Discovery of New Imidazole Derivatives Containing the 2,4-Dienone Motif with Broad-Spectrum Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction


2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry

2.2. Antifungal Susceptibility Assay
2.3. Conclusion of the Structure-Activity Relationship
2.4. Antibacterial Susceptibility Assay
| Compd. | R1 | R2 | Ar | Antifungal Activity MIC (μg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans ATCC 90028 | C. albicans 205 | C. albicans 64110 | C. krusei ATCC 6528 | C. tropicalis 657 | C. Glabrata 923 | C. Glabrata 186 | C. parapsilosis 27 | ||||
| 21 | H | 4-NO2 | phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 8 | 16 | >128 |
| 22 | H | 2-NO2 | phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 23 | H | 4-F | phenyl | 32 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 24 | H | 4-Br | phenyl | 2 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 25 | H | 4-MeO | phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 26 | H | 2,4-diCl | phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 27 | 4,5-diCl | 4-Br | phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 28 | 4-CH3 | 4-Br | phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 29 | H | 4-Br | 4-Br-phenyl | 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| 30 | H | 4-Br | 4-Cl-phenyl | 2 | >128 | >128 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 8 | >128 |
| 31 | H | 4-Br | 4-F-phenyl | 0.5 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 32 | H | 4-Br | 4-Me-phenyl | 2 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 33 | H | 4-Br | 4-MeO-phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 34 | H | 4-Br | 4-CN-phenyl | 2 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| 35 | H | 4-Br | 2,4-diCl-phenyl | 2 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 2 | >128 | >128 | 4 |
| 36 | H | 4-Br | 3,4-diF-phenyl | 2 | >128 | >128 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| 37 | H | 4-Br | 3-Cl-4-F-phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 32 | 32 | >128 |
| 38 | H | 4-Br | 3-Br-4-F-phenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 39 | H | 4-Br | 2,4-diF-phenyl | 0.5 | >128 | 64 | 64 | 16 | 32 | 32 | 8 |
| 40 | H | 4-Br | 2-NO2-4-F-phenyl | 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 41 | H | 4-Br | 1,1'-biphenyl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 42 | H | 4-Br | pyridin-2-yl | 4 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| 43 | H | 4-Br | 5-F-pyridin-2-yl | 4 | 32 | 64 | 8 | 2 | 64 | 64 | 1 |
| 44 | H | 4-Br | furan-2-yl | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 45 | 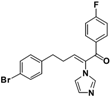 | 8 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 32 | ||
| 46 | 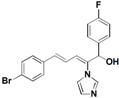 | 0.25 | 64 | 128 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 32 | 8 | ||
| Fluconazole | 0.5 | 8 | >128 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 32 | 1 | |||
| Compd. | Antibacterial Activity MIC (μg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecalis UA257 | Staphylococcus aureus UA1758 | Staphylococcus epidermidis UF843 | Klebsiella pneumonia UF222 | Escherichia coli UA45 | ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas aeruginosa UA1024 | Acinetobacter baumannii UA1037 | |
| 31 | >128 | 8 | 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 42 | >128 | 4 | 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| Amikacin | n.t.a | n.t.a | n.t.a | 2 | 8 | 3 | 3 | >256 |
| Cefoperazone | n.t.a | n.t.a | n.t.a | 8 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 32 |
| Vancomycin | 1.5 | 0.75 | 2 | n.t. a | n.t. a | n.t. a | n.t. a | n.t. a |
| Erythromycin | 2 | >256 | 24 | n.t. a | n.t. a | n.t. a | n.t. a | n.t. a |
2.5. Antifungal Activity in Vivo


| Compd. | ED50 (mg/kg/day) | 95% Confidence Interval (mg/kg/day) |
|---|---|---|
| 31 | 21.653 | 2.063–227.307 |
| 2.693 | 0.722–10.047 | |
| 42 | 6.812 | 3.232–14.359 |
| 6.944 | 2.698–17.871 | |
| Fluconazole | 100% a |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 18o
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 18r
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Bromoacetophenone Derivatives 19
| Compd. | Chemical Structure | Appearance Property, Yield and 1H-NMR |
|---|---|---|
| 19a |  | White solid; yield 72%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.99 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.62 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 4.47 (s, 2H). |
| 19k | 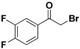 | Yellow solid; yield 68.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.87-7.82 (m, 1H), 7.81–7.76 (m, 1H), 7.33–7.27 (m, 1H), 4.39 (s, 2H). |
| 19m | 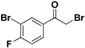 | Yellow oil; yield 27%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.22 (dd, J = 6.5, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.97–7.93 (m, 1H), 7.23 (dd, J = 15.7, 7.5 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (s, 2H), 2.59 (s, 1H). |
| 19n |  | Yellow oil; yield 86%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.04-7.97 (m, 1H), 7.22–7.14 (m, 2H), 4.66 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 2H). |
