 32, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2016 Alcohol Collaborators. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 392, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singal, A.K.; Bataller, R.; Ahn, J.; Kamath, P.S.; Shah, V.H. ACG Clinical Guideline: Alcoholic Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, J.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Hamberg, O.; Stanga, Z.; Ad Hoc ESPEN Working Group. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): A new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, J.; Kondrup, J.; Prokopowicz, J.; Schiesser, M.; Krahenbuhl, L.; Meier, R.; Liberda, M.; EuroOOPS Study Group. EuroOOPS: An international, multicentre study to implement nutritional risk screening and evaluate clinical outcome. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Raman, M.; Mourtzakis, M.; Merli, M. A practical approach to nutritional screening and assessment in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plauth, M.; Cabre, E.; Riggio, O.; Assis-Camilo, M.; Pirlich, M.; Kondrup, J.; Ferenci, P.; Holm, E.; Vom Dahl, S.; Muller, M.J.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokushige, K.; Ikejima, K.; Ono, M.; Eguchi, Y.; Kamada, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Akuta, N.; Yoneda, M.; Iwasa, M.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 2020. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, Y.; Okita, K.; Suzuki, K.; Moriwaki, H.; Kato, A.; Miwa, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Okuda, H.; Onji, M.; Kanazawa, H.; et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition 2007, 23, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Endo, R.; Kohgo, Y.; Ohtake, T.; Ueno, Y.; Kato, A.; Suzuki, K.; Shiraki, R.; Moriwaki, H.; Habu, D.; et al. Guidelines on nutritional management in Japanese patients with liver cirrhosis from the perspective of preventing hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oura, K.; Morishita, A.; Tani, J.; Masaki, T. Antitumor Effects and Mechanisms of Metabolic Syndrome Medications on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell Carcinoma 2022, 9, 1279–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Iwama, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Tani, J.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Nomura, T.; Morishita, A.; Yoneyama, H.; et al. Diabetes mellitus and metformin in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6100–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatalo, P.I.; Koivisto, H.M.; Hietala, J.P.; Puukka, K.S.; Bloigu, R.; Niemela, O.J. Effect of moderate alcohol consumption on liver enzymes increases with increasing body mass index. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamaguchi, M.; Obora, A.; Okamura, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kojima, T.; Fukui, M. Changes in metabolic complications in patients with alcoholic fatty liver disease monitored over two decades: NAGALA study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engler, P.A.; Ramsey, S.E.; Smith, R.J. Alcohol use of diabetes patients: The need for assessment and intervention. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Cederbaum, A.I. Cytochrome P450s and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Cederbaum, A.I. Cytochrome P4502E1, oxidative stress, JNK, and autophagy in acute alcohol-induced fatty liver. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.C.; Li, J.J.; Wang, E.J.; Princler, G.L.; Kauffman, F.C.; Kung, H.F. Ethanol down-regulates the transcription of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein gene. FASEB J. 1997, 11, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Hu, M.; Zhang, R.; Shen, Z.; Flatow, L.; You, M. MicroRNA-217 promotes ethanol-induced fat accumulation in hepatocytes by down-regulating SIRT1. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9817–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tadokoro, T.; Morishita, A.; Masaki, T. Diagnosis and Therapeutic Management of Liver Fibrosis by MicroRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, M.; Rafiq, N.; Younossi, Z.M. Components of metabolic syndrome are independent predictors of mortality in patients with chronic liver disease: A population-based study. Gut 2010, 59, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Overweight, obesity and risk of liver cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.L.; Morrison, D.S.; Batty, G.D.; Mitchell, R.J.; Davey Smith, G. Effect of body mass index and alcohol consumption on liver disease: Analysis of data from two prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2010, 340, c1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naveau, S.; Giraud, V.; Borotto, E.; Aubert, A.; Capron, F.; Chaput, J.C. Excess weight risk factor for alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 1997, 25, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasztelan-Szczerbinska, B.; Surdacka, A.; Slomka, M.; Rolinski, J.; Celinski, K.; Smolen, A.; Szczerbinski, M. Association of serum adiponectin, leptin, and resistin concentrations with the severity of liver dysfunction and the disease complications in alcoholic liver disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 148526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raynard, B.; Balian, A.; Fallik, D.; Capron, F.; Bedossa, P.; Chaput, J.C.; Naveau, S. Risk factors of fibrosis in alcohol-induced liver disease. Hepatology 2002, 35, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Sarin, S.K.; Wong, V.W.; Fan, J.G.