Antivaccine Movement and COVID-19 Negationism: A Content Analysis of Spanish-Written Messages on Twitter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
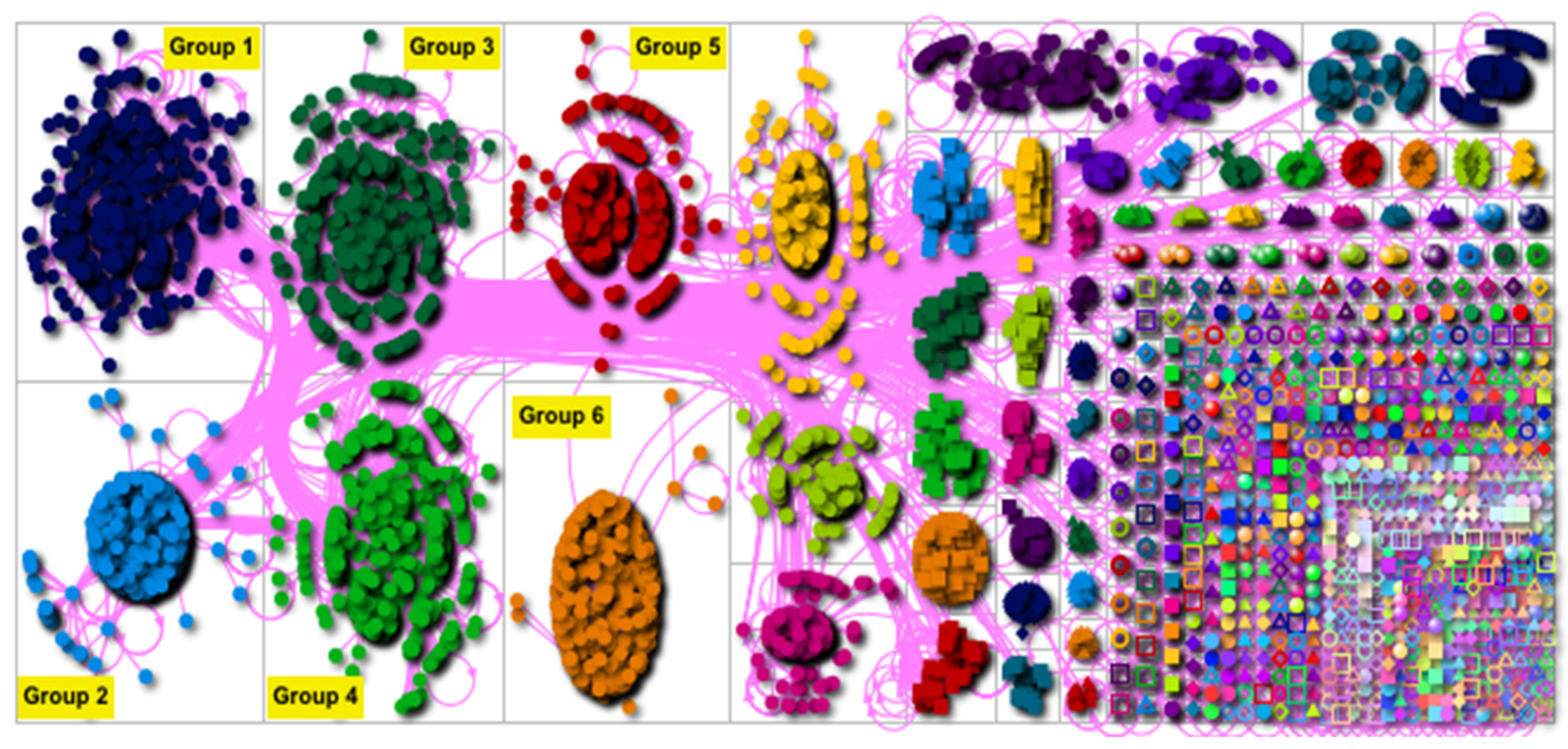
3.1. Social Network Analysis
3.2. User Analysis
3.3. Content Analysis
3.4. Anti-COVID-19 Vaccine Content Analylsis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothan, H.A.; Byrareddy, S.N. The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 26, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, T.; Rahman, R.; Whitelaw, D.; Jain, V.; Al-Taan, O.; Rashid, F.; Munasinghe, A.; Jambulingam, P. SARS-CoV-2 and the pandemic of COVID-19. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; López Segui, F.; Vidal-Alaball, J.; Katz, M.S. COVID-19 and the “film your hospital” conspiracy theory: Social netowork analysis of Twitter data. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e22374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, C.; Llopis, D.; Roman, A.; Alfayate, E.; Herrera-Peco, I. Spanish radiographers’ concerns about the COVID-19 pandemic. Radiography 2020, 27, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, Z.; Ahmad, T.; Kabar, S. Potential approaches to combat COVID-19: A mini review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 9939–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarate, K.G.; Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Temporal trends in anti-vaccine discourse on twitter. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4867–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.M.; Sharp, L.K. Anti-vaccinationists past and present. BMJ 2002, 325, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López Santamaría, M.A. Los movimientos antivacunación y su presencia en internet. Rev. Ene Enfermería 2015, 9. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, H.J. The biggest pandemic risk? Viral misinformation. Nature 2018, 562, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, W.Y.S.; Oh, A.; Klein, W.M.P. Addressing Health-Related Misinformation on Social Media. JAMA 2018, 320, 2417–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd Wilson, S.; Wiysonge, C. Social media and vaccine hesitancy. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e004206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, K.; Das, D.; Barman, B.; Borah, P. Are internet videos useful sources of information during global public health emergencies? A case study of Youtube videos during the 2015–2016 Zika virus pandemic. Pathog. Glob. Health 2018, 112, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, I.C.; Fu, K.W.; Chan, C.H.; Chan, B.S.; Cheung, C.N.; Abraham, T.; Tse, Z. Social Media’s Initial Reaction to Information and Misinformation on Ebola, August 2014: Facts and Rumors. Public Health Rep. 2016, 131, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allcott, H.; Gentzkow, M. Social Media and Fake News in the 2016 Election. J. Econ. Perspectiv. 