Neuroprotective, Anti-Amyloidogenic and Neurotrophic Effects of Apigenin in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
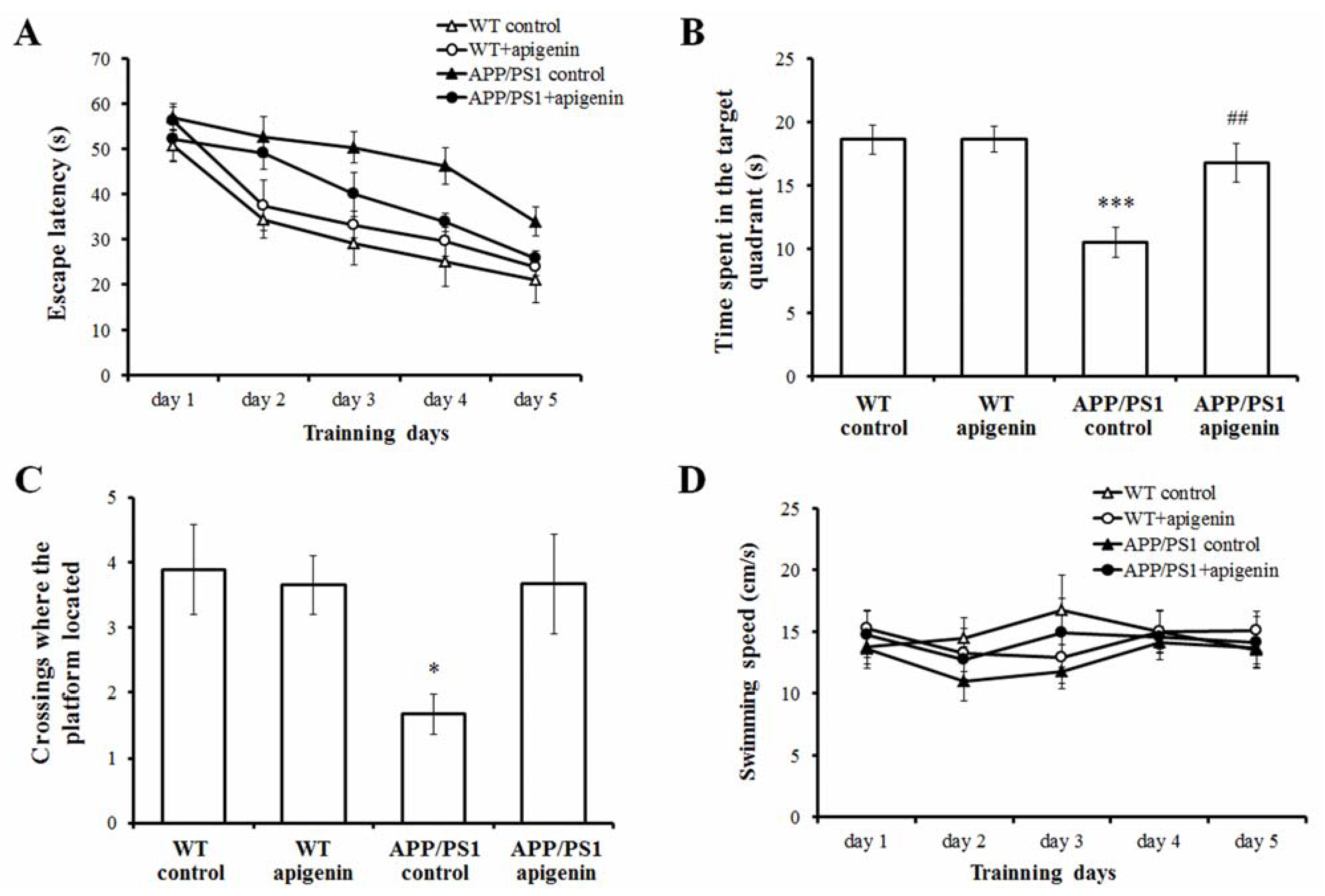
2.1. Apigenin Treatment Prevents Learning and Memory Deficits in APP/PS1 Mice
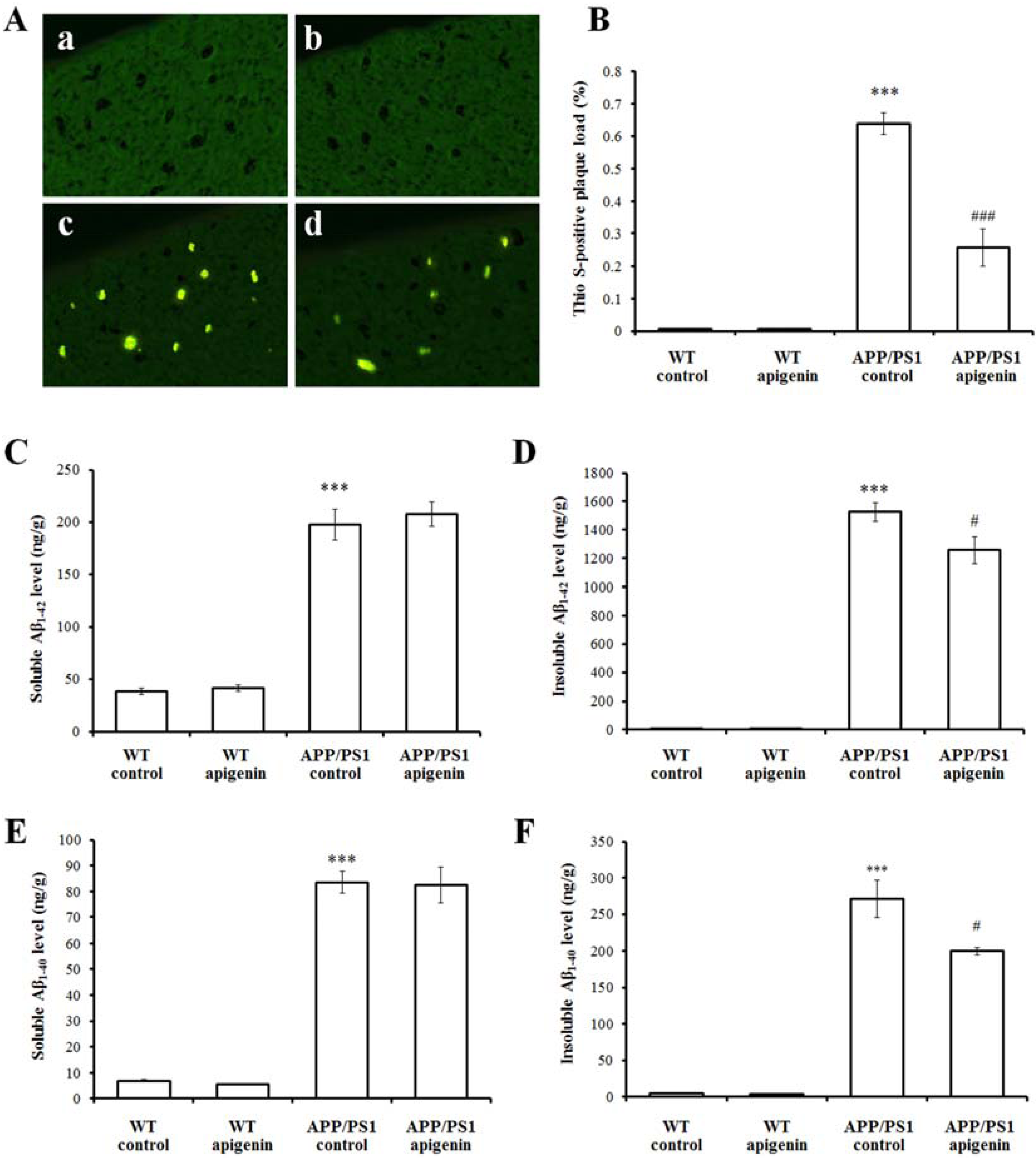
2.2. Apigenin Treatment Relieves Aβ Burden in APP/PS1 Mice
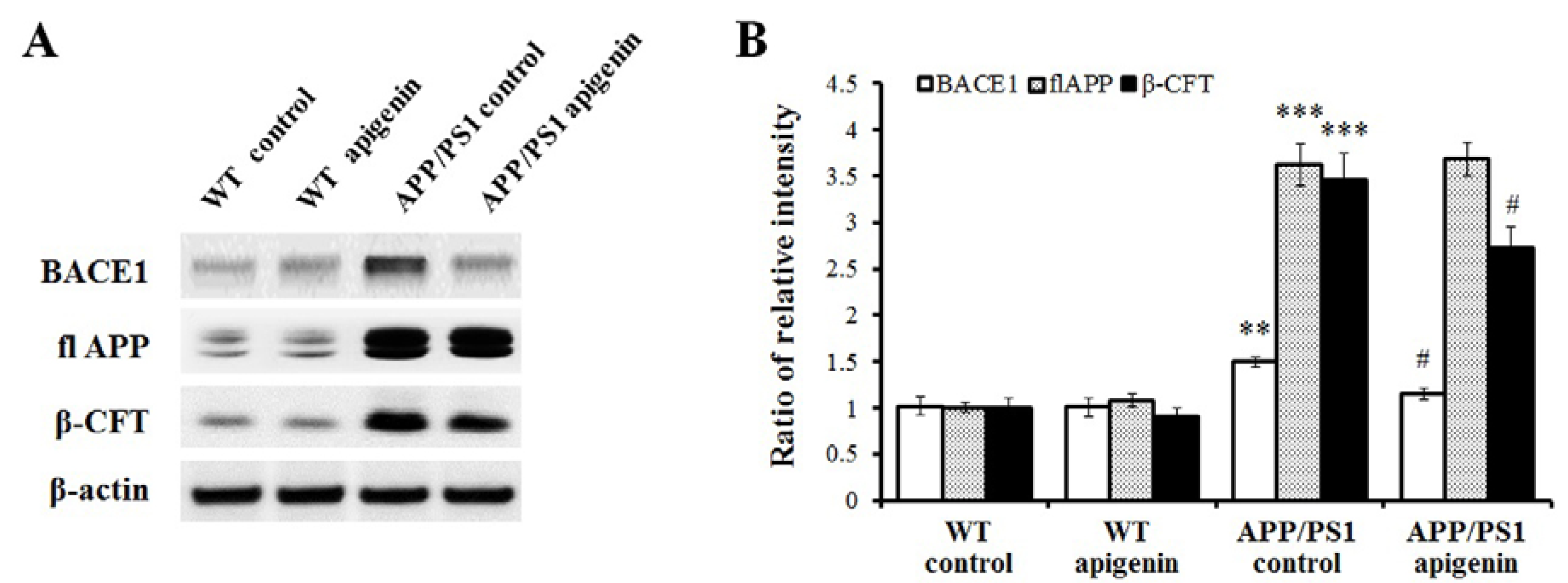
2.3. Apigenin Treatment Reduces BACE1 Level and β-Amyloidogenesis in APP/PS1 Mice
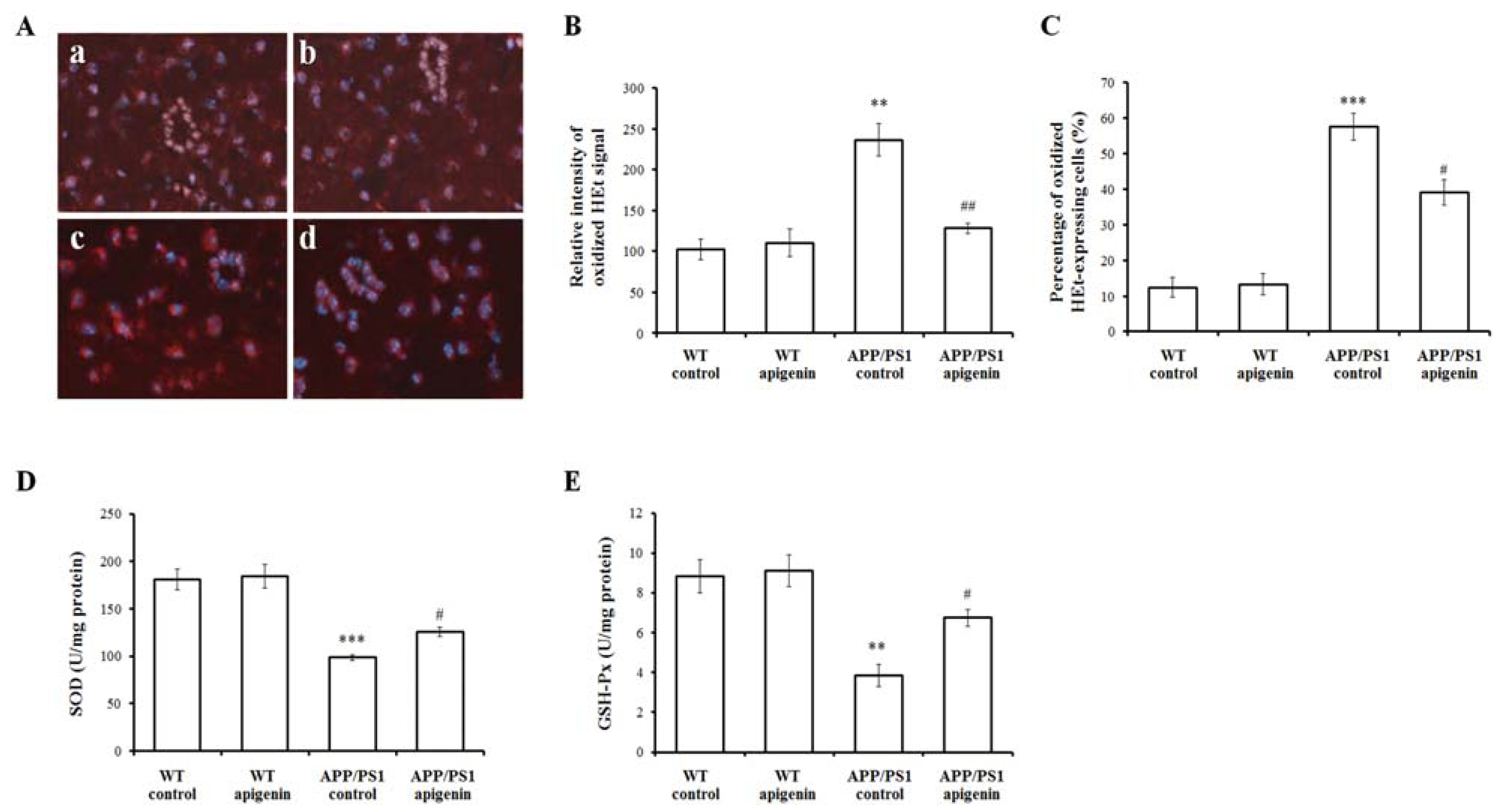
2.4. Apigenin Treatment Decreases Oxidative Stress in APP/PS1 Mice
2.5. Apigenin Treatment Restores ERK/CREB/BDNF Pathway of Cerebral Cortex in APP/PS1 Mice

3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents
3.2. APP/PS-1 Transgenic Mice and Drug Treatment
3.3. Morris Water Maze Performance
3.4. Thio S Staining for Aβ Deposition Measurement
3.5. Detection of Oxyradicals in Situ
3.6. ELISA Analyses for Cerebral Soluble and Insoluble Aβ Levels and BDNF Contents
3.7. Cerebral Oxidative Stress Measurement
3.8. Western Blot Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe, D.J. Normal and abnormal biology of the beta-amyloid precursor protein. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1994, 17, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2004, 430, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, K.S.; Knox, J.; Inglis, J.; Bernard, A.; Martin, S.J.; Justice, A.; McConlogue, L.; Games, D.; Freedman, S.B.; et al. A learning deficit related to age and beta-amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2000, 408, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.M.; Klyubin, I.; Fadeeva, J.V.; Cullen, W.K.; Anwyl, R.; Wolfe, M.S.; Rowan, M.J.; Selkoe, D.J. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid beta protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 2002, 416, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.; Su, J.H.; Cotman, C.W. DNA damage and apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: colocalization with c-Jun immunoreactivity, relationship to brain area, and effect of postmortem delay. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar]