| 19o | 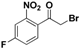 | Yellow oil; yield 37.8%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.94 (dd, J = 8.1, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.49 (m, 2H), 4.30 (s, 2H). |
| 19q |  | Yellow oil; yield 75%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.74 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 8.09–8.01 (m, 2H), 7.69 (m, 1H), 4.96 (s, 2H). |
| 19r | 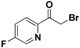 | Yellow oil; yield 47.7%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.51 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (dd, J = 8.7, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (m, 1H), 2.71 (s, 3H). |
| 19s | 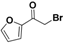 | Yellow solid; yield 46%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.92 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.54–7.48 (m, 1H), 6.74 (dd, J = 3.6, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 4.53 (s, 2H). |
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylethanone Derivatives 20
| Compd. | Chemical Structure | Appearance Property, Yield and 1H-NMR |
|---|---|---|
| 20a |  | Yellow solid; yield 60%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.99 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.67 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.50 (m, 3H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 6.97 (s, 1H), 5.43 (s, 2H). |
| 20b | 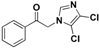 | Yellow solid; yield 65%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.00 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.70 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.46 (s, 1H), 5.37 (s, 2H). |
| 20c | 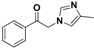 | Yellow solid; yield 86%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.99 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 2H), 7.68 (dd, J = 10.5, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.44 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (s, 1H), 5.34 (s, 2H), 2.28 (d, J = 0.7 Hz, 3H). |
| 20d | 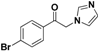 | Yellow solid; yield 55%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.85 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.69 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 3H), 7.18 (s, 1H), 6.97 (s, 1H), 5.43 (s, 2H). |
| 20e | 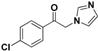 | Yellow solid; yield 45.6%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.92 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 3H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.40 (s, 2H). |
| 20f |  | Yellow solid; yield 56%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.06-7.99 (m, 2H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.26–7.18 (m, 2H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.40 (s, 2H). |
| 20g | 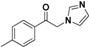 | Yellow solid; yield 53.6%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.88 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.40 (s, 2H), 2.45 (s, 3H). |
| 20h | 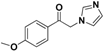 | Yellow solid; yield 58.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.98 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.98 (s, 1H), 5.39 (s, 2H), 3.92 (s, 3H). |
| 20i | 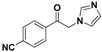 | Yellow solid; yield 55.3%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.08 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 7.17 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.44 (s, 2H). |
| 20j |  | Yellow solid; yield 69.2%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.58 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (s, 1H), 7.51 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.94 (s, 1H), 5.35 (s, 2H). |
| 20k | 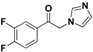 | Yellow solid; yield 56%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.88-7.80 (m, 1H), 7.80–7.74 (m, 1H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.35 (dd, J = 17.0, 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.39 (s, 2H). |
| 20l | 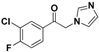 | Yellow solid; yield 47.2%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.08 (dd, J = 6.9, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.95–7.87 (m, 1H), 7.76 (s, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (s, 1H), 6.98 (s, 1H), 5.46 (s, 2H). |
| 20m | 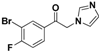 | Yellow solid; yield 55.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.22 (dd, J = 6.4, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.96–7.92 (m, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 6.95 (s, 1H), 5.39 (s, 2H). |
| 20n | 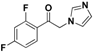 | Yellow solid; yield 17.4%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.10-8.06 (m, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 7.33–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.10 (d, J = 1.0 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.61 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 2H). |