2017, 31, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Meng, S.; Shi, J.; Lu, L. 2019-nCoV epidemic: Address mental health care to empower society. Lancet 2020, 395, e37–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James Rubin, G.; Wessely, S. The psychological effects of quarantining a city. BMJ 2020, 368, m313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evrony, A.; Caplan, A. The overlooked dangers of anti-vaccination groups’ social media presence. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 1475–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, W.L.; Livingston, S. The disinformation order: Disruptive communication and the decline of democratic institutions. Eur. J. Commun. 2018, 33, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Fuentes, M.D.C.; Herrera-Peco, I.; Molero Jurado, M.D.M.; Fátima-Oropesa, N.; Gázquez-Linarez, J.J. Predictors of threat from COVID-19: A cross-sectional study in the Spanish population. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Peco, I.; Ruiz-Núñez, C.; Jiménez-Gómez, B.; Romero-Magdalena, C.S.; Benítez de Gracía, E. COVID-19 and vaccination: Analysis of public institutions’ role in information spread through Twitter. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2021, 95, e202106084. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bavel, J.J.; Baicker, K.; Boggio, P.S.; Capraro, V.; Cichocka, A.; Cikara, M.; Crockett, M.J.; Crum, A.J.; Douglas, K.M.; Druckman, J.N.; et al. Using social and behavioural science to support COVID-19 pandemic responde. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselli, R.; Martini, M.; Bragazzi, N.L. The old and the new: Vaccine hesitancy in the era of the Web 2.0. Challenges and opportunities. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2016, 57, E47–E50. [Google Scholar]
- McStay, A. Empathic media and advertising: Industry, policy, legal and citizen perspectives (the case for intimacy). Big Data Soc. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burki, T. The online anti-vaccine movement in the age of COVID-19. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e504–e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, A.; Broniatowski, D.A.; Smith, M.C.; Parikh, K.S.; Malik, A.; Dredze, M.; Quinn, S.C. Adapting and Extending a Typology to Identify Vaccine Misinformation on Twitter. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, S331–S339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan Garcia, A.; Aguilar, I. Discurso antivacunas en las redes sociales: Análisis de los argumentos más frecuentes. Tiempos Enfermería y Salud 2018, 1, 50–53. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Merriam-Webster. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/words-were-watching-infodemic-meaning (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Centro Virtual Cervantes. El Español: Una Lengua Viva. Informe 2019. Available online: https://cvc.cervantes.es/lengua/anuario/anuario_19/informes_ic/p04.htm#np71n (accessed on 13 January 2021). (In Spanish).