- Behl, C.; Davis, J.B.; Lesley, R.; Schubert, D. Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid beta protein toxicity. Cell 1994, 77, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busciglio, J.; Lorenzo, A.; Yeh, J.; Yankner, B.A. Beta-amyloid fibrils induce tau phosphorylation and loss of microtubule binding. Neuron 1995, 14, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Zemianek, J.; Shea, T.B. Rapid, Reversible impairment of synaptic signaling in cultured cortical neurons by exogenously-applied amyloid-β. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 35, 395–402. [Google Scholar]
- Lue, L.F.; Kuo, Y.M.; Roher, A.E.; Brachova, L.; Shen, Y.; Sue, L.; Beach, T.; Kurth, J.H.; Rydel, R.E.; Rogers, J. Soluble amyloid beta peptide concentration as a predictor of synaptic change in Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Aboukhatwa, M.A.; Lei, D.L.; Manaye, K.; Khan, I.; Luo, Y. Anti-depressant natural flavonols modulate BDNF and beta amyloid in neurons and hippocampus of double Tg AD mice. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Thornton, P.L.; Balazs, R.; Cotman, C.W. Beta-amyloid-(1–42) impairs activity-dependent cAMP-response element-binding protein signaling in neurons at concentrations in which cell survival Is not compromised. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17301–17306. [Google Scholar]
- Cotman, C.W. The role of neurotrophins in brain aging: a perspective in honor of Regino Perez-Polo. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.L.; Liu, B.; Qin, H.L.; Lee, S.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Du, G.H. Anti-influenza virus activities of flavonoids from the medicinal plant Elsholtzia rugulosa. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.C.; Hong, J.T.; Oh, K.W. Protection of apigenin against kainate-induced excitotoxicity by anti-oxidative effects. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Markakis, E.A.; Palmer, T.D.; Randolph-Moore, L.; Rakic, P.; Gage, F.H. Novel neuronal phenotypes from neural progenitor cells. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2886–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, L.; Sun, H.J.; Yan, X.; Sun, X.F.; Li, J.G.; Bian, Y.; Chu, Y.; Liu, Q.S. Apigenin isolated from the medicinal plant Elsholtzia rugulosa prevents β-amyloid 25–35-Induces toxicity in rat cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 4005–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Lan, X.; Ying, J.; Du, G. The flavonoid apigenin protects brain neurovascular coupling against amyloid-beta25-35-induced toxicity in mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 24, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, F.N; Huang, T.F.; Teng, C.M. Vasodilatory action mechanisms of apigenin isolated from Apium graveolens in rat thoracic aorta. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1115, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losi, G.; Puia, G.; Garzon, G.; de Vuono, M.C.; Baraldi, M. Apigenin modulates GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission in cultured cortical neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 502, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Fa, X.Z. Apigenin attenuates copper-mediated β-amyloid neurotoxicity through antioxidation, mitochondrion protection and MAPK signal inactivation in an AD cell model. Brain Res. 2013, 1492, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Yoshiike, Y.; Takashima, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Naiki, H.; Yamada, M. Potent anti-amyloidogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects of polyphenols in vitro: implications for the prevention and therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2003, 7, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Nitta, A.; Itoh, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Nabeshima, T. β-Amyloid protein-induced Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 170, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Issa, A.M.; Seto, D.; Auld, D.S.; Collier, B.; Quirion, R. Amyloid β-peptide inhibits high-affinity choline uptake and acetylcholine release in rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson, E.M.; Lee, J.M.; Dong, X.W.; Hejna, M.J.; Lorens, S.A. Bilateral injections of amyloid-β 25–35 into the amygdala of young Fischer rats: behavioral, neurochemical, and time dependent histopathological effects. Neurobiol. Aging. 