The Use of Denoising and Analysis of the Acoustic Signal Entropy in Diagnosing Engine Valve Clearance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
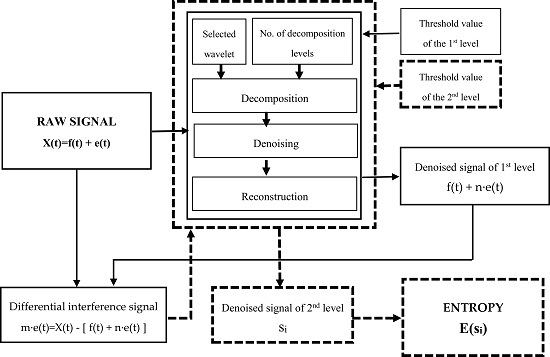
2. Signal Processing Method
- decomposition of the signal;
- assumption of the threshold coefficient and of the number of decomposition levels;
- cutting off the noise at each decomposition level;
- signal reconstruction.
3. Test Stand
- Engine I—capacity of 1.2 L, a mileage of 130,000 kilometres, eight-valve heads.
- Engine II—capacity of 1.6 L, a mileage of 160,000 kilometres, eight-valve heads, and an older generation engine.
- norsonic signal analysers along with a condenser microphone (Norsonic AS, Tranby, Norway) used to measure the acoustic pressure over the engine valve cover with distance 0.5 m (Figure 3);
- an optic sensor used to record the reference signal of the crankshaft positioning;
- a DSPT SigLab signal analyser (DSP Technologies Inc., Santa Barbara, CA, USA);
- a computer used for signal recording.
4. Results and Discussion
- the length of the analysed signal corresponded to a 720° crankshaft rotation of the tested combustion engines, recorded at the rotational speed of idling;
- Daubechies 2 wavelet;
- number of decomposition levels = 6;
- threshold value of the 1st level of denoising = 0.5 (engine I) or 1.1 (engine II);
- threshold value of the 2nd level of denoising = 0.17 (engine I) or 0.6 (engine II);
- soft thresholding;
- window length during calculation of entropy = 20 samples.
- the length of the analysed signal should correspond to a complete working cycle of a four-stroke engine, i.e., 720° of crankshaft rotation;
- the selected wavelet should approximate well the analysed signals;
- the decomposition levels and the threshold type and values should allow for maximum (in terms of quality) clearing of the signal of interference, without causing any substantial reduction in the contents in the information included in the signal; on the other hand, the dynamics of sensitivity of quantitative and qualitative changes in entropy to the detected valve clearance should be high.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dąbrowski, Z.; Zawisza, M. The choice of vibroacoustic signal measures, in mechanical fault diagnosis of diesel engines. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 236, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, A.; Komorska, I. Online fault diagnosis of automotive powernets by kalman filtering. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 588, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, A. A technique for the vibration signal analysis in vehicle diagnostics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 56, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczurowski, K.; Radkowski, S.; Walczak, D.; Trojgo, M.; Zieliński, Ł. Applying methods of acquisition of information from vehicle electronic components to improve work parameters of dual fuel engine. Diagnostyka 2015, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Czech, P.; Wojnar, G.; Folęga, P. Wibroakustyczna diagnostyka niesprawności układu zapłonowego samochodu z wykorzystaniem estymat amplitudowych. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2014, 83, 59–64. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Li, Z.-N.; Zhang, G. Study of fault diagnosis of diesel engine fuel injection based on adaptive parallel factor. Acta Armamentarii 2013, 34, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny, L.; Adamczyk, B.; Adamczyk, G. Diagnostyka i regeneracja wtryskiwaczy CR. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2015, 86, 65–73. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sebok, M.; Ostrica, L.; Gutten, M.; Korenciak, D.; Makyda, M. Diagnostics of ignition systems. J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 13, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Albarbar, A.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. Diesel engine fuel injection monitoring using acoustic measurements and independent component analysis. Measurement 2010, 43, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, P.; Ba̧kowski, H. Diagnosing of car engine fuel injectors damage using dwt analysis and PNN neural networks. Trans. Probl. 2013, 8, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J.; Feng, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, F. Vibration and noise source identification methods for a diesel engine. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figlus, T. The application of a continuous wavelet transform for diagnosing damage to the timing chain tensioner in a motorcycle engine. J. Vibroeng. 2015, 17, 1266–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Jedlinski, L.; Caban, J.; Krzywonos, L.; Wierzbicki, S.; Brumercik, F. Application of vibration signal in the diagnosis of IC engine valve clearance. J. Vibroeng. 