- Bello-Orgaz, G.; Hernandez-Castro, J.; Camacho, D. Detecting discussion communities on vaccination in twitter. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 66, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Center for Countering Digital Hate. Failure to Act. 2020. Available online: https://www.counterhate.co.uk/anti-vaxx-industry (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Sanchez, S.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Romero-Severson, E.; Hengartner, N.; Ke, R. High Contagiousness and Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. Anti-vaccine movement could undermine efforts to end coronavirus pandemic, researchers warn. Nature 2020, 581, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.F.; Velásquez, N.; Restrepo, N.J.; Leahy, R.; Gabriel, N.; El Oud, S.; Zheng, M.; Manrique, P.; Wuchty, S.; Lupu, Y. The online competition between pro- and anti-vaccinations views. Nature 2020, 582, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Bath, P.; Demartini, G. Using Twitter as a data source: An overview of ethical, legal, and methodological challenge. Adv. Res. Ethics Integr. 2017, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonnalagadda, S.; Peeler, R.; Topham, P. Discovering opinion leaders for medical topics using news articles. J. Biomed. Semant. 2012, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, W.; Vidal-Alaball, J.; Downing, J.; López Seguí, F. COVID-19 and the 5G conspiracy theory: Social network analysis of Twitter data. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, K.; Torous, J.; Ernala, S.K.; Rizuto, C.; Staffordm, A.; De Choudhury, M. A computation study of mental health awareness campaigns on social media. Transl. Behav. Med. 2019, 9, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, E.S.; Jaremko, K.M.; Park, B.H.; Stiegler, M.A.; Gamble, J.G.; Chu, L.F.; Utengen, A.; Mariano, E.R. I tweet, therefor I learn: An analysis of Twitter use across anesthesiology conferences. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 333340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauset, A.; Newman, M.; Moore, C. Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 70, 066111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, N.; Graham, T. Mapping the anti-vaccination movement on Facebook. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, M.S.; Dunn, A.G.; Wiley, K.E.; Leask, J. How organisations promoting vaccination respond to misinformation on social media: A qualitative investigation. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cano Garcinuño, M.; Arce García, S. Analysis of communication in social networks of the influenza vaccine campaign in Spain. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2020, 94, 202003008. [Google Scholar]
- Fournet, N.; Mollema, L.; Rujis, W.L.; Harmsen, I.A.; Keck, F.; Durand, J.Y.; Cunha, M.P.; Wamsiedel, M.; Reis, R.; French, J.; et al. Under-vaccinated groups in Europe and their beliefs, attitudes and reasons for non-vaccination; two systematic reviews. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo Park, H.; Park, S.; Chong, M. Conversations and Medical News Frames on Twitter: Infodemiological Study on COVID-19 in South Korea. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cori, L.; Bianchi, F.; Cadum, E.; Anthonj, C. Risk Perception and COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecke, O.; DeYoung, S.E. Anti-Vaccine Decision-Making and Measles Resurgence in the United States. Glob. Pediatric Health 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kata, A. A postmodern Pandora’s box: Anti-vaccination misinformation on the internet. Vaccine 2010, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, T. New variant of SARS-CoV-2 in UK causes surge of COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e20–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.; Deshpande, S.; Evans, W.; Obregon, R. Key guidelines in developing a pre-emptive COVID-19 vaccination uptake promotion strategy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, N.; Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H.; Gunaratne, K. Social media and vaccine hesitancy: New updates for the era of COVID-19 and globalized infectious diseases. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2020, 16, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tweet | Group from NodeXl | Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Caution! Vaccination was suspended in Rosario because ALL vaccinated people are having vomiting and fever. #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) #NoEsElCovidEsElTotalitarismo (#ItIsNotCovidItIsTotalitarism) | 1 | 5446 |
