Supra-molecular Association and Polymorphic Behaviour In Systems Containing Bile Acid Salts
Abstract
:Introduction
Results and Discussion
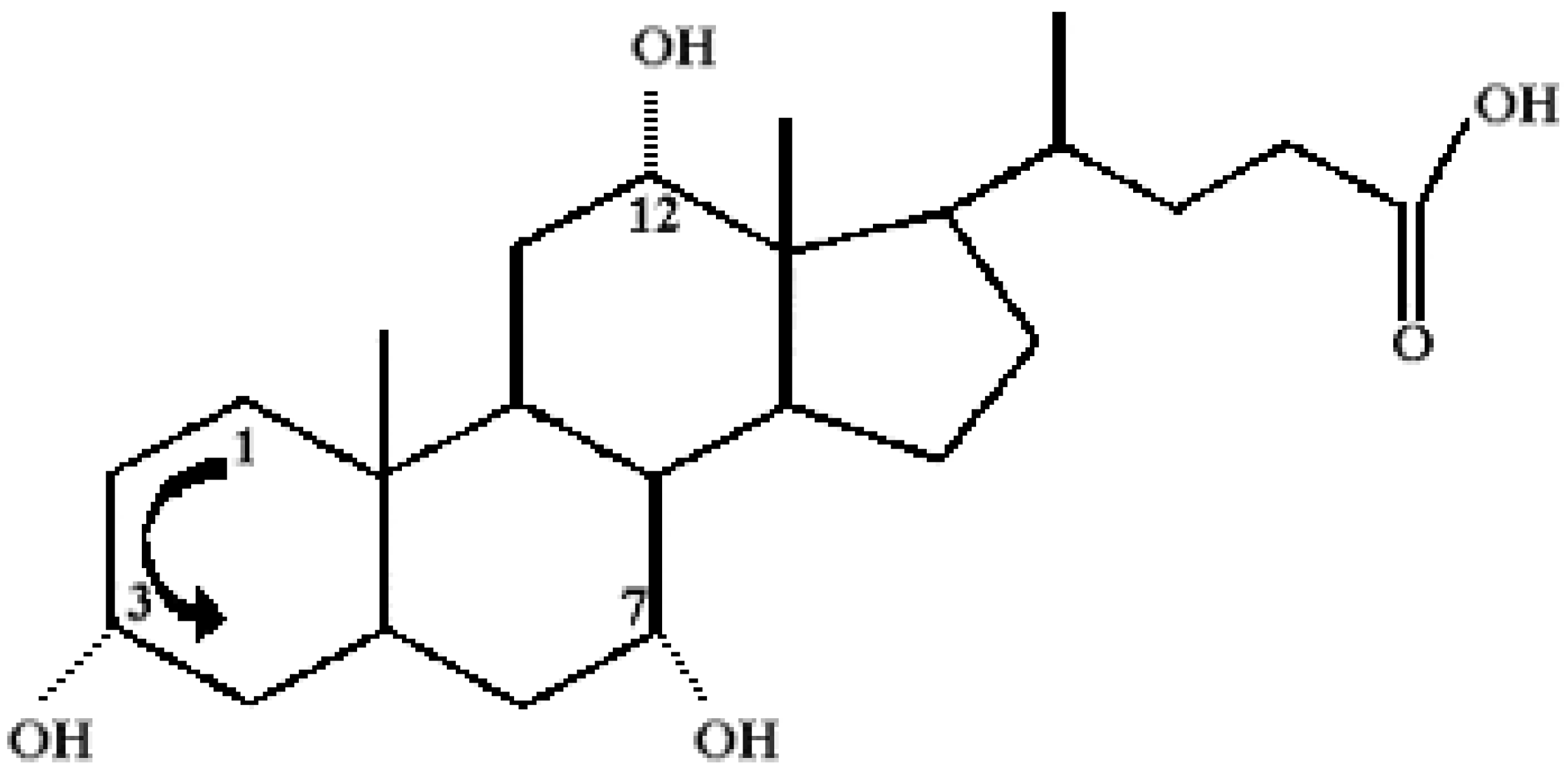
Chemical Structure of Bile Acid Salts
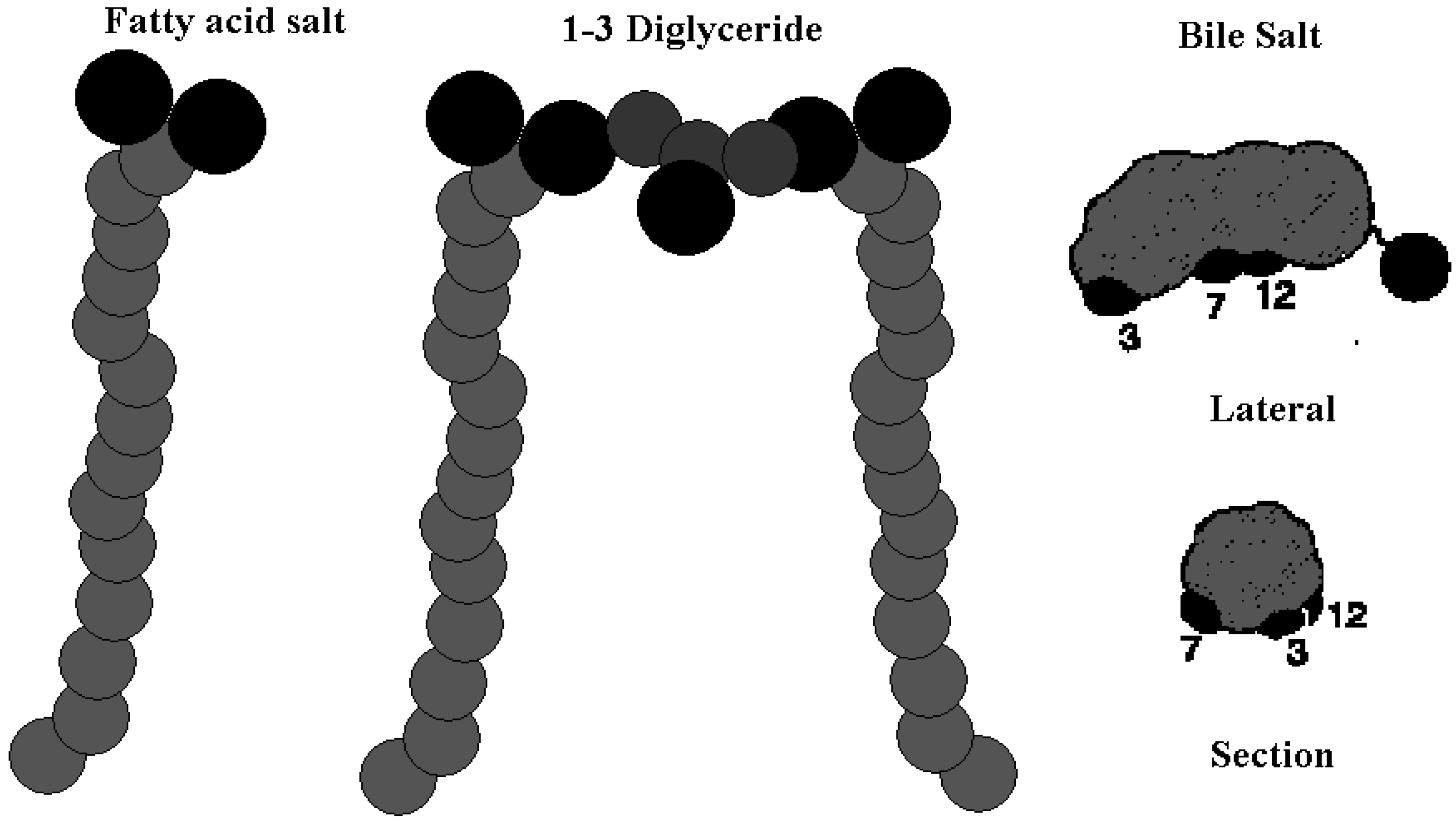
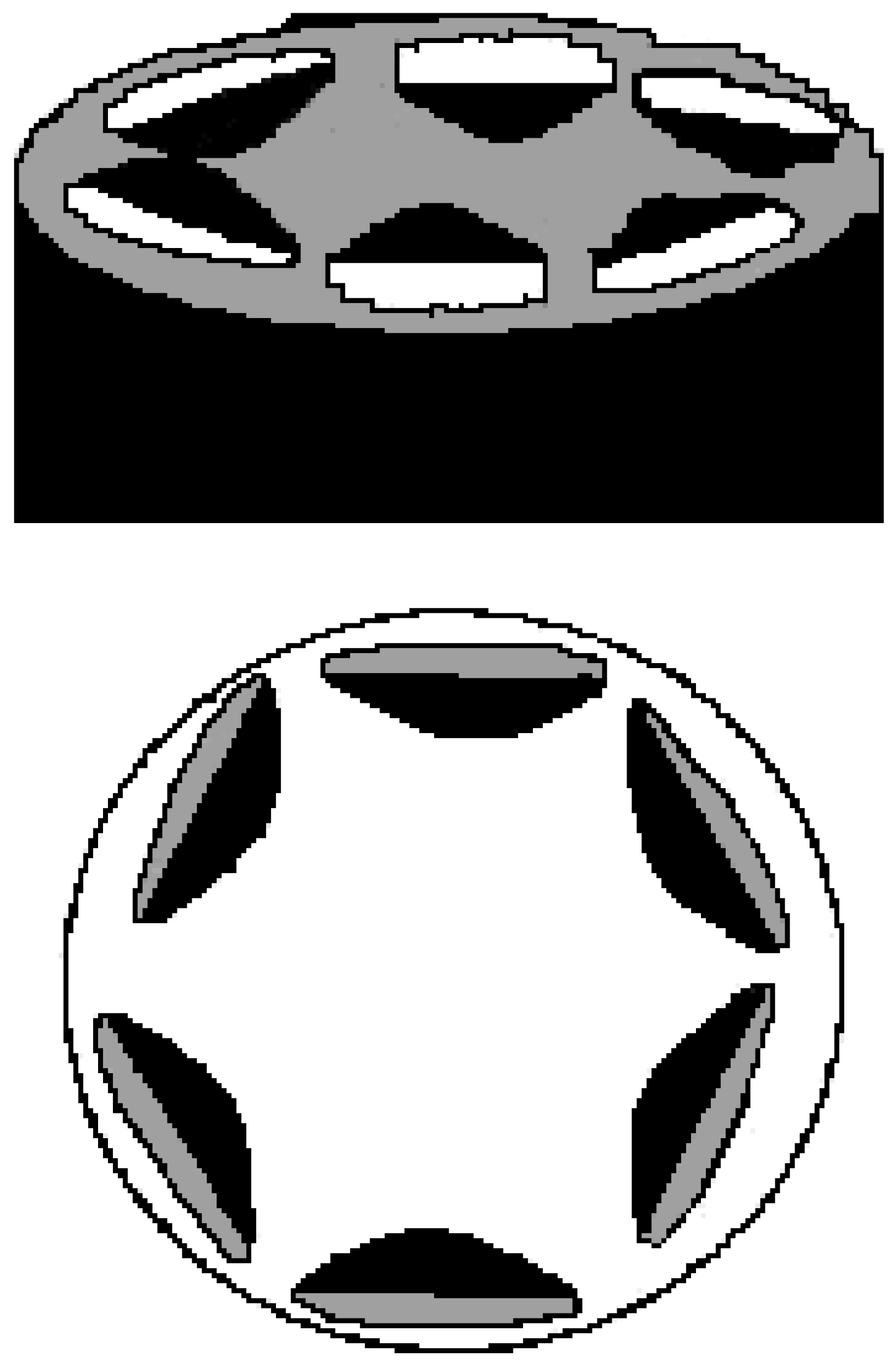
Supra-molecular association


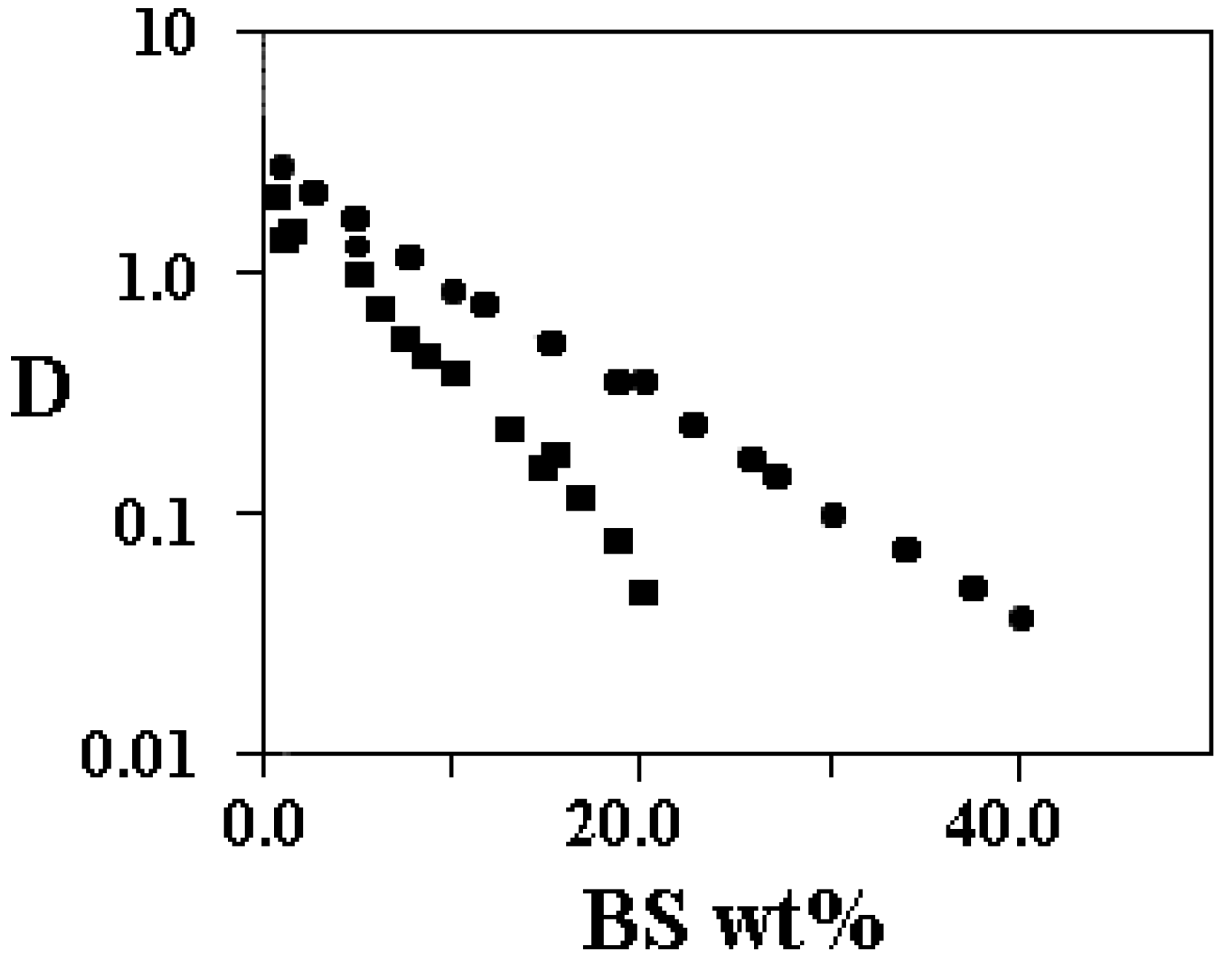
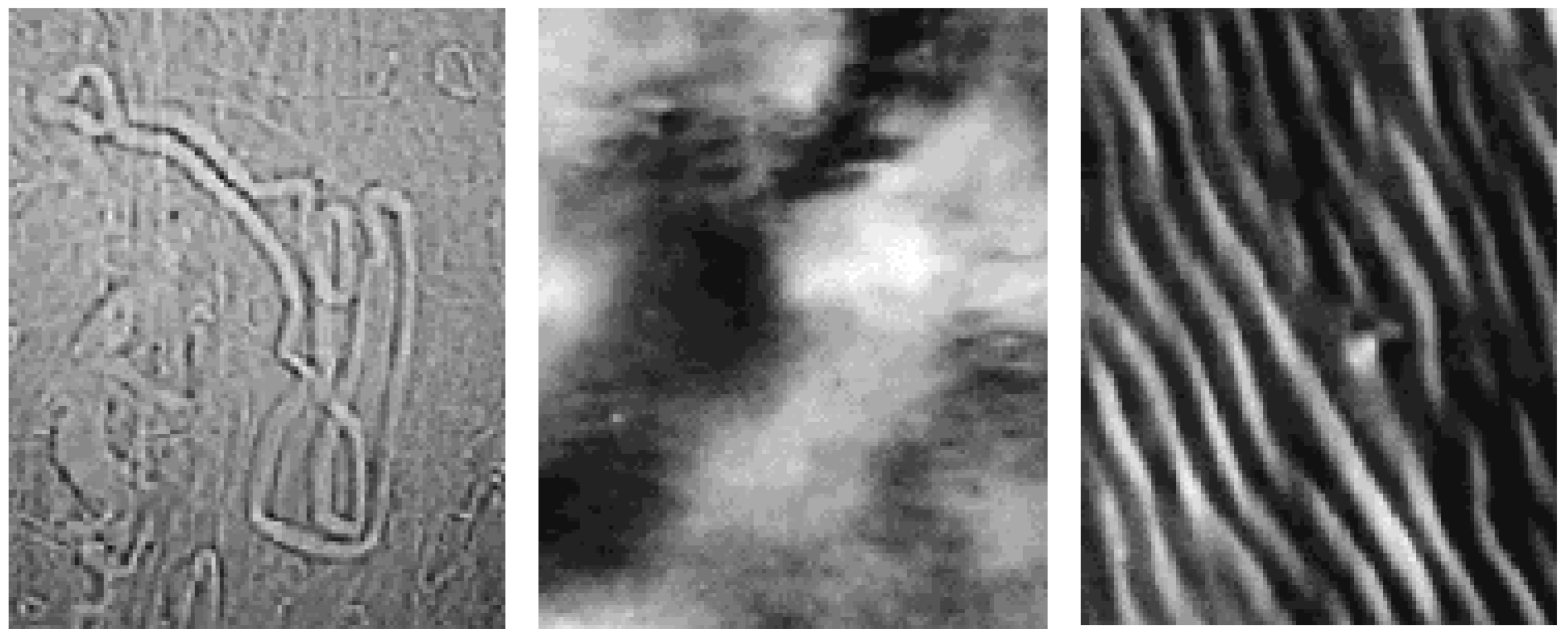
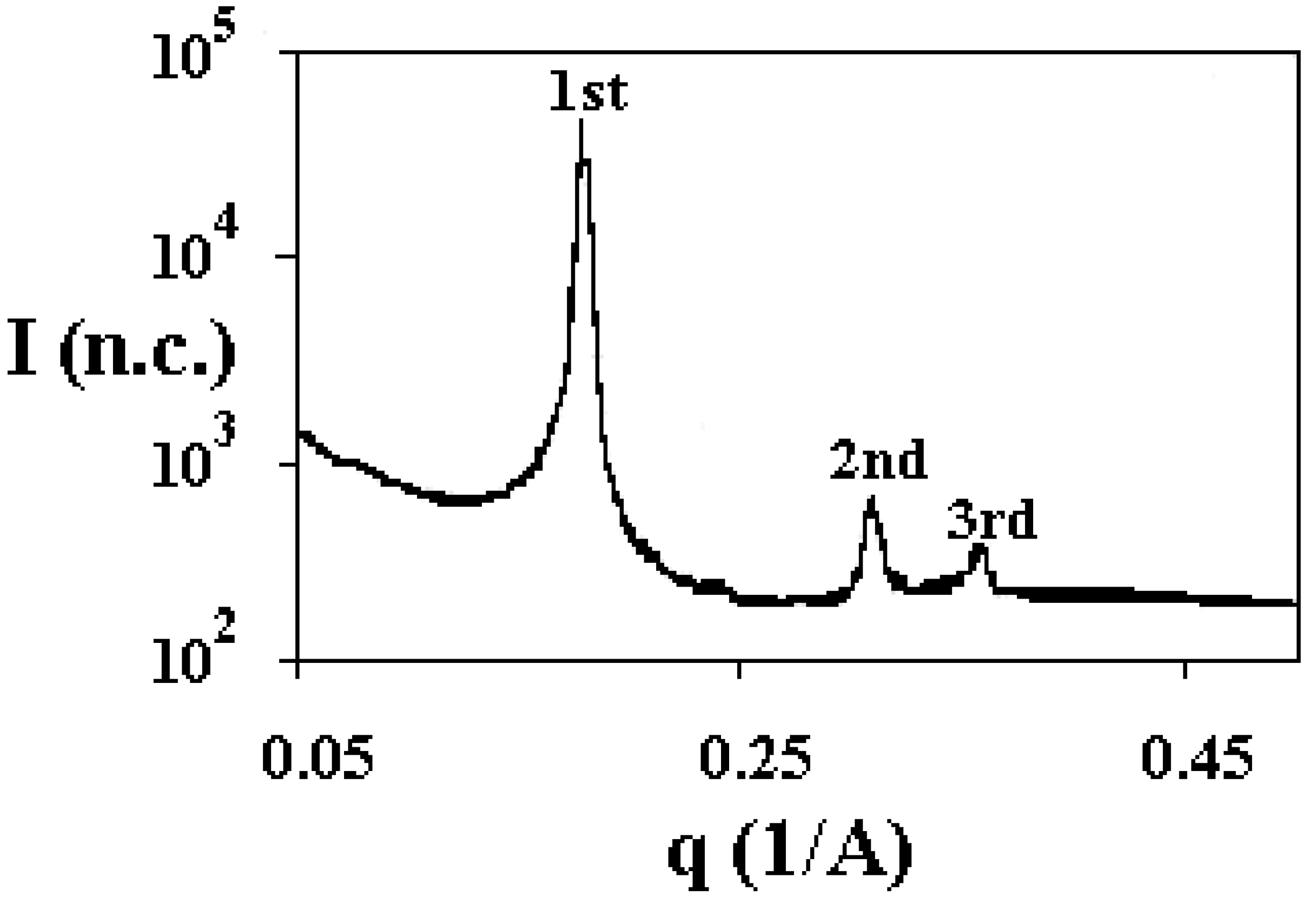
Structural organisation
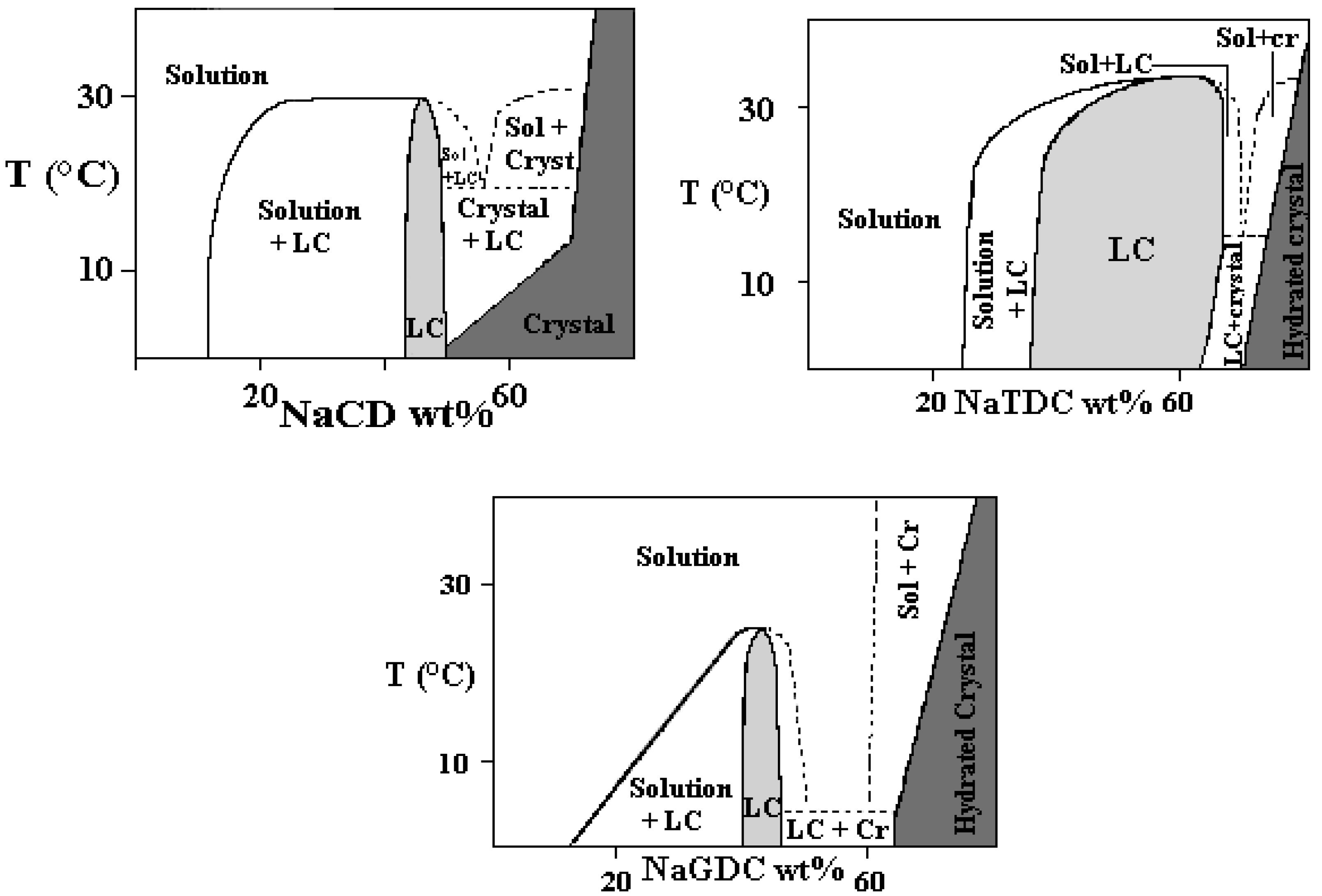
Binary Phase Diagrams

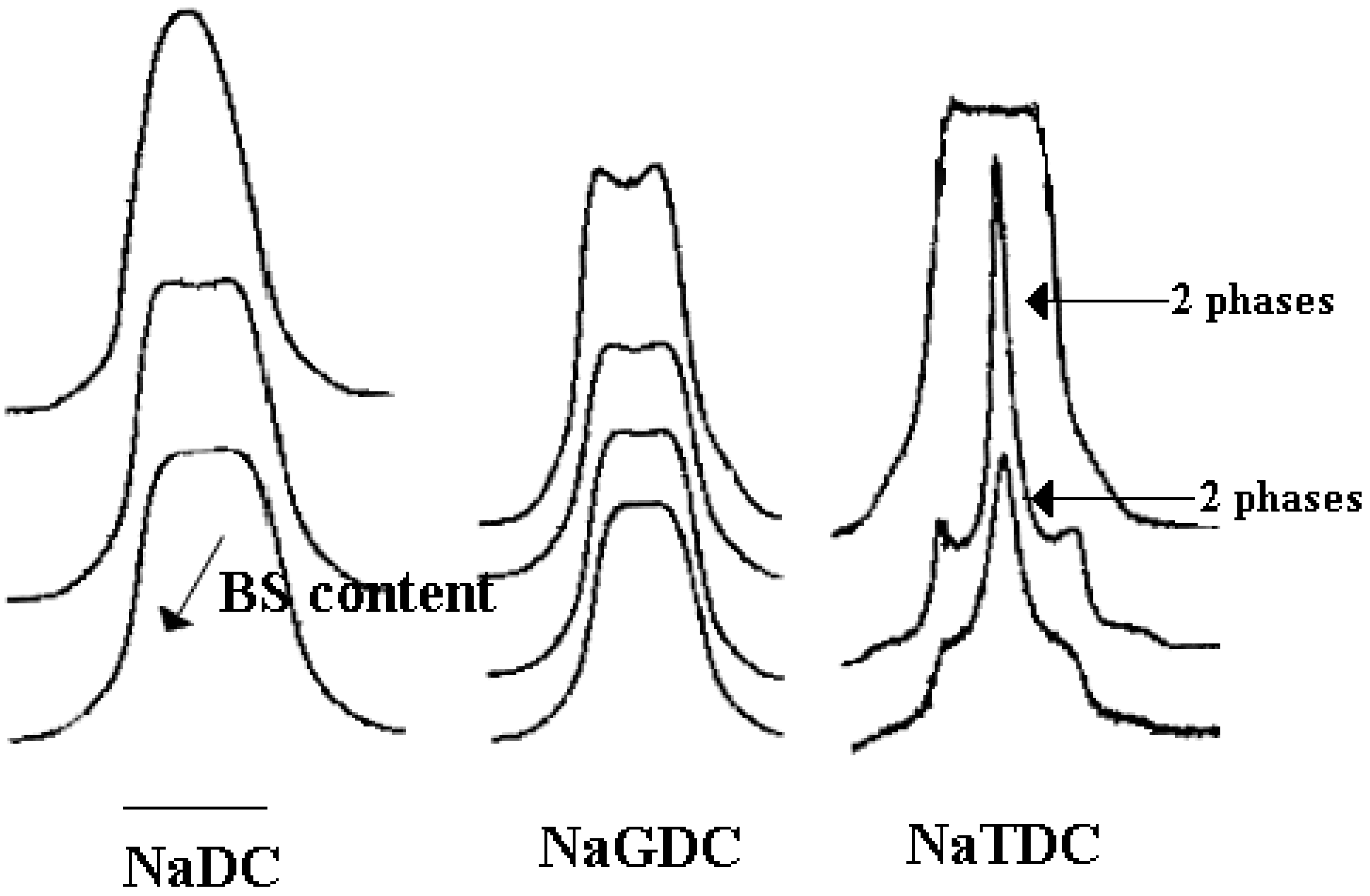
Ternary Systems
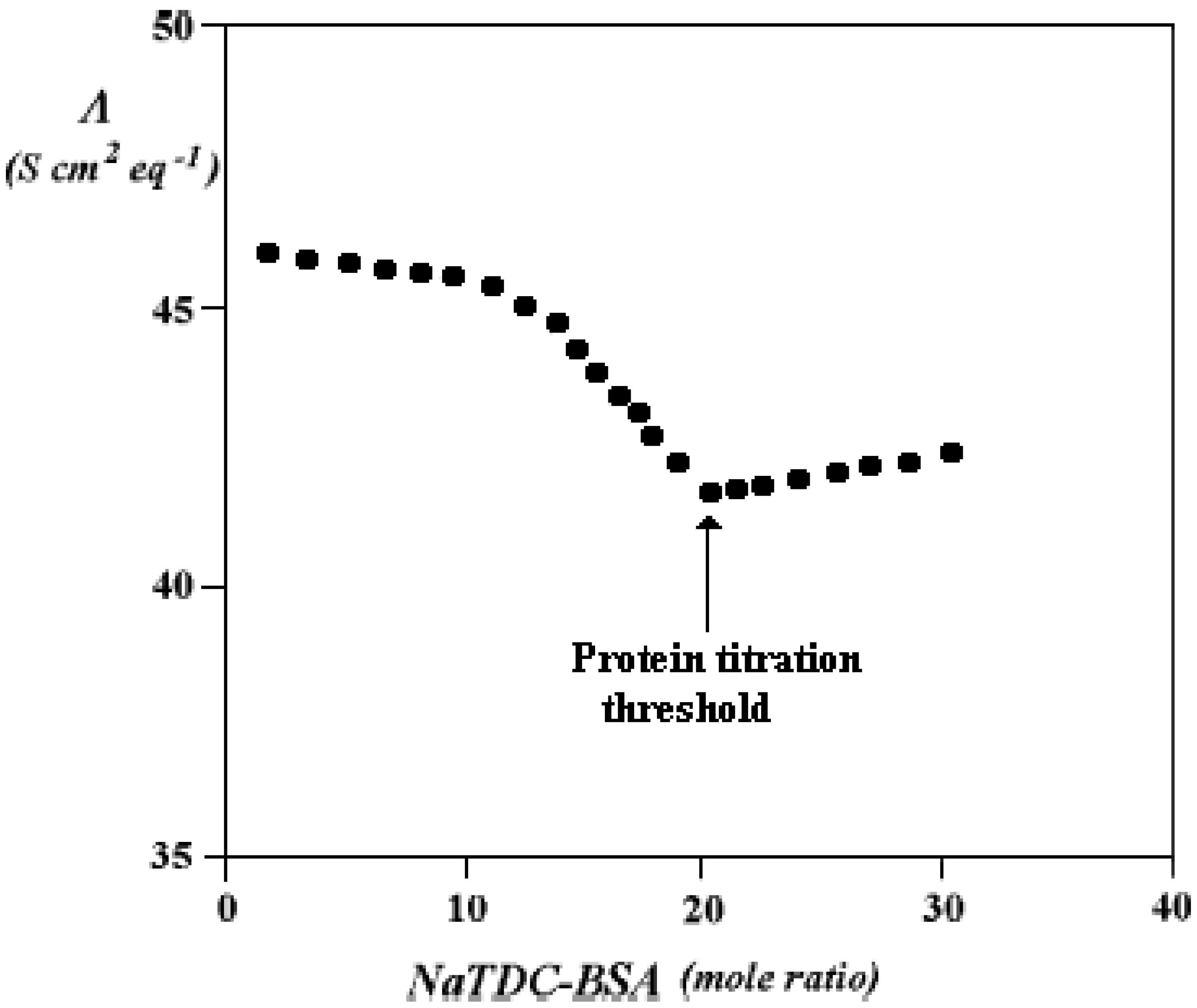
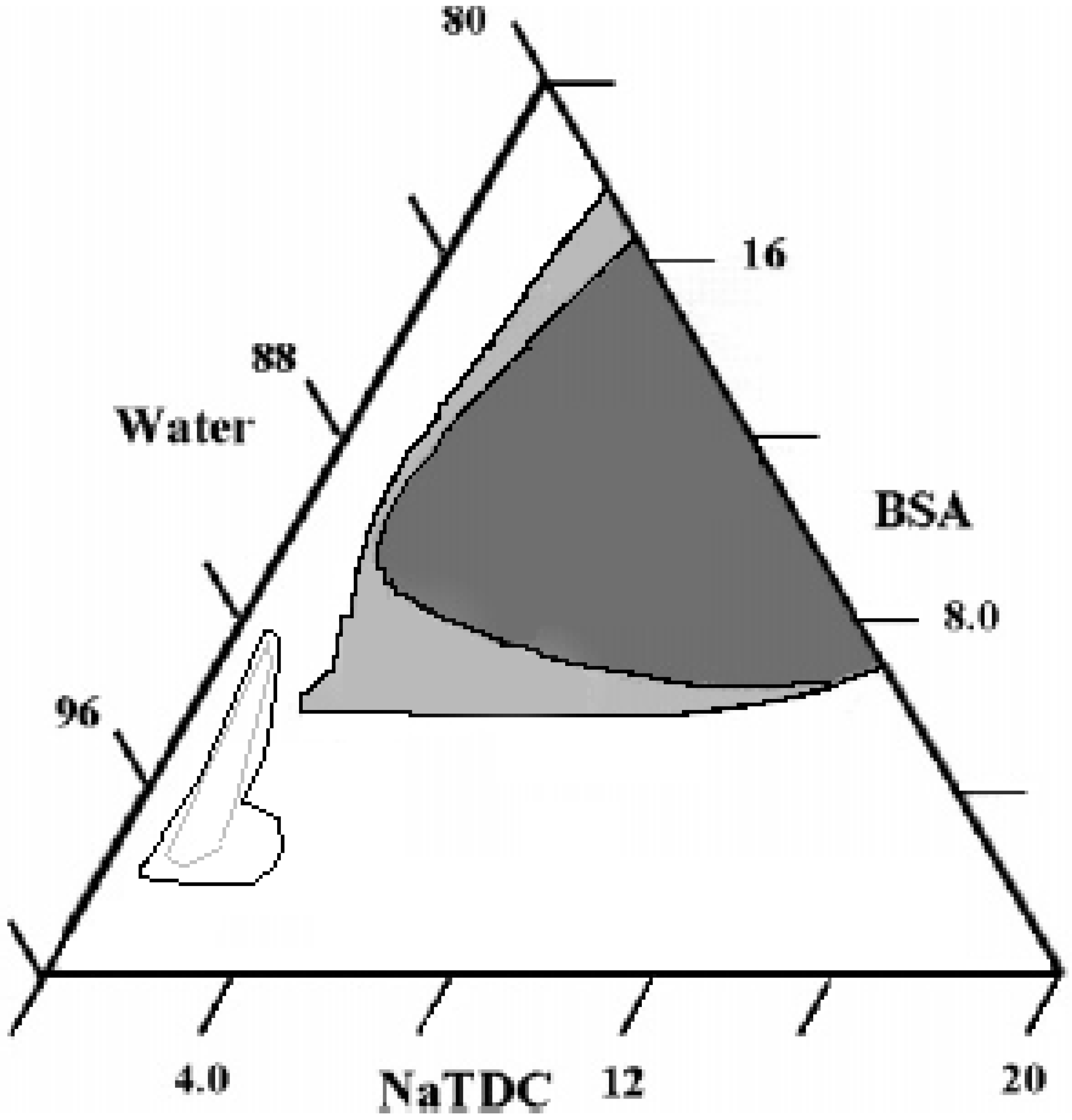
Higher Order Systems
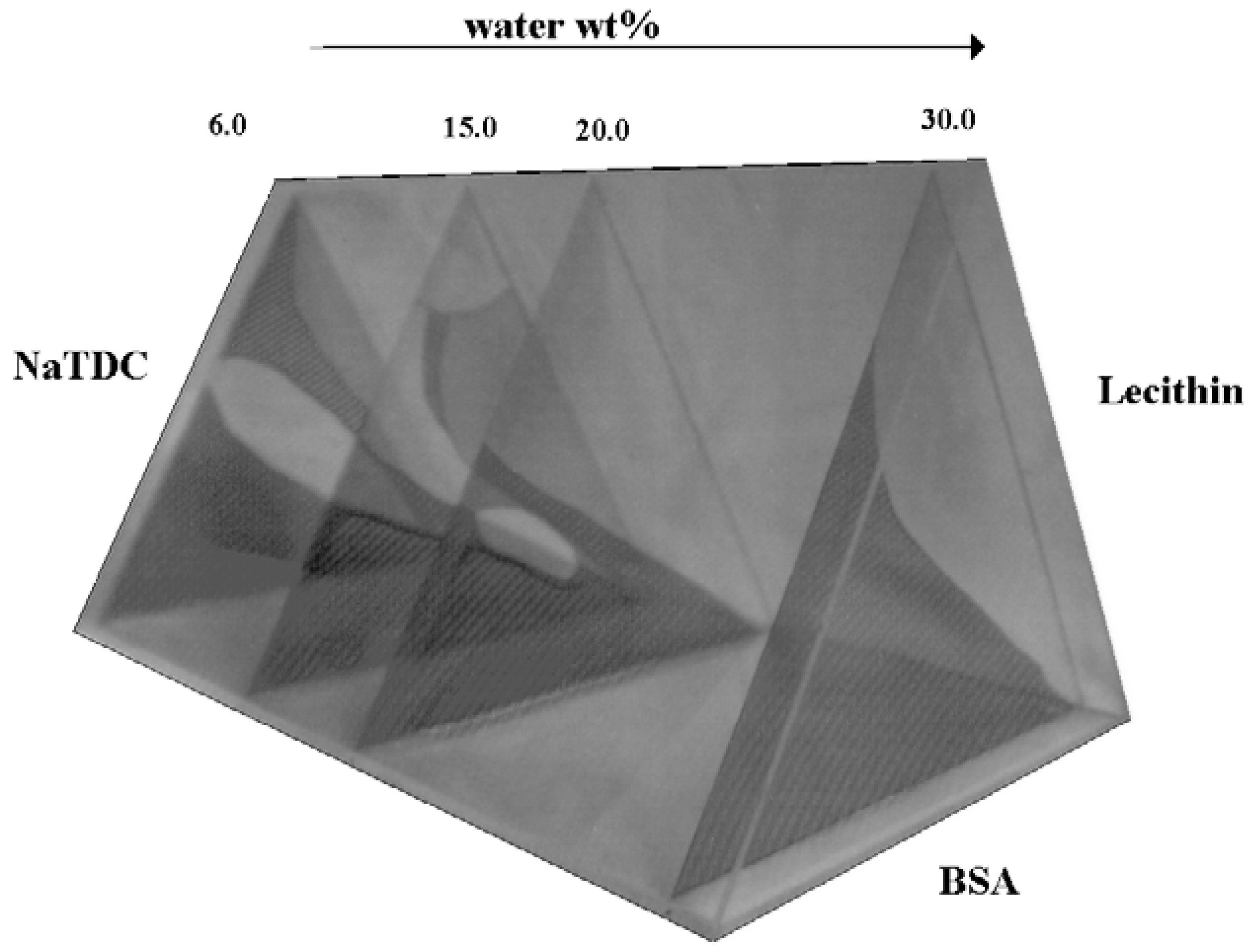
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Kullak-Ublick, G. A.; Stieger, B.; Hagenbuch, B; Meier, P. J. Hepatic transport of bile salts. Sem. Liver Dis. 2000, 20, 273–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D.M. Role of ABC transporters in secretion of cholesterol from liver into bile. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003, 100, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. M. Point mutations in the ileal bile salt transporter cause leaks in the enterohepatic circulation leading to severe chronic diarrhea and malabsorption. J. Clinical Invest. 1997, 99, 1807–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farthing, M. J. G.; Keusch, G. T.; Carey, M. C.; Varon, S. Effects of bile and bile salts on growth and membrane lipid uptake by Giardia lamblia. Possible implications for pathogenesis of intestinal disease. J. Clinical Invest. 1985, 76, 1727–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Mete, L.; Attili, A. F. Cholelithiasis: genetic hypothesis. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2000, 46, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Van Erpecum, K. J.; Wang, D. Q.-H.; Lammert, F.; Paigen, B.; Groen, A. K.; Carey, M. C. Phenotypic characterization of Lith genes that determine susceptibility to cholesterol cholelithiasis in inbred mice: soluble pronucleating proteins in gallbladder and hepatic biles. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. M. Gallstones. New Engl. J. Med. 1968, 279, 588–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, R. W.; Stephens, J. E.; Scharschmidt, B. F. Effects of ion substitution on bile acid-dependent and -independent bile formation by rat liver. J. Clinical Invest. 1982, 70, 505–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, C. M.; Doisy, E. A., Jr; Elliott, W. H. Bile acids. XLIV, quantitation of bile acids from the bile fistula rat given (4-14C) cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 380, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossey, E. C.; Ford, W. T.; Periyasamy, M. Carbon-13 NMR spectra of multifunctional bile acid derivatives. Magn. Res. Chem. 1991, 29, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, K. A. R.; Ulven, S. M.; Schuster, G. U.; Steineger, H. H.; Andresen, S. M.; Gustafsson, J.-A.; Nebb, H. I. Liver X receptors as insulin-mediating factors in fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10691–10697. [Google Scholar]
- Craven, P. A.; Pfanstiel, J.; De Rubertis, F. R. Role of reactive oxygen in bile salt stimulation of colonic epithelial proliferation. J. Clinical Invest. 1986, 77, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M. C.; Sutherland, E.; Simon, F. R. Regulation of hepatic transport of bile salt. Effect of protein synthesis inhibition on excretion of bile salts and their binding to liver surface membrane fractions. J. Clinical Invest. 1979, 63, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, E.; Sbarra, V.; Le Petit-Thevenin, J.; Valette, A.; Lombardo, D. Site-directed Mutagenesis of the Basic N-terminal Cluster of Pancreatic Bile Salt-dependent Lipase. Functional significance. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34987–34996. [Google Scholar]
