Abstract
The efficacy of the late-evening snack (LES) has been extensively studied due to the impact of the longest intermeal duration occurring at night in patients with cirrhosis. While actual clinical guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease recommend an LES, no specific nutritional compositions have been reported by the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) and the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN). Late-evening snacks vary greatly among studies, including natural foods and/or nutritional supplements, yet oral supplements still need to fully meet the LES’s nutritional composition. In addition, many hepatologists need to gain experience in nutritional approaches and have access to registered dieticians who can help them manage patients with liver disease. Therefore, this review study aims to summarise evidence regarding using LESs and the mechanisms behind long starvation in patients with cirrhosis. It also provides a practical nutritional guide with several LES options based on common natural foods tailored to special patients’ nutritional requirements and geographical backgrounds. In preventing accelerated starvation and related protein malnutrition and sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis, the nutritional composition of LESs is essential. The proper and straightforward application of the LES’s rational nutrition is an advantage to cirrhotic patients and should be carried out by healthcare professionals to enhance the overall liver function and nutritional status of patients with cirrhosis.
1. Introduction
A late-evening snack (LES) has been recommended as a strategy to address the nutritional needs of patients with liver diseases. Hepatologists often lack the resources, time, or expertise to adequately address these nutritional needs, leading to ineffective treatment prescriptions and consequences such as sarcopenia and hepatic encephalopathy. The optimal duration of LES administration is still being determined. However, the importance of shortening fasting intervals between meals, particularly during the longest intermeal duration at night, has been emphasised. An LES is a simple, safe, and cost-effective intervention to prevent catabolism and reverse sarcopenia. This review article aims to summarise the current evidence about the prescription of LESs in advanced chronic liver disease patients; moreover, we will offer a practical, nutritional, and graphical guide with several LES options based on common natural foods tailored to special patients’ nutritional requirements and their geographical backgrounds.
2. Data Sources and Searches
We searched English language publications on MEDLINE, Ovid, In-Process, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and PubMed up to June 2023. Literature searches were performed using the following keywords: Late-evening snack, snack, nutritional management, cirrhosis, liver diseases, chronic liver disease, advanced chronic liver disease, chronic disease, cirrhosis, sarcopenia, sarcopenic, muscle depletion, muscle mass, hepatic encephalopathy, and ascites.
3. Impact of Malnutrition in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as advanced chronic liver disease (ACLD), is the end stage of progressive liver fibrosis, in which regenerative hepatic nodules replace the hepatic architecture as a consequence of chronic liver inflammation, and it eventually determines liver failure; cirrhosis is widely prevalent and is associated with high morbidity and mortality [1]. An initial asymptomatic phase characterises the disease, called compensated cirrhosis (cACLD), which evolves to a symptomatic stage (decompensated dACLD), defined as the first occurrence of liver events such as ascites, esophageal variceal bleeding (EVB), and hepatic encephalopathy (HE); these complications lead to frequent hospitalisation, infections, impaired quality of life, and high mortality [2]. The management of liver cirrhosis is focused on treating the causes and complications [1].
Malnutrition is a condition of altered body composition and cell functions secondary to insufficient protein and energy intake [3]. The diagnosis, assessment, and grading of malnutrition, according to the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) [4] and the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) [5], requires the combination of a phenotypical criterion (weight loss, reduced body mass index or reduced muscle mass) and an etiological one (reduced food intake and assimilation and the presence of acute/chronic disease-related inflammation).
The prevalence of malnutrition in ACLD ranges from 5–92%, with high variability, which implies difficulties in malnutrition assessment and a knowledge gap [6]. Malnutrition prevalence increases with increasing disease severity (dACLD), but frequently malnutrition can be found even in patients in a compensated stage [7,8]. Malnutrition represents a complication of ACLD, being an independent negative predictor of disease progression and outcome (higher hospitalisation rate and mortality) [9]. Furthermore, malnutrition can be considered a predictor of other complications of ACLD [10], with a strong correlation with HE and infections [11,12].
Malnutrition in patients with cirrhosis shows a multifactorial etiology, which includes poor energy-protein intake, inflammation, malabsorption and intestinal protein loss, gut microbiome dysbiosis, nutrient metabolism dysregulation with decreased hepatic protein synthesis, hormonal disturbances, and hypermetabolism; moreover, external behaviours such as fasting periods and alcohol consumption can contribute to malnutrition [6]. In addition, other malnutrition-related diagnoses, such as sarcopenia and frailty, are commonly associated with liver cirrhosis [13,14,15]. Sarcopenia is defined as a progressive skeletal muscle depletion that involves a loss of muscle mass and strength function, and it is linked with increased adverse outcomes and mortality [16]. The prevalence of sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients ranges from 40 to 70%, with a large variability depending on the population evaluated (sex, ethnicity, degree of liver failure), methods of assessment, and the definition of sarcopenia used [17,18,19]. A meta-analysis of 22 published studies in the Journal of Hepatology in 2022 by X. Tantai et al. highlights that the overall prevalence of sarcopenia among patients with ACLD is 37.5%, with a higher prevalence in males, patients with alcohol-related liver disease, and patients with greater severity of cirrhosis (28.3% in Child-Pugh A, 37.9% in Child-Pugh B, and 46.7% in Child-Pugh C) [20]. The same authors show that sarcopenia is associated with an approximately two-fold higher risk of death in patients with cirrhosis and mortality rates at 1, 3, and 5 years of 23.4%, 35.7%, and 54.7%, respectively [20]. This high mortality risk is related to an increased risk of falls, fractures, reduced quality of life, and the development of liver-related complications [21]. Patients with liver disease are highly susceptible to sarcopenia due to multiple factors. These include symptoms like nausea, early satiety, and delayed gastric emptying caused by ascites and enteropathy. Anorexia due to elevated levels of leptin and tumour necrosis factor (TNF-a), physical inactivity, and obesity are also significant contributors. Additionally, hypermetabolism resulting from systemic inflammation, inadequate nutrition intake, and low socioeconomic status, commonly associated with alcoholism, also play a crucial role. Therefore, it is imperative to consider these factors while treating patients with liver disease to prevent or slow the onset of sarcopenia [22,23].
