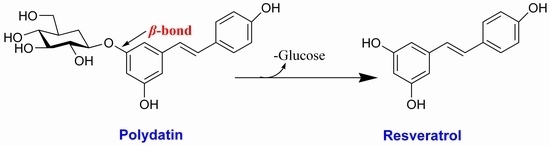
Highly Efficient Biotransformation of Polydatin to Resveratrol by Snailase Hydrolysis Using Response Surface Methodology Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
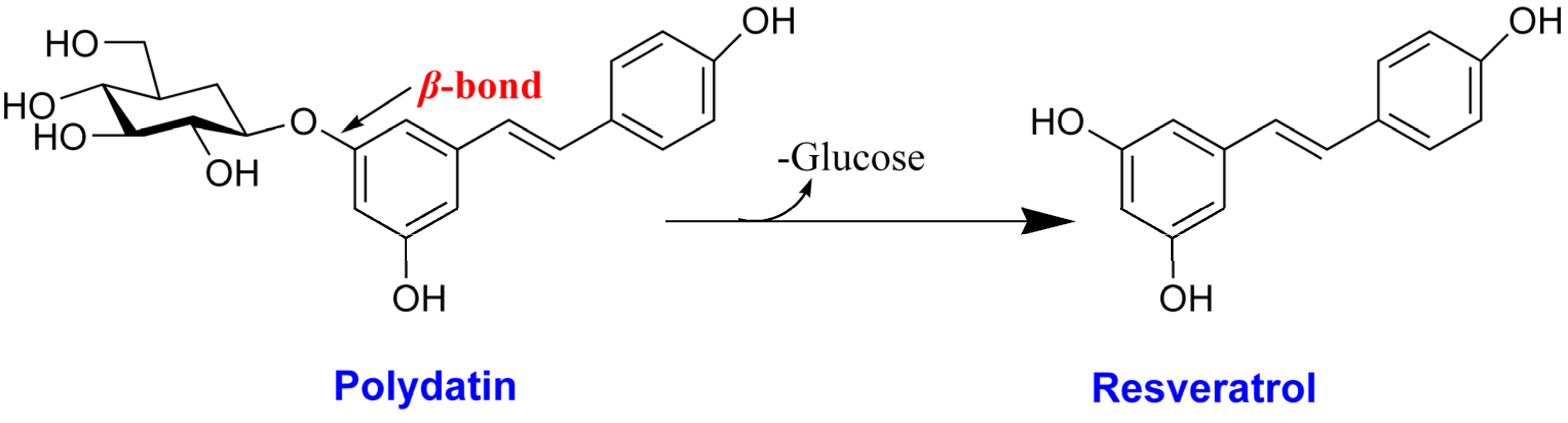
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Model Fitting
| Run | Coded variables levels | Y | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RV (mg/mL) | |||||
| X1, Reaction temperature (°C) | X2, Enzyme load (%) | X3, Reaction time (min) | Actual | Predicted | |
| 1 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 105.00 | 9.50 | 10.10 |
| 2 | 70.00 | 2.00 | 105.00 | 8.82 | 8.81 |
| 3 | 40.00 | 10.00 | 105.00 | 8.64 | 8.65 |
| 4 | 70.00 | 10.00 | 105.00 | 12.06 | 11.47 |
| 5 | 40.00 | 6.00 | 30.00 | 11.70 | 11.46 |
| 6 | 70.00 | 6.00 | 30.00 | 12.13 | 12.50 |
| 7 | 40.00 | 6.00 | 180.00 | 11.88 | 11.52 |
| 8 | 70.00 | 6.00 | 180.00 | 11.77 | 12.01 |
| 9 | 55.00 | 2.00 | 30.00 | 10.08 | 9.72 |
| 10 | 55.00 | 10.00 | 30.00 | 9.61 | 9.84 |
| 11 | 55.00 | 2.00 | 180.00 | 9.25 | 9.02 |
| 12 | 55.00 | 10.00 | 180.00 | 9.76 | 10.11 |
| 13 | 55.00 | 6.00 | 105.00 | 13.39 | 13.06 |
| 14 | 55.00 | 6.00 | 105.00 | 13.36 | 13.06 |
| 15 | 55.00 | 6.00 | 105.00 | 12.78 | 13.06 |
| 16 | 55.00 | 6.00 | 105.00 | 12.85 | 13.06 |
| 17 | 55.00 | 6.00 | 105.00 | 12.92 | 13.06 |
| Source | SS | DF | MS | F-value | Prob > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 43.27 | 9.00 | 4.81 | 18.89 | <0.0001 | significant |
| Residual | 1.78 | 7.00 | 0.25 | |||
| Lack of fit | 1.44 | 3.00 | 0.48 | 5.69 | 0.0063 | insignificant |
| Pure error | 0.34 | 4.00 | 0.08 |
 was the most significant at the level of p < 0.0001, the others (
