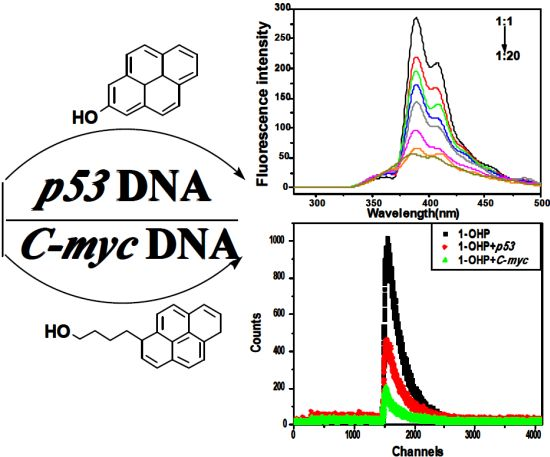
Studies on the Interaction Mechanism of Pyrene Derivatives with Human Tumor-Related DNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
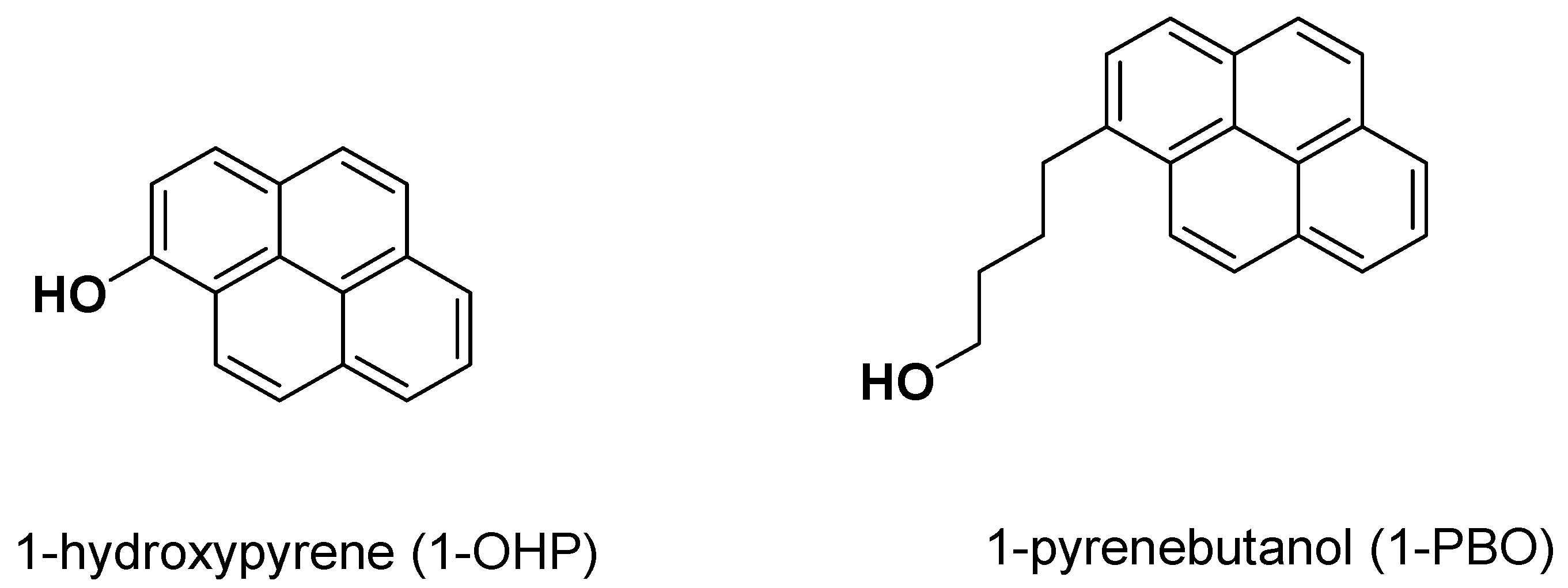
2. Results and Discussion
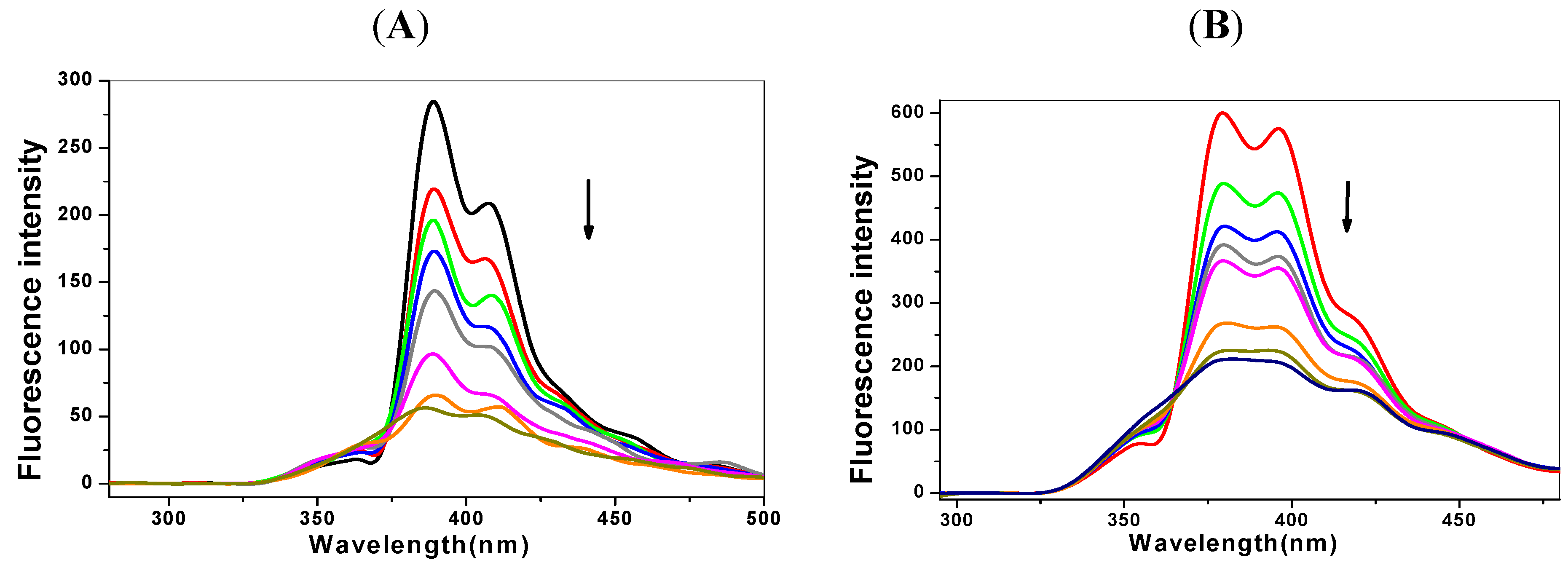
2.1. Steady State Fluorescence Studies
