Nanoribbon Biosensor-Based Detection of microRNA Markers of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Oligonucleotides
2.3. Preparation of Buffered Solution of Target oDNAs
2.4. Collection of Blood Plasma Samples
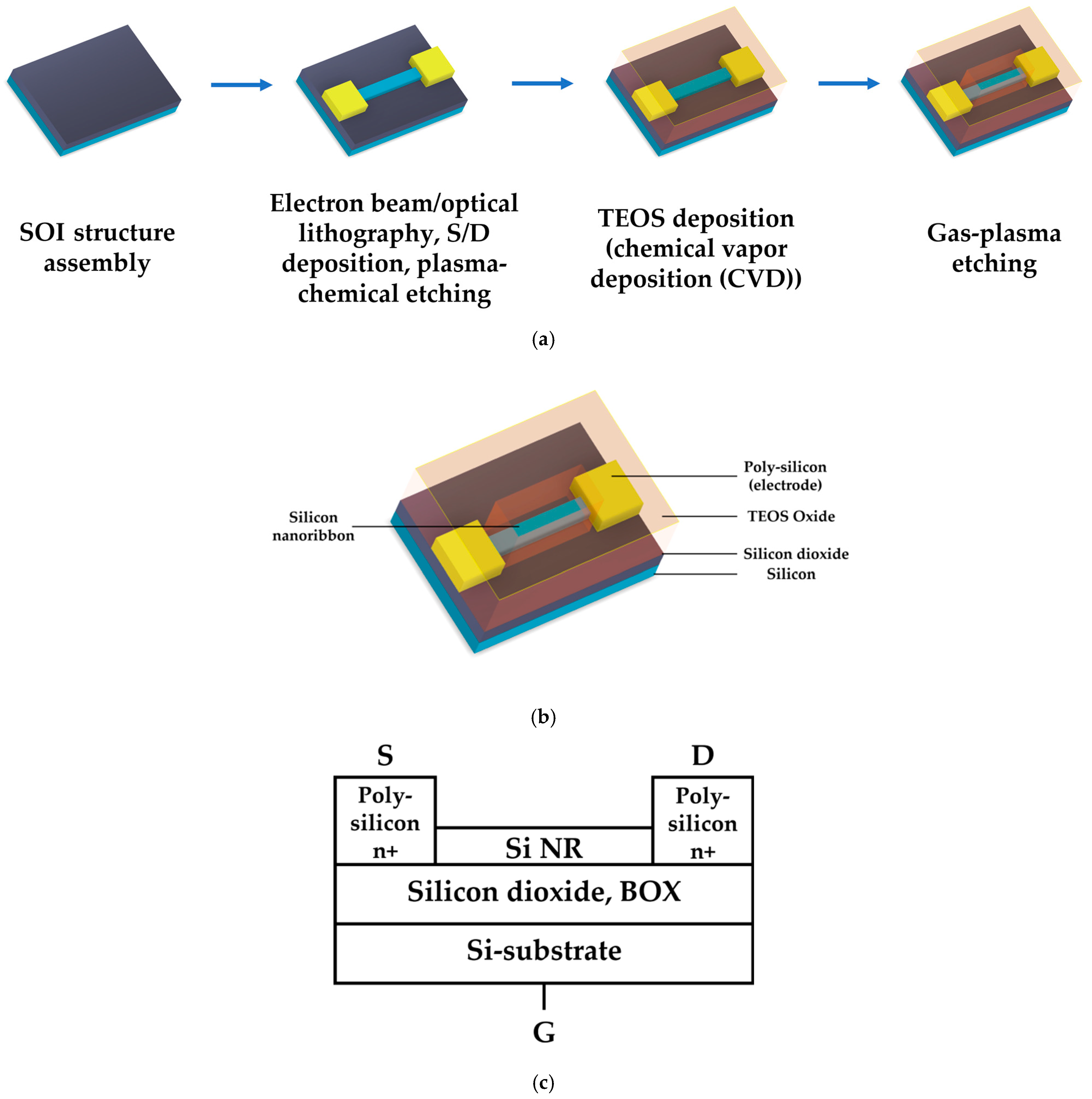
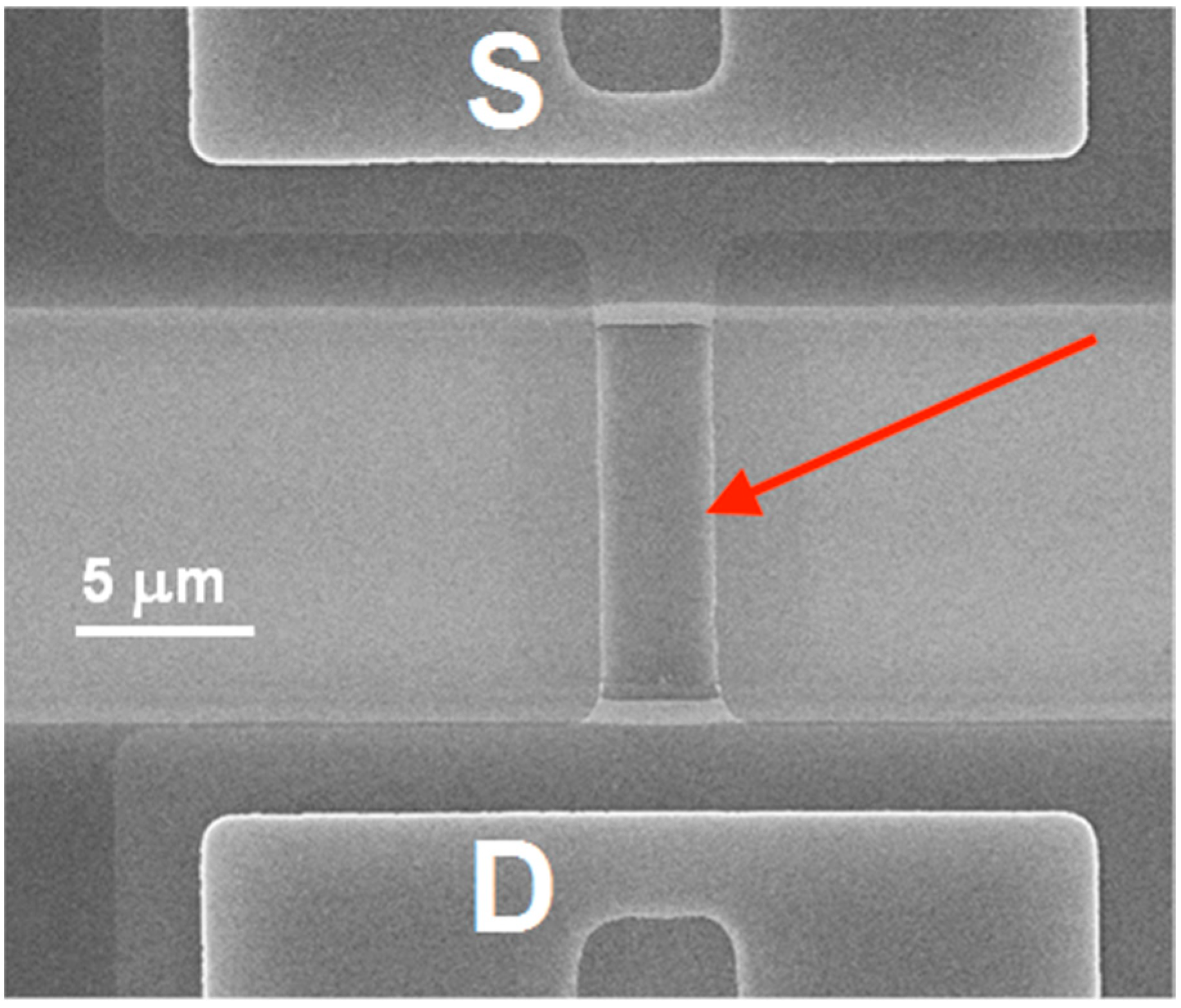
2.5. Fabrication of SOI-NR Chips
2.6. Surface Treatment of SOI-NR Chips
2.7. Sensitization of the Nanoribbons
2.8. SOI-NR Biosensor
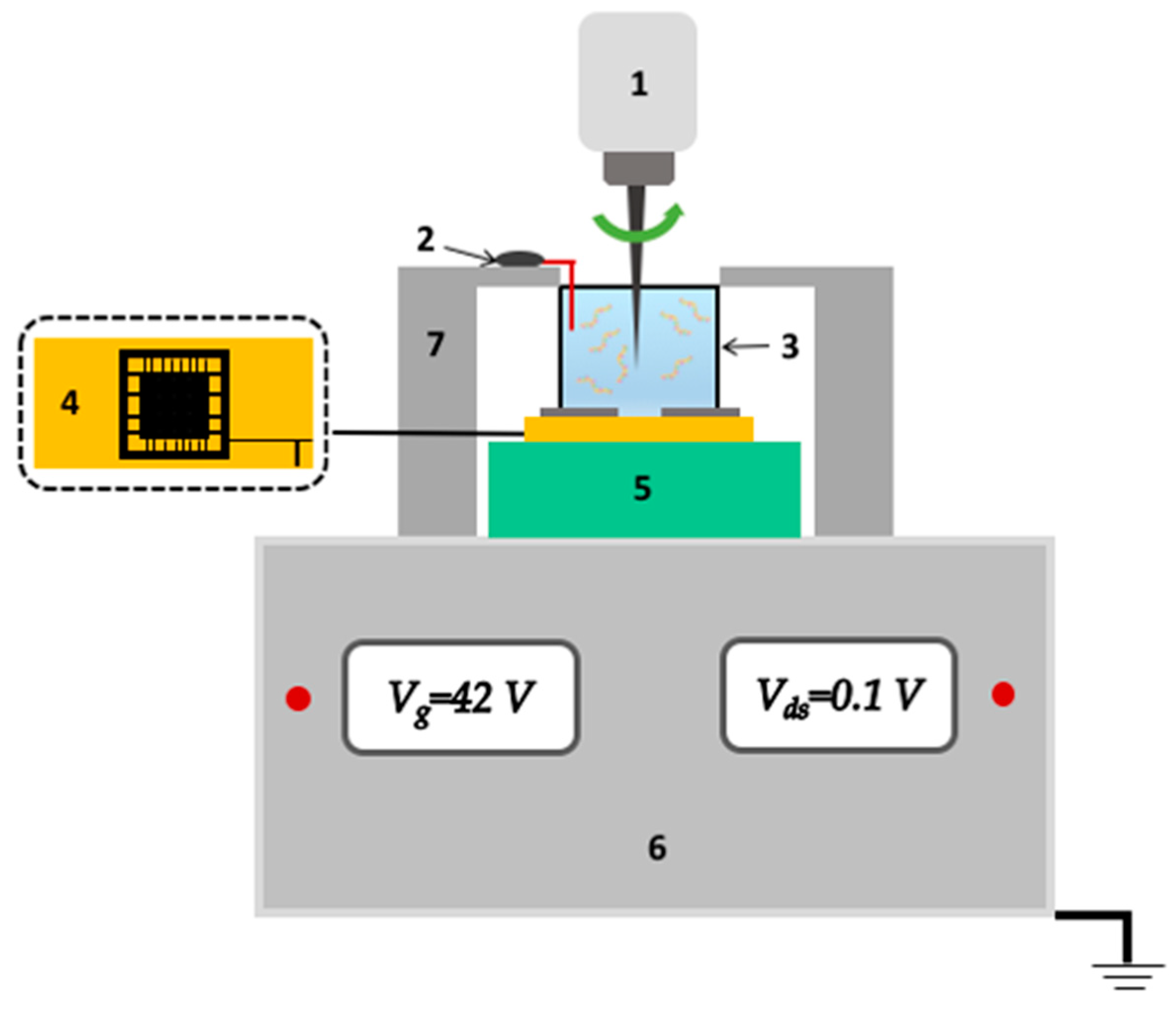
2.9. Electrical Measurements
2.10. Biosensor Measurements
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
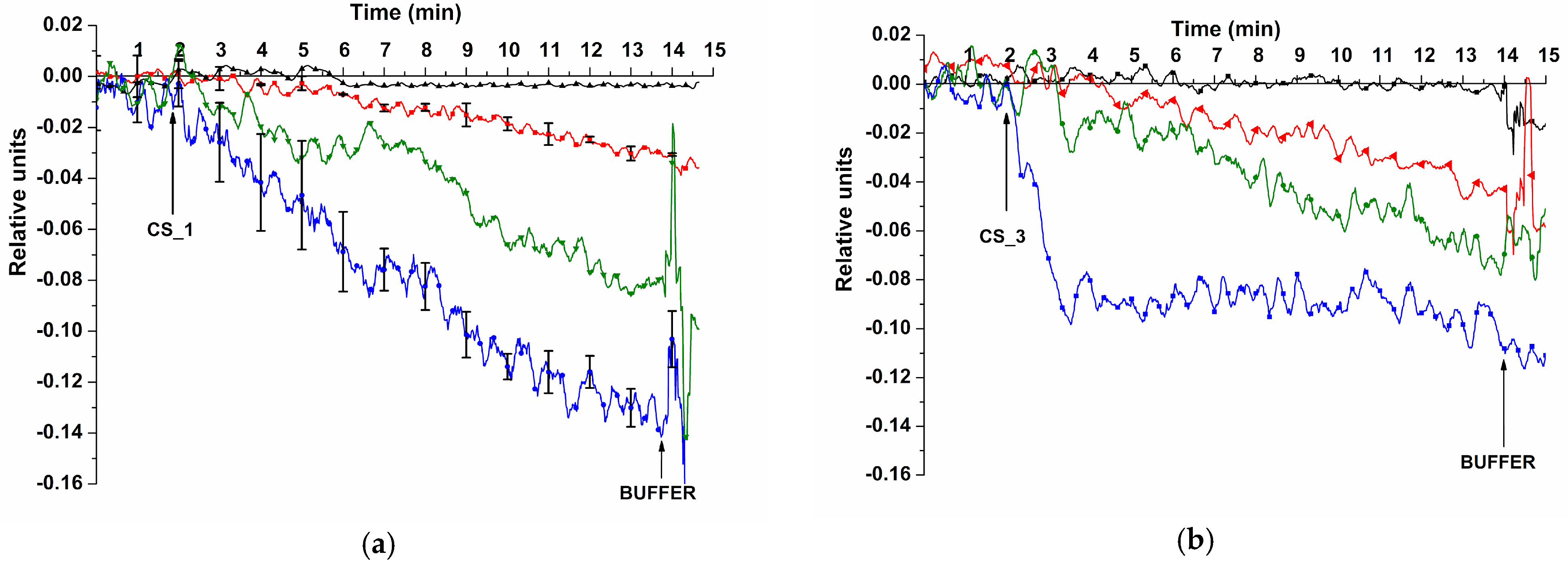
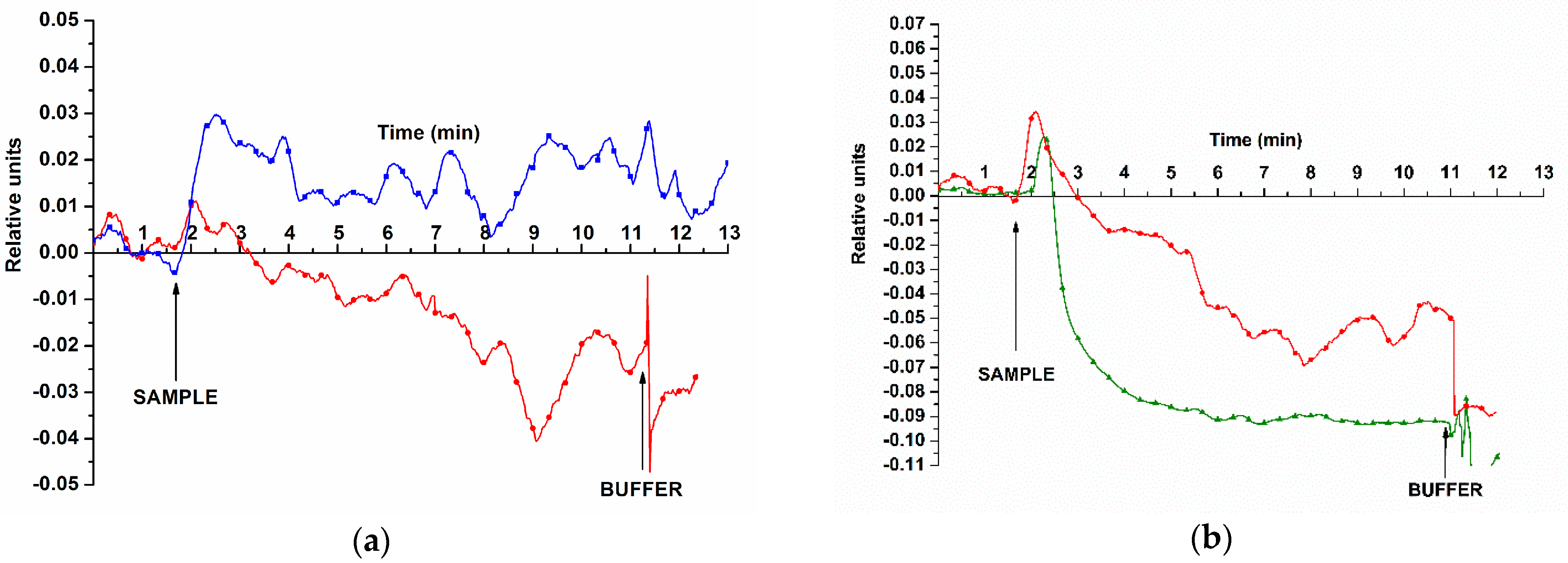
3.1. Determination of Method Sensitivity—Biospecific Detection of Target oDNAs in Buffer Solution
3.2. Biospecific Detection of miRNAs Isolated from Blood Plasma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Litwin, M.S.; Tan, H.-J. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer. A Review. JAMA 2017, 317, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barani, M.; Sabir, F.; Rahdar, A.; Arshad, R.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanotreatment and Nanodiagnosis of Prostate Cancer: Recent Updates. