Synthesis and Properties of Acyclic Ammonium-based Ionic Liquids with Allyl Substituents as Electrolytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and characterization of products
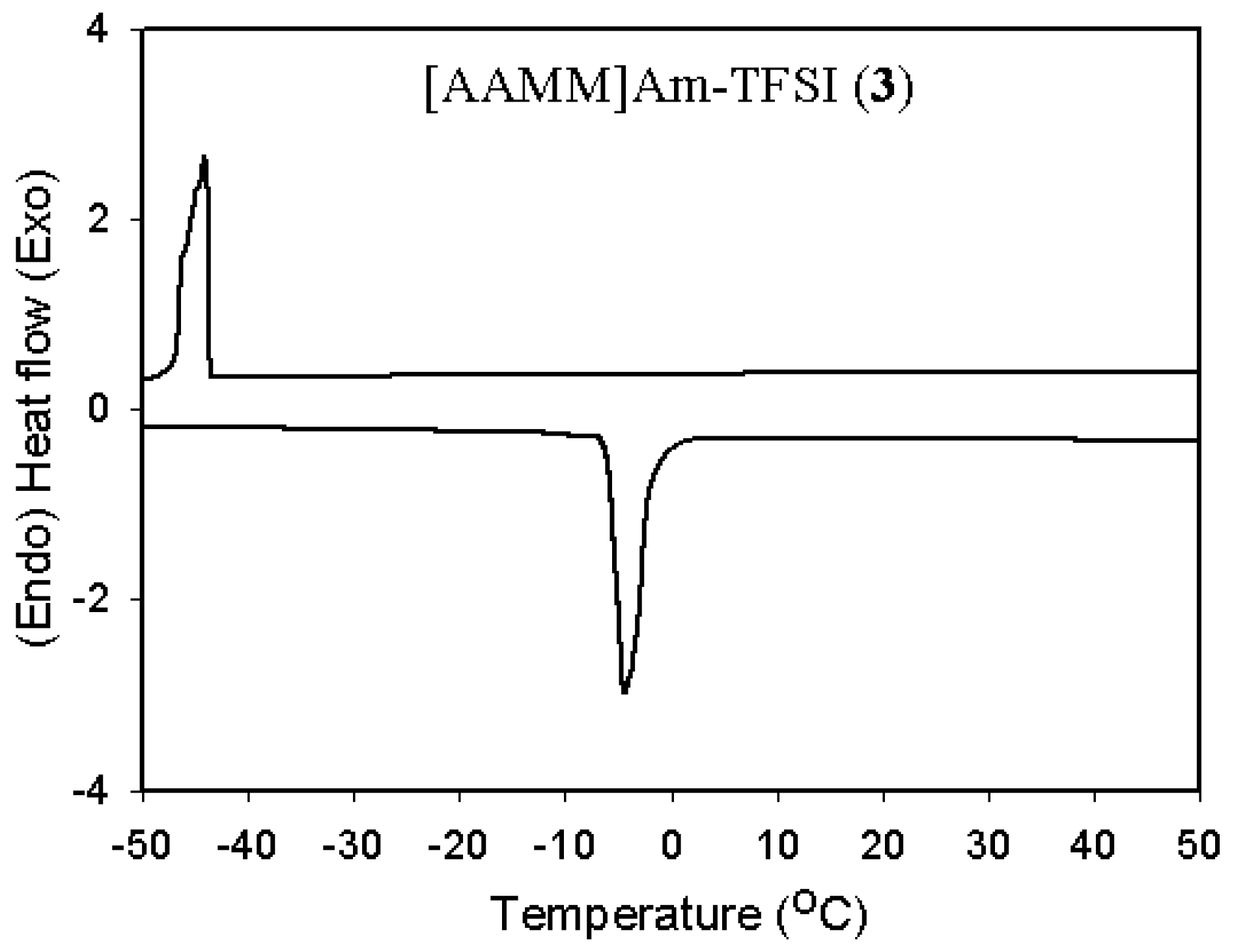
2.2. Thermal and physical properties
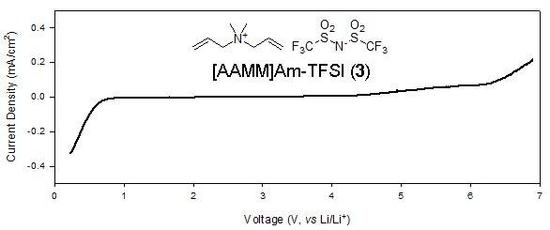
2.3. Electrochemical properties
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental
4.1. General
4.2. General procedure for the preparation of acyclic ammonium halides
4.3. General procedure for anion metathesis
5. Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
References and Notes
- Anthony, J.L.; Brennecke, J.F.; Holbrey, J.D.; Maginn, E.J.; Mantz, R.A.; Rogers, R.D.; Trulove, P.C.; Visser, A.E.; Welton, T. Ionic liquids in synthesis; Wasserscheid, P., Welton, T., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Chapter 3; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, S.; Ohno, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H.; Usami, A.; Mita, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Watanabe, M.; Hayamizu, K.; Tsuzuki, S.; Hattori, M.; Terada, N. Imidazolium-based room temperature ionic liquid for lithium secondary batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A173–A177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Quan, N.D.; Hwang, J.M.; Bae, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Cho, B.W.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H. Ionic liquids containing an ester group as potential electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunashima, K.; Yonekawa, F.; Sugiya, M. A lithium battery electrolyte based on a room-temperature phosphonium ionic liquid. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Kikuta, M.; Ishiko, E.; Kono, M. Pure ionic liquid electrolytes compatible with a graphitized carbon negative electrode in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.H.; Yim, T.; Lee, H.Y.; Huh, D.H.; Lee, E.; Mun, J.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, Y.G. Synthesis and properties of ionic liquids: imidazolium tetrafluoroborates with unsaturated side chains. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, 27, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.H.; Yim, T.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Mun, J.; Kim, S.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, Y.G. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of ionic liquids: 1-alkenyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium tetrafluoroborates. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, 28, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, T.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Mun, J.; Kim, S.