| Ksv (×105 L·mol−1) | Kq (×1013L·mol−1℘s−1) | Δ (%) * | n | Kb (L·mol−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-myc + 1-OHP | 1.97 | 1.97 | 72.34 | 1.07 | 4.04 × 105 |
| p53 + 1-OHP | 2.53 | 2.53 | 82.93 | 1.13 | 1.16 × 106 |
| C-myc + 1-PBO | 1.32 | 1.32 | 77.34 | 0.56 | 1.39 × 103 |
| p53 + 1-PBO | 1.57 | 1.57 | 78.38 | 0.58 | 2.04 × 103 |
2.2. The Binding Type of the Binary Complex and Thermodynamic Studies

| ΔH(kJ·mol−1) | ΔG(kJ·mol−1) | ΔS(J·mol−1·K−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-myc + 1-OHP | −48.62 | −31.98 | −55.84 |
| p53 + 1-OHP | −54.77 | −34.60 | −67.68 |
| C-myc + 1-PBO | −37.46 | −17.93 | −65.54 |
| p53 + 1-PBO | −40.94 | −18.88 | −70.34 |
2.3. Effect of the Ionic Strength on the Fluorescence Properties
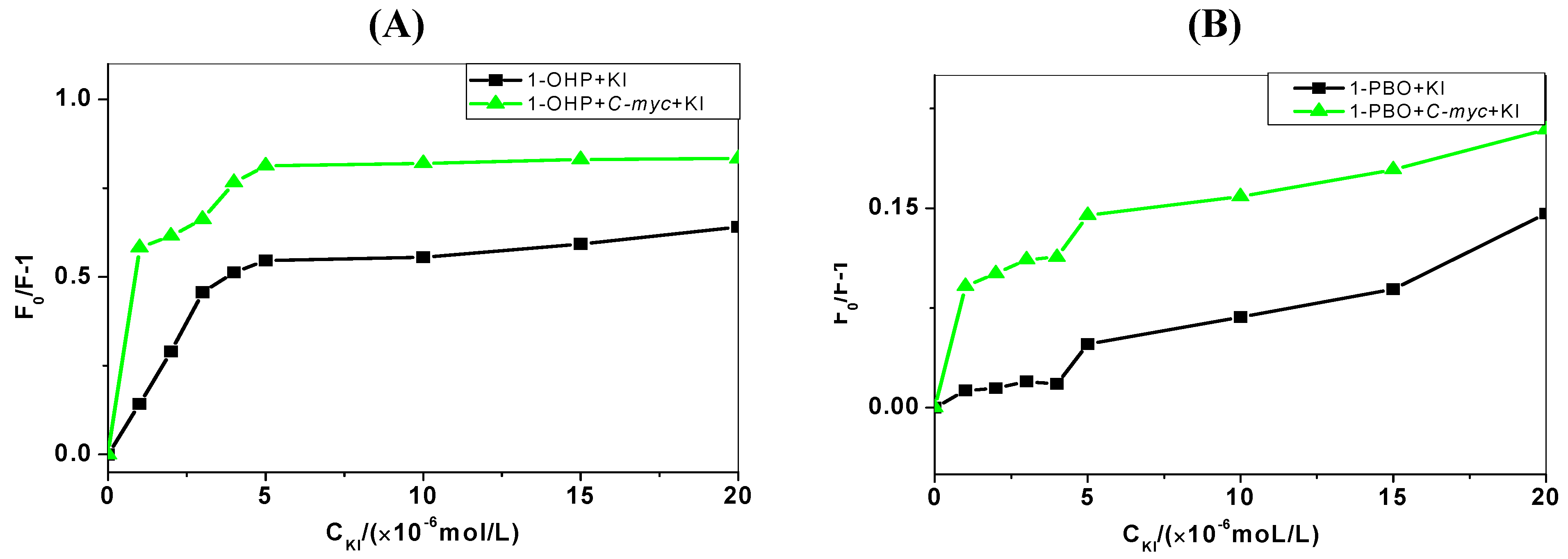