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Hashemy, S.I.; Sahebkar, A.; Aghaee Bakhtiari, S.H. MicroRNA Regulation of Androgen Receptor in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Premises, Promises, and Potentials. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.S.; Batool, R.; Masood, N.; Yasmin, A. Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer: A Multifactorial Case-Control Study. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2018, 42, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kwast, T.H.; Roobol, M.J. Defining the Threshold for Significant versus Insignificant Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2013, 10, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; Bussetti, M.; Panteghini, M. Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen Testing for Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: Managing the Gap between Clinical and Laboratory Practice. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Ding, T.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Hou, J.; Zhu, T.; Zheng, J.; et al. Circular RNA Expression Profiling Identifies Prostate Cancer- Specific CircRNAs in Prostate Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereverzev, A.S.; Kogan, M.Y. Prostate Cancer; Fakt: Kharkov, Ukraine, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- European Association of Urology. Guidelines, 2022 Edition. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/prostate-cancer (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Faiena, I.; Salmasi, A.; Mendhiratta, N.; Markovic, D.; Ahuja, P.; Hsu, W.; Elashoff, D.A.; Raman, S.S.; Reiter, R.E. PI-RADS Version 2 Category on 3 Tesla Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predicts Oncologic Outcomes in Gleason 3 + 4 Prostate Cancer on Biopsy. J. Urol. 2019, 201, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djavan, B.; Margreiter, M. Biopsy standards for detection of prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2007, 25, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, G.; Larré, S.; Gallina, A.; Lazar, A.; Faucon, H.; Chemama, S.; Allory, Y.; Patard, J.-J.; Vordos, D.; Hoznek, A.; et al. Extended 21-Sample Needle Biopsy Protocol for Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in 1000 Consecutive Patients. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djavan, B.; Ravery, V.; Zlotta, A.; Dobronski, P.; Dobrovits, M.; Fakhari, M.; Seitz, C.; Susani, M.; Borkowski, A.