| 20o |  | Yellow solid; yield 58.3%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.93 (dd, J = 8.0, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.64–7.59 (m, 1H), 7.44 (dd, J = 8.4, 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.98 (s, 1H), 5.15 (s, 2H). |
| 20p | 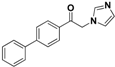 | Yellow solid; yield 75%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.18 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.78 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.52 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (s, 1H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 5.85 (s, 2H). |
| 20q | 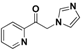 | Yellow solid; yield 46.7%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.73-8.72 (m, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (m, 1H), 7.62–7.53 (m, 2H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (s, 2H). |
| 20r | 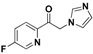 | Yellow solid; yield 58.3%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.54 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (dd, J = 8.7, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 7.59–7.56 (m, 1H), 7.53 (s, 1H), 7.12 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 5.62 (s, 2H). |
| 20s | 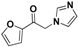 | Yellow solid; yield 40%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.67 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.29 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (s, 1H), 6.97 (s, 1H), 6.63 (dd, J = 3.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 5.25 (s, 2H). |
3.1.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 21–44 and 46
3.1.6. Synthesis of 45
3.2. Biological Assays
3.2.1. Antifungal Susceptibility Tests
| Compd. | Chemical Structure | Properties | Yield, 1H-NMR and HRMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 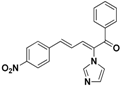 | Yellow solid, mp 150–151 °C | Yield 20.8%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.24 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.81 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.67 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (t, J= 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 6.98 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H15N3O3 (M+) 345.1106, found: 345.1113, 223.0860 (100%). |
| 22 | 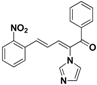 | Yellow solid, mp 162–165 °C | Yield 9.7%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.01 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.84–7.73 (m, 5H), 7.68–7.61(m, 3H), 7.55 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (s, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 6.91 (dd, J = 15.4, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H15N3O3 (M+) 345.1113, found: 345.1110, 105.0341 (100%). |
| 23 | 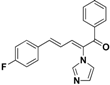 | Yellow solid, mp 161–163 °C | Yield 10%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, methanol-d4): δ 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.67 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.49 (m, 4H), 7.47 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (s, 1H), 7.26 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.21 (s, 1H), 7.12 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.72 (dd, J = 15.4, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H15FN2O (M+) 318.1168, found: 318.1164, 223.0870 (100%). |
| 24 | 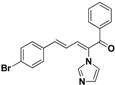 | Yellow solid, mp 117–120 °C | Yield 9.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.77 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (s, 1H), 7.66 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.46 (m, 6H), 7.39 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.34–7.25 (m, 2H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H15BrN2O (M+) 378.0368, found: 378.0360, 223.0864 (100%). |
| 25 | 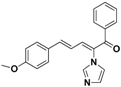 | Yellow solid, mp 133–137 °C | Yield 11.4%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.73 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 7.67–7.59 (m, 2H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.38 (dd, J = 15.6, 10.1 Hz, 3H), 7.19 (d, J = 18.7 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 6.72 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.56 (dd, J = 15.3, 11.3 Hz, 1H), 2.83 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 3H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C21H18N2O2 (M+) 314.1419, found: 314.1411, 343.1678 (100%). |
| 26 |  | Yellow solid, mp 190–192 °C | Yield 9.8%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, methanol-d4): δ 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.81 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.68 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.63–7.52 (m, 5H), 7.49 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H), 7.20 (s, 1H), 6.84 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H14Cl2N2O (M+) 368.0483, found: 368.0474, 223.0856 (100%). |