- Farruggia, B.; Pico, G. Role of electrostatic forces in hydroxy and keto bile salt-albumin interactions: some experimental observations. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1992, 11, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, J. M.; Benedek, G. B.; Carey, M. C. Self-association of human apolipoproteins A-I and A-II and interactions of apolipoprotein A-I with bile salts: quasi-elastic light scattering studies. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 8116–8125. [Google Scholar]
- Calcamuggi, G.; Lanzio, M.; Babini, G.; Martini, S.; Anfossi, G.; Emanuelli, G. Sodium taurocholate affects prostacyclin constitutive production by cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J. Labor. Clinical Med. 1990, 115, 756–760. [Google Scholar]
- Keynes, G. A Bibliography of the Writings of William Harvey, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: Cambridge, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, J. M.; Johnson, I. T. Interactions between hemolytic saponins, bile salts and small intestinal mucosa in the rat. J. Nutr. 1988, 118, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, G. S.; Oakenfull, D. G. A mechanism for the hypocholesterolemic activity of saponins. British J. Nutr. 1986, 55, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, J. M.; Jackson, A. A.; Carey, M. C. Molecular species composition of inter-mixed micellar/vesicular bile salt concentrations in model bile: dependence upon hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Schurtenberger, P.; Svård, M.; Wehrli, E.; Lindman, B. Vesicle formation in aqueous solutions of bile salt and monoacylglycerol. Biochim. Biophys.Acta, Gen. Sub. 1986, 882, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E. L.; Nassimbeni, L. R. Crystal and molecular structures of the inclusion compounds of cholic acid with methanol, ethanol and 1-propanol. Acta Crystallogr. B 1990, 46, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoswathananont, N.; Sada, K.; Miyata, M.; Akita, S.; Nakano, K. Dependence of selective enclathration on types of cholic acid crystals. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. M.; Dowling, R. H.; Redinger, R. N. Enterohepatic circulation of bile salts. Arch. Intern. Med. 1972, 130, 552–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redinger, R. N.; Small, D. M. Bile composition, bile salt metabolism, and gallstones. Arch. Intern. Med. 1972, 130, 618–630. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A. F.; Small, D. M. Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Ann. Rev. Med. 1967, 18, 333–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmius, J.; Lindblom, G.; Wennerström, H.; Johansson, L. B.-Å; Fontell, K.; Söderman, O.; Arvidson, G. Molecular organization in the liquid-crystalline phases of lecithin-sodium cholate-water systems studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. M. Physical chemistry of cholanic acids. In The Bile Acids; Nair, P. P., Kritchevsky, D., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, 1971; Vol. I, Chapt. IV; pp. 249–356. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, D. J.; Hamilton, J.A.; Small, D. M. The ionization behavior of bile acids in different aqueous environments. J. Lipid Res. 1986, 27, 334–343. [Google Scholar]
- D'Archivio, A. A.; Galantini, L.; Gavuzzo, E.; Giglio, E.; Scaramuzza, L. Possible Models for the Micellar Aggregates of Glycocholate and Taurocholate Salts from Crystal Structures, QELS, and CD Measurements. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4660–4667. [Google Scholar]