was the most significant at the level of p < 0.0001, the others (  ) were significant at the level of P<0.01. As for interaction quadratic parameters, the interaction effect of X1X2 was significant and that of X1X3 and X2X3 was insignificant (p > 0.01). Predicted response Y for the yield of RV could be expressed by the following second-order polynomial equation in term of coded values:
) were significant at the level of P<0.01. As for interaction quadratic parameters, the interaction effect of X1X2 was significant and that of X1X3 and X2X3 was insignificant (p > 0.01). Predicted response Y for the yield of RV could be expressed by the following second-order polynomial equation in term of coded values:

| Variables | DF | SS | MS | F-values | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 4.60 | 0.0692 |
| X2 | 1 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 2.86 | 0.1348 |
| X3 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.37 | 0.5639 |
| X1X2 | 1 | 4.21 | 4.21 | 16.55 | 0.0048 |
| X1X3 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.6091 |
| X2X3 | 1 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.93 | 0.3674 |
 | 1 | 1.29 | 1.29 | 5.09 | 0.0588 |
 | 1 | 31.85 | 31.85 | 125.16 | <0.0001 |
 | 1 | 1.70 | 1.70 | 6.68 | 0.0362 |
2.2. Analysis of Response Surface
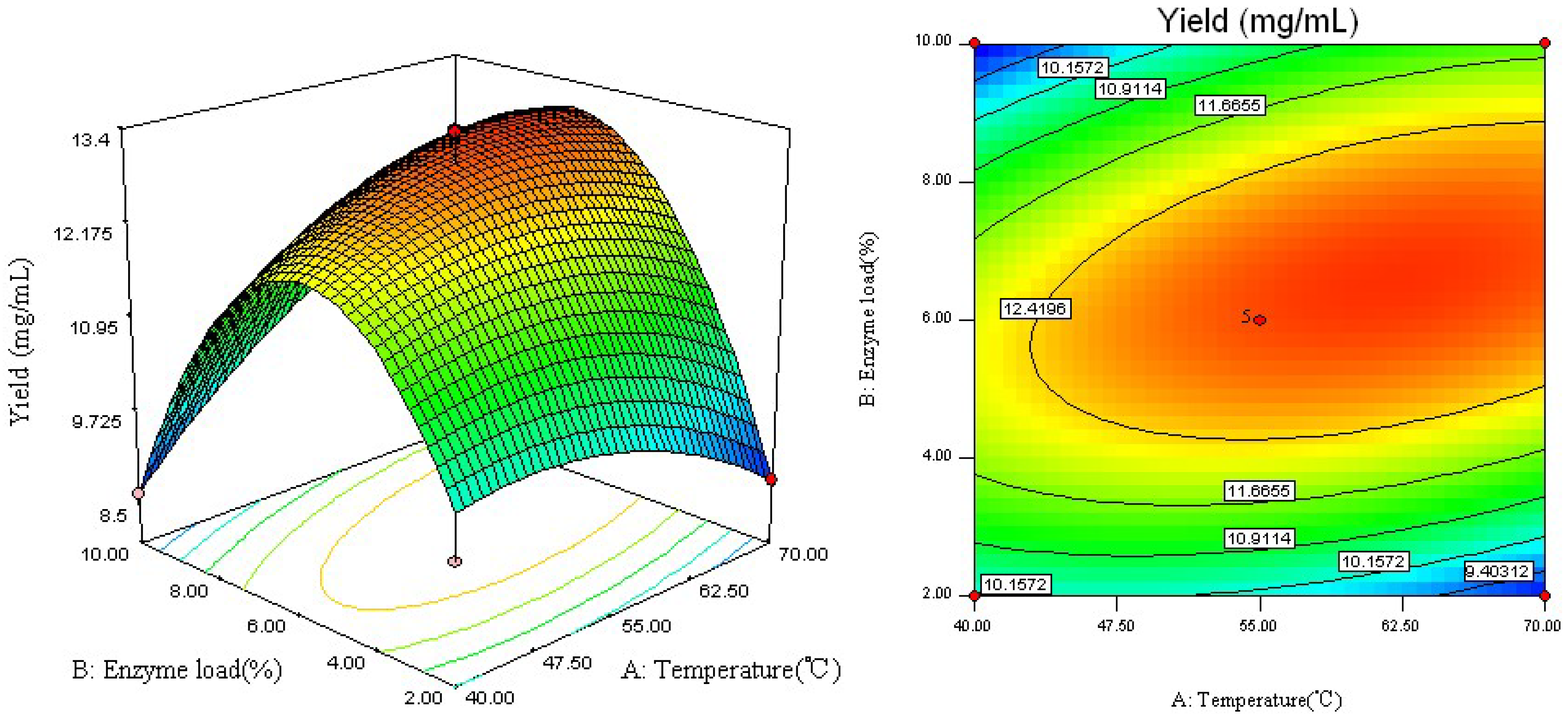
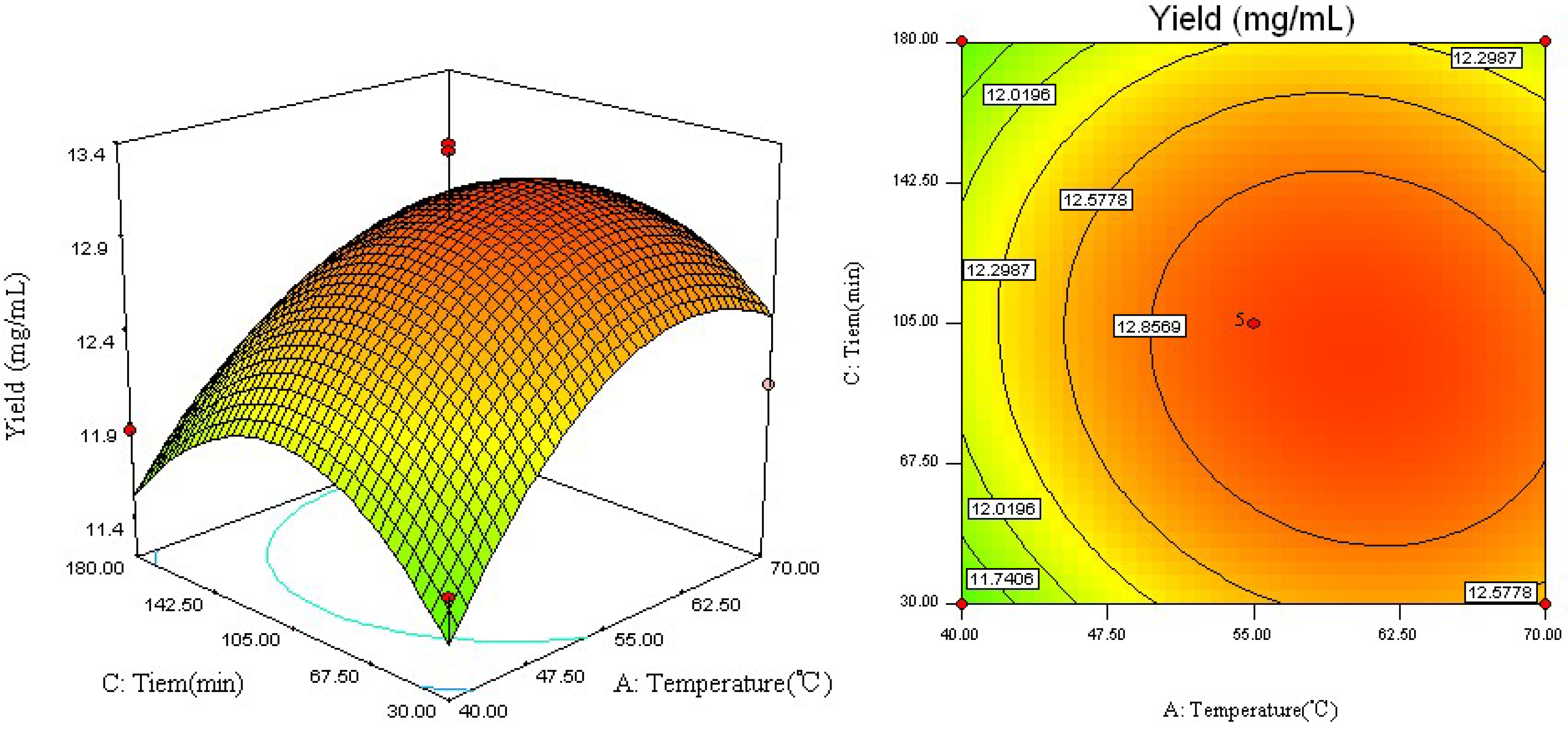
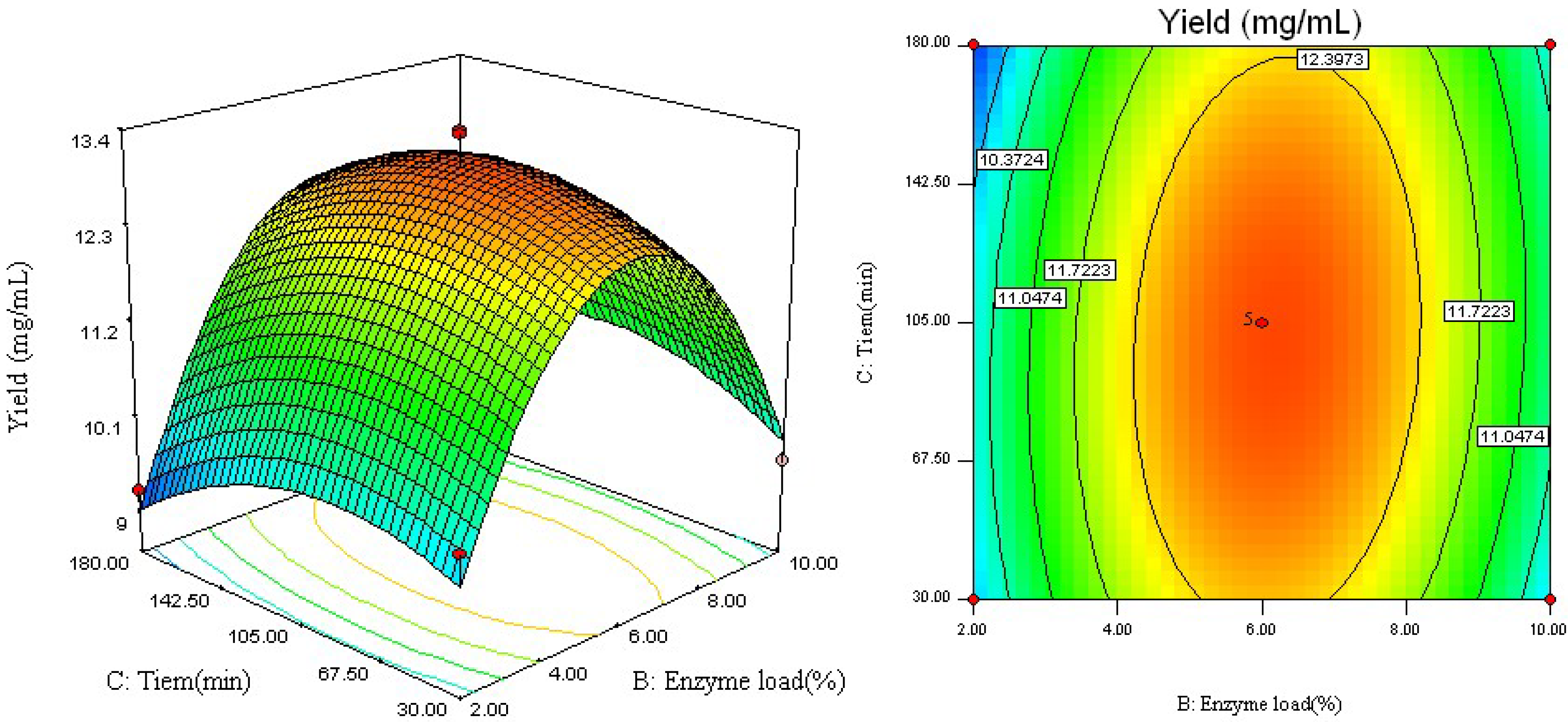
2.3. Optimal Conditions and Model Verification
| Reaction temperature (°C) | Enzyme load (%) | Reaction time (min) | Yield of RV (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimum conditions | 62.35 | 6.57 | 96.76 | 13.18 (predicted) |
| Modified conditions | 62.0 | 6.6 | 96.0 | 12.88 ± 0.27 (actual) |