| 27 | 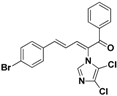 | Yellow solid, mp 181–183 °C | Yield 28%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.83 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 3H), 7.70 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.63–7.55 (m, 6H), 7.42 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13BrCl2N2O (M+) 445.9588, found: 445.9586, 105.0319 (100%). |
| 28 |  | Yellow solid, mp 172–173 °C | Yield 11.3%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.76 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.59–7.47 (m, 7H), 7.28 (dd, J = 15.9, 13.3 Hz, 2H), 7.01–6.92 (m, 2H), 2.20 (s, 3H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C21H17BrN2O (M+) 392.0524, found: 392.0522, 237.1022 (100%). |
| 29 | 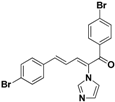 | Yellow solid, mp 162–164 °C | Yield 35.4%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.77–7.68 (m, 5H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.44 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H14Br2N2O (M+) 455.9473, found: 455.9465, 300.9948 (100%). |
| 30 | 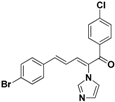 | Yellow solid, mp 150–153 °C | Yield 25.8%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.78 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H14BrClN2O (M+) 411.9978, found: 411.9976 257.0477 (100%). |
| 31 | 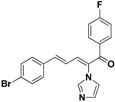 | Yellow solid, mp 115–116 °C | Yield 23.4%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.86 (dd, J = 8.7, 5.5 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.35–7.24 (m, 4H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H14BrFN2O (M+) 396.0274, found: 396.0272, 241.0771 (100%). |
| 32 | 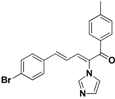 | Yellow solid, mp 153–155 °C | Yield 9.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.72–7.64 (m, 3H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (dd, J = 9.5, 4.0 Hz, 3H), 7.32–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.2 Hz, 1H), 2.42 (d, J = 14.3 Hz, 3H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C21H17BrN2O (M+) 392.0524, found: 392.0524, 237.1025 (100%). |
| 33 | 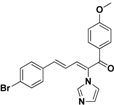 | Yellow solid, mp 166–167 °C | Yield 9.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.77 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.36–7.24 (m, 3H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H), 3.91 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 3H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C21H17BrN2O2 (M+) 408.0473, found: 408.0475, 253.0972 (100)%. |
| 34 |  | Yellow solid, mp 174–178 °C | Yield 55.3%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.95 (q, J = 8.6 Hz, 4H), 7.72 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (dd, J = 9.5, 7.8 Hz, 3H), 7.34 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.91 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C21H14BrN3O (M+) 403.0320, found: 403.0319, 248.0824 (100%). |
| 35 | 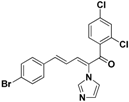 | Yellow solid, mp 197–199 °C | Yield 31%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.66 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 3H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 3H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (dd, J = 21.5, 13.3 Hz, 2H), 7.25 (s, 1H), 7.13 (s, 1H), 6.87 (dd, J = 15.1, 11.3 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13BrCl2N2O (M+) 445.9588, found: 445.9588, 291.0083 (100%). |
| 36 |  | Yellow solid, mp 132–133 °C | Yield 74.9%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.78–7.70 (m, 2H), 7.65 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.50 (t, J = 8.9 Hz, 4H), 7.34 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13BrF2N2O (M+) 414.0179, found: 414.0177, 259.0675. (100%). |
| 37 |  | Yellow solid, mp 111–112 °C | Yield 52.1%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.91 (dd, J = 7.2, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.80–7.77 (m, 1H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (dd, J = 13.0, 4.7 Hz, 4H), 7.34 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13BrClFN2O (M+) 429.9884, found: 429.9883, 275.0367 (100%). |
| 38 |  | Yellow solid, mp 133–134 °C | Yield 89%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.04 (dd, J = 6.7, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.84–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 3H), 7.44 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (s, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13Br2FN2O (M+) 473.9379, found: 473.9381, 318.9905 (100%). |
| 39 |  | Yellow solid, mp 148–150 °C | Yield 55.1%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.79–7.72 (m, 1H), 7.69 (s, 1H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (dd, J = 13.8, 9.9 Hz, 3H), 7.34 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.25–7.17 (m, 3H), 7.11 (s, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13BrF2N2O (M+) 414.0179, found: 414.0166, 259.0647 (100%). |
| 40 | 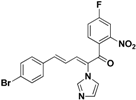 | Yellow solid, mp 183–184 °C | Yield 52.3%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.12 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (dd, J = 8.5, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 7.80–7.83 (m, 1H), 7.65 (s, 1H), 7.56 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.45 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.39 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 1H), 7.26–7.21 (m, 2H), 7.12 (s, 1H), 6.83 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H13BrFN3O3 (M+) 441.0124, found: 441.0130, 288.9987 (100%). |