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ahn, S.H.; Zheng, M.H.; Shiha, G.; Yilmaz, Y.; Gani, R.; et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 889–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Eslam, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yamamura, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nakano, D.; Koseki, M.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; et al. MAFLD better predicts the progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk than NAFLD: Generalized estimating equation approach. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Eslam, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; George, J.; Torimura, T. MAFLD identifies patients with significant hepatic fibrosis better than NAFLD. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kiguchi, D.; Izumoto, H.; Ueki, H.; Kaneto, M.; Kitahata, S.; Aibiki, T.; Okudaira, T.; Tomida, H.; et al. Efficacy of branched-chain amino acid supplementation and walking exercise for preventing sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, H.; Sato, T.; Natsui, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kamimura, K.; Tsuchiya, A.; Murayama, T.; Yokoyama, J.; Kawai, H.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Treatment of Sarcopenia in Liver Disease: A Review of Current Knowledge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kato, M.; Marui, K.; Murakami, T.; Onishi, K.; Adachi, T.; Matsuoka, J.; Ueki, H.; Yoshino, T.; Tsuruta, M.; et al. Easy clinical predictor for low BCAA to tyrosine ratio in chronic liver disease patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Usefulness of ALBI score as nutritional prognostic marker. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3584–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Anderson, S.; Weesner, R.E.; Goldberg, S.J.; Crolic, K.A. Protein-calorie malnutrition associated with alcoholic hepatitis. Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Alcoholic Hepatitis. Am. J. Med. 1984, 76, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, A.J.; O’Connor, J.F. Alcoholic liver disease: Proposed recommendations for the American College of Gastroenterology. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 2022–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, C.M.; Schenker, S. The role of nutritional therapy in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2006, 29, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taskinen, M.R.; Packard, C.J.; Boren, J. Dietary Fructose and the Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muriel, P.; Lopez-Sanchez, P.; Ramos-Tovar, E. Fructose and the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Miller, M.E.; Cave, M.C.; Joshi-Barve, S.; McClain, C.J. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Update on the Role of Dietary Fat. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Ma, L.J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wan, J.B. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, S116–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeki, S.; Shiojiri, H.; Nozawa, Y. Chronic ethanol administration decreases fatty acyl-CoA desaturase activities in rat liver microsomes. FEBS Lett. 1984, 169, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, B.J.; Moon, K.H.; Olsson, N.U.; Salem, N., Jr. Prevention of alcoholic fatty liver and mitochondrial dysfunction in the rat by long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campollo, O.; Sprengers, D.; Dam, G.; Vilstrup, H.; McIntyre, N. Protein tolerance to standard and high protein meals in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Moritz, T.E.; Roselle, G.A.; Morgan, T.R.; Nemchausky, B.A.; Tamburro, C.H.; Schiff, E.R.; McClain, C.J.; Marsano, L.S.; Allen, J.I.; et al. A study of oral nutritional support with oxandrolone in malnourished patients with alcoholic hepatitis: Results of a Department of Veterans Affairs cooperative study. Hepatology 1993, 17, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Moritz, T.E.; Roselle, G.A.; Morgan, T.R.; Nemchausky, B.A.; Tamburro, C.H.; Schiff, E.R.; McClain, C.J.; Marsano, L.S.; Allen, J.I.; et al. Protein energy malnutrition in severe alcoholic hepatitis: Diagnosis and response to treatment. The VA Cooperative Study Group #275. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 1995, 19, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schutz, T.; Plauth, M. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3533–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trieu, J.A.; Bilal, M.; Lewis, B.; Gou, E.; Sonstein, L.; Parupudi, S. Adherence to Appropriate Nutrition in Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis is Low. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabb, D.W.; Im, G.Y.; Szabo, G.; Mellinger, J.L.; Lucey, M.R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcohol-Associated Liver Diseases: 2019 Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2020, 71, 306–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 154–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halsted, C.H. Nutrition and alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Deltenre, P.; Senterre, C.; Louvet, A.; Gustot, T.; Bastens, B.; Hittelet, A.; Piquet, M.A.; Laleman, W.; Orlent, H.; et al. Intensive Enteral Nutrition Is Ineffective for Patients with Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis Treated with Corticosteroids. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 903–910.e908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantena, S.K.; King, A.L.; Andringa, K.K.; Eccleston, H.B.; Bailey, S.M. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of alcohol- and obesity-induced fatty liver diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malnick, S.D.H.; Alin, P.; Somin, M.; Neuman, M.G. Fatty Liver Disease-Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic: Similar but Different. Int, J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, O.E.; Trapp, V.E.; Reichard, G.A., Jr.; Mozzoli, M.A.; Moctezuma, J.; Paul, P.; Skutches, C.L.; Boden, G. Nature and quantity of fuels consumed in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Clin. Invest. 1983, 72, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshiji, H.; Nagoshi, S.; Akahane, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kurosaki, M.; Sakaida, I.; Shimizu, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis 2020. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.D.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Late evening snack: Exploiting a period of anabolic opportunity in cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Suzuki, K. How to select BCAA preparations. Hepatol. Res. 2004, 30S, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, H.; Yamanaka-Okumura, H.; Katayama, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Hosoda, A.; Kurata, N.; Amemiya, F. Late evening snacks with branched-chain amino acids improve the Fischer ratio with patients liver cirrhosis at fasting in the next morning. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 30, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.; Davuluri, G.; Singh, D.; Allawy, A.; Ten Have, G.A.; Thapaliya, S.; Schulze, J.M.; Barnes, D.; McCullough, A.J.; Engelen, M.P.; et al. Metabolic and molecular responses to leucine-enriched branched chain amino acid supplementation in the skeletal muscle of alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, N.; Nakajima, H.; Takashi, S.I. Administration of granulated BCAA and quality of life. Hepatol. Res. 2004, 30S, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plank, L.D.; Gane, E.J.; Peng, S.; Muthu, C.; Mathur, S.; Gillanders, L.; McIlroy, K.; Donaghy, A.J.; McCall, J.L. Nocturnal nutritional supplementation improves total body protein status of patients with liver cirrhosis: A randomized 12-month trial. Hepatology 2008, 48, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamaki, A.; Yokoyama, K.; Koyama, K.; Morita, S.; Abe, H.; Kamimura, K.; Takamura, M.; Terai, S. Obesity and accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue are poor prognostic factors in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K.; Tsuchiya, M.; Mori, K.; Kubo, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Sakaguchi, E.; Yamashita, S.; Sakaida, I. Effect of a late evening snack on outpatients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, B.; Dao, T.; Joubert, C.; Dupont-Lucas, C.; Gloro, R.; Nguyen-Khac, E.; Beaujard, E.; Mathurin, P.; Vastel, E.; Musikas, M.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Enteral nutrition does not improve the long-term outcome of alcoholic cirrhotic patients with jaundice. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ledinghen, V.; Beau, P.; Mannant, P.R.; Borderie, C.; Ripault, M.P.; Silvain, C.; Beauchant, M. Early feeding or enteral nutrition in patients with cirrhosis after bleeding from esophageal varices? A randomized controlled study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, J.G.; Argo, C.K.; Al-Osaimi, A.M.; Northup, P.G. Mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with cirrhosis: A case series. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, S.S.; Goyal, O.; Singh, S.; Kishore, H.; Chhina, R.S.; Sidhu, S.S. Early feeding after esophageal variceal band ligation in cirrhotics is safe: Randomized controlled trial. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leevy, C.M.; Moroianu, S.A. Nutritional aspects of alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2005, 9, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyumpa, A.M. Mechanisms of vitamin deficiencies in alcoholism. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1986, 10, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llibre-Nieto, G.; Lira, A.; Vergara, M.; Sole, C.; Casas, M.; Puig-Divi, V.; Sole, G.; Humanes, A.; Grau, L.; Barradas, J.M.; et al. Micronutrient Deficiencies in Patients with Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Stein, A.C. Assessment and Management of Nutrition Status in the Hospitalized Patient with Cirrhosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 12, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hombali, A.S.; Solon, J.A.; Venkatesh, B.T.; Nair, N.S.; Pena-Rosas, J.P. Fortification of staple foods with vitamin A for vitamin A deficiency. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 5, CD010068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, A.H.; Mousa, O.Y.; Pham, L.E.; Corral-Hurtado, J.E.; Pungpapong, S.; Keaveny, A.P. An Argument for Vitamin D, A, and Zinc Monitoring in Cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Marcocci, C.; Carmeliet, G.; Bikle, D.; White, J.H.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lips, P.; Munns, C.F.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Giustina, A.; et al. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1109–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jachvadze, M.; Cholokava, N.; Gogberashvili, K. Influence of Vitamin D on Human Health (Review). Georgian Med. News 2021, 321, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, P.J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, A.C. Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.; Bergeron, G.; Bourassa, M.W.; Brown, K.H.; Calvo, M.S.; Cashman, K.D.; Combs, G.; De-Regil, L.M.; et al. Global prevalence and disease burden of vitamin D deficiency: A roadmap for action in low- and middle-income countries. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1430, 44–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Liu, T.; Shi, Y.; Tian, F.; Hu, H.; Deb, D.K.; Chen, Y.; Bissonnette, M.; Li, Y.C. Gut Epithelial Vitamin D Receptor Regulates Microbiota-Dependent Mucosal Inflammation by Suppressing Intestinal Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, E.D.; Meydani, S.N.; Wu, D. Regulatory role of vitamin E in the immune system and inflammation. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, K.D.; Gupta, M. Vitamin B1 Thiamine Deficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kaferle, J.; Strzoda, C.E. Evaluation of macrocytosis. Am. Fam. Phys. 2009, 79, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Barve, S.; Chen, S.Y.; Kirpich, I.; Watson, W.H.; McClain, C. Development, Prevention, and Treatment of Alcohol-Induced Organ Injury: The Role of Nutrition. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 289–302. [Google Scholar]
- Welzel, T.M.; Katki, H.A.; Sakoda, L.C.; Evans, A.A.; London, W.T.; Chen, G.; O’Broin, S.; Shen, F.M.; Lin, W.Y.; McGlynn, K.A. Blood folate levels and risk of liver damage and hepatocellular carcinoma in a prospective high-risk cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persson, E.C.; Schwartz, L.M.; Park, Y.; Trabert, B.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Graubard, B.I.; Freedman, N.D.; McGlynn, K.A. Alcohol consumption, folate intake, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver disease mortality. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maywald, M.; Rink, L. Zinc in Human Health and Infectious Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaka, A.; Fujitani, Y. Role of Zinc Homeostasis in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabbani, P.; Prasad, A.S. Plasma ammonia and liver ornithine transcarbamoylase activity in zinc-deficient rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1978, 235, E203–E206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himoto, T.; Masaki, T. Associations between Zinc Deficiency and Metabolic Abnormalities in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G.; Jiang, H. Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryzen, E. Magnesium homeostasis in critically ill patients. Magnesium 1989, 8, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, S.; Rausch, V. The role of iron in alcohol-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 815, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Nunes, A.; Jakszyn, P.; Agudo, A. Iron and cancer risk—A systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers. Prev. 2014, 23, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehta, K.J.; Farnaud, S.J.; Sharp, P.A. Iron and liver fibrosis: Mechanistic and clinical aspects. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahng, J.W.S.; Alsaadi, R.M.; Palanivel, R.; Song, E.; Hipolito, V.E.B.; Sung, H.K.; Botelho, R.J.; Russell, R.C.; Sweeney, G. Iron overload inhibits late stage autophagic flux leading to insulin resistance. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahelic, D.; Kujundzic, M.; Romic, Z.; Brkic, K.; Petrovecki, M. Serum concentration of zinc, copper, manganese and magnesium in patients with liver cirrhosis. Coll. Antropol. 