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Isolation and Purification of Polydatin
3.3. Enzymatic Preparation of RV from Polydatin
3.4. HPLC analysis of the Bioconversion Process
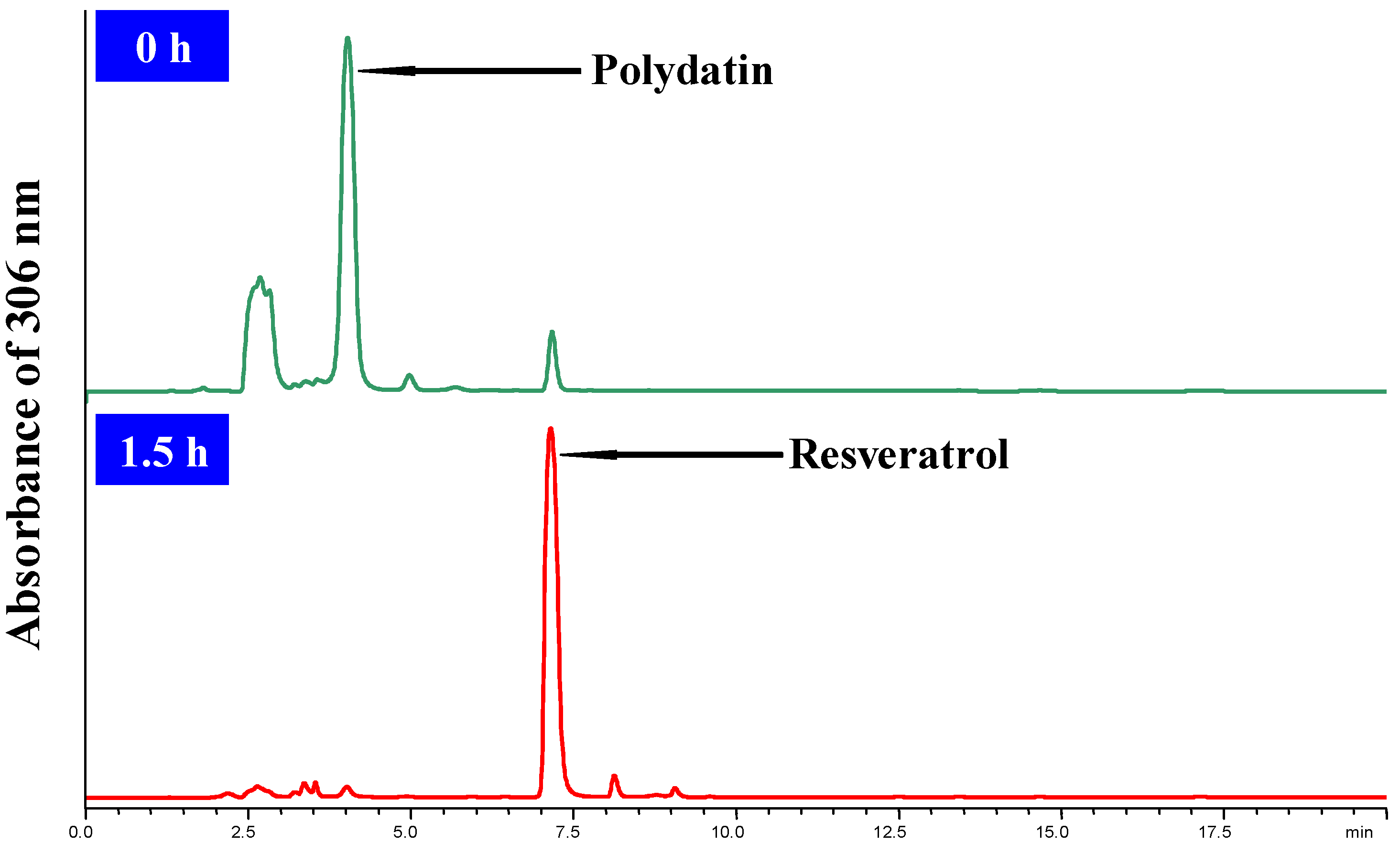
3.5. Experimental Design

3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakata, R.; Takahashi, S.; Inoue, H. Recent advances in the study on resveratrol. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V. Perspectives for production and application of resveratrol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 9, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marier, J.F.; Vachon, P.; Gritsas, A.; Zhang, J.; Moreau, J.P.; Ducharme, M.P. Metabolism and disposition of resveratrol in rats: extent of absorption, glcuronidation, and enterohepatic recirculation evidenced by a linked-rat model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 30, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwumah, Y.; Walker, L.; Vogler, B.; Verghese, M. In vitro absorption of dietary trans-resveratrol from boiled and roasted peanuts in Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12323–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T.; Hsieh, F.; DeLegge, M.H.; Oatis, J.E.; Walle, U.K. High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Das, D.K. Resveratrol and cardiovascular health. Mol. Aspects Med. 2010, 31, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Sanabria, S.E.; Robertson, I.M.; Sykes, B.D. Structure of trans-resveratrol in complex with the cardiac regulatory protein troponin C. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D. Resveratrol and cancer prevention. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 7, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, Y.; Singh, R. Resveratrol and cellular mechanisms of cancer prevention. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibach, E.; Prus, E.; Bianchi, N.; Zuccato, C.; Breveglieri, G.; Salvatori, F.; Finotti, A.; di Lipucci, P.M.; Brognara, E., Lampronti; et al. Resveratrol: Antioxidant activity and induction of fetal hemoglobin in erythroid cells from normal donors and beta-thalassemia patients. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 974–982. [Google Scholar]
- Escote, X.; Miranda, M.; Menoyo, S.; Rodriguez-Porrata, B.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Jungwirth, H.; Madeo, F.; Cordero, R.R.; Mas, A.; Tinahones, F.; et al. Resveratrol induces antioxidant defence via transcription factor Yap1p. Yeast 2012, 29, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.M.; Waget, A.; Klopp, P.; Serino, M.; Vachoux, C.; Pechere, L.; Drucker, D.J.; Champion, S.; Barthelemy, S.; Barra, Y.; et al. Resveratrol increases glucose induced GLP-1 secretion in mice: a mechanism which contributes to the glycemic control. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.R.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, E.J. Resveratrol prevents streptozotocin-induced diabetes by inhibiting the apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cell and the cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Endocr. J. 2012, 59, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirino, A.; Takasuka, Y.; Nishi, A.; Kawabe, S.; Yamashita, H.; Kimoto, M.; Ito, H.; Tsuji, H. Analysis and functionality of major polyphenolic components of Polygonum cuspidatum (itadori). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2012, 58, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Marcella, Guiso.; Carolina, Marra.; Angela, Farina. A new efficient resveratrol synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Ye, L.