2.4. Iodide Quenching Studies
2.5. Competitive Binding between EB and Pyrene Derivatives for DNA
| Solution | R (%) |
|---|---|
| C-myc + 1-OHP | −5.46 |
| p53 + 1-OHP | −13.17 |
| C-myc + 1-PBO | −8.74 |
| p53 + 1-PBO | −8.85 |
2.6. CD Spectra Characteristics
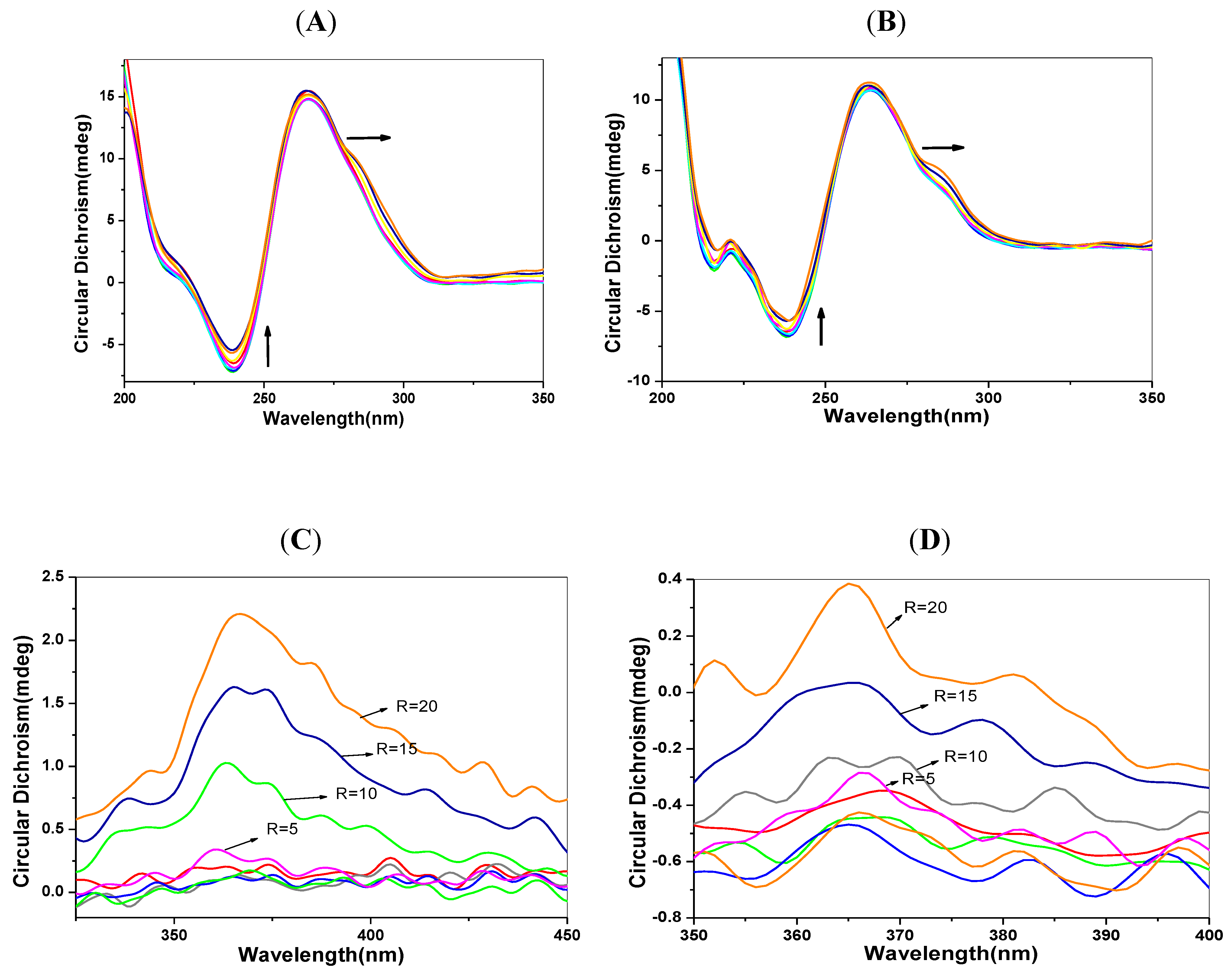
2.7. Transient Fluorescence Studies
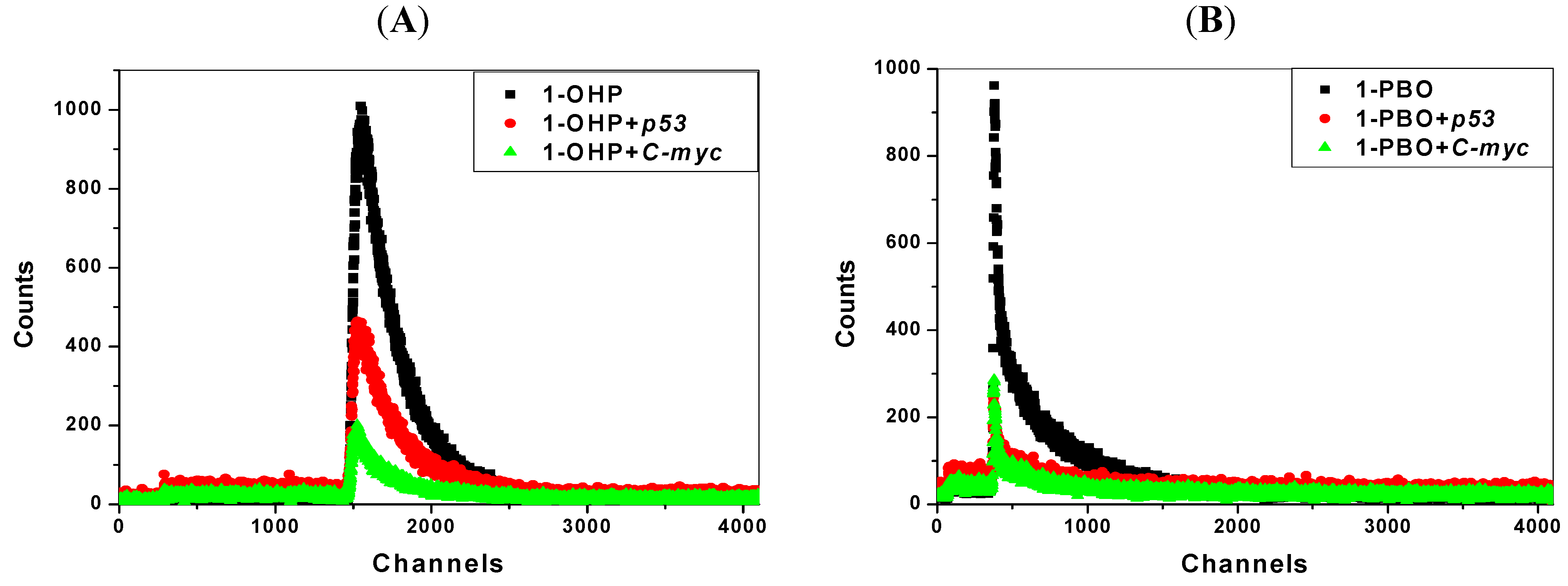