- De Sanctis Candeloro, S.; D'Archivio, A. A.; Galantini, L.; Gavuzzo, E.; Giglio, E. On the role of hydronium ions in the protonated micellar aggregates of bile salts. Perkin 2 2000, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin, R. G. The Aqueous Phase Behavior of Surfactants; Academic Press: San Diego, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Hofmann, A. F.; Ton, N.; Huong, T.; Schteingart, C. D.; Mysels, K. J. Solubility of calcium salts of unconjugated and conjugated natural bile acids. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 635–646. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A. F.; Mysels, K. J. Bile acid solubility and precipitation in vitro and in vivo: the role of conjugation, pH, and Ca2+ ions. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 617–626. [Google Scholar]
- Tanford, C. The Hydrophobic Effect. Formation of Micelles, Vesicles and Membranes, 2nd ed; Academic Press: New York, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mukerjee, P.; Mysels, K. J. Critical Micelle Concentration of Aqueous Surfactant Systems; NSR-DS, NBS: Washington, DC, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda, K.; Hutchinson, E. Pseudo-phase separation model for thermodynamic calculations on micellar solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1958, 62, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Stilbs, P. Fourier transform pulsed-gradient spin-echo studies of molecular diffusion. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1987, 19, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kratohvil, J. P.; Hsu, W. P.; Kwok, D. I. How large are the micelles of di-a-hydroxy bile salts at the critical micellization concentrations in aqueous electrolyte solutions? Results for sodium taurodeoxycholate and sodium deoxycholate. Langmuir 1986, 2, 256–258. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, A.; Hofmann, A. F.; Mysels, K. J. The influence of bile salt structure on self-association in aqueous solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 6362–6370. [Google Scholar]
- van Os, N. M.; Haak, J. R.; Rupert, L. A. M. Physico-Chemical Properties of Selected Anionic, Cationic and Nonionic Surfactants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ekwall, P. Concentration limits in association colloid solutions. J. Colloid Sci. 1954, Suppl.1, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desnoyers, J. E.; Caron, G.; De Lisi, R.; Roberts, D.; Roux, A.; Perron, G. Thermodynamic properties of alkyldimethylamine oxides in water. Application of a mass-action model for micellization. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. M. Size and structure of bile salt micelles. Influence of structure, concentration, counterion concentration, pH, and temperature. Adv. Chem. Ser. 1968, 84, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakenfull, D. G.; Fisher, L. R. The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bile salt micelles. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 1838–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Zana, R. The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bile salt micelles. Comments. J. Phys. Chem. 1978, 82, 2440–2443. [Google Scholar]