1997, 18, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, V.; Moussaoui, S.; Czech, C.; Touchet, N.; Bonici, B.; Planche, M.; Canton, T.; Jedidi, I.; Gohin, M.; Wirths, O.; et al. Time sequence of maturation of dystrophic neurites associated with Abeta deposits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 184, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Slunt, H.H.; Ratovitski, T.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Borchelt, D.R. Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS: A comparison of strategies. Biomol. Eng. 2001, 17, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchese, F.; Liu, S.; Battaglia, F.; Walter, S.; Mathews, P.M.; Arancio, O. Progressive age-related development of Alzheimer-like pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.S.; Singh, V.P.; Satyanarayan, P.S.; Jain, N.K.; Singh, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Protective effect of flavonoids against aging- and lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in mice. Pharmacology 2003, 69, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Qiao, A.; Wang, Z.; Goodwin, J.S.; Lee, E.S.; Block, M.L.; Allsbrook, M.; McDonald, M.P.; Fan, G.H. Retinoic acid attenuates beta-amyloid deposition and rescues memory deficits in an Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11622–11634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miners, J.S.; Morris, S.; Love, S.; Kehoe, P.G. Accumulation of insoluble amyloid-β in down’s syndrome is associated with increased BACE-1 and neprilysin activities. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, R.; Yazdanparast, R.; Bahramikia, S. Apigenin reduces human insulin fibrillation in vitro and protects SK-N-MC cells against insulin amyloids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60C, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.L.; Vassar, R. The role of amyloid precursor protein processing by BACE1, the beta-secretase, in Alzheimer disease pathophysiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 29621–29625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Browne, A.; Divito, J.R.; Stevenson, J.A.; Romano, D.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Z.; Tanzi, R.E. Amyloid-beta production via cleavage of amyloid-beta protein precursor is modulated by cell density. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 22, 683–984. [Google Scholar]