Recently, due to an increasing diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) related cirrhosis, more cirrhotic patients with overweight and obesity are observed [24]. Sarcopenic obesity is a term used to define the co-presence of muscle mass depletion and strength reduction with an excess of visceral adiposity; in this case, sarcopenia can be highly overlooked due to the presence of body weight excess [25]. Obesity and sarcopenic obesity worsen the prognosis of cirrhotic patients [26] and are associated with poor transplant waitlist mortality [27,28]. Given these observations, malnutrition and sarcopenia should be promptly recognised and treated. Current treatment strategies for sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis, which are mainly in investigational stages, include hormone replacement, antibiotics and gut microbiota manipulation, ammonia reduction, myostatin antagonists, nutritional supplementation such as branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) and L-carnitine supplements, and treatment of portal hypertension [29]. Although nutritional interventions and exercise, particularly resistance training, have been considered the main strategies to prevent sarcopenia in various populations [17,21,30].
4. Nutritional Requirements in Liver Cirrhosis Patient
The energy requirements of cACLD patients are not greater than those of healthy individuals (calculated as REE × 1.3), while their recommended protein intake is 1.2 g/kg/day; specific nutrition counselling should be provided to modify patients’ behaviour educating them about the benefits of a healthy diet adapted to their clinical condition. Nutrition counselling and diet prescriptions need to be shaped in response to the severity of the disease [31]. During the natural course of the disease, ACLD patients may exhibit a decreased appetite with a reduction in dietary intake, especially following the first hepatic decompensation event, exactly when energy expenditure is increased [32]. According to the last nutritional guidelines, a daily energy intake of at least 30–35 kcal/kg body weight in non-obese cirrhotic patients is recommended [31,33]. In patients with ascites and fluid retention, the energy intake should be calculated on dry weight, using post-paracentesis weight or subtracting a weight percentage depending on the fluid retention grade: mild, 5%; moderate, 10%; severe, 15%; additional 5% in those presenting bilateral pedal oedema to the knees [33]. In the case of body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m2, weight-based energy intake recommendations may be modified to 25–35 kcal/kg/day for patients with BMI 30–40 kg/m2 and 20–25 kcal/kg/day for patients with BMI ≥ 40 kg/m [34], even if data are lacking. As for protein intake, the recommended daily protein intake is 1.2–1.5 g/kg ideal body weight [31,33], although ESPEN advises specifically to provide 1.5 g/kg/day in patients with malnutrition and muscle depletion [31]. For those with cACLD, it is advised to obtain their protein intake from a balanced combination of sources. This includes one-third of dairy protein (which contains casein), one-third of vegetable protein (which is rich in branched-chain amino acids), and one-third of animal protein (which is of high quality). Animal proteins are rich in aromatic amino acids not metabolised by skeletal muscle and may worsen HE if present. In the case of the ACLD patient who expresses a preference for different dietary habits, it is acceptable to make changes to prioritise their overall daily protein intake rather than focusing exclusively on exact proportions [35,36].
According to the established nutritional guidelines, it is advisable to divide one’s daily food intake into three primary meals, namely early breakfast, lunch, and dinner, while also incorporating three snacks, which may be consumed in the mid-morning, mid-afternoon, and late evening. Additionally, it is recommended to consume smaller, frequent meals, with no more than a 3–4 h gap between each meal, to maintain a consistent meal schedule and minimise prolonged fasting periods [21,31,33].
5. Rationale and Pathophysiological Principles of the Late-Evening Snack (LES)
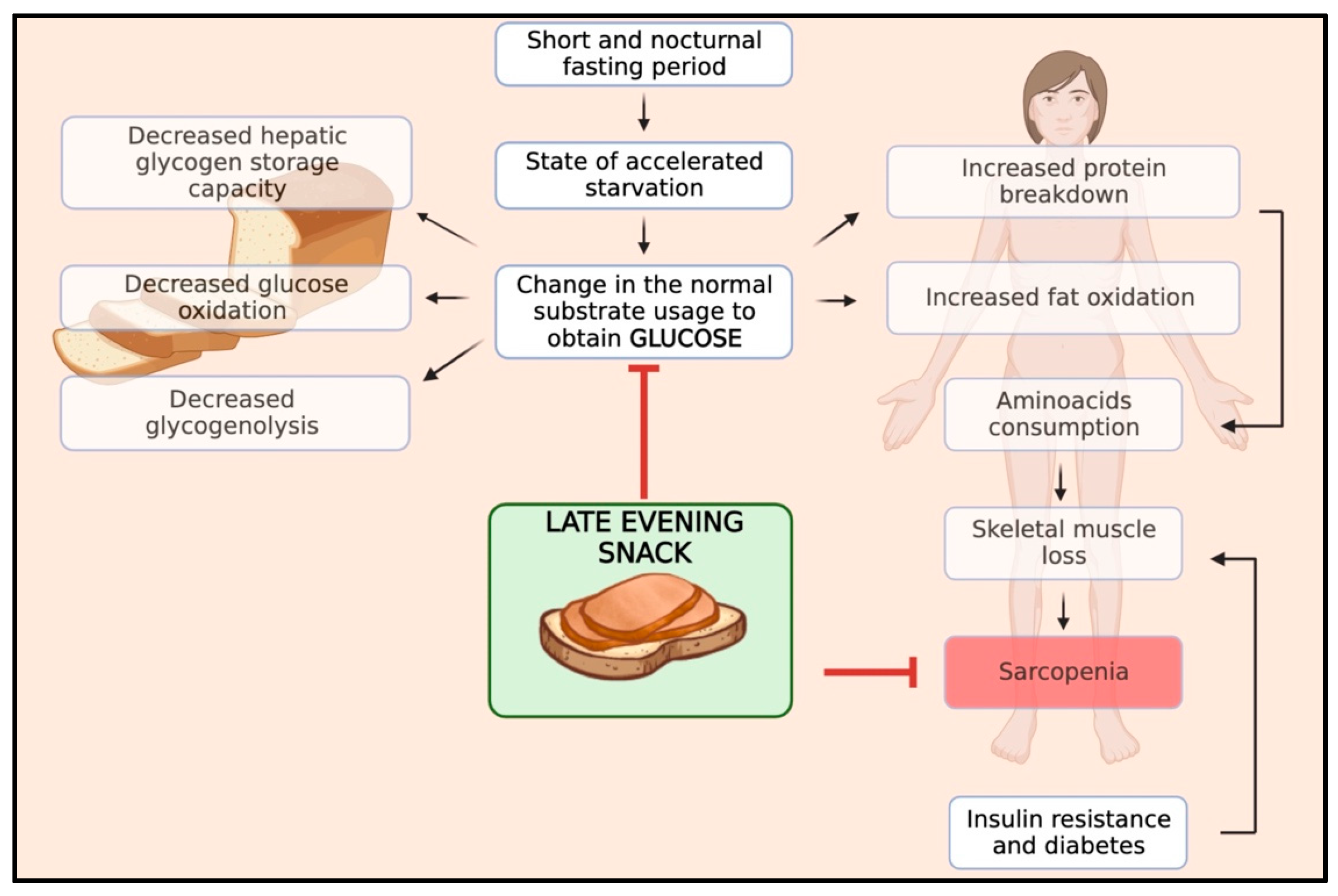
Skeletal muscle mass results from a balance between muscle protein synthesis, which occurs during the fed state, and protein breakdown, which occurs during the fasting state. In patients with cirrhosis, this balance is characterised by reduced rates of body protein synthesis and increased rates of body protein breakdown during fasting periods due to abnormal metabolism [37,38]. In particular, cirrhosis shows a state of accelerated starvation after a short fasting period, with a change in the normal substrate usage, leading to an early shift from glucose to lipid and protein utilisation for energy due to a reduction in hepatic glycogen storage capacity, implying the need to generate glucose from alternate sources [39]. After overnight fasting, cirrhotic patients exhibit a different metabolic pattern than healthy individuals. While healthy individuals typically develop this pattern after 2–3 days of starvation, cirrhotic patients experience increased fat oxidation and gluconeogenesis while glucose oxidation and glycogenolysis decrease. Gluconeogenesis and protein oxidation lead to increased consumption of amino acids and skeletal muscle protein loss, which results in sarcopenia [40]. Furthermore, ACLD patients frequently experience complications like insulin resistance and hepatogenic diabetes. These conditions further intensify the process of muscle wasting.
