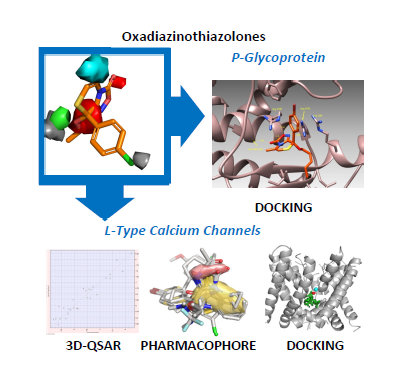
Playing with Opening and Closing of Heterocycles: Using the Cusmano-Ruccia Reaction to Develop a Novel Class of Oxadiazolothiazinones, Active as Calcium Channel Modulators and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction



2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Oxadiazolothiazinones

2.2. Biological Activity of Oxadiazolothiazinones as L-Type Calcium Channel Blockers
2.2.1. Functional Data
| Left Atrium | Right Atrium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative Inotropy | Negative Chronotropy | |||||
| Compd | Activity a (M ± SEM) | EC50 b (µM) | 95% conf lim (×10−6) | Activity c (M ± SEM) | EC30 b (µM) | 95% conf lim (×10−6) |
| 24 | 78 ± 3.5 | 0.79 | 0.70–0.85 | 94 ± 5.6 d | 0.07 | 0.064−0.075 |
| 25 e | 77 ± 1.7 d | 0.04 | 0.03−0.05 | 5 ± 0.2 f | ||
| 26 g | 76 ± 2.5 h | 0.022 | 0.015−0.031 | 4 ± 0.1 | ||
| 27 e | 81 ± 2.9 i | 0.63 | 0.45–0.80 | 20 ± 1.1 i | ||
| 28 g | 81 ± 3.9 d | 0.013 | 0.0085–0.018 | 7 ± 0.2 f | ||
| 29 g | 75 ± 1.7 d | 0.0060 | 0.0042–0.0087 | 7 ± 0.3 f | ||
| 30 | 87 ± 2.3 | 0.36 | 0.26–0.48 | 2 ± 0.2 | ||
| 31 | 82 ± 2.6 i | 0.44 | 0.32–0.61 | 2 ± 0.1 f | ||
| 32 | 76 ± 2.7 | 3.67 | 2.91–4.12 | 56 ± 3.1 | 5.06 | 4.38−5.91 |
| 33 | 88 ± 0.4 i | 5.25 | 3.29–8.36 | 52 ± 1.9 | 6.25 | 5.14−7.36 |
| 34 | 95 ± 1.3 i | 0.057 | 0.040–0.082 | 7 ± 0.1 | ||
| 35 | 88 ± 3.6 | 0.13 | 0.090–0.17 | 28 ± 1.6 f | ||
| 36 | 85 ± 3.2 | 0.039 | 0.024–0.064 | 34 ± 1.4 | ||
| 37 | 85 ± 4.2 | 1.11 | 0.76–1.61 | 16 ± 0.7 | ||
| 38 | 68 ± 2.3 | 4.23 | 3.45–5.26 | 29 ± 1.6 | ||
| 39 | 95 ± 3.6 f | 1.08 | 0.67–1.93 | 5 ± 0.3 | ||
| 40 | 92 ± 3.4 f | 0.76 | 0.52–1.12 | 16 ± 0.9 | ||
| Compd | Aorta | Ileum | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity a (M ± SEM) | IC50 b (μM) | 95% conf lim (×10−6) | Activity a (M ± SEM) | IC50 b (μM) | 95% conf lim (×10−6) | |
| 24 | 88 ± 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.2–3.1 | 98 ± 1.5 c | 0.11 | 0.085−0.13 |
| 25 d | 19 ± 0.9 e | 3 ± 0.2 | ||||
| 26 f | 28 ± 1.7 | 73 ± 0.2 | 25.94 | 18.97−35.45 | ||
| 27 d | 11 ± 0.8 e | * | ||||
| 28 f | 4 ± 0.3 | 87 ± 1.5 | 8.32 | 6.37−10.85 | ||
| 29 f | 21 ± 0.9 | 54 ± 2.1 | 11.79 | 4.33−18.21 | ||
| 30 | 57 ± 3.3 | 25.82 | 13.54–49.24 | 90 ± 1.6 e | 19.73 | 8.25–23.12 |
| 31 | 10 ± 0.9 | 58 ± 1.4 | 13.99 | 10.67–18.34 | ||
| 32 | 43 ± 2.3 | 85 ± 1.6 g | 3.26 | 2.58–4.11 | ||
| 33 | 31 ± 2.9 | 64 ± 2.4 g | 5.51 | 4.36–6.96 | ||
| 34 | 70 ± 2.9 | 29.88 | 18.35–31.07 | 98 ± 1.0 | 13.22 | 10.67–16.38 |