- Shimmyo, Y.; Kihara, T.; Akaike, A.; Niidome, T.; Sugimoto, H. Flavonols and flavones as BACE-1 inhibitors: Structure-activity relationship in cell-free, cell-based and in silico studies reveal novel pharmacophore features. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhong, Z.; Lindholm, K.; Berning, L.; Lee, W.; Lemere, C.; Staufenbiel, M.; Li, R.; Shen, Y. Deletion of tumor necrosis factor death receptor inhibits amyloid beta generation and prevents learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s mice. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rithidech, K.N.; Tungjai, M.; Reungpatthanaphong, P.; Honikel, L.; Simon, S.R. Attenuation of oxidative damage and inflammatory responses by apigenin given to mice after irradiation. Mutat. Res. 2012, 749, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Huang, K.M. In vitro anti-inflammatory effect of apigenin in the Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratico, D.; Sung, S. Lipid peroxidation and oxidative imbalance: early functional events in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2004, 6, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Pratico, D.; Uryu, K.; Leight, S.; Trojanoswki, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Increased lipid peroxidation precedes amyloid plaque formation in an animal model of Alzheimer amyloidosis. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4183–4187. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, M.A.; Ehmann, W.D.; Butler, S.M.; Markesbery, W.R. Elevated thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and antioxidant enzyme activity in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1995, 45, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Perry, G.; Richey, P.L.; Sayre, L.M.; Anderson, V.E.; Beal, M.F.; Kowall, N. Oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s. Nature 1996, 382, 120–121. [Google Scholar]