Therefore, the optimal management of meal timing and frequency is of the utmost importance in preventing sarcopenia in patients with ACLD. Protein homeostasis, a balance between protein synthesis and breakdown, is disrupted in these patients, skewing toward elevated protein degradation, particularly during the protracted nocturnal fasting period. The interval from dinner to breakfast typically represents the longest fasting span, during which proteolysis is favoured over protein synthesis, thereby escalating muscle wasting [41]. By harnessing the potential benefits of nutritional interventions, such as late-evening snacks (LES), we can effectively curtail the duration of the night fasting period, thereby extending the patient’s fed state, facilitating the accelerated progression to a catabolic state and reversing sarcopenia. Moreover, an LES has been shown to stabilise blood glucose levels, curbing abrupt glucose and insulin spikes and promoting overall metabolic homeostasis. Therefore, an LES serves a dual purpose in ACLD patients by aiding in muscle preservation as well as managing typical cirrhotic implications such as insulin resistance complications. In Figure 1, we schematised the pathophysiology and rationale of an LES in patients with ACLD.
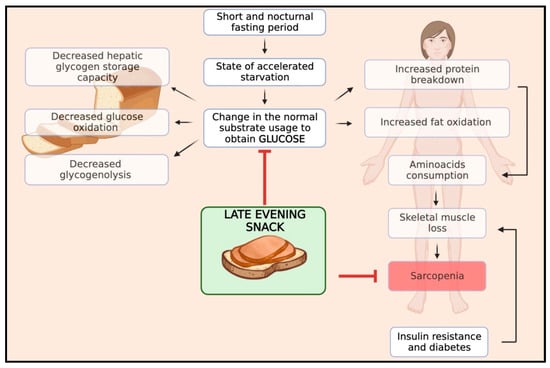
Figure 1.
Impact of an LES on the pathophysiology of sarcopenia in cirrhosis.
6. Evidence of an LES in Patients with ACLD
While the reasoning behind using an LES in patients with ACLD is understood, the concrete evidence pertaining to its benefit in disorder complications and overall prognosis remains partially unexplored, and its research seems to progress in a discontinuous or sporadic way. The concept of an LES for patients with cirrhosis was initially established by Swart et al. [42] in the late 1980s through a randomised controlled trial (RCT). This study, which observed a cohort of nine cirrhotic patients admitted to the ward for a few days, noted an improvement in nitrogen balance in patients who received evening meals. Subsequent studies, particularly from the Asia region, have produced a significant body of evidence supporting the clinical effectiveness of an LES in patients with ACLD. Indeed, a systematic review of trials about an LES in cirrhotic patients published up to December 2011 summarised the results of 15 articles, six short-term studies that analysed substrate utilisation and nine longer-term studies that examined the impact of an LES on clinical nutritional indices. Results showed that an LES reverses the substrate utilisation pattern in cirrhosis, switching to a more physiological pattern of glucose utilisation instead of lipid oxidation and gluconeogenesis. Moreover, an LES led to an increase in the respiratory quotient, an improvement of nitrogen balance, independently of the composition or formulation used, improvement of fat-free mass and primarily skeletal muscle mass (especially in subjects with less advanced disease). Additional benefits may include a reduction in the frequency and severity of HE because skeletal muscle mass preservation may enhance non-hepatic ammonia removal since skeletal muscle is the main ammonia disposal organ via glutamine synthesis [41]. More recently, new studies have been published evaluating changes in biochemical and energy parameters before and after an LES intervention. A systematic review and meta-analysis by Ying-jje Guo et al., published in 2018, combined 14 clinical studies from 1997 to 2017 with a population of 478 patients who received an LES for at least one week. Results showed that the levels of serum albumin, prealbumin, and cholinesterase, which are hepatic synthetic metabolism biomarkers, were significantly increased with the LES treatment [43]. Moreover, a recent paper by Hiraoka et al. [44] has shown, in a cohort of 33 Japanese liver cirrhotic patients, that a lifestyle intervention based on the supplementation of BCAA, and walking exercise improves muscle volume and strength, suggesting a possible improvement in sarcopenia. Finally, a recent meta-analysis and systematic review by Chen-Ju Chen et al. found that an LES administration reduced ALT, AST, PT, and ammonia levels in patients with liver diseases and reduced ascites and HE occurrence. In the studies considered, it emerged that long-term administration is preferable to short-term treatment; however, there has yet to be a consensus on the length of LES administration required to improve liver function [45]. Otherwise, the effect of an LES on other complications of cirrhosis, such as the real impact on sarcopenia prevention and decreased mortality or need for transplantation, is yet unknown. In Table 1, we summarised the current evidence in the application of an LES in patients with ACLD.