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Prostate Cancer Detected on Biopsies 1, 2, 3 and 4: When Should We Stop? J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-Molecule Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Detects Serum Proteins at Subfemtomolar Concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Choo, J. Simultaneous immunoassays of dual prostate cancer markers using a SERS-based microdroplet channel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axel, E.M.; Matveev, V.B. Statistics of malignant tumors of urinary and male urogenital organs in Russia and the countries of the former USSR. Cancer Urol. 2019, 15, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draisma, G.; Etzioni, R.; Tsodikov, A.; Mariotto, A.; Wever, E.; Gulati, R.; Feuer, E.; de Koning, H. Lead Time and Overdiagnosis in Prostate-Specific Antigen Screening: Importance of Methods and Context. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H.B.; Albertsen, P.C.; Barry, M.J.; Etzioni, R.; Freedland, S.J.; Greene, K.L.; Holmberg, L.; Kantoff, P.; Konety, B.R.; Murad, M.H.; et al. Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: AUA Guideline. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.H.; Roobol, M.; Jenster, G.; Schröder, F.H.; Bangma, C.H. Screening for Prostate Cancer in 2008 II: The Importance of Molecular Subforms of Prostate-Specific Antigen and Tissue Kallikreins. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, N.W.; Hart, C.A.; Brown, M.D. Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2009, 11, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Shiraishi, T.; Miles, N.; Trock, B.J.; Kulkarni, P.; Getzenberg, R.H. Nanowire Analysis of Cancer-Testis Antigens as Biomarkers of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Urology 2015, 85, 704.e1–704.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, Y.Y.; Ptitsyn, K.G.; Radko, S.P.; Zgoda, V.G.; Archakov, A.I. Droplet Digital PCR, a Prospective Technological Approach to Quantitative Profiling of microRNA. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2016, 10, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dr.Manish. Micro-RNA (MiRNA) in Oncology-Current Perspectives—Retrieved from [DentalReach]. Available online: https://dentalreach.today/dental-education/micro-rna-mirna-in-oncology-current-perspectives-2/ (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Homo Sapiens MiRNA (1872 Sequences). Available online: http://www.mirbase.org/cgibin/mirna_summary.pl?org=hsa (accessed on 21 March 2014).