| Solution | Lifetime(ns) * | Solution | Lifetime(ns) ** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | Average | |||
| 1-OHP | 13.8 | 1-PBO | 90.7 | 4.90 | 40.6 |
| 1-OHP + p53 | 14.0 | 1-PBO + p53 | 86.9 | 3.79 | 35.1 |
| 1-OHP + C-myc | 13.6 | 1-PBO + C-myc | 87.7 | 3.96 | 28.2 |
2.8. PAGE Studies
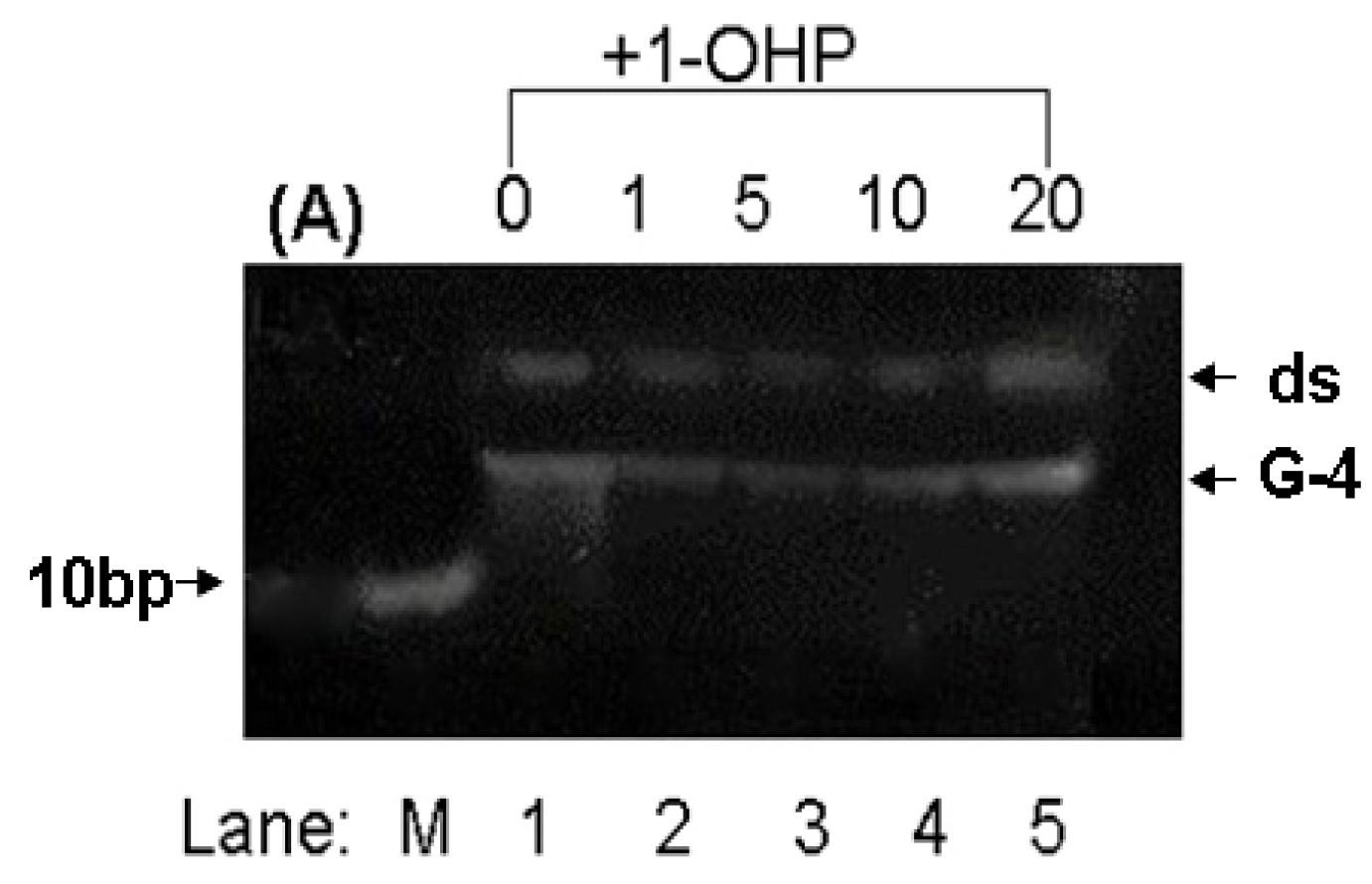
3. Experimental
3.1. Apparatus
3.2. Reagents
3.3. General Procedures
3.3.1. Fluorescence Quenching Experiments
3.3.2. Ionic Strength Experiments
3.3.3. KI Quenching Experiments
3.3.4. EB Competition Experiments
3.3.5. Circular Dichroism Spectra Experiments
3.3.6. Transient Fluorescence Experiments
3.3.7. PAGE Experiments
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
- Sample Availability: Not available.