Table 1.
Summary of the evidence published on an LES in patients with liver cirrhosis.
7. Nutritional Composition of the Late-Evening Snack (LES)
To mitigate accelerated starvation and related proteolysis, a key dietary strategy involves consuming food every 4 to 6 h, thereby reducing the fasting intervals between meals. While the longest intermeal duration typically occurs at night, the efficacy of a late-evening snack (LES) has been extensively researched. The Clinical Guidelines on Nutrition in chronic liver disease by the European Association for the Study of the Liver [33] and the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) [31] recommend an LES but do not specify the nutritional composition. Recent reviews and meta-analyses, however, indicate that an LES containing complex carbohydrates and proteins can reduce lipid oxidation and improve nutritional status, nitrogen balance, muscle mass, liver function, and overall quality of life in patients with cirrhosis [41,43,45]. The International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism 2013 consensus article [34] suggests that an LES should contain at least 50 g of complex carbohydrates. In most clinical studies, various night meal compositions seem effective as they contain a reasonable amount of complex carbohydrates (at least 30 g/LES) and protein (about 13.5 g/LES) [43,45,69]. The energy intake from an LES may vary approximately between 200 and 250 kcal [43,45,69]. However, no specific recommendations are available for other nutrients. Due to the pathophysiology of ascites, a moderate dietary sodium intake (60 mmol/day = 1360 mg/day) is typically advised.
When recommending a low-sodium diet, it is important to consider its poor palatability, which may lead to reduced energy and protein intake. Its potential benefit in treating ascites should be balanced against the increased risk of even lower food consumption [31]. Studies of the LES have shown varying compositions, including natural foods and nutritional supplements with varying BCAA content. However, oral food supplements can only partially satisfy the recommended nutrition for SLE, in particular, due to an inappropriate glucoside intake from a qualitative–quantitative point of view. Therefore, from published evidence, we reported here in Table 2 the summary of the nutritional composition of the LES proposed for patients with ACLD.

