Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation on Peptide Dynamics and Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- KC: H2N-CGYRQSDIDTHNRIKDEL-OH
- KCL: H2N-CGY[KLiss]RQSDIDTHNRIKDEL-OH
- MB: H2N-CGYQNASSLNIA-OH
- MBL: H2N-CGY[KLiss]QNASSLNIA-OH
- NC: H2N-CGYHGEGHGEGHGEGK-OH
- NCL: H2N-CGY[KLiss]HGEGHGEGHGEGK-OH
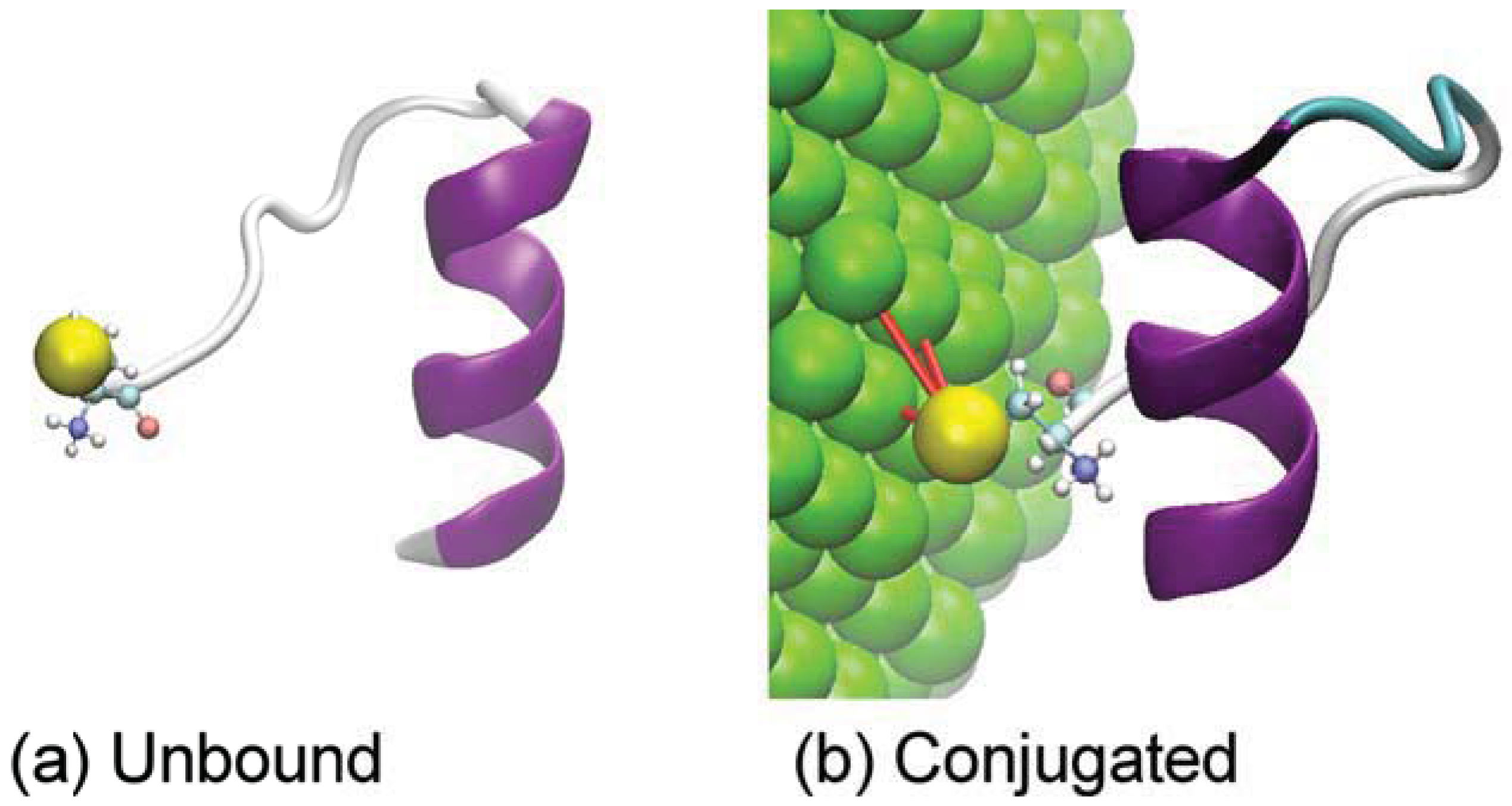
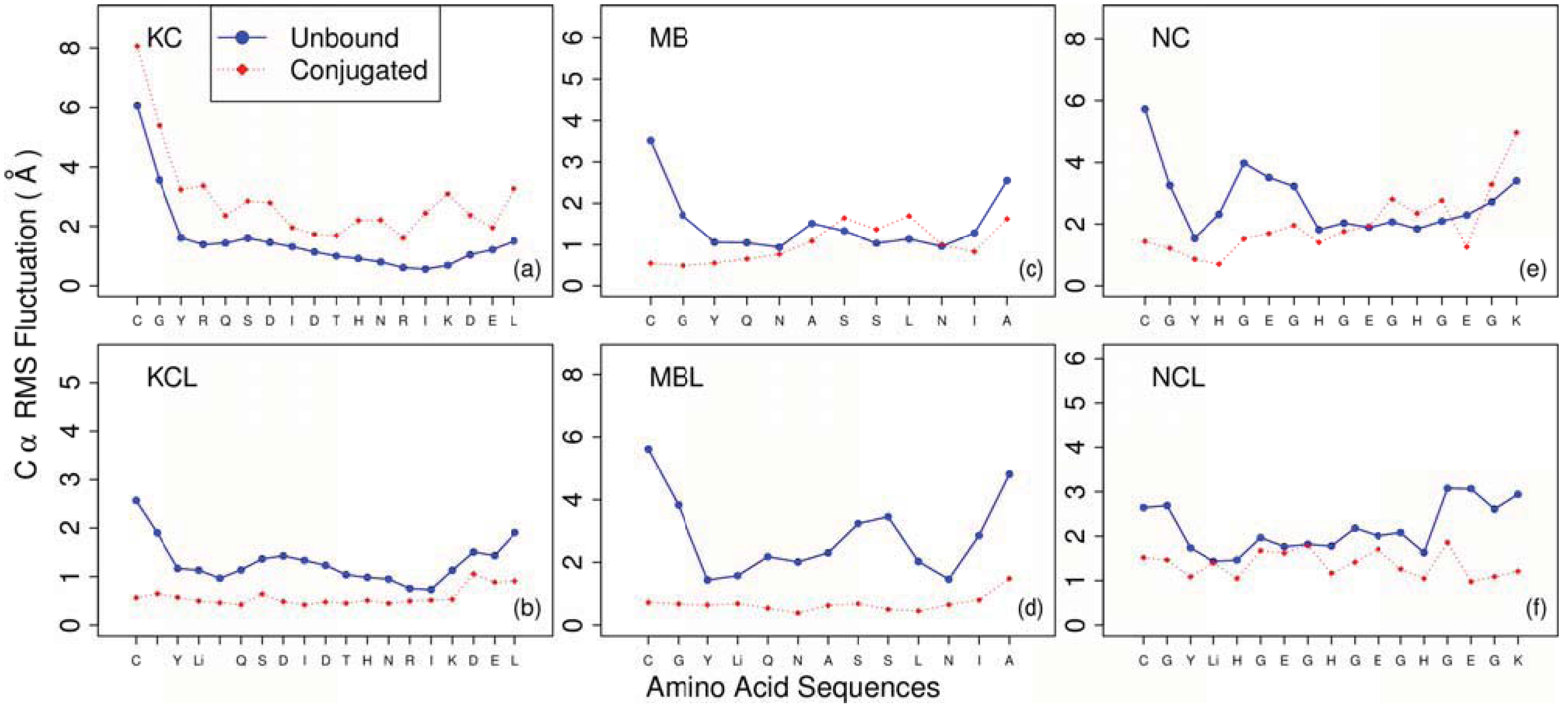
3. Results and Discussion
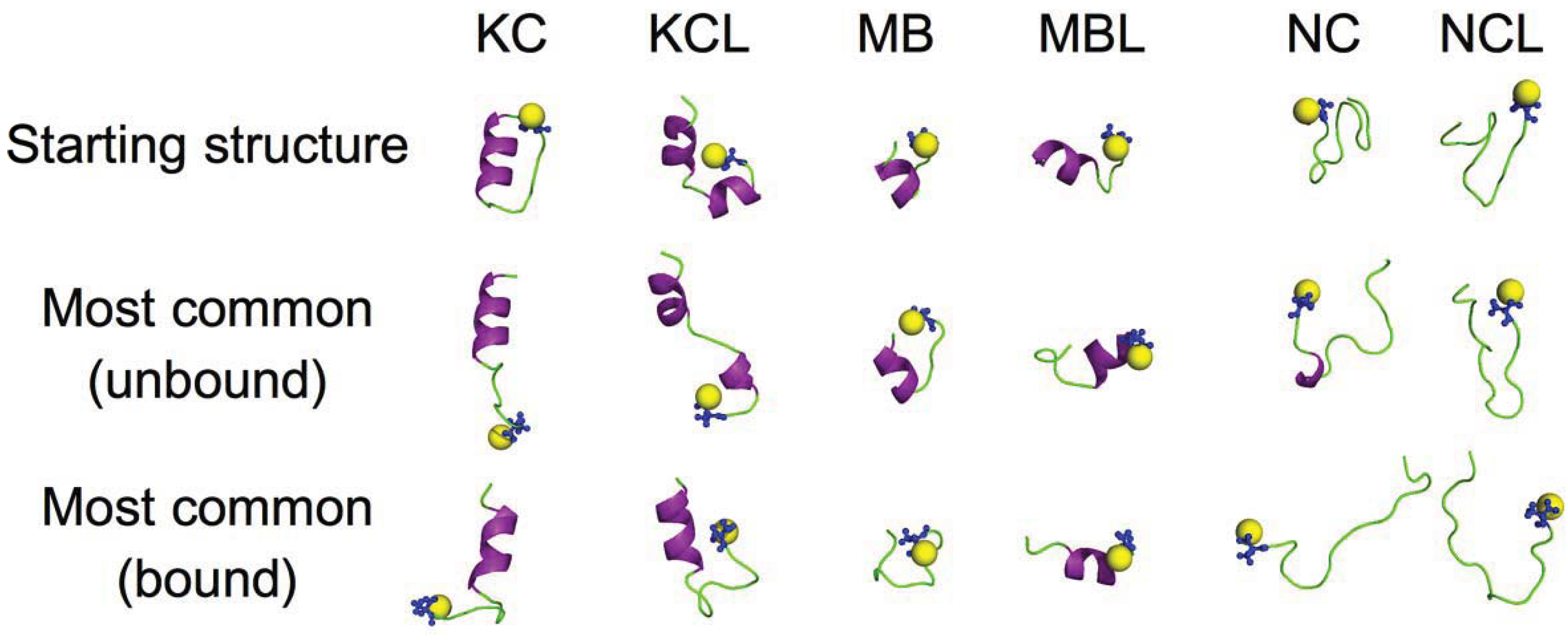
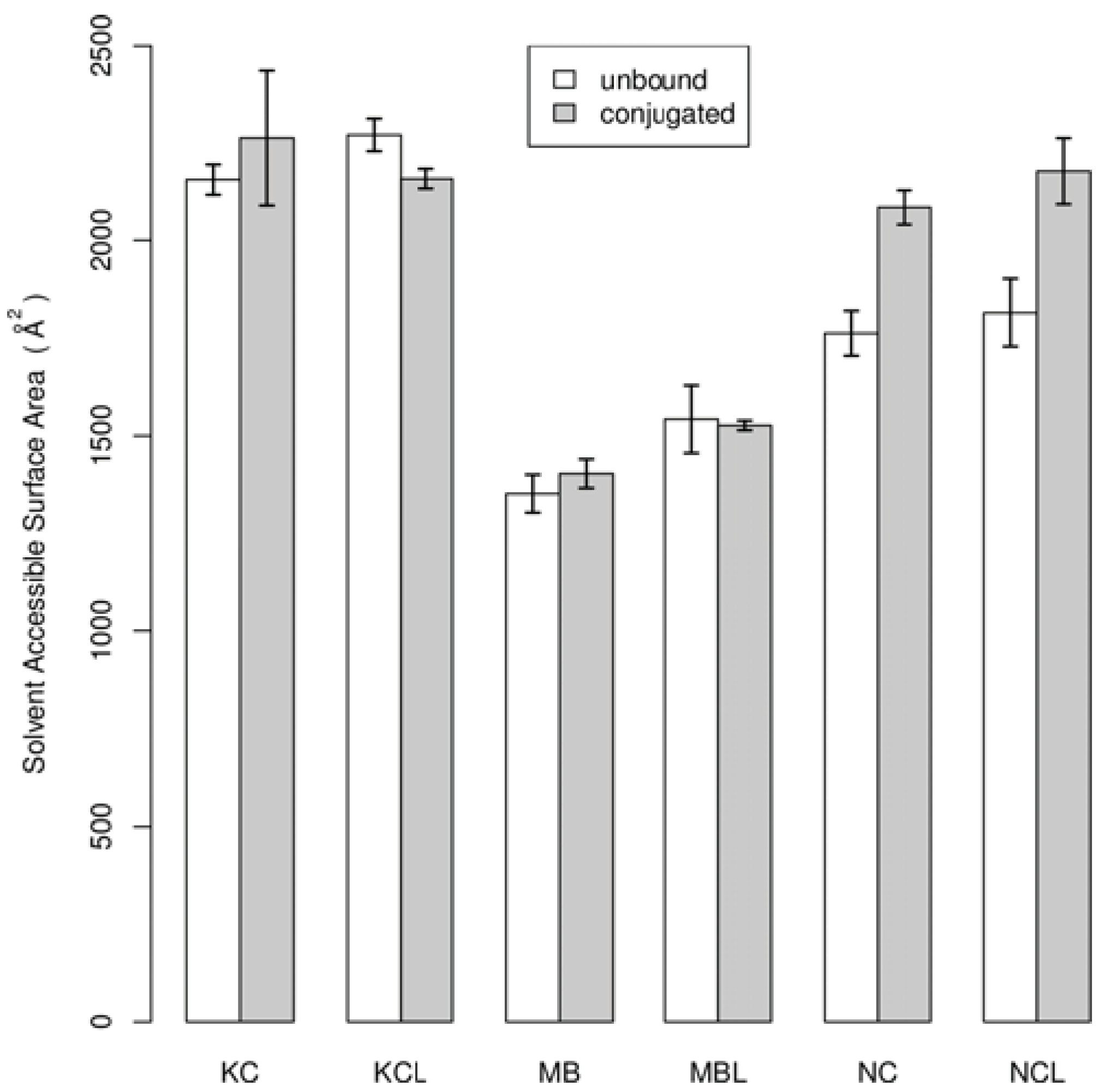
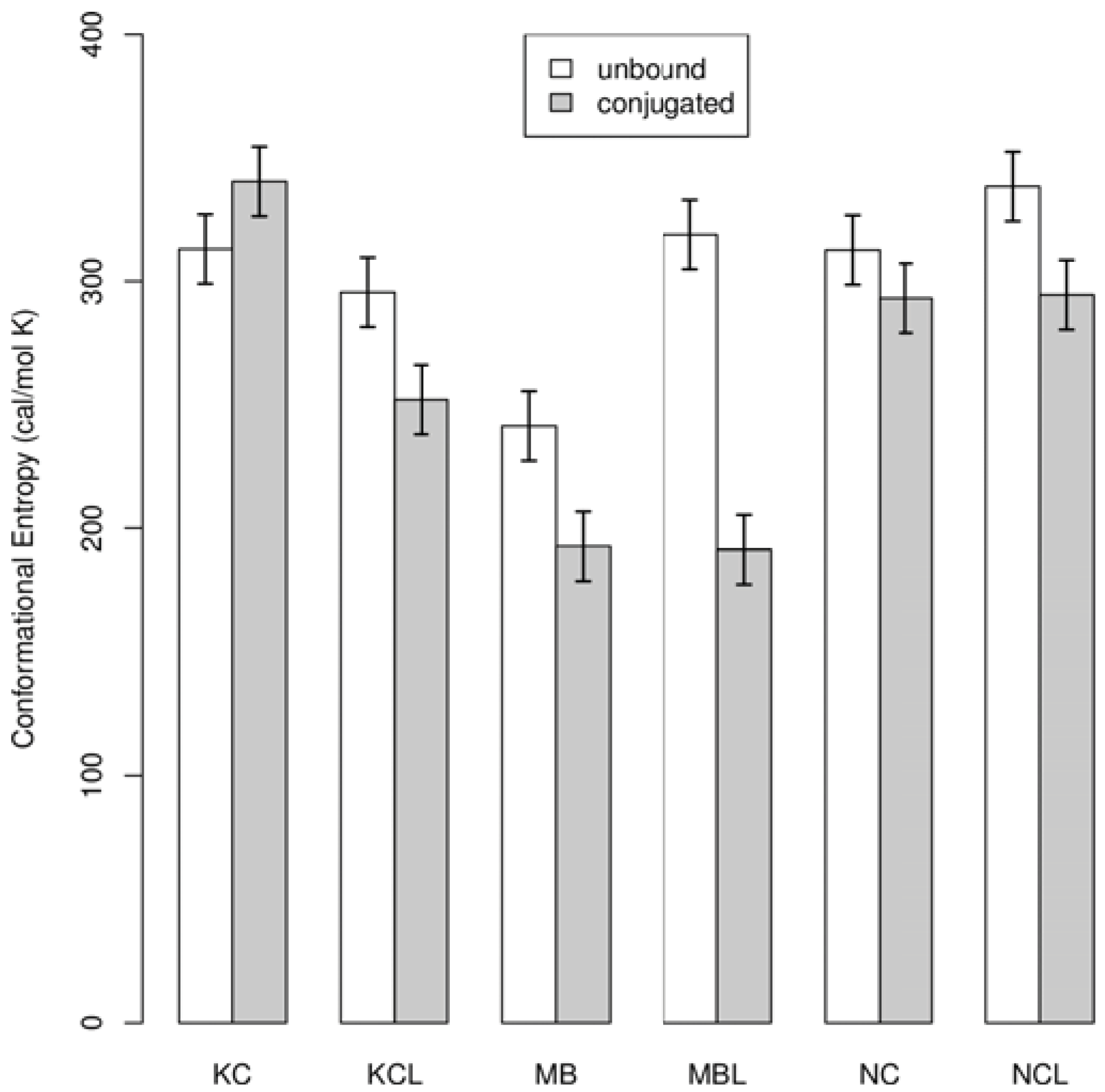

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Medintz, I.L.; Konnert, J.H.; Clapp, A.R.; Stanish, I.; Twigg, M.E.; Mattoussi, H.; Mauro, J.M.; Deschamps, J.R. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived structure of a quantum dot-protein bioconjugate nanoassembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 9612–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Howarth, M.; Greytak, A.B.; Zheng, Y.; Nocera, D.G.; Ting, A.Y.; Bawendi, M.G. Compact biocompatible quantum dots functionalized for cellular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchez, M.J.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yang, L.; Petros, J.A.; Marshall, F.F.; Simons, J.W.; Nie, S. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuberger, T.; Schöpf, B.; Hofmann, H.; Hofmann, M.; von Rechenberg, B. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Possibilities and limitations of a new drug delivery system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.-C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, E.; Mwamuka, J.; Gole, A.