Antiviral Screen against Canine Distemper Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Stable Transfection
2.3. Compound Library
2.4. Nanoluciferase (nLuc)-Based Assay for High-Throughput Screening
2.5. CDV Inhibition Assay
2.6. Viability Assay
2.7. In Silico Studies—Molecular Docking with the F-Protein
3. Results
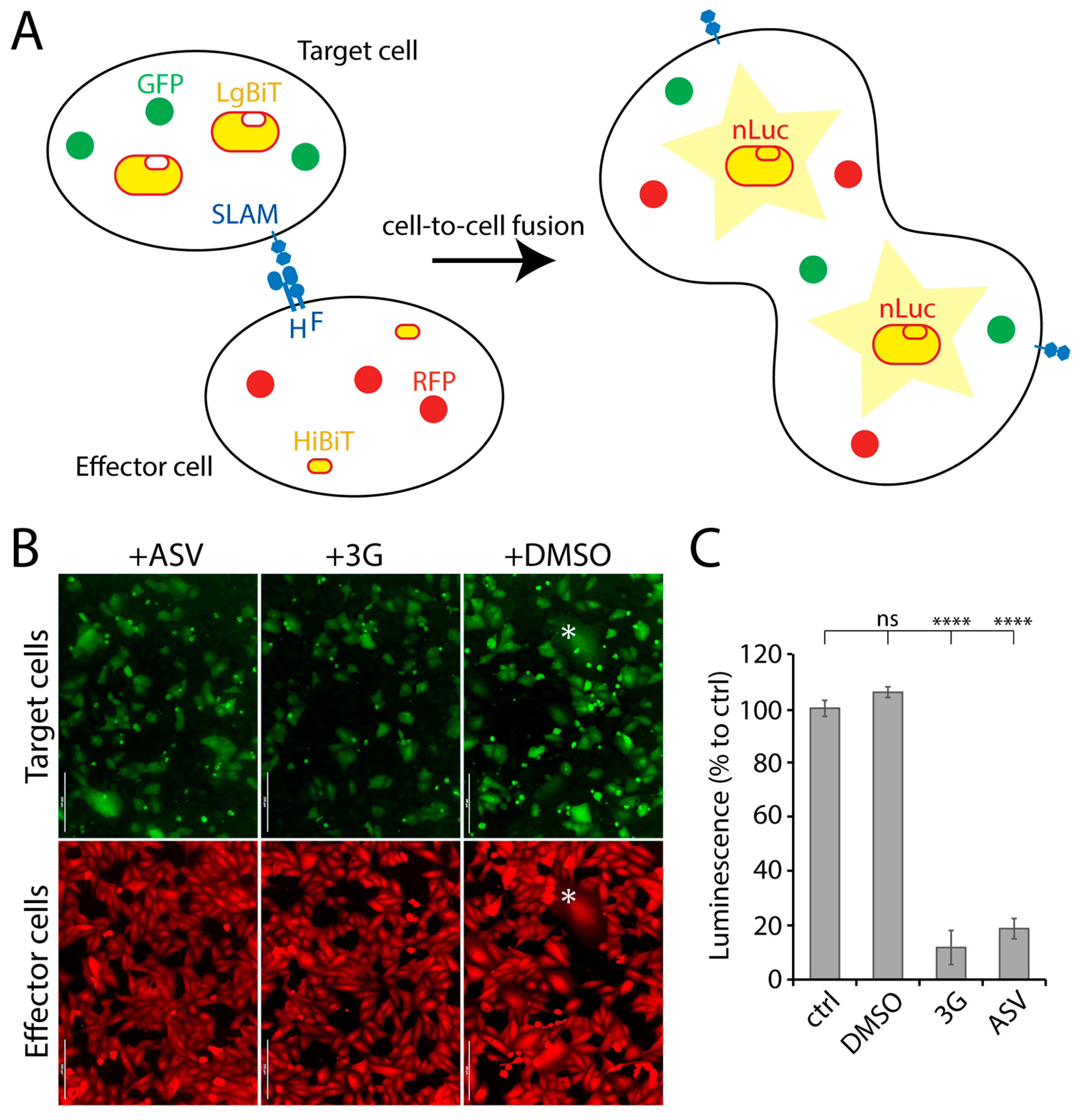
3.1. Establishment of a Quantitative Cell-Based Fusion Assay
3.2. Screening of Small Molecules Using a Quantitative Cell-Based Fusion Assay
3.3. Potency of the Newly Discovered Fusion Inhibitors
3.4. F2736-3056 Partly Preserved Fusion-Inhibition Activity against a 3G-Escape CDV F-Protein Variant
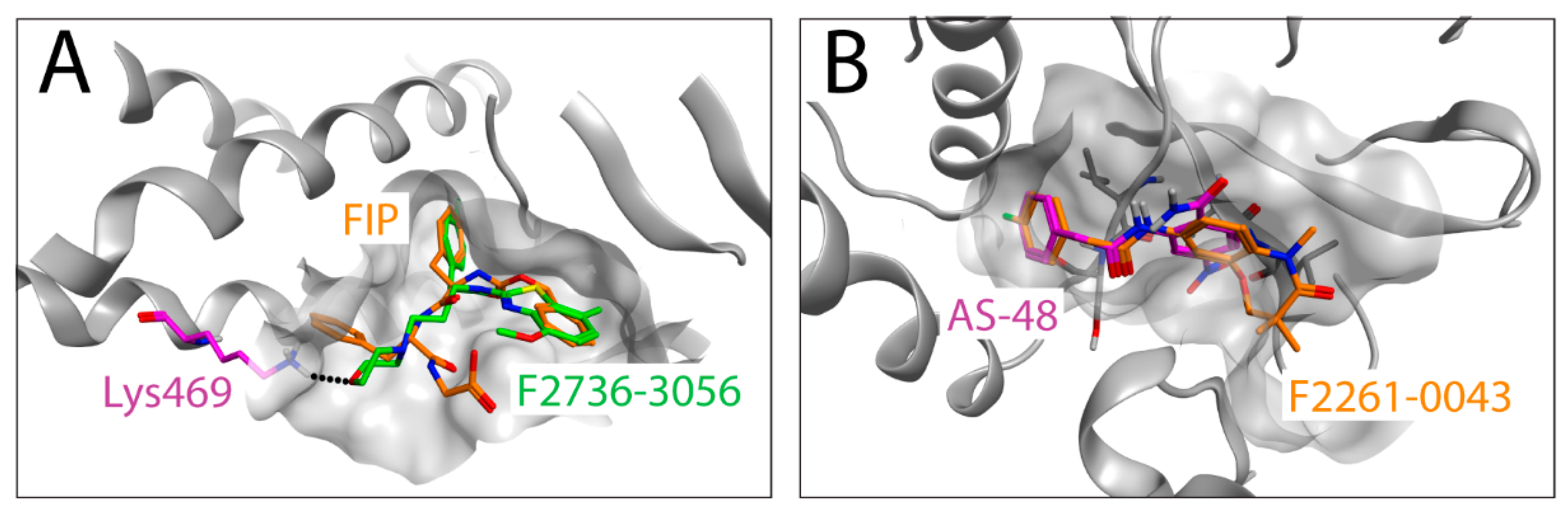
3.5. In Silico Analysis Suggests a CDV F-Protein Hydrophobic Pocket as a Common Binding Site for Diverse Inhibitory Compounds
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarthy, A.J.; Shaw, M.-A.; Goodman, S.J. Pathogen evolution and disease emergence in carnivores. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2007, 274, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, V.; Bianchi, A.; Bertoletti, I.; Pedrotti, L.; Gugiatti, A.; Catella, A.; Cordioli, P.; Lucente, M.S.; Elia, G.; Buonavoglia, C. Canine Distemper Epizootic among Red Foxes, Italy, 2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 2007–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Diversity of susceptible hosts in canine distemper virus infection: A systematic review and data synthesis. BMC Veter. Res. 2016, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.; Miquelle, D.G.; Goodrich, J.M.; Reeve, R.; Cleaveland, S.; Matthews, L.; Joly, D.O. Estimating the Potential Impact of Canine Distemper Virus on the Amur Tiger Population (Panthera tigris altaica) in Russia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wilker, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, N.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wilker, P.; et al. Fatal canine distemper virus infection of giant pandas in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.D.; Ludlow, M.; De Jong, A.; Rennick, L.J.; Verburgh, R.J.; Van Amerongen, G.; Van Riel, D.; Van Run, P.R.W.A.; Herfst, S.; Kuiken, T.; et al. Delineating morbillivirus entry, dissemination and airborne transmission by studying in vivo competition of multicolor canine distemper viruses in ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, F.; Ono, N.; Yamaguchi, R.; Yanagi, Y. Efficient Isolation of Wild Strains of Canine Distemper Virus in Vero Cells Expressing Canine SLAM (CD150) and Their Adaptability to Marmoset B95a Cells. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9943–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatsky, B.; Cattaneo, R.; Von Messling, V. Canine Distemper Virus Spread and Transmission to Naive Ferrets: Selective Pressure on Signaling Lymphocyte Activation Molecule-Dependent Entry. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon-Marin, S.; Budaszewski, R.D.F.; Canal, C.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Tropism and molecular pathogenesis of canine distemper virus. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, B.; Greisen, H.A.; Appel, M. Canine distemper encephalomyelitis: Variation with virus strain. J. Comp. Pathol. 1984, 94, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.A.C.; Khosravi, M.; Avila, M.; Ader-Ebert, N.; Bringolf, F.A.; Zurbriggen, A.; Vandevelde, M.; Plattet, P. SLAM- and Nectin-4-Independent Noncytolytic Spread of Canine Distemper Virus in Astrocytes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5724–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, M.; Montali, R.J.; Brownstein, D.; James, A.E., Jr.; Appel, M.J. Vaccine-induced canine distemper in a lesser panda. J. Am. Veter. Med. Assoc. 1976, 169, 959–960. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, J.W.; Appel, M.J.; Erickson, R.C.; Novilla, M.N. Fatal vaccine-induced canine distemper virus infection in black-footed ferrets. J. Am. Veter. Med. Assoc. 1976, 169, 961–964. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Tokiyoshi, S.; Hirayama, N.; Nakamura, K.; Ohashi, K.; Wakasa, C.; Mikami, T.; Kai, C. Antigenic differences in the H proteins of canine distemper viruses. Veter. Microbiol. 2000, 71, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, O.; Botelho, C.; Ferreira, C.; Ferreira, H.; Santos, M.; Diaz, M.; Oliveira, T.; Soares-Martins, J.; Almeida, M.; Júnior, A.S. In vitro inhibition of canine distemper virus by flavonoids and phenolic acids: Implications of structural differences for antiviral design. Res. Veter. Sci. 2013, 95, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Avila, L.M.; Morales-Martínez, M.E.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Zapata-Benavides, P.; Morán-Santibañez, K.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. In vitro anti-canine distemper virus activity of fucoidan extracted from the brown alga Cladosiphon okamuranus. VirusDisease 2014, 25, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, L.; Wong, G.; Sun, P.; Zheng, X.; Xia, X. Antiviral efficacy of favipiravir against canine distemper virus infection in vitro. BMC Veter. Res. 2019, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemper, R.K.; Erlandson, K.J.; Lakdawala, A.S.; Sun, A.; Prussia, A.; Boonsombat, J.; Aki-Sener, E.; Yalcin, I.; Yildiz, I.; Temiz-Arpaci, O.; et al. A target site for template-based design of measles virus entry inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5628–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemper, R.K.; Doyle, J.; Sun, A.; Prussia, A.; Cheng, L.