2006, 30, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Zuccoli, G.; Siddiqui, N.; Bailey, A.; Bartoletti, S.C. Neuroimaging findings in pediatric Wernicke encephalopathy: A review. Neuroradiology 2010, 52, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Reimers, E.; Monedero-Prieto, M.J.; Gonzalez-Perez, J.M.; Duran-Castellon, M.C.; Galindo-Martin, L.; Abreu-Gonzalez, P.; Sanchez-Perez, M.J.; Santolaria-Fernandez, F. Relative and combined effects of selenium, protein deficiency and ethanol on hepatocyte ballooning and liver steatosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 154, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clugston, R.D.; Blaner, W.S. The adverse effects of alcohol on vitamin A metabolism. Nutrients 2012, 4, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleynik, S.I.; Leo, M.A.; Ma, X.; Aleynik, M.K.; Lieber, C.S. Polyenylphosphatidylcholine prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation while it attenuates liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 1997, 27, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, M.; Labenz, C.; Dobbermann, H.; Czauderna, C.; Wallscheid, N.C.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Worns, M.A.; Galle, P.R.; Marquardt, J.U. Suppressed serological vitamin A in patients with liver cirrhosis is associated with impaired liver function and clinical detoriation. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardelli, V.S.; Lago, M.; Silveira, D.X.D.; Fidalgo, T.M. Vitamin D and alcohol: A review of the current literature. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 248, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.Q.; Bo, Q.L.; Chu, L.L.; Hu, Y.D.; Fu, L.; Wang, G.X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.X. Vitamin D Deficiency Aggravates Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation during Chronic Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 5715893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okubo, T.; Atsukawa, M.; Tsubota, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Arai, T.; Iwashita, A.N.; Itokawa, N.; Kondo, C.; Iwakiri, K. Relationship between serum vitamin D level and sarcopenia in chronic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, C.S.; Volmer, D.A.; Grunhage, F.; Lammert, F. Vitamin D in chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepo, E.; Ouziel, R.; Pradat, P.; Momozawa, Y.; Quertinmont, E.; Gervy, C.; Gustot, T.; Degre, D.; Vercruysse, V.; Deltenre, P.; et al. Marked 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency is associated with poor prognosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, T.; Atsukawa, M.; Tsubota, A.; Ono, H.; Kawano, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Arai, T.; Hayama, K.; Itokawa, N.; Kondo, C.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Volume and Strength in Patients with Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis Undergoing Branched Chain Amino Acids Supplementation: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Pilot Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G. Not enough vitamin D: Health consequences for Canadians. Can. Fam. Physician 2007, 53, 841–854. [Google Scholar]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M.; Endocrine, S. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Van Natta, M.L.; Kleiner, D.E.; Clark, J.M.; Kowdley, K.V.; Loomba, R.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Tonascia, J.; Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Vitamin E and changes in serum alanine aminotransferase levels in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leo, M.A.; Rosman, A.S.; Lieber, C.S. Differential depletion of carotenoids and tocopherol in liver disease. Hepatology 1993, 17, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Shalini, S.; Bansal, M.P. Influence of vitamin E on alcohol-induced changes in antioxidant defenses in mice liver. Toxicol Mech. Methods 2010, 20, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdinia, R.; Goudarzi, I.; Lashkarbolouki, T.; Salmani, M.E. Vitamin E attenuates alterations in learning, memory and BDNF levels caused by perinatal ethanol exposure. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervaux, A.; Laqueille, X. Thiamine (vitamin B1) treatment in patients with alcohol dependence. Presse Med. 2017, 46, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, R.; Brathen, G.; Ivashynka, A.; Hillbom, M.; Tanasescu, R.; Leone, M.A. EFNS guidelines for diagnosis, therapy and prevention of Wernicke encephalopathy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon-Ospina, C.A.; Nava-Mesa, M.O.; Paez-Hurtado, A.M. Update on Safety Profiles of Vitamins B1, B6, and B12: A Narrative Review. Ther. Clin. Risk. Manag. 2020, 16, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Rey, M.; Woodhoo, A.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Mato, J.M.; Lu, S.C. Alcohol, DNA methylation, and cancer. Alcohol Res. 2013, 35, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Hu, F.B.