- Oakenfull, D. G.; Fisher, L. R. The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bile salt micelles. Reply to comments. J. Phys. Chem. 1978, 82, 2443–2445. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan, N.; Vadnere, M.; Lindenbaum, S. Thermodynamics of aqueous bile salt solutions: heat capacity, enthalpy and entropy of dilution. J. Solution Chem. 1981, 10, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, G.; Yamakawa, K.; Murata, Y.; Tanaka, M. Effects of pH, pNa, and temperature on micelle formation and solubilization of cholesterol in aqueous solutions of bile salts. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 2784–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Kodera, Y.; Sugihara, G. Colloid chemistry of free bile salts. II. Recent information on mechanism of micelle formation. Fukuoka Daigaku Rigaku Shuho 1978, 8, 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Briganti, G.; D'Archivio, A. A.; Galantini, L.; Giglio, E. Structural Study of the Micellar Aggregates of Sodium and Rubidium Glyco- and Taurodeoxycholate. Langmuir 1996, 12, 1180–1187, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, A.; Blow, D. M. Formation of a helical steroid complex. Nature 1958, 182, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- D’Archivio, A. A.; Galantini, L.; Giglio, E. X-Ray, QELS, and CD Studies of the Micellar Aggregates of Calcium Taurodeoxycholate. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4197–4203. [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli, A. R.; Candeloro De Sanctis, S.; Giglio, E.; Petriconi, S. The structure of helices of rubidium deoxycholate-water(3/10), 3(Rb+.C24H39O4-).10H2O. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 1984, 40, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, A. R.; Candeloro De Sanctis, S.; Giglio, E.; Scaramuzza, L. A model for micellar aggregates of a bile salt: crystal structure of sodium taurodeoxycholate monohydrate. J. Lipid Res. 1987, 28, 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli, A. R.; Candeloro DeSanctis, S.; Chiessi, E.; D’Alagni, M.; Giglio, E.; Scaramuzza, L. Sodium glyco- and taurodeoxycholate: possible helical models for conjugated bile salt micelles. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli, A. R.; Candeloro DeSanctis, S.; Galantini, L.; Giglio, E.; Scaramuzza, L. A possible helical model for sodium glycocholate micellar aggregates. J. Inclus. Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem. 1991, 10, 367–377. [Google Scholar]
- Galantini, L.; Giglio, E.; La Mesa, C.; Pavel, N. V.; Punzo, F. Sodium Taurodeoxycholate Structure from Solid to Liquid Phase. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2812–2816. [Google Scholar]
- Fontell, K. Micellar behavior in solutions of bile acid salts. III. Viscosity and density measurements in aqueous solutions. Koll. Z. u. Z. Polym. 1971, 246, 614–625. [Google Scholar]
- Plowiec, R.; Kielczynski, P.; D'Arrigo, G.; La Mesa, C. Dynamic shear viscosity measurements in aqueous sodium deoxycholate solutions. Adv. Mol. Relax. Interact. Proc. 1982, 24, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arrigo, G.; La Mesa, C. Temperature and Concentration Effects on the Viscoelasticity of Concentrated Aqueous Solutions of Bile Salts in the Ultrasonic Range. Phys. Rev. A 1981, 24, 2187–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Sesta, B.; La Mesa, C.; Bonincontro, A.; Cametti, C.; Di Biasio, A. Molecular aggregation of sodium deoxycholate in water and water-urea mixtures; a multistep process. Ber. Bunsen. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 798–803. [Google Scholar]
- Sesta, B.; La Mesa, C.; Bonincontro, A.; Cametti, C.; Di Biasio, A. Micellization processes in concentrated sodium deoxycholate solutions - effect of different counterions. Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 664–670. [Google Scholar]
- Mazer, N. A.; Kwasnick, R. F.; Carey, M. C.; Benedek, G. B. Quasielastic light scattering spectroscopic studies of aqueous bile salt, bile salt-lecithin and bile salt-lecithin-cholesterol solutions. In Micellization, Solubilization, Microemulsions; Mittal, K. L., Ed.; Plenum: New York, 1977; Vol. 1, pp. 383–402. [Google Scholar]