- Garzon, R.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs and Cancer: Introduction. Semin. Oncol. 2011, 38, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjaly, K.; Tiku, A.B. MicroRNA Mediated Therapeutic Effects of Natural Agents in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 5759–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-Z.; Xi, Q.-H.; Ge, W.-L.; Zhang, X.-Q. Identification of Serum MicroRNA-21 as a Biomarker for Early Detection and Prognosis in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Wong, B.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Yuen, A.P.; Wei, W.I. Mature MiR-184 Aspotential Oncogenic MicroRNA of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hruby, G.W.; McKiernan, J.M.; Gurvich, I.; Lipsky, M.J.; Benson, M.C.; Santella, R.M. Dysregulation of Circulating MicroRNAs and Prediction of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2012, 72, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Ahmad, M.K.; Serajuddin, M.; Bhaskar, V.; Sankhwar, S.N.; Mahdi, A.A. MicroRNA-183-5p: A New Potential Marker for Prostate Cancer. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 34, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K. MiRNAs Can Predict Prostate Cancer Biochemical Relapse and Are Involved in Tumor Progression. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabahi, A.; Salahandish, R.; Gha_arinejad, A.; Omidinia, E. Electrochemical nano-genosensor for highly sensitive detection of miR-21 biomarker based on SWCNT-grafted dendritic Au nanostructure for early detection of prostate cancer. Talanta 2020, 209, 120595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshchi, F.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. A novel electroconductive interface based on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle and cysteamine functionalized AuNPs: Preparation and application as signal amplification element to minoring of antigen-antibody immunocomplex and biosensing of prostate cancer. J. Mol. Recognit. 2019, 33, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Deng, D.; Wang, Y.; Fang, C.; Li, S.-J. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric method for the detection of prostate-specific antigen. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Y.; Pleshakova, T.; Malsagova, K.; Kurbatov, L.; Popov, V.; Glukhov, A.; Smirnov, A.; Enikeev, D.; Potoldykova, N.; Alekseev, B.; et al. Detection of Marker MiRNAs, Associated with Prostate Cancer, in Plasma Using SOI-NW Biosensor in Direct and Inversion Modes. Sensors 2019, 19, 5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Z.; Bai, Z.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Shen, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Dual-color magnetic-quantum dot nanobeads as versatile fluorescent probes in test strip for simultaneous point-of-care detection of free and complexed prostate-specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Rong, M.; Shao, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Dong, B.; Xue, W.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Pan, J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of serum accurately detects prostate cancer in patients with prostate-specific antigen levels of 4–10 ng/mL. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Wagner, R.; Sigworth, F.J.; Breaker, R.; Fahmy, T.M.; Reed, M.A. Importance of the Debye Screening Length on Nanowire Field Effect Transistor Sensors. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3405–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, E.; Vacic, A.; Rajan, N.; Criscione, J.M.; Park, J.; Ilic, B.R.; Mooney, D.J.; Reed, M.A.; Fahmy, T.M. Label-free biomarker detection from whole blood. Nat. Nanotech. 2010, 5, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Patolsky, F.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.U.; Lieber, C.M. Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Y.D.; Malsagova, K.A.; Popov, V.P.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Kozlov, A.F.; Galiullin, R.A.; Shumov, I.D.; Kapustina, S.I.; Tikhonenko, F.V.; Ziborov, V.S.; et al. Nanoribbon-Based Electronic Detection of a Glioma-Associated Circular MiRNA. Biosensors 2021, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Y.D.; Malsagova, K.A.