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small 2005, 1, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Male, K.B.; Lachance, B.; Hrapovic, S.; Sunahara, G.; Luong, J.H. Assessment of cytotoxicity of quantum dots and gold nanoparticles using cell-based impedance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5487–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Cheng, J.; Teply, B.A.; Sherifi, I.; Jon, S.; Kantoff, P.W.; Richie, J.P.; Langer, R. Targeted nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer chemotherapy in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 6315–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Jon, S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Tran, T.-N.T.; LaVan, D.A.; Langer, R. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates: A new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7668–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.D.; Nativo, P.; Smith, J.-A.; Stirling, D.; Edwards, P.R.; Venugopal, B.; Flint, D.J.; Plumb, J.A.; Graham, D.; Wheate, N.J. Gold nanoparticles for the improved anticancer drug delivery of the active component of oxaliplatin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4678–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Samia, A.C.; Meyers, J.D.; Panagopoulos, I.; Fei, B.; Burda, C. Highly efficient drug delivery with gold nanoparticle vectors for in vivo photodynamic therapy of cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10643–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Klibanov, A.M. Conjugation to gold nanoparticles enhances polyethylenimine's transfer of plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 9138–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, H.M.; Bhumkar, D.R.; Joshi, K.; Pokharkar, V.; Sastry, M. Gold nanoparticles as carriers for efficient transmucosal insulin delivery. Langmuir 2006, 22, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin-Tam, M.-E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Gold nanoparticle-cytochrome c complexes: The effect of nanoparticle ligand charge on protein structure. Langmuir 2005, 21, 12080–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin-Tam, M.-E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Structure and function of nanoparticle-protein conjugates. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Nakade, H.; Simard, J.M.; Rotello, V.M. Recognition and stabilization of peptide α-helices using templatable nanoparticle receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10806–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Rotello, V.M. Surface recognition of biomacromolecules using nanoparticle receptors. Chem. Commun. 2005, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slocik, J.M.; Naik, R.R. Probing peptide-nanomaterial interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3454–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, C.R.; Kulp, J.L., III; Oren, E.E.; Zareie, H.; Tamerler, C.; Evans, J.S.; Sarikaya, M. Molecular recognition and supramolecular self-assembly of a genetically engineered gold binding peptide on Au {111}. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, R.; Sarikaya, M.; Schulten, K. Genetically engineered gold-binding polypeptides: Structure prediction and molecular dynamics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefling, M.; Iori, F.; Corni, S.; Gottschalk, K.