| 35 | 26 ± 2.5 | 66 ±2.4 | 34.36 | 27.72–42.59 | ||
| 36 | 27 ± 1.6 | 86 ± 1.7 | 16.63 | 13.63–20.27 | ||
| 37 | 45 ± 0.7 | 59 ± 0.1 g | 7.87 | 6.73–9.20 | ||
| 38 | 31 ± 0.7 | 78 ± 2.4 g | 3.49 | 2.77–4.42 | ||
| 39 | 22 ± 2.1 | 91 ± 3.4 | 21.35 | 17.26–26.40 | ||
| 40 | 19 ± 0.9 | 52 ± 0.3 g | 9.97 | 8.39–10.85 | ||
2.2.2. Electrophysiology and Binding Data


2.3. 3D-QSAR Model for the LTCC Negative Inotropic Activity of the Oxadiazolothiazinones



2.4. Docking of Oxadiazolothiazinones into Human P-glycoprotein 1 Homology Model


3. Experimental
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Functional Assays
3.4. Electrophysiology Experiments
3.4.1. Tail Main Artery Dissection
3.4.2. Cell Isolation Procedure for IBa Recordings
3.4.3. Whole-Cell Patch Clamp Recordings
3.4.4. IBa Recordings
3.5. Binding Studies
3.5.1. Cardiomyocytes Isolation
3.5.2. [3H]Diltiazem Binding Assays
3.6. Multidrug Resistance Studies
3.7. Molecular Modelling of Calcium Channels Blockers
3.8. Molecular Modelling of P-glycoprotein Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trost, B.M.; Fleming, I. (Eds.) Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1991.
- Rees, C.W.; Katritzky, A.R. (Eds.) Heterocyclic Chemistry: The Structure, Reactions, Synthesis and Uses of Heterocyclic Compounds; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1984.
- Rees, C.W.; Katritzky, A.R.; Scriven, E.F.V. (Eds.) Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II. A Review of the Literature 1982-1995; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1996.
- Katritzky, A.R.; Ramsden, C.; Scriven, E.F.V.; Taylor, R. (Eds.) Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III. A Review of the Literature 1995-2007; Elsevier: London, UK, 2008.
- Ruccia, M.; Vivona, N.; Spinelli, D. Mononuclear heterocyclic rearrangements. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 1981, 29, 141–169. [Google Scholar]
- Vivona, N.; Buscemi, S.; Frenna, V.; Cusmano, G. Ring transformation of five-membered heterocycles. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 1993, 56, 49–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pozharskii, A.F.; Soldatenkov, A.T.; Katritzky, A.R. (Eds.) Heterocycles in Life and Society: An Introduction to Heterocyclic Chemistry and Biochemistry and the Role of Heterocycles in Science, Technology, Medicine and Agriculture; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, England, 1997; pp. 1–314.