Table 2.
Suggested nutritional composition of the LES in patients with cirrhosis.
8. Practical Approach to a Late-Evening Snack (LES) for ACLD
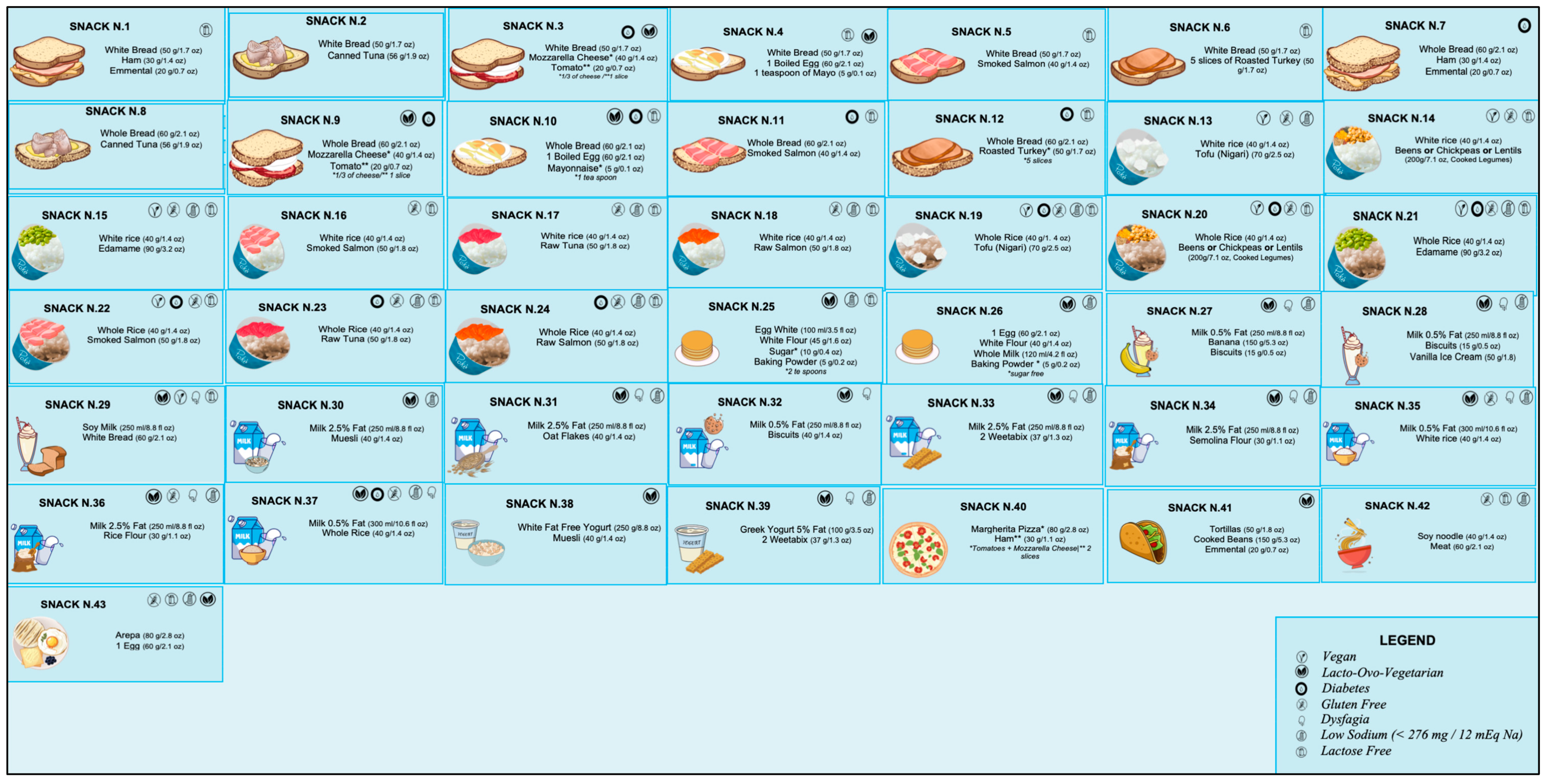
The current literature on what should be included in a late-evening snack (LES) for patients diagnosed with liver diseases is quite varied, thus necessitating the need for a more precise consensus. Hepatologists possess limited knowledge regarding the exact composition and prescription of an LES, and there is a scarcity of dieticians specialising in patients with liver disease. Our objective is to present practical and easy-to-prescribe examples of LESs for ACLD patients, supported by the most recent evidence. We have proposed 43 different options that use commonly available natural foods to achieve the nutritional characteristics and objectives outlined in Table 2. These LES options were developed using validated food composition databases [70,71,72].
Figure 2 reported all the LESs developed (Supplementary File shows the specific composition for each snack). In order to ensure that individuals diagnosed with ACLD receive the appropriate treatment for their clinical condition or personal preferences, specific symbols are utilised to indicate the suitability of a particular LES. For example, a gluten-free LES is offered for patients with celiac disease, while a low-sugar LES is recommended for those with diabetes. A modified texture LES is available for individuals with dysphagia, whereas a lactose-free LES is provided for those with lactose intolerance. Additionally, a low sodium (<276 mg/snack) LES is recommended for patients with severe ascites. Furthermore, we have identified alternative oral nutritional supplements that could potentially serve as an LES based on their compositions (Table 3).
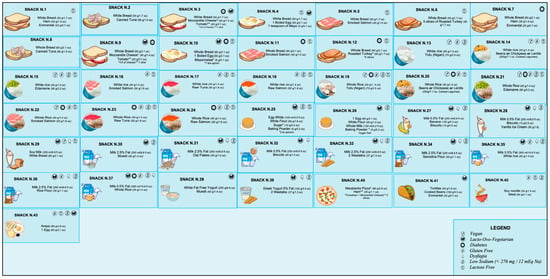
Figure 2.
Proposal for late-evening snacks. For bromatologic compositions, see Supplementary File.

Table 3.
Compatible and commercial oral nutritional supplements such as an LES.
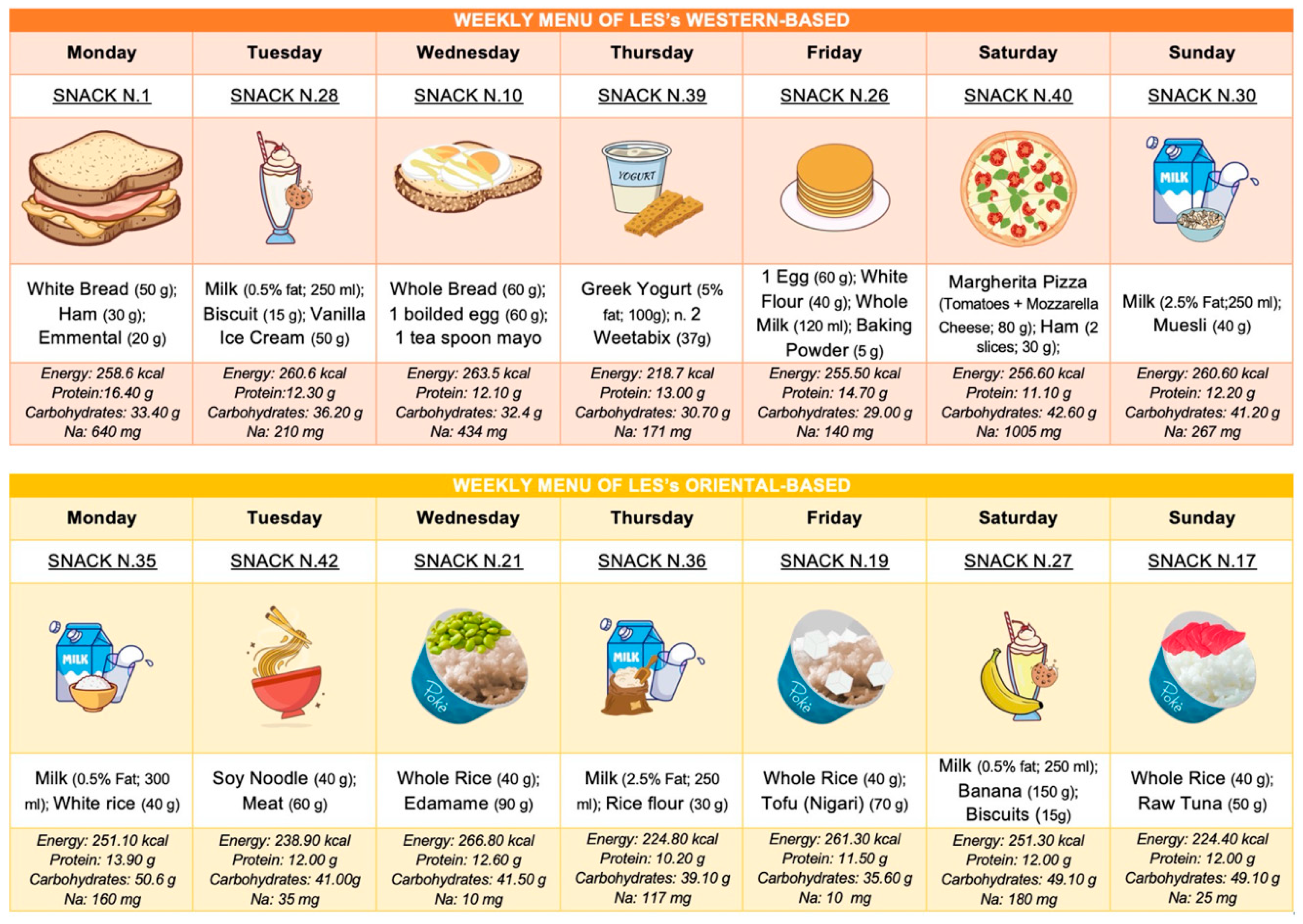
Finally, we also developed the LES by considering gastronomic cultures worldwide and specific dietary patterns such as vegan and lacto-ovo vegetarian. As shown in Figure 3, we have provided two weekly meal plans for the LES—one inspired by a typical Western diet and the other by an Oriental diet.