-E. Interaction of amino acids with the Au (111) surface: Adsorption free energies from Molecular dynamics simulations. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8347–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila Verde, A.; Acres, J.M.; Maranas, J.K. Investigating the specificity of peptide adsorption on gold using molecular dynamics simulations. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, O.-S.; Schatz, G.C. Interaction between DNAs on a gold surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 15941–15947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.-S.; Schatz, G.C. Molecular dynamics simulation of DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 2316–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largo, J.; Starr, F.W.; Sciortino, F. Self-assembling DNA dendrimers: A numerical study. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5896–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Papasani, M.R.; Hrdlicka, P.J.; Hill, R.A. Role of serum proteins in the cellular uptake of gold-peptide nanoconjugates. NSTI-Nanotech 2010, 3, 304–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R.; Department of Animal and Veterinary Science, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID 83844, USA. Personal Communication, 2010.
- Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tuffery, P. PEP-FOLD: An online resource for de novo peptide structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W498–W503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Lu, W.; Luo, Y. Length dependence of coherent electron transportation in metal-alkanedithiol-metal and metal-alkanemonothiol-metal junctions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 400, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.; Karplus, M. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Seminario, J.M. Molecular dynamics simulations of the vibrational signature transfer from a glycine peptide chain to nanosized gold clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 8366–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iori, F.; Di Felice, R.; Molinari, E.; Corni, S. GolP: An atomistic force-field to describe the interaction of proteins with Au(111) surfaces in water. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, H.; Vaia, R.; Farmer, B.L.; Naik, R.R. Accurate simulation of surfaces and interfaces of face-centered cubic metals using 12−6 and 9−6 lennard-jones potentials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 17281–17290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gunsteren, W.F.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Rullmann, J.A.C. Stochastic dynamics for molecules with constraints Brownian dynamics of normal-alkanes. Mol. Phys. 1981, 44, 69–95. [Google Scholar]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: The Langevin piston method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N.log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graphics 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andricioaei, I.; Karplus, M. On the calculation of entropy from covariance matrices of the atomic fluctuations. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 6289–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitter, J. Estimation of absolute and relative entropies of macromolecules using the covariance matrix. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 215, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, H.; Mark, A.E.; van Gunsteren, W.F. Absolute entropies from molecular dynamics simulation trajectories. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 7809–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.S., Jr.; Steitz, T.A. Glucose-induced conformational change in yeast hexokinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1978, 75, 4848–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.H.; Ytreberg, F.M. Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation on Peptide Dynamics and Structure. Entropy 2012, 14, 630-641. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040630
Lee KH, Ytreberg FM. Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation on Peptide Dynamics and Structure. Entropy. 2012; 14(4):630-641. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040630
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kuo Hao, and F. Marty Ytreberg. 2012. "Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation on Peptide Dynamics and Structure" Entropy 14, no. 4: 630-641. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040630
APA StyleLee, K. H., & Ytreberg, F. M. (2012). Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation on Peptide Dynamics and Structure. Entropy, 14(4), 630-641. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040630