| Having chips in vaccines is a crackpot thing, right? It is not But don’t worry, it is just a barcode to check your lot and expiration date #COVID19 #Plandemia #YoNoMeVacuno (#Plandemic #IDoNotGetVaccinated) | 2 | 350 |
| My body, MY CHOICE #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) | 3 | 1151 |
| Vaccine does not guarantee anything!! #YoMeVacuno #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoGetVaccinated #IDoNotGetVaccinated) | 4 | 124 |
| Pedro Cavadas | Encephalitis: the “adverse effect” of the “quick” anti-coronavirus vaccines noted by Dr. Cavadas. This is the only EXPERT I trust… #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) | 5 | 1216 |
| #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated), but not because I do not want to. I live in Colombia. Here, there are no vaccines. Our president is rehearsing for his reality show. | 6 | 1748 |
| Rank | Account Description | BCS | Pagerank | Followers | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User1 | Anonymous profile focused on offering the truth. | 12,047,282.99 | 218.69 | 7446 | G2 |
| User2 | User defined as writer and senator in Colombia | 5,590,037.244 | 232.249 | 1,004,405 | G6 |
| User3 | Citizen focused on political activism | 4,022,155.431 | 143.997 | 2676 | G7 |
| User4 | Citizen defined as feminist | 3,818,752.493 | 20.593 | 3787 | G10 |
| User5 | Citizen defined as writer | 3,722,722.425 | 123.186 | 11,292 | G5 |
| User6 | Official account of Colombia Ministry of Health) | 3,317,916.869 | 1.416 | 1,395,041 | G4 |
| User7 | User defined as a freethinker | 227,136.274 | 8.388 | 6297 | G10 |
| User8 | Anonymous profile | 2,191,083.218 | 55.656 | 1183 | G3 |
| User9 | Citizen defined as engineer | 2,089,182.493 | 0.878 | 2206 | G10 |
| User10 | Anonymous profile focused on political activism | 2,085,652.241 | 44.616 | 15,344 | G1 |
| Category | Sub-Category | Tweets vs. Total Tweets (N, %) | Tweets vs. Category Tweets (N, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conspiracy theory tweets | 270 (16.97) | ||
| 5G and chip inoculation | 14 (5.18) | ||
| Genocide | 78 (28.89) | ||
| New World Order and control of population | 178 (65.93) | ||
| Criticizing politicians and/or government | 218 (13.7) | ||
| Deniers of COVID-19 | 53 (3.33) | ||
| Reluctant but open-minded tweets | 31 (1.95) | ||
| Antivaccine tweets | 494 (31.05) | ||
| Vaccine safety | 313 (63.36) | ||
| Vaccine efficacy | 44 (8.9) | ||
| Vaccine importance | 43 (8.7) | ||
| Beliefs about COVID-19 vaccine | 93 (18.83) | ||
| Pro-COVID-19 vaccine tweets | 66 (4.15) | ||
| General tweets not expressing a view or opinion | 459 (28.85) | ||
| Category | N (%) | Most Representative Tweets |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccines safety (272 tweets) | ||
| Adverse effects | 250 (79.87) | As an infectiologist, it is my civic duty to warn the population about the risk of taking an untested vaccine. The government will be responsible for a criminal, genocidal action. I wwill not hesitate to sue our nation if this happens. That is why #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| New strain of SARS-CoV-2 | 22 (7.03) | It is no coincidence that the UK started “vaccination” 13 days ago, and today they are announcing a new strain? Watch out! #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| Vaccine efficacy (44 tweets) | ||
