A Recyclable Nanoparticle-Supported Rhodium Catalyst for Hydrogenation Reactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Hydrogenation reactions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- McNamara, C.A.; Dixon, M.J.; Bradley, M. Recoverable catalysts and reagents using recyclable polystyrene-based supports. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3275–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMorn, P.; Hutchings, G.J. Heterogeneous enantioselective catalysts: Strategies for the immobilisation of homogeneous catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrorilli, P.; Nobile, C.F. Supported catalysis from polymerisable transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrorilli, P.; Nobile, C.F. Catalytic activity of macromolecules obtained from metal-containing monomers. In Metal-coordination polymers; Abd-El-Aziz, A.S., Carraher, C.E., Pittman, C.U., Zelding, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 227–257. [Google Scholar]
- Heitbaum, M.; Glorius, F.; Escher, I. Asymmetric Heterogeneous Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4732–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Silica-Bound Homogenous Catalysts as Recoverable and Reusable Catalysts in Organic Synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 1391–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Han, X.; Ma, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Ji, X. Palladium-guanidine complex immobilized on SBA-16: A highly active and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki coupling and alcohol oxidation. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbebi, A.; Schwartz, V.; Overbury, S.H.; Spivey, J.J. Effect of Li Promoter on titania-supported Rh catalyst for ethanol formation from CO hydrogenation. Catal. Today 2010, 149, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swennenhuis, B.H.G.; Chen, R.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M.; de Vries, J.G.; Kamer, P.C.J. Supported Chiral Monodentate Ligands in Rhodium-Catalysed Asymmetric Hydrogenation and Palladium-Catalysed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 5796–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, Y.; Takasaki, M.; Yoon, S.-H.; Mochida, I.; Nagashima, H. Rhodium Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon Nanofibers as an Arene Hydrogenation Catalyst Highly Tolerant to a Coexisting Epoxido Group. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5042–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, T.; Makino, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Watanuki, H.; Niki, T.; Shimizu, S.; Kojima, Y.; Sano, M. Alcohol synthesis by hydrogenation of fatty acid methyl esters on supported Ru-Sn and Rh-Sn catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 364, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, A.S. Anilines: Historical Background. In The Chemistry of Anilines; Rappoport, Z., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Ishii, H.; Sudo, M.; Tsuchitani, M. Potential of neurotoxicity after a single oral dose of 4-bromo-, 4-chloro-, 4-fluoro- or 4-iodoaniline in rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2003, 23, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rylander, P.N. Hydrogenation Methods; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Baltzly, R.; Phillips, A.P. The catalytic hydrogenolysis of halogen compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhong, H. Hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene over polymer-stabilized palladium–platinum bimetallic colloidal clusters. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1999, 147, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; He, J.; Cao, S. Catalytic behaviors of the palladium complex of MgO-supported melamino-formaldehyde polymer for hydrogenations of different substrates. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1999, 147, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, B.; Surendra Reddy, P.; Keerthi Devi, D. Direct one-pot reductive amination of aldehydes with nitroarenes in a domino fashion: Catalysis by gum-acacia-stabilized palladium nanoparticles. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 8806–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Deng, Z.; Liu, H. Modification of metal complex on hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene over polymer-stabilized platinum colloidal clusters. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1999, 144, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khilnani, V.L.; Chandalia, S.B. Selective hydrogenation. I. para-chloronitrobenzene to para-chloroaniline platinum on carbon as catalyst. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2001, 5, 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liang, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Selective hydrogenation of bromonitrobenzenes over Pt/γ-Fe2O3. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 273, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Excellent catalytic properties over nanocomposite catalysts for selective hydrogenation of halonitrobenzenes. J. Catal. 2008, 255, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, Y.; Kamo, K.; Nagashima, H. Catalysis in polysiloxane gels: Platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation of polymethylhydrosiloxane leading to reusable catalysts for reduction of nitroarenes. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Yan, N.; Xiao, C.; Li, C.; Fei, Z.; Cai, Z.; Kou, Y.; Dyson, P.J. Highly selective hydrogenation of aromatic chloronitro compounds to aromatic chloroamines with ionic-liquid-like copolymer stabilized platinum nanocatalysts in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, W.; Liu, H. Selective hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene over polymer-stabilized ruthenium colloidal catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1999, 138, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.L.; Wu, N.Z.; Peng, L.D.; Gui, L.L.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, R.M.; Yu, D.P. An efficient ruthenium catalyst for selective hydrogenation of ortho-chloronitrobenzene prepared via assembling ruthenium and tin oxide nanoparticles. J. Catal. 2004, 222, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.; Das, P.; Das, S. Transfer hydrogenation using recyclable polymer-supported formate (PSF): Efficient and chemoselective reduction of nitroarenes. Mol. Divers. 2005, 9, 259–262, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaubal, N.S.; Sawant, M.R. Nitro compounds reduction via hydride transfer using mesoporous mixed oxide catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 261, 232–241, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Gu, H.; Yan, X. A novel transfer hydrogenation with high hydrogen utilization for the hydrogenation of halogenated nitrobenzene without hydrodehalogenation. Catal. Lett. 2009, 132, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Anna, M.M.; Mastrorilli, P.; Rizzuti, A.; Suranna, G.P.; Nobile, C.F. Synthesis and copolymerization of rhodium(I) and palladium(II) complexes with the deprotonated form of 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2000, 304, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrorilli, P.; Nobile, C.F.; Suranna, G.P.; Corradi, A.; Leonelli, C.; Veronesi, P. Morphological characterization of poly(phenylacetylene) nanospheres prepared by homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 17, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the rhodium supported catalyst are available from the authors. |


| Entry | Substrate | Time (h) | PH2 (bar) | Conv. (%) | Products | Selectivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 a | 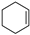 | 2 | 1 | 100 |  | 100 |
| 2 a |  | 4 | 1 | 100 |  | 100 |
| 3 a | 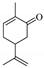 (−)-carvone | 6.5 | 1 | 100 | 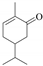  | 77 23 |
| 4 b | 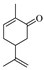 (−)-carvone | 23 | 1 | 100 |   | 92 8 |
| 5 b | 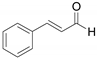 | 8 | 20 | 95 |   | 72 24 |
| 6 a | 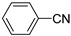 | 1 | 20 | 83 | 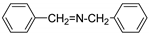 | 100 |
| 7 a,c | 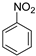 | 18 | 1 | 100 |  | 100 |
| Entry | Pressure (bar) | Time (h) | Conversion (%) | Selectivity for 2a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 72 | 65 | 100 |
| 2 | 20 | 72 | 100 | 98 |
| 3 | 50 | 72 | 100 | 65 |
| Entry | Substrate | Time (h) | Conversion (%) | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1b | 7 | 100 | 2b | 95 |
| 2 3 a | 1a ” | 3 2 | 100 100 | 2a ”; | 98 94 |
| 4 5 a | 1c ” | 1 0.5 | 98 100 | 2c ” | 90 90 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dell’Anna, M.M.; Gallo, V.; Mastrorilli, P.; Romanazzi, G. A Recyclable Nanoparticle-Supported Rhodium Catalyst for Hydrogenation Reactions. Molecules 2010, 15, 3311-3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053311
Dell’Anna MM, Gallo V, Mastrorilli P, Romanazzi G. A Recyclable Nanoparticle-Supported Rhodium Catalyst for Hydrogenation Reactions. Molecules. 2010; 15(5):3311-3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053311
Chicago/Turabian StyleDell’Anna, Maria Michela, Vito Gallo, Piero Mastrorilli, and Giuseppe Romanazzi. 2010. "A Recyclable Nanoparticle-Supported Rhodium Catalyst for Hydrogenation Reactions" Molecules 15, no. 5: 3311-3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053311
APA StyleDell’Anna, M. M., Gallo, V., Mastrorilli, P., & Romanazzi, G. (2010). A Recyclable Nanoparticle-Supported Rhodium Catalyst for Hydrogenation Reactions. Molecules, 15(5), 3311-3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053311