References
- Yates, K.; Davies, I.M.; Webster, L.; Pollard, P.; Lawton, L.; Moffat, C.F. Application of silicone rubber passive samplers to investigate the bioaccumulation of PAHs by Nereis virens from marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3351–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.J.; Han, I.K.; Hu, M.; Shao, M.; Zhang, J.F.; Tang, X.Y. Personal exposure to particulate PAHs and anthraquinone and oxidative DNA damages in humans. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvrevik, J.; Arlt, V.M.; Øya, E.; Nagy, E.; Mollerup, S.; Phillips, D.H.; Låg, M.; Holme, J.A. Differential effects of nitro-PAHs and amino-PAHs on cytokine and chemokine responses in human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2010, 242, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Costas-Mora, I.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. Rapid screening of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in waters by directly suspended droplet microextraction-microvolume fluorospectrometry. Talanta 2012, 89, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; Wei, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Spectroscopy and Speciation Studies on the Interactions of Aluminum (III) with Ciprofloxacin and β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate in Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2012, 17, 9379–9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdine, G.; Fichet, D.; Louis, M.; Lemoine, S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediment and oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae) from mangrove of Guadeloupe: Levels, bioavailability, and effects. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2012, 79, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egistelli, L.; Chichiarelli, S.; Gaucci, E.; Eufemi, M.; Schinina, M.E.; Giorgi, A.; Lascu, I.; Turano, C.; Giartosio, A.; Cervoni, L. IFI16 and NM23 Bind to a Common DNA Fragment Both in the P53 and the cMYC Gene Promoters. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 106, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. Structure-function-rescue: the diverse nature of common p53 cancer mutants. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2226–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Miething, C.; Dickins, R.A.; Hernando, E.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature 2007, 445, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigni, R.; Bossa, C. Mechanisms of Chemical Carcinogenicity and Mutagenicity: A Review with Implications for Predictive Toxicology. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2507–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Zipursky, S.L. Matsudaira,Molecular Cell Biology, 4th ed; Freeman,W. H. & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Mora, R.C.; Aranda-Anzaldo, A. Reorganization of the DNA-Nuclear Matrix Interactions in a 210 kb Genomic Region Centered on c-myc After DNA Replication In Vivo. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 113, 2451–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Uppstad, H.; Osnes, G.H.; Cole, K.J.; Phillips, D.H.; Haugen, A.; Mollerup, S. Sex differences in susceptibility to PAHs is an intrinsic property of human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Lung Cancer 2011, 71, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Wang, D.; Mao, C.; Ou, S.; Lian, Z.; Huang, S.; Lin, Q.; Ding, R.; She, J. Preliminary study of children’s exposure to PAHs and its association with 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine in Guangzhou, China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laali, K.K.; Chun, J.H.; Okazaki, T. Electrophilic chemistry of Thia-PAHs: Stable carbocations (NMR and DFT), S-Alkylated onium salts, model electrophilic substitutions (Nitration and bromination), and mutagenicity assay. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 8383–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.A.; Ahmed, S.R.; Jayaram, B. A molecular thermodynamic view of DNA-drug interactions: a case study of 25 minor-groove binders. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 429, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.H.; Yeo, G.Y.; Jang, K.J.; Lee, D.J.; Noh, S.G.; Cho, T.S. A Novel Topoisomerase Inhibitor, Daurinol, Suppresses Growth of HCT116 Cells with Low Hematological Toxicity Compared to Etoposide. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, K.A.; Post, P.L.; Hahn, K.M.; Taylor, D.L. A fluorescent protein biosensor of myosin II regulatory light chain phosphorylation reports a gradient of phosphorylated myosin II in migrating cells. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Struct. 1995, 24, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, B.P.; Seetharamappa, J. Mechanism of interaction of vincristine sulphate and rifampicin with bovine serum albumin: A spectroscopic study. J. Chem. Sci. 2005, 117, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, M. Static quenching of bovine serum albumin conjugated with small size CdS nanocrystalline quantum dots. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternack, R.F.; Brigandi, R.A.; Abrams, M.J.; Williams, A.P.; Gibbs, E. Interactions of porphyrins and metalloporphyrins with single- stranded poly(dA). J. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 4483–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.V.; Asuncion, E.H. DNA binding studies and site selective fluorescence sensitization of an anthryl probe. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 6, 470–472. [Google Scholar]