2015, 17, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zawisza, M. Energy loss and the choice of damper of torsional vibration combustion engines. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 236, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figlus, T.; Wilk, A. Application of a continuous wavelet transform for the diagnosing of excessive valve clearance of the combustion engine. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 236, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figlus, T.; Liščák, Š.; Wilk, A.; Łazarz, B. Condition monitoring of engine timing system by using wavelet packet decomposition of a acoustic signal. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnicka, D. Vibroacoustic symptom of the exhaust valve damage of the internal combustion engine. J. Vibroeng. 2014, 16, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Szymański, G.M.; Tomaszewski, F. Diagnostics of automatic compensators of valve clearance in combustion engine with the use of vibration signal. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 68–69, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabis, P.; Flekiewicz, M.; Madej, H.; Wojnar, G. Influence of piston slap on engine block vibration; SAE Technical Paper 2007-01-2163; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Chen, J. Investigation into piston-slap-induced vibration for engine condition simulation and monitoring. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 282, 735–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postrzednik, S.; Przybyla, G.; Zmudka, Z. Main conditions and effectiveness of gas fuel use for powering of dual fuel IC self-ignition engine. Trans. Probl. 2015, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Flekiewicz, M.; Szymonik, M. Sterowanie paliwa gazowego w układzie “master-slave”. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2015, 86, 13–20. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Szczurowski, K.; Radkowski, S.; Walczak, D.; Zieliński, L. The effect of addition of LPG and Camelina oil esters on noise and vibration in a dual fuel CI engine. Diagnostyka 2014, 15, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Uludamar, E.; Tosun, E.; Aydin, K. Experimental and regression analysis of noise and vibration of a compression ignition engine fuelled with various biodiesels. Fuel 2016, 177, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, V.; Kumar, P.R.; Rashmi, A.A.; Jain, S.; Agarwal, A.K. Experimental investigations of combustion, performance and emission characteristics of a hydrogen enriched natural gas fuelled prototype spark ignition engine. Fuel 2016, 178, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Masato, M. Effect of hydrogen addition to intake air on combustion noise from a diesel engine. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4153–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Gong, Y. Shocking fault component of abnormal sound signal in the fault engine extract method based on linear superposition method and cross-correlation analysis. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, T. Source identification of gasoline engine noise based on continuous wavelet transform and EEMD-RobustICA. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 100, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Bi, F.; Guo, Q.; Chen, K.; Ma, L. Diesel engine noise source identification based on EEMD, coherent power spectrum analysis and improved AHP. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 095010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.X.; Guo, G.X.; Ren, H.F. Engine fault diagnosis based on EEMD difference energy spectrum. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 598, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayong, N.; Changle, S.; Yongjun, G.; Zengmeng, Z.; Jiaoyi, H. Extraction of fault component from abnormal sound in diesel engines using acoustic signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 75, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarbar, A. An investigation into diesel engine air-borne acoustics using continuous wavelet transform. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.T.; Pan, H.X. The engine fault diagnosis based on time domain and frequency domain. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 936, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, J.; Ducleaux, N.; Nghiem, G.; Wang, S. Separation of combustion noise in IC engines under cyclo-non-stationary regime. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 38, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, J.; Zhou, R.; Liang, C. Determination of knock characteristics in spark ignition engines: An approach based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 045109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Mao, J.G.; Wang, H.Q.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.F.; Wei, T.T. Knock detection and evaluation of kerosene piston engine. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 568–570, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li., W.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D.; Leung, A.Y.; Phipps, C.E. A study of the noise from diesel engines using the independent component analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2001, 15, 1165–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-M.; Li, H.-Y.; Qiao, X.-Y.; Li, X.-L.; Shi, Y.-P. Engine cylinder pressure identification method based on cylinder head vibration signals. Chin. Int. Combust. Engine Eng. 2013, 34, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, S. A review of diesel engine acoustics. FME Trans. 2014, 42, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.Q.; Ge, H.J. Study on the combustion noise characteristic of low speed diesel engine. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 945–949, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuszkiewicz, P.; Pankiewicz, J.; Dziurdź, J.; Zawisza, M. Modeling of powertrain system dynamic behavior with torsional vibration damper. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1036, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.T.; Pan, H.X. Engine fault diagnosis based on improved BP neural network with conjugate gradient. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 536–537, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Ma, Q.H.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.T.; Zhao, L.H. An intelligent approach for engine fault diagnosis based on Hilbert–Huang transform and support vector machine. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Naber, J.; Blough, J.; Zekavat, S.A. Accelerometer-based combustion metrics reconstruction with radial basis function neural network for a 9 L diesel engine. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2014, 136, 031507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Ideal de-noising in an orthonormal basis chosen from a library of bases. Comptes Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences 1994, 319, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L. De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1995, 41, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedlinski, L. Multi-channel registered data denoising using wavelet transform. Maint. Reliab. 2012, 14, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L. Progress in wavelet analysis and WVD: A ten minute tour. In Progress in Wavelet Analysis and Applications; Meyer, Y., Roques, S., Eds.; Editions Frontières: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 1994, 81, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M.; Kerkyacharian, G.; Picard, D. Wavelet shrinkage: Asymptopia. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1995, 57, 301–369. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniadis, A.; Oppenheim, G. (Eds.) Wavelets and statistics. In Lecture Notes in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 103.
- Coifman, R.R.; Wickerhauser, M.V. Entropy-based Algorithms for best basis selection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1992, 38, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Yang, J. Denoising of hydropower unit vibration signal based on variational mode decomposition and approximate entropy. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2016, 38, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-B.; Xu, M.-Q.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Huang, W.-H. A study on rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on hierarchical fuzzy entropy and ISVM-BT. J. Vib. Eng. 2016, 29, 184–192. [Google Scholar]





| Engine I | αin | 7° | αex | 41° |
| βin | 43° | βex | 5° | |
| Engine II | αin | 6° | αex | 48° |
| βin | 44° | βex | 2° |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figlus, T.; Gnap, J.; Skrúcaný, T.; Šarkan, B.; Stoklosa, J. The Use of Denoising and Analysis of the Acoustic Signal Entropy in Diagnosing Engine Valve Clearance. Entropy 2016, 18, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18070253
Figlus T, Gnap J, Skrúcaný T, Šarkan B, Stoklosa J. The Use of Denoising and Analysis of the Acoustic Signal Entropy in Diagnosing Engine Valve Clearance. Entropy. 2016; 18(7):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18070253
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiglus, Tomasz, Jozef Gnap, Tomáš Skrúcaný, Branislav Šarkan, and Jozef Stoklosa. 2016. "The Use of Denoising and Analysis of the Acoustic Signal Entropy in Diagnosing Engine Valve Clearance" Entropy 18, no. 7: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18070253
APA StyleFiglus, T., Gnap, J., Skrúcaný, T., Šarkan, B., & Stoklosa, J. (2016). The Use of Denoising and Analysis of the Acoustic Signal Entropy in Diagnosing Engine Valve Clearance. Entropy, 18(7), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18070253