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Shieh, C.J. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of the botanical dietary supplement resveratrol and other constituents of Polygonum cuspidatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Xiu, Z.L. Microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of piceid, resveratrol and emodin from Polygonum cuspidatum by ethanol/ammonium sulphate systems. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Yan, A.; Yang, X.; Cai, Y.; Chen, J. An optimum fermentation model established by genetic algorithm for biotransformation from crude polydatin to resveratrol. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.X.; Dong, Y.S.; Zhang, D.J.; Xiu, Z.L. Biotransformation of piceid in Polygonum cuspidatum to resveratrol by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnez, E.; Jeandet, P.; Clément, C.; Courot, E. Bioproduction of resveratrol and stilbene derivatives by plant cells and microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Delaunois, B.; Aziz, A.; Donnez, D.; Vasserot, Y.; Cordelier, S.; Courot, E. Potential engineering of plants and yeast for the production of the biologically active hydroxystilbene, resveratrol. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 579089. [Google Scholar]
- Jeandet, P.; Vasserot, Y.; Chastang, T.; Courot, E. Engineering microbial cells for the biosynthesis of natural compounds of pharmaceutical significance. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 780145. [Google Scholar]
- Rabesiaka, M.; Rakotondramasy-Rabesiaka, L.; Mabille, I.; Porte, C.; Havet, J.L. Extraction of trans-resveratrol from red wine and optimization by response surface methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C.; Min, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Enzymatic transformation of the major ginsenoside Rb2 to minor compound Y and compound K by a ginsenoside-hydrolyzing beta-glycosidase from Microbacterium esteraromaticum. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, L.H.; Min, J.W.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Enzymatic biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to compound K by recombinant beta-glucosidase from Microbacterium esteraromaticum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3776–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.L. Purification of a ginsenoside-Rb1 hydrolase from Helix snailase. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2005, 21, 929–933. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.Y.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Ji, X.J.; Lu, J.; Tong, Q.; Wei, P.; Cong, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, H. Enzymatic hydrolysis and extraction of arachidonic acid rich lipids from Mortierella alpina. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6088–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, L.C.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.N.; Liang, J.; Wang, H. Response surface methodology to optimize enzymatic preparation of deapio-platycodin d and platycodin d from radix platycodi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4089–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, Y.N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, Y.J.; Gu, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. Snailase preparation of ginsenoside M1 from protopanaxadiol-type ginsenoside and their protective effects against CCl4-induced chronic hepatotoxicity in mice. Molecules 2011, 16, 10093–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Aybastıer, O.; Işık, E. Optimisation of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of antioxidant compounds from Artemisia absinthium using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qu, H.; Mao, G.; Zhao, T.; Li, F.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X. Optimization of subcritical water extraction of polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa using response surface methodology. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2013, 9, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.-C.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.-X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J. Highly Efficient Biotransformation of Polydatin to Resveratrol by Snailase Hydrolysis Using Response Surface Methodology Optimization. Molecules 2013, 18, 9717-9726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089717
Wang Z, Zhao L-C, Li W, Zhang L-X, Zhang J, Liang J. Highly Efficient Biotransformation of Polydatin to Resveratrol by Snailase Hydrolysis Using Response Surface Methodology Optimization. Molecules. 2013; 18(8):9717-9726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089717
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zi, Li-Chun Zhao, Wei Li, Lian-Xue Zhang, Jing Zhang, and Jian Liang. 2013. "Highly Efficient Biotransformation of Polydatin to Resveratrol by Snailase Hydrolysis Using Response Surface Methodology Optimization" Molecules 18, no. 8: 9717-9726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089717