- Bird, C.W. Heteroaromaticity, 5, A unified aromaticity index. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, A.T.; Oniciu, D.C.; Katritzky, A.R. Aromaticity as a Cornerstone of Heterocyclic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2777–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, D.; Mugnoli, A.; Andreani, A.; Rambaldi, M.; Frascati, S. A new ring transformation: Conversion of 6-p-chlorophenyl-3-methyl-5-nitrosoimidazo[2,1-b]thiazole into 8-p-chlorophenyl-8-hydroxy-5-methyl-3-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolo[3,4-c][1,4]thiazine by the action of mineral acids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 1394–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Budriesi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Ioan, P.; Lanza, C.Z.; Spinelli, D.; Chiarini, A. Cardiovascular characterization of [1,4]thiazino[3,4-c][1,2,4]oxadiazol-3-one-derivatives: Selective myocardial calcium channel modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3475–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budriesi, R.; Carosati, E.; Chiarini, A.; Cosimelli, B.; Cruciani, G.; Ioan, P.; Spinelli, D.; Spisani, R. A New Class of Selective Myocardial Calcium Channel Modulators. 2. The Role of the Acetal Chain in Oxadiazol-3-one Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viale, M.; Cordazzo, C.; Cosimelli, B.; de Totero, D.; Castagnola, P.; Aiello, C.; Severi, E.; Petrillo, G.; Cianfriglia, M.; Spinelli, D. Inhibition of MDR1 Activity in vitro by a Novel Class of Diltiazem Analogues: Towards New Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosano, C.; Viale, M.; Cosimelli, B.; Severi, E.; Gangemi, R.; Ciogli, A.; de Totero, A.; Spinelli, D. ABCB1 Structural Models, Molecular Docking and Synthesis of New Oxadiazolothiazin-3-ones Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusmano, S.; Ruccia, M. Sui nitrosoimidazoli. Azione dell’acido cloridrico sul 4-(o-5)nitroso-2-5-(o-4)difenilimidazolo. Nota IV. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1955, 85, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Cusmano, S.; Ruccia, M. Sui nitrosoimidazoli. I nitrosoderivati del 5(o-4)-fenil- e del 2-metil-5(o-4)-fenilimidazolo e loro comportamento reattivo. Nota VI. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1958, 88, 463–481. [Google Scholar]
- Cosimelli, B.; Guernelli, S.; Spinelli, D.; Buscemi, S.; Frenna, V.; Macaluso, G. On the Synthesis and Reactivity of the Z-2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone of 5-Amino-3-benzoyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6124–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreani, A.; Billi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Mugnoli, A.; Rambaldi, M.; Spinelli, D. Ring-ring interconversion: The rearrangement of 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-5-nitrosoimidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazole into 8-(4-chlorophenyl)-8-hydroxy-5-methyl-8H-[1,4]thiazino[3,4-c][1,2,4]oxadiazol-3-one. Elucidation of the reaction product through spectroscopic and X-ray crystal structure analysis. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1997, 2, 2407–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Spinelli, D.; Rambaldi, M. Ring-ring interconversions. Part 2. Effect of the Substituent on the Rearrangement of 6-Aryl-3-methyl-5-nitrosoimidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazoles into 8-Aryl-8-hydroxy-5-methyl-8H-[1,4]thiazino[3,4-c][1,2,4]oxadiazol-3-ones. A Novel Class of Potential Antitumor Agents. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 5433–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Leoni, A.; Spinelli, D. Ring-ring Interconversions. Part 3. On the effect of the substituents on the thiazole moiety in the ring-opening/ring-closing reactions of nitrosoimidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazoles with hydrochloric acid. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2000, 37, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosimelli, B.; Frenna, V.; Rambaldi, M.; Severi, E.; Spinelli, D. On the reactivity of nitrosoimidazoles with acids (the Cusmano-Ruccia reaction): A continuous source of new ring-into-ring conversion. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Spinelli, D.; Andreani, A.; Leoni, A. Ring-ring Interconversions of Nitrosoimidazoles. The Effect of Some Condensed Six-membered Rings on the Reactivity. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 6527–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budriesi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Ioan, P.; Carosati, E.; Ugenti, M.P.; Spisani, R. Diltiazem Analogues: The Last Ten Years on Structure Activity Relationships. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, M.M.T.; Grant, S.M.; Goa, K.L.; McTavish, D.; Sorkin, E.M. Diltiazem: A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1990, 39, 757–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggle, D.J. Calcium channel antagonists: Clinical uses—Past, present and future. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carosati, E.; Ioan, P.; Barrano, G.B.; Caccamese, S.; Cosimelli, B.; Devlin, F.J.; Severi, E.; Spinelli, D.; Superchi, S.; Budriesi, R. Synthesis and Absolute Configuration Determination of New Oxadiazolothiazinones Active as L-Type Calcium Channel Blockers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bottoni, A.; Calvaresi, M.; Ciogli, A.; Cosimelli, B.; Mazzeo, G.; Pisani, L.; Severi, E.; Spinelli, D.; Superchi, S. Selective and Practical Oxidation of Sulfides to Diastereopure Sulfoxides: A Combined Experimental and Computational Investigation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2013, 355, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarida, R.J.; Murray, R.B. Manual of Pharmacologic Calculations with Computer Programs, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Karaki, H.; Ozaki, H.; Hori, M.; Mitsui-Saito, M.; Amano, K.-I.; Harada, K.-I.; Miyamoto, S.; Nakazawa, H.; Won, K.-J.; Sato, K. Calcium movements, distribution, and function in smooth muscle. Pharmacol. Rev. 1997, 49, 157–230. [Google Scholar]
- Irvine, R.F. Inositol phosphates and Ca2+ entry: Toward a proliferation or a simplification? FASEB J. 1992, 6, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen, C.; Saida, K. Cellular mechanisms regulating [Ca2+]i smooth muscle. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1989, 51, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyama, H.; Kitamura, K.; Nabata, H. Pharmacological and physiological significance of ion channels and factors that modulate them in vascular tissues. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995, 47, 387–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mugnai, P.; Durante, M.; Sgaragli, G.; Saponara, S.; Paliuri, G.; Bova, S.; Fusi, F. L-type Ca2+ channel current characteristics are preserved in rat tail artery myocytes after one-day storage. Acta Physiol. 2014, 211, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, T.F.; Pelzer, S.; Trautwein, W.; Pelzer, D.J. Regulation and modulation of calcium channels in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 365–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Timin, E.N.; Berjukow, S.; Hering, S. Concepts of state-dependent pharmacology of calcium channels. In Calcium Channel Pharmacology; McDonough, S.I., Ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Carosati, E.; Cruciani, G.; Chiarini, A.; Budriesi, R.; Ioan, P.; Spisani, R.; Spinelli, D.; Cosimelli, B.; Fusi, F.; Frosini, M.; et al. Calcium Channel Antagonists Discovered by a Multidisciplinary Approach. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5206–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruciani, G.; Watson, K.A. Comparative molecular field analysis using GRID force-field and GOLPE variable selection methods in a study of inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase b. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2589–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Discovery Website. Available online: http://www.moldiscovery.com (accessed on 1 June 2014).
- Baroni, M.; Cruciani, G.; Sciabola, S.; Perruccio, F.; Mason, J.S. A Common Reference Framework for Analyzing/Comparing Proteins and Ligands. Fingerprints for Ligands and Proteins (FLAP): Theory and Application. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S.; Baroni, M.; Carosati, E.; Benedetti, P.; Clementi, S. FLAP: GRID Molecular Interaction Fields in Virtual Screening. Validation using the DUD Data Set. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, F. Third Generation PLS. Some Elements and Applications; Solfjädern Offset AB: Umeå, Sweden, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, S.; Baroni, M.; Goracci, L.; Cruciani, G. GRID-Based Three-Dimensional Pharmacophores I: FLAPpharm, a Novel Approach for Pharmacophore Elucidation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Benzothiazepines in L-type Calcium Channel: Insights from Molecular Modeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17594–17604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, W.D.; Cieplak, P.; Bayly, C.I.; Gould, I.R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Ferguson, D.M.; Spellmeyer, D.C.; Fox, T.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A. A Second Generation Force Field for the Simulation of Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Organic Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5179–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prijs, B.; Ostertag, J.; Erlenmeyer, H. Nitrothiazole compounds. II. Helv. Chim. Acta 1947, 30, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buu-Hoi, N.P.; Xuong, N.D.; THU-CUC, T. Reaction of ω-bromoacetophenones with 2-aminothiazole and 2-aminobenzothiazoles. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1966, 4, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarval, R.; Sumran, G. Hypervalent Iodine in the Synthesis of Bridgehead heterocycles: A Facile Route to the Synthesis of 6-Arylimidazo[2,1-b]thiazoles Using [Hydroxy(tosyloxy)iodo]benzene. Synth. Commun. 2006, 36, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pyl, T.; Wünschm, K.-H.; Beyer, H. Nitrosierung und Azokupplung von 6-Phenyl-imidazo[2,1-b]thiazolen. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1962, 657, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motulsky, H.J.; Christopoulos, A. Fitting Models to Biological Data Using Linear and Non Linear Regression. 2003. Available online: http://www.graphpad.com (accessed on 10 May 2010).