- Mazer, N. A.; Carey, M. C.; Kwasnick, R. F.; Benedek, G. B. Quasielastic light scattering studies of aqueous biliary lipid systems. Size, shape, and thermodynamics of bile salt micelles. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 3064–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galantini, L.; Giglio, E.; Pavel, N. V.; Punzo, F. QELS and X-ray study of two dihydroxy bile salt aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Engineer. Asp. 2004, 248, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, R. E.; Gosselin, G. J.; Donovan, J. M.; Carey, M. C.; Roberts, M. F. Influence of dilution on the physical state of model bile systems: NMR and quasi-elastic light-scattering investigations. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm, R. P.; Schteingart, C. D.; Hofmann, A. F.; Thiyagarajan, P. Structure of Conjugated Bile Salt-Fatty Acid-Monoglyceride Mixed Colloids: Studies by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 197–211. [Google Scholar]
- Lindman, B. Micelles and microemulsions in ionic surfactant and bile salt systems studied by self-diffusion. Hepatology 1984, 4, 103S–109S. [Google Scholar]
- Schurtenberger, P.; Lindman, B. Coexistence of simple and mixed bile salt-lecithin micelles: an NMR self-diffusion study. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 7161–7165. [Google Scholar]
- D'Arrigo, G.; Sesta, B.; La Mesa, C. Evidence of viscoelastic effects in highly concentrated aqueous solutions of the bile salt sodium deoxycholate by ultrasonic measurements. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 73, 4562–4568. [Google Scholar]
- Berchiesi, G.; Berchiesi, M. A.; La Mesa, C.; Sesta, B. Static and dynamic studies on sodium taurodeoxycholate micellar aggregation in water in the range 25-45°C. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 3665–3669. [Google Scholar]
- Bonincontro, A.; D'Archivio, A. A.; Galantini, L.; Giglio, E.; Punzo, F. X-ray, Electrolytic Conductance, and Dielectric Studies of Bile Salt Micellar Aggregates. Langmuir 2000, 16, 10436–10443. [Google Scholar]
- Capalbi, A.; Gente, G.; La Mesa, C. Solution properties of alkyl glucosides, alkyl thioglucosides and alkyl maltosides. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 246, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M. L.; Capalbi, A.; Gente, G.; Palacios, A. C.; Sallustio, S.; La Mesa, C. Thermodynamic properties of the bovine serum albumin-sodium taurodeoxycholate system. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 246, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, A. C.; Antonelli, M. L.; La Mesa, C. Interactions between bovine serum albumin and sodium taurodeoxycholate: thermodynamic properties. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 418, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, J. Chromonic liquid crystal phases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. M. Liquid crystals in living and dying systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 58, 581–602. [Google Scholar]
- Edlund, H.; Khan, A.; La Mesa, C. Formation of a Liquid Crystalline Phase in the Water-Sodium Taurodeoxycholate System. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3691–3697. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, E. F.; Edlund, H.; La Mesa, C.; Khan, A. Liquid Crystals and Phase Equilibria Binary Bile Salt-Water Systems. Langmuir 2000, 16, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar]