| 41 | 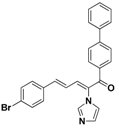 | Yellow solid, mp 167–168 °C | Yield 52.3%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.90 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.78 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 4H), 7.66–7.50 (m, 5H), 7.46 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (s, 1H), 7.12 (s, 1H), 6.98 (dd, J = 15.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C26H19BrN2O (M+) 454.0681, found: 454.0683, 299.1186 (100%). |
| 42 | 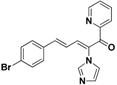 | Yellow solid, mp 114–116 °C | Yield 6.5%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.72 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 8.13 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.69–7.62 (m, 2H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.21 (s, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 6.84 (dd, J = 15.6, 11.2 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C19H14BrN3O (M+) 379.0320, found: 379.0318, 224.0823 (100%). |
| 43 | 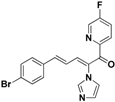 | Yellow solid, mp 156–157 °C | Yield 4.3%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 8.66 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.16–8.08 (m, 2H), 7.93–7.89 (m, 1H), 7.69 (s, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.52 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (s, 1H), 7.13 (s, 1H), 6.88 (dd, J = 15.6, 11.2 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C19H13BrFN3O (M+) 397.0226, found: 397.0227, 242.0732 (100%). |
| 44 | 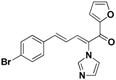 | Yellow solid, mp 180–182 °C | Yield 21.1%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.90 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (s, 1H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (s, 1H), 7.17 (s, 1H), 6.78 (dd, J = 15.6, 11.2 Hz, 1H), 6.65 (dd, J = 3.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.57 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C18H13BrN2O2 (M+) 368.0160, found: 368.0157, 213.0664 (100%). |
| 45 | 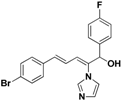 | Yellow oil | Yield 66%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.50 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (s, 1H), 7.36–7.32 (m, 4H), 7.04 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.99 (s, 1H), 6.94 (s, 1H), 6.89 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 1H), 6.57 (dd, J = 15.7, 10.9 Hz, 1H), 5.64 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H).HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H16BrFN2O (M+) 398.0430, found: 398.0424, 243.0927 (100%). |
| 46 | 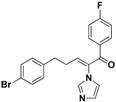 | Yellow oil | Yield 20.1%. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 7.76 (dd, J = 8.5, 5.6 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 3H), 7.26 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.03 (d, J = 10.1 Hz, 2H), 6.74 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (q, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H). HRMS (EI) calculated for C20H16BrFN2O (M+) 398.0430, found: 398.0433, 123.0243 (100%). |
3.2.2. Antibacterial Susceptibility Tests
3.2.3. Mice Toxicity Assays
3.2.4. In Vivo Antifungal Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danishuddin, M.; Kaushal, L.; Hassan Baig, M.; Khan, A.U. AMDD: Antimicrobial drug database. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform. 2012, 10, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, M.D.; Sun, L.; Lister, I.; Keating, J.; Nantel, A.; Long, L.; Ghannoum, M.; North, J.; Lee, R.E.; Coleman, K.; et al. Potentiation of Azole Antifungals by 2-Adamantanamine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3585–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.H. Alternatives to conventional antimicrobial drugs: A review of future prospects. Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhou, C.H; Geng, R.X. Advance in the research of antimicrobial drugs with sulfamide group. Chin. J. New Drug. 2010, 19, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar]
- MTunçbilek, M.; Kiper, T.; Altanlar, N. Synthesis and in vitro antimicrobial activity of some novel substituted benzimidazole derivatives having potent activity against MRSA. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Narasimhan, B.; Kumar, P.; Jalbout, A. Synthesis and QSAR evaluation of 2-(substituted phenyl)-1H-benzimidazoles and [2-(substituted phenyl)-benzimidazol-1-yl]-pyridin-3-yl-methanones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Gangal, S.; Rauf, A. Convenient one-pot synthesis of novel 2-substituted benzimidazoles tetrahydrobenzimidazoles and imidazoles and evaluation of their in vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.M.; Cai, G.X.; Zhou, C.H. Recent developments in azole compounds as antibacterial and antifungal agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1963–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, K.M.; Morgan, J.; Wannemuehler, K.A.; Mirza, S.A.; Gould, S.M.; Mhlongo, N.; Moeng, P.; Maloba, B.R.; Crewe-Brown, H.H.; Brandt, M.E.; et al. Population-based surveillance for cryptococcosis in an antiretroviral-naive South African province with a high HIV seroprevalence. AIDS 2006, 20, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiani, M.; Gonzalez, M. Imidazole and benzimidazole derivatives as chemotherapeutic agents. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhainaut, A.; Tizot, A.; Raimbaud, E.; Lockhart, B.; Lestage, P.; Goldstein, S. Synthesis, structure, and neuroprotective properties of novel imidazolyl nitrones. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, N.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, G.K.; Singh, R. Imidazoles as potential antifungal agents: A review. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1626–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.K.; Jain, P. Antifungal agents and immunomodulators in systemic mycoses. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 2000, 42, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sud, I.J.; Chou, D.L.; Feingold, D.S. Effect of free fatty acids on liposome susceptibility to imidazole antifungals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1979, 16, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudabadi, A.; Drucker, D. Effect of Amphotericin B, Nystatin and Miconazole on the polar lipids of C. albicans and C. Dubliniensis. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2006, 38, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossche, H.V.; Engelen, M.; Rochette, F. Antifungal agents of use in animal health—Chemical, biochemical and pharmacological aspects. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 26, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwano, Y.; Tabuchi, T.; Kanai, K.; Hamaguchi, H.; Uchida, K.; Yamaguchi, H. Short-term topical therapy of experimental Tinea pedisin guinea pigs with Lanoconazole, a new imidazole antimycotic agent. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2353–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwano, Y.; Ohmi, T.; Seo, A.; Kodama, H.; Koga, H.; Sakai, A. Lanoconazole and its related optically active compound NND-502: Novel antifungal imidazoles with a ketene dithioacetal structure. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Infect. Agents 2003, 2, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Geary, I.; Lee, M.E.; Duerden, B.I. Comparison of the in vitro activities of fenticonazole, other imidazoles, metronidazole, and tetracycline against organisms associated with bacterial vaginosis and skin infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1989, 33, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, B.; Mazumder, P.M.; Sasmal, D.; Ganguly, S. Biologically active azoles: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of some 1-substituted imidazoles. Pharm. Lett. 2010, 2, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, K.S.; Li, X.-C.; Jacob, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Khan, S.I.; Ferreira, D.; Clark, A.M. Synthesis, antifungal activity, and structure-activity relationships of coruscanone A analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7877–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbot, S.C.; Boice, G.N.; Buettelmann, B.; Goldstein, D.M.; Gong, L.; Hogg, J.H.; Iyer, P.; McCaleb, K.L.; Tan, Y.-C. Dihydroquinone and Dihydronaphthridine Inhibitors of JNK. U.S. Patent 20080287458 A1, 20 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, L.; Ioannidis, S.; Lamb, M.; Su, M. Pyrazolyl-Amino-Substituted Pyrazines and Their Use for the Treatment of Cancer. WO2008117050 A1, 2 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Shi, C.; Mao, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wei, B.; Zhu, J.; Xiang, M.; Li, J. Discovery of New Imidazole Derivatives Containing the 2,4-Dienone Motif with Broad-Spectrum Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2014, 19, 15653-15672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191015653
Liu C, Shi C, Mao F, Xu Y, Liu J, Wei B, Zhu J, Xiang M, Li J. Discovery of New Imidazole Derivatives Containing the 2,4-Dienone Motif with Broad-Spectrum Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules. 2014; 19(10):15653-15672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191015653
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunli, Ce Shi, Fei Mao, Yong Xu, Jinyan Liu, Bing Wei, Jin Zhu, Mingjie Xiang, and Jian Li. 2014. "Discovery of New Imidazole Derivatives Containing the 2,4-Dienone Motif with Broad-Spectrum Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity" Molecules 19, no. 10: 15653-15672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191015653
APA StyleLiu, C., Shi, C., Mao, F., Xu, Y., Liu, J., Wei, B., Zhu, J., Xiang, M., & Li, J. (2014). Discovery of New Imidazole Derivatives Containing the 2,4-Dienone Motif with Broad-Spectrum Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules, 19(10), 15653-15672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191015653