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Galiullin, R.A.; Kozlov, A.F.; Shumov, I.D.; Popov, V.P.; Kapustina, S.I.; Ivanova, I.A.; Isaeva, A.I.; et al. Aptamer-Sensitized Nanoribbon Biosensor for Ovarian Cancer Marker Detection in Plasma. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Gao, A.; Dai, P.; Song, S.; Fan, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, T. CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistors for Ultrasensitive and Label-Free MicroRNAs Sensing. Small 2014, 10, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malsagova, K.A.; Ivanov, Y.D.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Kaysheva, A.L.; Shumov, I.D.; Kozlov, A.F.; Archakov, A.I.; Popov, V.P.; Fomin, B.I.; Latyshev, A.V. A SOI-Nanowire Biosensor for the Multiple Detection of D-NFATc1 Protein in the Serum. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8078–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malsagova, K.A.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Galiullin, R.A.; Kozlov, A.F.; Shumov, I.D.; Popov, V.P.; Tikhonenko, F.V.; Glukhov, A.V.; Ziborov, V.S.; Petrov, O.F.; et al. Highly Sensitive Detection of CA 125 Protein with the Use of an N-Type Nanowire Biosensor. Biosensors 2020, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, Y.D.; Goldaeva, K.V.; Malsagova, K.A.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Galiullin, R.A.; Popov, V.P.; Kushlinskii, N.E.; Alferov, A.A.; Enikeev, D.V.; Potoldykova, N.V.; et al. Nanoribbon Biosensor in the Detection of MiRNAs Associated with Colorectal Cancer. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfström, N.; Juhasz, R.; Sychugov, I.; Engfeldt, T.; Karlström, A.E.; Linnros, J. Surface Charge Sensitivity of Silicon Nanowires: Size Dependence. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, C.; Pittino, F.; Verhoeven, H.A.; Lemay, S.G.; Selmi, L.; Jongsma, M.A.; Widdershoven, F.P. Real-Time Imaging of Microparticles and Living Cells with CMOS Nanocapacitor Arrays. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, J.I.; Lieber, C.M. Direct Ultrasensitive Electrical Detection of DNA and DNA Sequence Variations Using Nanowire Nanosensors. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selth, L.A.; Townley, S.; Gillis, J.L.; Ochnik, A.M.; Murti, K.; Macfarlane, R.J.; Chi, K.N.; Marshall, V.R.; Tilley, W.D.; Butler, L.M. Discovery of Circulating MicroRNAs Associated with Human Prostate Cancer Using a Mouse Model of Disease. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-M.; Mahon, K.L.; Spielman, C.; Gurney, H.; Mallesara, G.; Stockler, M.R.; Bastick, P.; Briscoe, K.; Marx, G.; Swarbrick, A.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Circulating MicroRNA Biomarkers in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhu, B.; Chen, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H. Downregulation of MicroRNA-429 Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Targeting P27Kip1 in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- miRBase: The microRNA Database. Available online: https://www.mirbase.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Ivanov, Y.D.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Kozlov, A.F.; Malsagova, K.A.; Krohin, N.V.; Shumyantseva, V.V.; Shumov, I.D.; Popov, V.P.; Naumova, O.V.; Fomin, B.I.; et al. SOI Nanowire for the High-Sensitive Detection of HBsAg and α-Fetoprotein. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5104–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yoshii, S.; Kumagai, S.; Fujiwara, I.; Nishio, K.; Okuda, M.; Matsukawa, N.; Yamashita, I. High-Density and Highly Surface Selective Adsorption of Protein–Nanoparticle Complexes by Controlling Electrostatic Interaction. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 4259–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.; Rishi, A.; Gupta, S.; Kannan, S.; Mahantshetty, U.; Tongaonkar, H.; Bakshi, G.; Prabhash, K.; Bhanushali, P.; Shinde, B.; et al. Clinical impact of prostate specific antigen (PSA) inter-assay variability on management of prostate cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C. Silicon Nanowires Length and Numbers Dependence on Sensitivity of the Field-Effect Transistor Sensor for Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdari, P.; Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A. Recent Advances in Silicon Nanowire Biosensors: Synthesis Methods, Properties, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, T. A controllable fabrication improved silicon nanowire array sensor on (111) SOI for accurate bio-analysis application. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7468–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambhorkar, P.; Wang, Z.; Ko, H.; Lee, S.; Koo, K.-i.; Kim, K.; Cho, D.-i. Nanowire-Based Biosensors: From Growth to Applications. Micromachines 2018, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonous, Z.A.; Shayeh, J.S.; Yazdian, F.; Yadegari, A.; Hashemi, M.; Omidi, M. An electrochemical biosensor for prostate cancer biomarker detection using graphene oxide-gold nanostructures. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, D.; Pachauri, V.; Madaboosi, N.; Jolly, P.; Vu, X.-T.; Estrela, P.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P.; Ingebrandt, S. Top-Down Fabricated Silicon Nanowire Arrays for Field-Effect Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8471–8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.J.; Hwang, S.G.; Lim, E.-K.; Jung, J.; Lee, T.J.; Park, H.-S.; Kang, T.; Kim, B. Attomolar Detection of Extracellular MicroRNAs Released from Living Prostate Cancer Cells by Plasmonic Nanowire Interstice Sensor. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17387–17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| oDNA Probe Name | oDNA Probe Sequence |
|---|---|
| probe_1 | 5′-(NH2)-(T)10TCGTGGATCTGTCTCTGCTCTGTTTATGGCCCTTCGGTAATTCACTGACTGAGACTGTTCACAGTGAATTCTACCAGTGCCATACACAGAACAGGAGTCACACTGCGG |
| probe_2 | 5′-(NH2)-(T)10CCGCTCTGCCCAGGCAGCTGCAGGCCCAGCCCCTGCCTCCTTCAGAGCAACAGAGAGGCAGGCATGCGGGCAGACAGACGCCCAACACAGAGACC |
| probe_3 | 5′-(NH2)-(T)10GCAGCGGATGGACGGTTTTACCAGACAGTATTAGACAGAGGGCCAGGTCTAACCATGTCTGGTAAGACGCCCATCGGCCGGCG |
| probe_4 | 5′-(NH2)-(T)10CGCCAAAAAAGCCAGGGTCACCCCCCGGGAAAGTCCCTATTTAGGGGTTTATCGGGAGGGGACTGAGCCTGACGAGGCT |
| Model oDNA Name | Model oDNA Probe Sequence | Respective Target miRNA Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS_1 | CCGCAGAGTGTGACTCCTGTTCTGTGTATGGCACTGGTAGAATTCACTGTGAACAGTCTCAGTCAGTGAATTACCGAAGGGCCATAAACAGAGCAGAGACAGATCCACGA | hsa-mir-183 | [31] |
| CS_2 | GGTCTCTGTGTTGGGCGTCTGTCTGCCCGCATGCCTGCCTCTCTGTTGCTCTGAAGGAGGCAGGGGCTGGGCCTGCAGCTGCCTGGGCAGAGCGG | hsa-mir-346 | [51] |
| CS_3 | CGCCGGCCGATGGGCGTCTTACCAGACATGGTTAGACCTGGCC CTCTGTCTAATACTGTCTGGTAAAACCGTCCATCCGCTGC | hsa-mir-429 | [52] |
| CS_4 | AGCCTCGTCAGGCTCAGTCCCCTCCCGATAAACCCCTAAATAGGGACTTTCCCGGGGGGTGACCCTGGCTTTTTTGGCG | hsa-mir-484 | [53] |
| Sample | Age | Gender | Diagnosis | TNM Stage | Total Gleason Score (Points) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC samples | Sample No. 44 | 68 | male | prostate cancer | T1cN0M0 | 6 |
| Sample No. 5 | 59 | male | prostate cancer | T2cN0M0 | 6 | |
| Control | Sample No. 27 | 51 | male | cyst of the left kidney | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanov, Y.D.; Malsagova, K.A.; Goldaeva, K.V.; Kapustina, S.I.; Pleshakova, T.O.; Popov, V.P.; Kozlov, A.F.; Galiullin, R.A.; Shumov, I.D.; Enikeev, D.V.; et al. Nanoribbon Biosensor-Based Detection of microRNA Markers of Prostate Cancer. Sensors 2023, 23, 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177527
Ivanov YD, Malsagova KA, Goldaeva KV, Kapustina SI, Pleshakova TO, Popov VP, Kozlov AF, Galiullin RA, Shumov ID, Enikeev DV, et al. Nanoribbon Biosensor-Based Detection of microRNA Markers of Prostate Cancer. Sensors. 2023; 23(17):7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177527
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanov, Yuri D., Kristina A. Malsagova, Kristina V. Goldaeva, Svetlana I. Kapustina, Tatyana O. Pleshakova, Vladimir P. Popov, Andrey F. Kozlov, Rafael A. Galiullin, Ivan D. Shumov, Dmitry V. Enikeev, and et al. 2023. "Nanoribbon Biosensor-Based Detection of microRNA Markers of Prostate Cancer" Sensors 23, no. 17: 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177527
APA StyleIvanov, Y. D., Malsagova, K. A., Goldaeva, K. V., Kapustina, S. I., Pleshakova, T. O., Popov, V. P., Kozlov, A. F., Galiullin, R. A., Shumov, I. D., Enikeev, D. V., Potoldykova, N. V., Ziborov, V. S., Petrov, O. F., Dolgoborodov, A. Y., Glukhov, A. V., Novikov, S. V., Grabezhova, V. K., Yushkov, E. S., Konev, V. A., ... Archakov, A. I. (2023). Nanoribbon Biosensor-Based Detection of microRNA Markers of Prostate Cancer. Sensors, 23(17), 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177527