- Amenitsch, H.; Edlund, H.; Khan, A.; Marques, E. F.; La Mesa, C. Bile salts form lyotropic liquid crystals. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 213, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mesa, C. A. Supra-molecular association in bile salts. Recent Res. Develop. Surf. Colloids 2004, 1, 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- La Mesa, C.; Coppola, L. Krafft point solubility phenomena. Colloids Surf. 1989, 35, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosevear, F. B. The microscopy of the liquid crystalline neat and middle phases of soaps and synthetic detergents. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1954, 31, 628–639. [Google Scholar]
- Rosevear, F. B. Liquid crystals: the mesomorphic phases of surfactant compositions. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1968, 19, 581–594. [Google Scholar]
- Ekwall, P. Composition, properties, and structures of liquid crystalline phases in systems of amphiphilic compounds. In Advances in Liquid Crystals; Brown, G. H., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, 1975; Vol. I, pp. 1–142. [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati, V.; Mustacchi, H.; Skoulios, A.E.; Husson, F. The structure of association colloids. I. The liquid-crystalline phases of the amphiphile-water system. Acta Crystallogr. 1960, 13, 660–667. [Google Scholar]
- Fontell, K. Liquid crystallinity in lipid-water systems. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1982, 63, 59–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lindman, B.; Söderman, O.; Wennerström, H. NMR studies of surfactant systems. In Surfactant Solutions. New Methods of Investigation; Zana, R., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 1986; Chap. VI; pp. 295–357. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Fontell, K.; Lindblom, G.; Lindman, B. Liquid crystallinity in a calcium surfactant system. Phase equilibriums and phase structures in the system calcium octyl sulfate/decan-1-ol/water. J. Phys Chem. 1982, 86, 4266–4271. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, E.; Khan, A.; Miguel, M. G.; Lindman, B. Self-assembly in mixtures of a cationic and an anionic surfactant: the sodium dodecyl sulfate-didodecyldimethylammonium bromide-water system. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 4729–4736. [Google Scholar]
- Tiddy, G. J. T. Surfactant-water liquid crystal phases. Phys. Rep. 1980, 57, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jönsson, B.; Wennerström, H. Phase equilibria in the mixed sodium and calcium di-2-ethylhexylsulfosuccinate aqueous system. An illustration of repulsive and attractive double-layer forces. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 5180–5184. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, K. Lipids - Molecular Organisation, Physical Functions and Technical Applications; The Oily Press: Dundee, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A. F. Micellar solubilization of fatty acids and monoglycerides by bile salt solutions. Nature 1961, 190, 1106–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C. A.; Hofmann, A. F.; Mysels, K. J.; Roda, A. The effect of calcium and sodium ion concentration on the properties of dilute aqueous solutions of glycine conjugated bile salts: phase behavior and solubility products of the calcium salts of the common glycine conjugated bile acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 114, 452–470. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. M.; Bourges, M.; Dervichian, D. G. Ternary and quaternary aqueous systems containing bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol. Nature 1966, 211, 816–818. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. M.; Bourges, M.; Dervichian, D. G. The biophysics of lipidic associations. I. The ternary systems: lecithin-bile salt-water. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Lip. Lipid Metabol. 1966, 125, 563–580. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. M.; Bourges, M. Lyotropic paracrystalline phases obtained with ternary and quaternary systems of amphiphilic substances in water: Studies on aqueous systems of lecithin, bile salt, and cholesterol. Mol. Cryst. 1966, 1, 541–561. [Google Scholar]