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, Y.G. Synthesis and properties of pyrrolidinium and piperidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ionic liquids with allyl substituents. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, 28, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, T.; Choi, C.Y.; Mun, J.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, Y.G. Synthesis and properties of allyl-containing ammonium-type ionic liquids as secondary battery electrolytes. Presented in part at The 3rd Asian Conference on Electrochemical Power Sources, Seoul, Korea, November 10-14, 2008. Abst. No. IB-19. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yanagida, M.; Tanimoto, K.; Nomura, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Highly conductive room temperature molten salts based on small trimethylalkylammonium cations and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Chem. Lett. 2000, 29, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H. Electrochemical aspects of ionic liquids; Ohno, H., Ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Chapter 4; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.T.; Lin, Y.W.; Jan, Y.S. Allyl ethyl carbonate as an additive for lithium-ion battery electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2004, 132, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Sakaebe, H.; Tatsumi, K. Preparation of room temperature ionic liquids based on aliphatic onium cations and asymmetric amide anions and their electrochemical properties as a lithium battery electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To the best of our knowledge, there are no literature precedents of the use of diallyldimethylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([AAMM]Am-TFSI, CAS No. 521942-10-9) as an electrolyte, although there have been several patents employing it as an additive for its antistatic or antimicrobial properties. There have been also some reports utilizing poly(diallyldimethylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide) as an electrolyte that consists of a cyclic N,N-dimethylpyrrolidinium structure instead of the acyclic diallyldimethylammonium ([AAMM]Am) structure. The N,N-dimethylpyrrolidinium structure is derived from polymerization of a bifunctional monomer of the diallyldimethylammonium cation. Diallyldimethylammonium chloride (CAS No. 7398-69-8) and poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (CAS No. 26062-79-3) are commercially available. For example, see: Pappenfus, T.M.; Henderson, W.A.; Owens, B.B.; Mann, K.R.; Smyrl, W.H. Complexes of Lithium Imide Salts with Tetraglyme and Their Polyelectrolyte Composite Materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A209–A215. [Google Scholar]Pappenfus, T.M.; Mann, K.R.; Smyrl, W.H. Polyelectrolyte Composite Materials with LiPF6 and Tetraglyme. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, A254–A255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: All products reported in this paper are available from the authors. |