- Markesbery, W.R. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.; Anrather, J.; Zhou, P.; Frys, K.; Pitstick, R.; Younkin, S.; Carlson, G.A.; Iadecola, C. NADPH-oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species mediate the cerebrovascular dysfunction induced by the amyloid beta peptide. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.N.; Chi, C.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, C.F.; Shiao, Y.J. The neuroprotective effects of phytoestrogens on amyloid beta protein-induced toxicity are mediated by abrogating the activation of caspase cascade in rat cortical neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5287–5295. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.M.; Chen, C.T.; Lee, H.H.; Lin, J.K. Prevention of cellular ROS damage by isovitexin and related flavonoids. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyürek, M.; Bektaşoğlu, B.; Güçlü, K.; Apak, R. Measurement of xanthine oxidase inhibition activity of phenolics and flavonoids with a modified cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 636, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhou, D.; Bai, X.Y.; Zhou, W.L.; Huang, C.; Song, J.K.; Meng, F.R.; Wu, C.X.; Li, L.; et al. Quercetin protects against the Aβ(25-35)-induced amnesic injury: involvement of inactivation of rage-mediated pathway and conservation of the NVU. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carew, T.J. Molecular enhancement of memory formation. Neuron 1996, 16, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, A.; Pittenger, C.; Kandel, E.R. CREB, Memory enhancement and the treatment of memory disorders: promises, pitfalls and prospects. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2003, 7, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.A.; Impey, S.; Storm, D.R.; Stryker, M.P. CRE-mediated gene transcription in neocortical neuronal plasticity during the developmental critical period. Neuron 1999, 22, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Cammarota, M.; Igaz, L.M.; Bevilaqua, L.R.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Persistence of long-term memory storage requires a late protein synthesis- and BDNF-dependent phase in the hippocampus. Neuron 2007, 53, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldt, S.A.; Stanek, L.; Chhatwal, J.P.; Ressler, K.J. Hippocampus-specific deletion of BDNF in adult mice impairs spatial memory and extinction of aversive memories. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, W.J.; Alonso, M.; Bramham, C.R.; Pozzo-Miller, L.D. From acquisition to consolidation: on the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in hippocampal-dependent learning. Learn Mem. 2002, 9, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Balazs, R.; Thornton, P.L.; Cotman, C.W. Beta-amyloid peptide at sublethal concentrations downregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor functions in cultured cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6799–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, H.; Feng, N.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. L-3-n-butylphthalide reduces tau phosphorylation and improves cognitive deficits in AβPP/PS1-Alzheimers transgenic mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 29, 379–391. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compound apigenin are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Wang, J.-L.; Liu, R.; Li, X.-X.; Li, J.-F.; Zhang, L. Neuroprotective, Anti-Amyloidogenic and Neurotrophic Effects of Apigenin in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Molecules 2013, 18, 9949-9965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089949
Zhao L, Wang J-L, Liu R, Li X-X, Li J-F, Zhang L. Neuroprotective, Anti-Amyloidogenic and Neurotrophic Effects of Apigenin in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Molecules. 2013; 18(8):9949-9965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089949
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Le, Jun-Li Wang, Rui Liu, Xiao-Xu Li, Jian-Fei Li, and Lu Zhang. 2013. "Neuroprotective, Anti-Amyloidogenic and Neurotrophic Effects of Apigenin in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model" Molecules 18, no. 8: 9949-9965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089949
APA StyleZhao, L., Wang, J.-L., Liu, R., Li, X.-X., Li, J.-F., & Zhang, L. (2013). Neuroprotective, Anti-Amyloidogenic and Neurotrophic Effects of Apigenin in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Molecules, 18(8), 9949-9965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089949