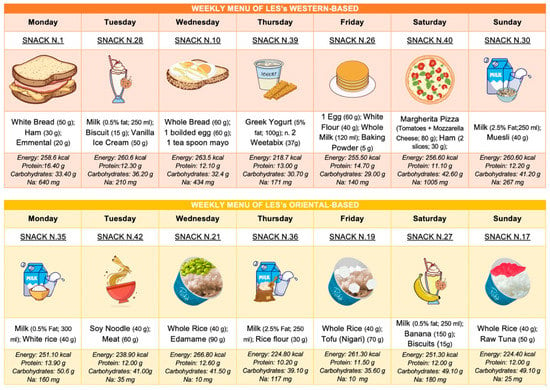
Figure 3.
Weekly meal plans for LESs based on different geographic cultures.
9. Conclusions
While the potential of the LES intervention in managing the issues and its positive influence on ACLD patients’ quality of life is evident from extant research, further investigation is required to delineate its direct impact on survival outcomes. Nonetheless, it underscores the importance of nutritional adjustments in managing ACLD, making an LES an advised practice within the broader framework of these patients’ nutritional management strategy. However, it is critical to individualise dietary strategies accounting for the patient’s overall health conditions, preferences, and cirrhosis-specific complications to maximise the intervention’s efficacy. The LES supplementation, ideally rich in complex carbohydrates and with a moderate amount of protein, influences physiological regulation by providing a consistent supply of amino acids for protein synthesis. This method reduces the onset of proteolytic catabolism to sustain glycogen levels, ultimately diminishing protein and fat degradation, which is essential in maintaining muscle mass and improving the patient’s nutritional status.
Supplementary Materials
The supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15153471/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L., F.V. and F.R.; methodology, F.R.; writing—original draft preparation, F.R., L.L., F.V., R.B., M.V., C.S. and M.P.; writing—review and editing, A.C., R.M. and F.R.; supervision, A.C. and R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Fabio Catalano for his valuable and outstanding graphic contributions to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver Cirrhosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Morabito, A.; D’Amico, M.; Pasta, L.; Malizia, G.; Rebora, P.; Valsecchi, M.G. Clinical States of Cirrhosis and Competing Risks. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Definitions and Terminology of Clinical Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM Criteria for the Diagnosis of Malnutrition—A Consensus Report from the Global Clinical Nutrition Community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Bosaeus, I.; Barazzoni, R.; Bauer, J.; Van Gossum, A.; Klek, S.; Muscaritoli, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Ockenga, J.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Malnutrition—An ESPenteral Nutrition Consensus Statement. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, J.; Reiss, L.; Aliwa, B.; Stadlbauer, V. Malnutrition in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, A.; Toori, K.U.; Shaikh, J.I. To Determine Correlation between Biochemical Parameters of Nutritional Status with Disease Severity in HCV Related Liver Cirrhosis. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, I.H.; Mahmood, K.; Salekeen, S.; Akhter, S.T. Determining the Frequency and Severity of Malnutrition and Correlating It with the Severity of Liver Cirrhosis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 24, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharshi, S.; Sharma, B.C.; Srivastava, S. Malnutrition in Cirrhosis Increases Morbidity and Mortality: Malnutrition in Cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, E.J.; Trip, E.J.; Siersema, P.D.; van Hoek, B.; van Erpecum, K.J. Protein Energy Malnutrition Predicts Complications in Liver Cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 23, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, C.; Majeed, A.; Wahlin, S. Body Composition Assessed by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Predicts Early Infectious Complications after Liver Transplantation. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 30, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Macías-Rodríguez, R.U.; Ampuero, J.; Cubero, F.J.; Chi-Cervera, L.; Ríos-Torres, S.L.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Espinosa-Cuevas, Á.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Torre, A. Low Phase Angle Is Associated with the Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aby, E.S.; Saab, S. Frailty, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition in Cirrhotic Patients. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, G.; Dajti, E.; Ravaioli, F.; Brocchi, S.; Rossini, B.; Alemanni, L.V.; Peta, G.; Bartalena, L.; Golfieri, R.; Festi, D.; et al. Clinical Impact of Sarcopenia Assessment in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, P.; Zanetto, A.; Piano, S.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dasarathy, S. Liver Transplantation in the Patient with Physical Frailty. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, P.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; Lai, J.C.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia and Frailty in Decompensated Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S147–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajti, E.; Renzulli, M.; Ravaioli, F.; Marasco, G.; Milandri, M.; Rossini, B.; Colecchia, L.; Alemanni, L.V.; Ferrarese, A.; Tamè, M.; et al. Sarcopenia Predicts Ascitic Decompensation and Mortality Independently of Portal Hypertension Status in Patients with Advanced Chronic Liver Disease Outside the Liver Transplantation Setting. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, G.; Dajti, E.; Serenari, M.; Alemanni, L.V.; Ravaioli, F.; Ravaioli, M.; Vestito, A.; Vara, G.; Festi, D.; Golfieri, R.; et al. Sarcopenia Predicts Major Complications after Resection for Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Compensated Cirrhosis. Cancers 2022, 14, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantai, X.; Liu, Y.; Yeo, Y.H.; Praktiknjo, M.; Mauro, E.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Engelmann, C.; Zhang, P.; Jeong, J.Y.; van Vugt, J.L.A.; et al. Effect of Sarcopenia on Survival in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Meta-Analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Tandon, P.; Bernal, W.; Tapper, E.B.; Ekong, U.; Dasarathy, S.; Carey, E.J. Malnutrition, Frailty, and Sarcopenia in Patients With Cirrhosis: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1611–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasques, J.; Guerreiro, C.S.; Sousa, J.; Pinto, M.; Cortez-Pinto, H. Nutritional Support in Cirrhotic Patients with Sarcopenia. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 33, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casciola, R.; Leoni, L.; Cuffari, B.; Pecchini, M.; Menozzi, R.; Colecchia, A.; Ravaioli, F. Creatine Supplementation to Improve Sarcopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: Facts and Perspectives. Nutrients 2023, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Rinella, M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Busetto, L.; Bischoff, S.C.; Cederholm, T.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Batsis, J.A.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Dicker, D.; et al. Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Sarcopenic Obesity: ESPEN and EASO Consensus Statement. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhariwal, S.; Roy, A.; Taneja, S.; Bansal, A.; Gorsi, U.; Singh, S.; De, A.; Verma, N.; Premkumar, M.; Duseja, A.; et al. Assessment of Sarcopenia Using Muscle Ultrasound in Patients With Cirrhosis and Sarcopenic Obesity (AMUSE STUDY). J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022. publish ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.B.; Fan, B.; Shui, A.M.; Huang, C.-Y.; Brandman, D.; Lai, J.C. CT-Quantified Sarcopenic Visceral Obesity Is Associated with Poor Transplant Waitlist Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 2023. publish ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaioli, F.; De Maria, N.; Di Marco, L.; Pivetti, A.; Casciola, R.; Ceraso, C.; Frassanito, G.; Pambianco, M.; Pecchini, M.; Sicuro, C.; et al. From Listing to Recovery: A Review of Nutritional Status Assessment and Management in Liver Transplant Patients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Burra, P.; Zanetto, A.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Current Treatment Strategies and Future Possibilities for Sarcopenia in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.; Gow, P.J.; Testro, A.; Chapman, B.; Sinclair, M. Exercise Physiology in Cirrhosis and the Potential Benefits of Exercise Interventions: A Review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2687–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauth, M.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schütz, T.; Bischoff, S.C. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in Liver Disease. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 485–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, J.; Müller, M.J. Energy and Protein Requirements of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 1997, 27, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, M.; Berzigotti, A.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Dasarathy, S.; Montagnese, S.; Genton, L.; Plauth, M.; Parés, A. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on Nutrition in Chronic Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, P.; Bemeur, C.; Butterworth, R.; Cordoba, J.; Kato, A.; Montagnese, S.; Uribe, M.; Vilstrup, H.; Morgan, M.Y. The Nutritional Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Cirrhosis: International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism Consensus. Hepatology 2013, 58, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, A.C. Nutrition and Muscle in Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2017, 7, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaioli, F.; Pivetti, A.; Di Marco, L.; Chrysanthi, C.; Frassanito, G.; Pambianco, M.; Sicuro, C.; Gualandi, N.; Guasconi, T.; Pecchini, M.; et al. Role of Vitamin D in Liver Disease and Complications of Advanced Chronic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, A.J.; Mullen, K.D.; Kalhan, S.C. Body Cell Mass and Leucine Metabolism in Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, A.J.; Mullen, K.D.; Kalhan, S.C. Defective Nonoxidative Leucine Degradation and Endogenous Leucine Flux in Cirrhosis during an Amino Acid Infusion. Hepatology 1998, 28, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, O.E.; Reichle, F.A.; Mozzoli, M.A.; Kreulen, T.; Patel, M.S.; Elfenbein, I.B.; Golsorkhi, M.; Chang, K.H.; Rao, N.S.; Sue, H.S.; et al. Hepatic, Gut, and Renal Substrate Flux Rates in Patients with Hepatic Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, J. Comments on Metabolic Needs for Glucose and the Role of Gluconeogenesis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, s107–s111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.D.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Late Evening Snack: Exploiting a Period of Anabolic Opportunity in Cirrhosis: Evening Snack for Cirrhotic Sarcopenia. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, G.R.; Zillikens, M.C.; Van Vuure, J.K.; Van Den Berg, J.W. Effect of a Late Evening Meal on Nitrogen Balance in Patients with Cirrhosis of the Liver. BMJ 1989, 299, 1202–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, N.; Ding, X.; Mao, T.; Jing, X. Effects of Late Evening Snack on Cirrhotic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 9189062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kiguchi, D.; Izumoto, H.; Ueki, H.; Kaneto, M.; Kitahata, S.; Aibiki, T.; Okudaira, T.; Tomida, H.; et al. Efficacy of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation and Walking Exercise for Preventing Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Kuo, H.; Fang, Y.; Lee, H. Significant Effects of Late Evening Snack on Liver Functions in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zillikens, M.C.; Van Den Berg, J.W.O.; Wattimena, J.L.D.; Rietveld, T.; Swart, G.R. Nocturnal Oral Glucose Supplementation. J. Hepatol. 1993, 17, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboeket-van De Venne, W.P.; Westerterp, K.R.; Van Hoek, B.; Swart, G.R. Energy Expenditure and Substrate Metabolism in Patients with Cirrhosis of the Liver: Effects of the Pattern of Food Intake. Gut 1995, 36, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, W.-K.; Chao, Y.-C.; Tang, H.-S.; Lang, H.-F.; Hsu, C.-T. Effects of Extra-Carbohydrate Supplementation in the Late Evening on Energy Expenditure and Substrate Oxidation in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1997, 21, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, Y. Improvement of Fuel Metabolism by Nocturnal Energy Supplementation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2000, 18, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M. Effect of Oral Branched Chain Amino Acid Supplementation in the Late Evening on the Nutritional State of Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2001, 21, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, Y.; Harada, N.; Kakui, S.; Okada, K.; Takahashi, A.; Inoi, J.; Ito, S. Severe Catabolic State after Prolonged Fasting in Cirrhotic Patients: Effect of Oral Branched-Chain Amino-Acid-Enriched Nutrient Mixture. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Miwa, Y.; Ida, E.; Kuriyama, S.; Toda, K.; Shimomura, Y.; Sugiyama, A.; Sugihara, J.; Tomita, E.; Moriwaki, H. Nocturnal Branched-Chain Amino Acid Administration Improves Protein Metabolism in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Comparison with Daytime Administration. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2003, 27, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sako, K. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Supplements in the Late Evening Decrease the Frequency of Muscle Cramps with Advanced Hepatic Cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2003, 26, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaida, I.; Tsuchiya, M.; Okamoto, M.; Okita, K. Late Evening Snack and the Change of Blood Glucose Level in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2004, 30, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka-Okumura, H.; Nakamura, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Miyake, H.; Katayama, T.; Arai, H.; Taketani, Y.; Fujii, M.; Shimada, M.; Takeda, E. Effect of Late Evening Snack with Rice Ball on Energy Metabolism in Liver Cirrhosis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, L.D.; Gane, E.J.; Peng, S.; Muthu, C.; Mathur, S.; Gillanders, L.; McIlroy, K.; Donaghy, A.J.; McCall, J.L. Nocturnal Nutritional Supplementation Improves Total Body Protein Status of Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Randomized 12-Month Trial. Hepatology 2008, 48, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, Y.; Okita, K.; Suzuki, K.; Moriwaki, H.; Kato, A.; Miwa, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Okuda, H.; Onji, M.; Kanazawa, H.; et al. BCAA-Enriched Snack Improves Nutritional State of Cirrhosis. Nutrition 2007, 23, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Nakao, K.; Miyaaki, H.; Shibata, H.; Matsuzaki, T.; Muraoka, T.; Honda, T.; Otani, M.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A Snack Enriched with Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acids Prevents a Fall in Albumin in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Undergoing Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Naota, T.; Miyaaki, H.; Miuma, S.; Isomoto, H.; Takeshima, F.; Nakao, K. Effect of an Oral Branched Chain Amino Acid-Enriched Snack in Cirrhotic Patients with Sleep Disturbance: Effect of BCAA for LC with Sleep Disturbance. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harima, Y.; Yamasaki, T.; Hamabe, S.; Saeki, I.; Okita, K.; Terai, S.; Sakaida, I. Effect of a Late Evening Snack Using Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Enriched Nutrients in Patients Undergoing Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Effects of LES on Advanced HCC during HAIC. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka-Okumura, H.; Nakamura, T.; Miyake, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Katayama, T.; Morine, Y.; Imura, S.; Shimada, M.; Takeda, E. Effect of Long-Term Late-Evening Snack on Health-Related Quality of Life in Cirrhotic Patients: Long-Term Nutritional Intervention. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, H.; Ushio, A.; Miyamoto, Y.; Sawara, K.; Oikawa, K.; Kasai, K.; Endo, R.; Takikawa, Y.; Kato, A.; Suzuki, K. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Enriched Nutrient for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Radiofrequency Ablation: A One-Year Prospective Trial: Effect of BCAA for HCC Patients after RFA. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, P.; Castaldo, G.; Tarantino, L.; Bracigliano, A.; Perrella, A.; Perrella, O.; Fiorentino, F.; Vecchione, R.; D’ Angelo, S. Preservation of Nutritional-Status in Patients with Refractory Ascites Due to Hepatic Cirrhosis Who Are Undergoing Repeated Paracentesis: Nutritional-Support in RA. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morihara, D.; Iwata, K.; Hanano, T.; Kunimoto, H.; Kuno, S.; Fukunaga, A.; Yotsumoto, K.; Takata, K.; Tanaka, T.; Sakurai, K.; et al. Late-Evening Snack with Branched-Chain Amino Acids Improves Liver Function after Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: LES with BCAA Improves Liver Function. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Kutsukake, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Aoki, I.; Nakano, S.; Asaba, N.; Minamino, T.; Takada, J.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. The Efficacy of Nocturnal Administration of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Granules to Improve Quality of Life in Patients with Cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Shinkai, N.; Iio, E.; Joh, T. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation after Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized Trial. Nutrition 2017, 33, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Lv, Z.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Q. Long-Term Carbohydrate-Containing Late-Evening Snack Significantly Improves the Ratio of Branched Chain Amino Acids to Aromatic Amino Acids in Adults with Liver Cirrhosis Due to Hepatitis B. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1074565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Meng, Q.-H. Late Evening Snack and Oral Amino Acid Capsules Improved Respiratory Quotient and Fischer Ratio in Patients with Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 28, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Rabinowich, L.; Bentov, I.; Deutsch, L. Nutritional Evaluation and Treatment of the Cirrhotic Patient. Clin. Liver Dis. 2021, 25, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnagnarella, P.; Parpinel, M. Food Composition Database for Epidemiological Studies in Italy. 2022. Available online: http://www.bda-ieo.it/wordpress/en/ (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- Consiglio per la ricerca in agricoltura e l’analisi dell’economia agraria (CREA). Tabelle Di Composizione Degli Alimenti (CREA). 2019. Available online: https://www.crea.gov.it/-/tabella-di-composizione-degli-alimenti (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Food Data Central. 2019. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 11 July 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).