| No | Ionic liquids | Tm (oC) | Tc (oC) | Td (oC) | η (cP) | σ (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [AEMM]Am-TFSI (1) | 13 | -30 | 320 | 67 | 2.5 |
| 2 | [AMMP]Am-TFSI (2) | 2 | -35 | 297 | 79 | 2.1 |
| 3 | [AAMM]Am-TFSI (3) | -4 | -44 | 294 | 66 | 3.2 |
| 4 | [ABMM]Am-TFSI (4) | 2 | -58 | 297 | 113 | 2.5 |
| 5 | [A(Ha)MM]Am-TFSI (5) | ND | ND | 306 | 98 | 1.9 |
| 6 | [AMM(MOM)]Am-TFSI (6) | ND | ND | 268 | 47 | 3.9 |
| 7 | [A(EOM)MM]Am-TFSI (7) | ND | ND | 255 | 49 | 3.0 |
| 8 | [AMM(MTM)]Am-TFSI (8) | ND | ND | 229 | 161 | 1.1 |
| No | Ionic liquids | Cathodic Limit (V) | Anodic Limit (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [AEMM]Am-TFSI (1) | -2.6 | 2.6 |
| 2 | [AMMP]Am-TFSI (2) | -2.5 | 2.5 |
| 3 | [AAMM]Am-TFSI (3) | -2.5 | 3.4 |
| 4 | [ABMM]Am-TFSI (4) | -2.6 | 2.0 |
| 5 | [A(Ha)MM]Am-TFSI (5) | -2.2 | 2.8 |
| 6 | [AMM(MOM)]Am-TFSI (6) | -2.5 | 2.5 |
| 7 | [A(EOM)MM]Am-TFSI (7) | -2.5 | 2.3 |
| 8 | [AMM(MTM)]Am-TFSI (8) | -2.5 | 2.2 |
| No | Ionic liquids | Cathodic Limit (V) | Anodic Limit (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Carbonatesb | 0.66 | 4.76 |
| 2 | [EM]Im-TFSI | 0.75 | 5.21 |
| 3 | [MMPP]Am-TFSI | 0.66 | 5.78 |
| 4 | [AMMP]Am-TFSI (2) | 0.46 | 5.59 |
| 5 | [AAMM]Am-TFSI (3) | 0.51 | 6.43 |
| 6 | [AMM(MOM)]Am-TFSI (6) | 0.50 | 5.61 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yim, T.; Choi, C.Y.; Mun, J.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, Y.G. Synthesis and Properties of Acyclic Ammonium-based Ionic Liquids with Allyl Substituents as Electrolytes. Molecules 2009, 14, 1840-1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051840
Yim T, Choi CY, Mun J, Oh SM, Kim YG. Synthesis and Properties of Acyclic Ammonium-based Ionic Liquids with Allyl Substituents as Electrolytes. Molecules. 2009; 14(5):1840-1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051840
Chicago/Turabian StyleYim, Taeeun, Chang Young Choi, Junyoung Mun, Seung M. Oh, and Young Gyu Kim. 2009. "Synthesis and Properties of Acyclic Ammonium-based Ionic Liquids with Allyl Substituents as Electrolytes" Molecules 14, no. 5: 1840-1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051840
APA StyleYim, T., Choi, C. Y., Mun, J., Oh, S. M., & Kim, Y. G. (2009). Synthesis and Properties of Acyclic Ammonium-based Ionic Liquids with Allyl Substituents as Electrolytes. Molecules, 14(5), 1840-1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051840