-T.; Rota, P.A.; Liotta, D.C.; Snyder, J.P.; Compans, R.W. Design of a Small-Molecule Entry Inhibitor with Activity against Primary Measles Virus Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3755–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.D.; Scheid, A.; Choppin, P.W. Specific inhibition of paramyxovirus and myxovirus replication by oligopeptides with amino acid sequences similar to those at the N-termini of the Fl or HA2 viral polypeptides. Virology 1980, 105, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singethan, K.; Hiltensperger, G.; Kendl, S.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Plattet, P.; Holzgrabe, U.; Schneider-Schaulies, J. N-(3-Cyanophenyl)-2-phenylacetamide, an effective inhibitor of morbillivirus-induced membrane fusion with low cytotoxicity. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Prussia, A.; Zhan, W.; Murray, E.E.; Doyle, J.; Cheng, L.-T.; Yoon, J.-J.; Radchenko, E.V.; Palyulin, V.A.; Compans, R.W.; et al. Nonpeptide Inhibitors of Measles Virus Entry. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5080–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumm, S.A.; Yan, D.; Hovingh, E.S.; Evers, T.J.; Enkirch, T.; Reddy, G.P.; Sun, A.; Saindane, M.T.; Arrendale, R.F.; Painter, G.; et al. An Orally Available, Small-Molecule Polymerase Inhibitor Shows Efficacy Against a Lethal Morbillivirus Infection in a Large Animal Model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 232ra52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, L.K.; Yoon, J.-J.; Lee, J.K.; Sun, A.; Du, Y.; Fu, H.; Snyder, J.P.; Plemper, R.K. Nonnucleoside Inhibitor of Measles Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Complex Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.K.; Jacobs, C.L.; Huo, Y.; Yang, J.; Krumm, S.A.; Plemper, R.K.; Tsien, R.Y.; Lin, M.Z. Tunable and reversible drug control of protein production via a self-excising degron. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torriani, G.; Trofimenko, E.; Mayor, J.; Fedeli, C.; Moreno, H.; Michel, S.; Heulot, M.; Chevalier, N.; Zimmer, G.; Shrestha, N.; et al. Identification of Clotrimazole Derivatives as Specific Inhibitors of Arenavirus Fusion. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, M.; Alves, L.; Khosravi, M.; Ader-Ebert, N.; Origgi, F.; Schneider-Schaulies, J.; Zurbriggen, A.; Plemper, R.K.; Plattet, P.; Lyles, D.S. Molecular Determinants Defining the Triggering Range of Prefusion F Complexes of Canine Distemper Virus. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 2951–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattet, P.; Zweifel, C.; Wiederkehr, C.; Belloy, L.; Cherpillod, P.; Zurbriggen, A.; Wittek, R. Recovery of a persistent Canine distemper virus expressing the enhanced green fluorescent protein from cloned cDNA. Virus Res. 2004, 101, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Chung, T.D.Y.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbermatter, D.; Shrestha, N.; Ader-Ebert, N.; Herren, M.; Moll, P.; Plemper, R.K.; Altmann, K.