- Motulsky, H.J. Prism 5 Statistics Guide; GraphPad Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007. Available online: http://www.graphpad.com (accessed on 10 May 2010).
- Fusi, F.; Saponara, S.; Gagov, H.; Sgaragli, G.P. 2,5-Di-t-butyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone (BHQ) inhibits vascular L-type Ca2+ channel via superoxide anion generation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, O.P.; Marty, A.; Neher, E.; Sakmann, B.; Sigworth, F.J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflüg. Arch. 1981, 391, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiato, A.; Fabiato, F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J. Physiol. 1979, 75, 463–505. [Google Scholar]
- Petkov, G.V.; Fusi, F.; Saponara, S.; Gagov, H.; Sgaragli, G.P.; Boev, K.K. Characterization of voltage-gated calcium currents in freshly isolated smooth muscle cells from rat tail main artery. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 173, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusi, F.; Sgaragli, G.; Ha, L.M.; Cuong, N.M.; Saponara, S. Mechanism of osthole inhibition of vascular Cav1.2 current. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 680, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansfeld, C.; Mathie, A. Recording membrane currents of peripheral neurones in short-term culture. In Electrophysiology. A Practical Approach; Wallis, D.I., Ed.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- The Version 2.0 of the Software FLAP Is Distributed by Molecular Discovery Ltd. Available online: http://www.moldiscovery.com (accessed on 1 September 2014).
- Sali, A.; Blundell, T.L. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaen, O.; Leulliot, N.; Sizun, C.; Ulryck, N.; Pamlard, O.; Lallemand, J.Y.; Tilbeurgh, H.; Jacquet, E. Structure of the human multidrug resistance protein 1 nucleotide binding domain 1 bound to Mg2+/ATP reveals a non-productive catalytic site. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 359, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spinelli, D.; Budriesi, R.; Cosimelli, B.; Severi, E.; Micucci, M.; Baroni, M.; Fusi, F.; Ioan, P.; Cross, S.; Frosini, M.; et al. Playing with Opening and Closing of Heterocycles: Using the Cusmano-Ruccia Reaction to Develop a Novel Class of Oxadiazolothiazinones, Active as Calcium Channel Modulators and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors. Molecules 2014, 19, 16543-16572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016543
Spinelli D, Budriesi R, Cosimelli B, Severi E, Micucci M, Baroni M, Fusi F, Ioan P, Cross S, Frosini M, et al. Playing with Opening and Closing of Heterocycles: Using the Cusmano-Ruccia Reaction to Develop a Novel Class of Oxadiazolothiazinones, Active as Calcium Channel Modulators and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors. Molecules. 2014; 19(10):16543-16572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016543
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpinelli, Domenico, Roberta Budriesi, Barbara Cosimelli, Elda Severi, Matteo Micucci, Massimo Baroni, Fabio Fusi, Pierfranco Ioan, Simon Cross, Maria Frosini, and et al. 2014. "Playing with Opening and Closing of Heterocycles: Using the Cusmano-Ruccia Reaction to Develop a Novel Class of Oxadiazolothiazinones, Active as Calcium Channel Modulators and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors" Molecules 19, no. 10: 16543-16572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016543
APA StyleSpinelli, D., Budriesi, R., Cosimelli, B., Severi, E., Micucci, M., Baroni, M., Fusi, F., Ioan, P., Cross, S., Frosini, M., Saponara, S., Matucci, R., Rosano, C., Viale, M., Chiarini, A., & Carosati, E. (2014). Playing with Opening and Closing of Heterocycles: Using the Cusmano-Ruccia Reaction to Develop a Novel Class of Oxadiazolothiazinones, Active as Calcium Channel Modulators and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors. Molecules, 19(10), 16543-16572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016543