- Karlovsky, P.; Decock, A.W. Buoyant density of DNA-Hoechst 33258 (bisbenzimide) complexes in CsCl gradients: Hoechst 33258 binds to single AT base pairs. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 194, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, K.D.; Dervan, P.B. Molecular recognition of B-DNA by Hoechst 33258. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 4825–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaugea, T.; Turelb, I.; Sletten, E. Interaction between ciprofloxacin and DNA mediated by Mg2+-ions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2002, 239, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, M.S.; Boman, N.L.; Wiseman, D.J.; Saxon, D.; Sutton, K.; Wong, K.F.; Logan, P.; Hope, M.J. Antibacterial efficacy against an in vivo Salmonella typhimurium infection model and pharmacokinetics of a liposomal ciprofloxacin formulation. Antimicr. Agents. Ch. 1998, 42, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, S.; Flasher, D.; Friend, D.S.; Nassos, P.D.; Yajko, W.K.; Hadley, N. Efficacies of liposome-encapsulated streptomycin and ciprofloxacin against Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex infections in human peripheral blood monocyte/macrophages. Antimicr. Agents. Ch. 1992, 36, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroslav, K.; Iva, K.; Daniel, R.; Michaela, V. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.; Arya, D.P. Recognition of B-DNA by Neomycin−Hoechst 33258 Conjugates. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10217–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Fei, X.C.; Wang, S.L.; Gao, H.W. Binding of bisphenol A and acrylamide to BSA and DNA: insights into the comparative interactions of harmful chemicals with functional biomacromolecules. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenmark, S. Induced circular dichroism by chiral molecular interaction. Chirality 2003, 15, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Meneni, S.; Cho, B.P. Induced circular dichroism characteristics as conformational probes for carcinogenic aminofluorene-DNA adducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpolícková, J.; Beranová, L.; Stepánek, M.; Benda, A.; Procházka, K.; Hof, M. Fluorescence Lifetime Correlation Spectroscopy Reveals Compaction Mechanism of 10 and 49 kbp DNA and Differences between Polycation and Cationic Surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16823–16829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.G.; Wang, Z.B. Fluorescence Analysis, 3rd ed; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, A.; Chakravorti, S. Modification of a Styryl dye binding mode with calf thymus DNA in vesicular medium: From minor groove to intercalative. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 5226–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benninger, R.K.P.; Hofmann, O.; Onfelt, B.; Munro, I.; Dunsby, C.; Davis, D.M.; Neil, M.A.A.; French, P.M.W.; de Mello, A.J. Fluorescence-lifetime imaging of DNA-dye interactions within continuous-flow microfluidic systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 2228–2231. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Marriott, G. Analysis of protein interactions using fluorescence technologies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.H.; Valdez, J.G.; Steinkamp, J.A.; Crissman, H.A. Fluorescence lifetime-based discrimination and quantification of cellular DNA and RNA with phase-sensitive flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2003, 52A, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneta, T.; Ogura, T.; Yamato, S.; Imasaka, T. Fluorescence lifetime-based discrimination and quantification of cellular DNA and RNA with phase-sensitive flow cytometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.A.; Munde, M.; Wang, S.; Rettig, M.; Le, V.; Machha, V.; Wilson, W.D. Complexity in the binding of minor groove agents: Netropsin has two thermodynamically different DNA binding modes at a single site. Nuleic Acids Res. 2011, 22, 9649–9658. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Li, H.; Yang, X. Studies on the Interaction Mechanism of Pyrene Derivatives with Human Tumor-Related DNA. Molecules 2012, 17, 14159-14173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214159
Li L, Lu J, Xu C, Li H, Yang X. Studies on the Interaction Mechanism of Pyrene Derivatives with Human Tumor-Related DNA. Molecules. 2012; 17(12):14159-14173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214159
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Jia Lu, Chongzheng Xu, Huihui Li, and Xiaodi Yang. 2012. "Studies on the Interaction Mechanism of Pyrene Derivatives with Human Tumor-Related DNA" Molecules 17, no. 12: 14159-14173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214159
APA StyleLi, L., Lu, J., Xu, C., Li, H., & Yang, X. (2012). Studies on the Interaction Mechanism of Pyrene Derivatives with Human Tumor-Related DNA. Molecules, 17(12), 14159-14173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214159