-H.; Langedijk, J.P.; Gall, F.M.; Lindenmann, U.; et al. Primary resistance mechanism of the canine distemper virus fusion protein against a small-molecule membrane fusion inhibitor. Virus Res. 2019, 259, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Matsuoka, R.; Kuroda, D.; Kubota, M.; Shirogane, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tsumoto, K.; Kohda, D.; Plemper, R.K.; et al. Structures of the prefusion form of measles virus fusion protein in complex with inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbermatter, D.; Shrestha, N.; Gall, F.M.; Wyss, M.; Riedl, R.; Plattet, P.; Fotiadis, D. Cryo-EM structure of the prefusion state of canine distemper virus fusion protein ectodomain. J. Struct. Biol. X 2020, 4, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beineke, A.; Baumgärtner, W.; Wohlsein, P. Cross-species transmission of canine distemper virus—An update. One Health 2015, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loots, A.K.; Mitchell, E.; Dalton, D.L.; Kotzé, A.; Venter, E.H. Advances in canine distemper virus pathogenesis research: A wildlife perspective. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Liao, G.; Hu, R. Canine Distemper Outbreak in Rhesus Monkeys, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Nagata, N.; Ami, Y.; Seki, F.; Suzaki, Y.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Suzuki, T.; Fukushi, S.; Mizutani, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. Lethal Canine Distemper Virus Outbreak in Cynomolgus Monkeys in Japan in 2008. J. Virol. 2012, 87, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, A.; Ye, H.; Shi, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, L. Natural infection with canine distemper virus in hand-feeding Rhesus monkeys in China. Veter. Microbiol. 2010, 141, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haig, D.A. “Canine Distemper-Immunization with avianised virus,” Onderstepoort. J. Vet. Res. 1956, 27, 20–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rockborn, G. An Attenuated Strain of Canine Distemper Virus in Tissue Culture. Nat. Cell Biol. 1959, 184, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairley, R.; Knesl, O.; Pesavento, P.; Elias, B. Post-vaccinal distemper encephalitis in two Border Collie cross littermates. N. Z. Veter. J. 2014, 63, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, H.J.; Thompson, H.; A McCandlish, I.; Macartney, L.; Nash, A.S. Encephalitis in dogs associated with a batch of canine distemper (Rockborn) vaccine. Veter. Rec. 1988, 122, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbrooks, R.D.; Swango, L.J.; Schnurrenberger, P.R.; Mitchell, F.E.; Hill, E.P. Response of gray foxes to modified live-virus canine distemper vaccines. J. Am. Veter. Med Assoc. 1981, 179, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland-Smith, M.R.; Rideout, B.A.; Mikolon, A.B.; Appel, M.J.; Morris, P.J.; Shima, A.L.; Janssen, D.J. Vaccine-induced canine distemper in European mink, Mustela lutreola. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1997, 28, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stephensen, C.B.; Welter, J.; Thaker, S.R.; Taylor, J.; Tartaglia, J.; Paoletti, E. Canine distemper virus (CDV) infection of ferrets as a model for testing Morbillivirus vaccine strategies: NYVAC- and ALVAC-based CDV recombinants protect against symptomatic infection. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coke, R.L.; Backues, K.A.; Hoover, J.P.; Saliki, J.T.; Ritchey, J.W.; West, G.D. Serologic responses after vaccination of fennec foxes (Vulpes zerda) and meerkats (Suricata suricatta) with a live, canarypox-vectored canine distemper virus vaccine. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2005, 36, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, E.; Deem, S.L.; Sanchez, C.; Murray, S. Serologic response to a canarypox-vectored canine distemper virus vaccine IN the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2007, 38, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimsatt, J.; Biggins, D.; Innes, K.; Taylor, B.; Garell, D. Evaluation of oral and subcutaneous delivery of an experimental canarypox recombinant canine distemper vaccine in the Siberian polecat (Mustela eversmanni). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2003, 34, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, R.A.; Ramsay, E.; McAloose, D.; Rush, R.; Wilkes, R.P. Evaluation of two canine distemper virus vaccines in captive tigers (Panthera tigris). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2016, 47, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattet, P.; Alves, L.; Herren, M.; Aguilar, H.C. Measles Virus Fusion Protein: Structure, Function and Inhibition. Viruses 2016, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, N.; Gall, F.M.; Vesin, J.; Chambon, M.; Turcatti, G.; Fotiadis, D.; Riedl, R.; Plattet, P. Antiviral Screen against Canine Distemper Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion Activity. Viruses 2021, 13, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010128
Shrestha N, Gall FM, Vesin J, Chambon M, Turcatti G, Fotiadis D, Riedl R, Plattet P. Antiviral Screen against Canine Distemper Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion Activity. Viruses. 2021; 13(1):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010128
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Neeta, Flavio M. Gall, Jonathan Vesin, Marc Chambon, Gerardo Turcatti, Dimitrios Fotiadis, Rainer Riedl, and Philippe Plattet. 2021. "Antiviral Screen against Canine Distemper Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion Activity" Viruses 13, no. 1: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010128
APA StyleShrestha, N., Gall, F. M., Vesin, J., Chambon, M., Turcatti, G., Fotiadis, D., Riedl, R., & Plattet, P. (2021). Antiviral Screen against Canine Distemper Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion Activity. Viruses, 13(1), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010128