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Spiegelman, D.; Rosner, B.A.; Willett, W.C. Joint association of alcohol and folate intake with risk of major chronic disease in women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 158, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McClain, C.J.; Su, L.C.; Gilbert, H.; Cameron, D. Zinc-deficiency-induced retinal dysfunction in Crohn’s disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1983, 28, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; McClain, C.J.; Cave, M.; Kang, Y.J.; Zhou, Z. The role of zinc deficiency in alcohol-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver. Physiol. 2010, 298, G625–G633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menzano, E.; Carlen, P.L. Zinc deficiency and corticosteroids in the pathogenesis of alcoholic brain dysfunction—A review. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1994, 18, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, C.; Vatsalya, V.; Cave, M. Role of Zinc in the Development/Progression of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2017, 15, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Enomoto, M.; Murata, K.; Takeda, S.; Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; et al. Dual therapy with zinc acetate and rifaximin prevents from ethanol-induced liver fibrosis by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 8323–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flink, E.B. Magnesium deficiency in alcoholism. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1986, 10, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.; Shane, S.R.; Jacobs, W.H.; Flink, E.B. Magnesium balance studies in chronic alcoholism. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1969, 162, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.T.; Soman, S.S.; Yee, J. Magnesium Balance and Measurement. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanoni, F.O.; Milani, G.P.; Agostoni, C.; Treglia, G.; Fare, P.B.; Camozzi, P.; Lava, S.A.G.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Janett, S. Magnesium Metabolism in Chronic Alcohol-Use Disorder: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Zhou, T.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Chen, P. The effect of magnesium supplementation on muscle fitness: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Magnes. Res. 2017, 30, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, K.; Cheung, T.K.; Murphy, T.; Walters, M.; Anderson, G.; Crawford, D.G.; Fletcher, L.M. Hepcidin is down-regulated in alcoholic liver injury: Implications for the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milic, S.; Mikolasevic, I.; Orlic, L.; Devcic, E.; Starcevic-Cizmarevic, N.; Stimac, D.; Kapovic, M.; Ristic, S. The Role of Iron and Iron Overload in Chronic Liver Disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibazaki, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Tsuda, K.; Taniuchi, N. Copper deficiency caused by excessive alcohol consumption. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, M.C.; Park, J.M.; Chung, A.S. Antitumor Effects of Selenium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rua, R.M.; Ojeda, M.L.; Nogales, F.; Rubio, J.M.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Funuyet, J.; Murillo, M.L.; Carreras, O. Serum selenium levels and oxidative balance as differential markers in hepatic damage caused by alcohol. Life Sci. 2014, 94, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Flieger, W.; Teresinski, G.; Buszewicz, G.; Sitarz, R.; Forma, A.; Karakula, K.; Maciejewski, R. Magnesium, Calcium, Potassium, Sodium, Phosphorus, Selenium, Zinc, and Chromium Levels in Alcohol Use Disorder: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Alcoholic Liver Diseases | Recommended Total Energy and Nutrient Intake | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic hepatitis | Total energy: 35–40 kcal/kg/day | [25] |
| Protein: 1.2–1.5 g/kg/day | ||
| Alcoholic fatty liver or steatosis | Total energy: 20–40 kcal/kg/day | [25,26] |
| Protein: 1.0–1.5 g/kg/day | ||
| Carbohydrate: 50–60% of total energy | ||
| Lipid (low saturated fatty acid): 15–20% of total energy | ||
| Alcoholic cirrhosis | Total energy: 25–40 kcal/kg/day including LES | [25,27,28] |
| Total energy: 25 kcal/kg/day in the presence of glucose intolerance | ||
| Protein: 1.2–1.5 g/kg/day including BCAA preparations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadokoro, T.; Morishita, A.; Himoto, T.; Masaki, T. Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061360
Tadokoro T, Morishita A, Himoto T, Masaki T. Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061360
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadokoro, Tomoko, Asahiro Morishita, Takashi Himoto, and Tsutomu Masaki. 2023. "Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061360
APA StyleTadokoro, T., Morishita, A., Himoto, T., & Masaki, T. (2023). Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nutrients, 15(6), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061360