| COVID-19 vaccine is ineffective | 24 (54.55) | If the vaccine does not stop you from getting #COVID19 or transmitting it, then what the fuck is it good for? Why do they insist that we get vaccinated? #Plandemia (#Plandemic) #NWO #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| COVID-19 vaccine could work or does not | 16 (36.36) | Then what the fuck is the point of this vaccine?????!!! #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| There are more effective methods | 4 (9.09) | The FDA and WHO lied about #dioxidodechlorine by spreading falsehoods: that it was toxic, that it was a poison, that people could die… and thousands and thousands of people have been cured but, as it is a free patent, it is not sellable. That is why I do not believe in the vaccine. #holachilelared (#hellochilenetwork) #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| Vaccine Importance (43 tweets) | ||
| It is better to be COVID-19-positive and acquire natural immunity | 19 (44.19) | I have never had a flu shot in my fucking life. I get it every year, pass it, and drop it. It is called the immune system, so how about we let it work like it has been doing for hundreds of thousands of years? #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| Government and pharmaceutical industries are allies | 24 (55.81) | How nice of the pharmaceutical companies to let us buy cheap vaccines so that our governments can buy them (with our money) while the treatments for real and serious diseases (cancer, leukemia…) are priced for the rich. #YoNoMeVacuno #Plandemia #COVID19 (#IDoNotGetVaccinated #Plandemic) |
| Beliefs about COVID-19 vaccine (93 tweets) | ||
| Misinformation about vaccines | 71 (76.34) | The Vatican endorses vaccines using cell lines from aborted fetuses #AbortoEsGenocidio #Asesinos #YoNoMeVacuno (#AbortionIsGenocide #Murderers #IDoNotGetVaccinated). |
| Natural/divine alternatives | 14 (15.05) | …Meanwhile, in Tel Aviv (Israel) they manage to cure 99.9% of COVID pathogens in 30 s by simply using an ultraviolet light. #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) |
| Vaccines are a fraud from pharmaceutical industries | 8 (8.6) | #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) because they use you as a guinea pig. It makes no sense to apply a vaccine when you are advised to continue using a mask and social distance because the vaccine does not fully immunize you. Then why should I get the shot? This is a business from laboratories and governments. |
| Gene Manipulation (40 tweets) | ||
| DNA alterations | #YoNoMeVacuno (#IDoNotGetVaccinated) because I am free and responsible for my own body, because I love myself and I refuse to be genetically manipulated or poisoned. Wake up! Let us get this over with (46 retweets) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Peco, I.; Jiménez-Gómez, B.; Romero Magdalena, C.S.; Deudero, J.J.; García-Puente, M.; Benítez De Gracia, E.; Ruiz Núñez, C. Antivaccine Movement and COVID-19 Negationism: A Content Analysis of Spanish-Written Messages on Twitter. Vaccines 2021, 9, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060656
Herrera-Peco I, Jiménez-Gómez B, Romero Magdalena CS, Deudero JJ, García-Puente M, Benítez De Gracia E, Ruiz Núñez C. Antivaccine Movement and COVID-19 Negationism: A Content Analysis of Spanish-Written Messages on Twitter. Vaccines. 2021; 9(6):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060656
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Peco, Ivan, Beatriz Jiménez-Gómez, Carlos Santiago Romero Magdalena, Juan José Deudero, María García-Puente, Elvira Benítez De Gracia, and Carlos Ruiz Núñez. 2021. "Antivaccine Movement and COVID-19 Negationism: A Content Analysis of Spanish-Written Messages on Twitter" Vaccines 9, no. 6: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060656
APA StyleHerrera-Peco, I., Jiménez-Gómez, B., Romero Magdalena, C. S., Deudero, J. J., García-Puente, M., Benítez De Gracia, E., & Ruiz Núñez, C. (2021). Antivaccine Movement and COVID-19 Negationism: A Content Analysis of Spanish-Written Messages on Twitter. Vaccines, 9(6), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060656