- Bourges, M.; Small, D. M.; Dervichian, D. G. Biophysics of lipid associations. III. Quaternary systems lecithin-bile salt-cholesterol-water. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Lip. Lipid Metabol. 1967, 144, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, L.; Oakenfull, D. The environment of solubilized molecules in bile salt micelles. Aust. J. Chem. 1979, 32, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fontell, K. Micellar behavior in solutions of bile acid salts. Koll. Z. u. Z. Polym. 1972, 250, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, D.W.; Cahalane, M. J.; Timofeyeva, N.; Carey, M. C. Molecular species of lecithins in human gallbladder bile. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Fontell, K. Micellar behavior in solutions of bile acid salts. VI. Solutions of the three-component system bile acid salt, n-decanol, and water. Koll. Z. u. Z. Polym. 1972, 250, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, B.; Wennerström, H. Phase equilibria in a three-component water-soap-alcohol system. A thermodynamic model. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 338–352. [Google Scholar]
- La Mesa, C.; Khan, A.; Fontell, K.; Lindman, B. Phase diagrams and NMR studies of some ternary sodium deoxycholate-surfactant-water systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1985, 103, 373–391. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson-Vethamuthu, M.; Almgren, M.; Bergenståhl, B.; Mukhtar, E. The hexagonal phase and cylindrical micelles in the system alkyltrimethylammonium bromide-sodium desoxycholate-water as studied by x-ray diffraction and fluorescence quenching. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 178, 538–548. [Google Scholar]
- Svärd, M.; Schurtenberger, P.; Fontell, K.; Jönsson, B.; Lindman, B. Micelles, vesicles, and liquid crystals in the monoolein-sodium taurocholate-water system: phase behavior, NMR, self-diffusion, and quasi-elastic light scattering studies. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 2261–2270. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, E. F.; Regev, O.; Edlund, H.; Khan, A. Micelles, Dispersions, and Liquid Crystals in the Catanionic Mixture Bile Salt-Double-Chained Surfactant. The Bile Salt-Rich Area. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8255–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, J.; Baranyi, L.; Savay, S.; Milosevits, J.; Bunger, R.; Laverman, P.; Metselaar, J.; Storm, G.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Liebes, L.; Muggia, F. M.; Cohen, R.; Barenholz, Y. Role of complement activation in hypersensitivity reactions to doxil and HYNIC PEG liposomes: experimental and clinical studies. J. Liposome Res. 2002, 12, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, L. private communication.
- Orioni, B.; Roversi, M.; La Mesa, C.; Asaro, F.; Pellizer, D’Errico, G. Polymorphic Behavior in Protein-Surfactant Mixtures: The Water-Bovine Serum Albumin-Sodium Taurodeoxycholate System. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 12129–12140. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, A. C.; Sarnthein-Graf, C.; La Mesa, C. Equilibrium between phases in water-protein-surfactant systems. Colloids Surf. A, Physicochem. Engineer. Asp. 2003, 228, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagnolari, F.; Roda, A.; Fini, A.; Grigolo, B. Thermodynamic features of bile salt-human serum albumin interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1984, 791, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Era, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Sogami, M.; Hayashi, T.; Muratami, M. Conformational changes in seventeen cystine disulfide bridges of bovine serum albumin proved by Raman spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1997, 417, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ferre, M. L.; Duchowicz, R.; Carrasco, B.; Garcia de la Torre, J.; Acuna, A. U. The conformation of serum albumin in solution: a combined phosphorescence depolarization-hydrodynamic modeling study. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar]
- Moren, A. K.; Khan, A. Phase Equilibria of an anionic surfactant (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate) and an Oppositely Charged Protein (Lysozyme) in Water. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar]
- Moren, A. K.; Khan, A. Surfactant Hydrophobic Effect on the Phase Behavior of Oppositely Charged Protein and Surfactant Mixtures: Lysozyme and Sodium Alkyl Sulfates. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6818–6826. [Google Scholar]
- Sesta, B.; Gente, G.; Iovino, A.; Laureti, F.; Michiotti, P.; Paiusco, O.; Palacios, A. C.; Persi, L.; Princi, A.; Sallustio, S.; Sarnthein-Graf, C.; Capalbi, A.; La Mesa, C. Supramolecular Association in the System Water-Lysozyme-Lithium Perfluorononanoate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3036–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Roversi, M.; La Mesa, C. Rheological properties of protein-surfactant based gels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Aldini, R.; Montagnani, M.; Roda, A.; Hrelia, S.; Biagi, P. L.; Roda, E. Intestinal absorption of bile acids in the rabbit: different transport rates in jejunum and ileum. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Calabresi, M.; La Mesa, C. Manuscript in preparation.
- Fletcher, P. D. I.; Robinson, B. H.; Freedman, R. B.; Oldfield, C. Activity of lipase in water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Chem Soc. Faraday Trans. 1985, 81, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T. A. Albumin: Structure, Function and Uses; Rosenoer, V. M., Oratz, M., Rothschild, M. A., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, 1977; p. 255. [Google Scholar]
- Boye, J. J.; Inteaz, A.; Ismail, A.A. Interactions Involved in the Gelation of Bovine Serum Albumin. J. Agr. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenstam, A.; Montalvo, G.; Grillo, I.; Gradzielski, M. Small Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Lysozyme-Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 12331–12338. [Google Scholar]
- La Mesa, C. Polymer-surfactant and protein-surfactant interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Calabresi, M.; Andreozzi, P.; La Mesa, C. Supra-molecular Association and Polymorphic Behaviour In Systems Containing Bile Acid Salts. Molecules 2007, 12, 1731-1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/12081731
Calabresi M, Andreozzi P, La Mesa C. Supra-molecular Association and Polymorphic Behaviour In Systems Containing Bile Acid Salts. Molecules. 2007; 12(8):1731-1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/12081731
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalabresi, Marco, Patrizia Andreozzi, and Camillo La Mesa. 2007. "Supra-molecular Association and Polymorphic Behaviour In Systems Containing Bile Acid Salts" Molecules 12, no. 8: 1731-1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/12081731
APA StyleCalabresi, M., Andreozzi, P., & La Mesa, C. (2007). Supra-molecular Association and Polymorphic Behaviour In Systems Containing Bile Acid Salts. Molecules, 12(8), 1731-1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/12081731



