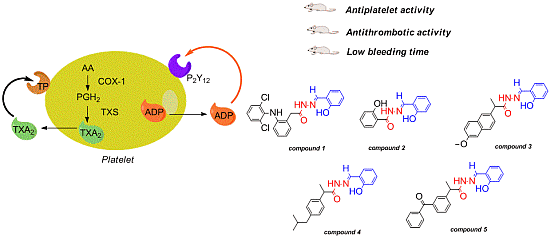
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Activities of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Containing an N-Acyl Hydrazone Subunit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
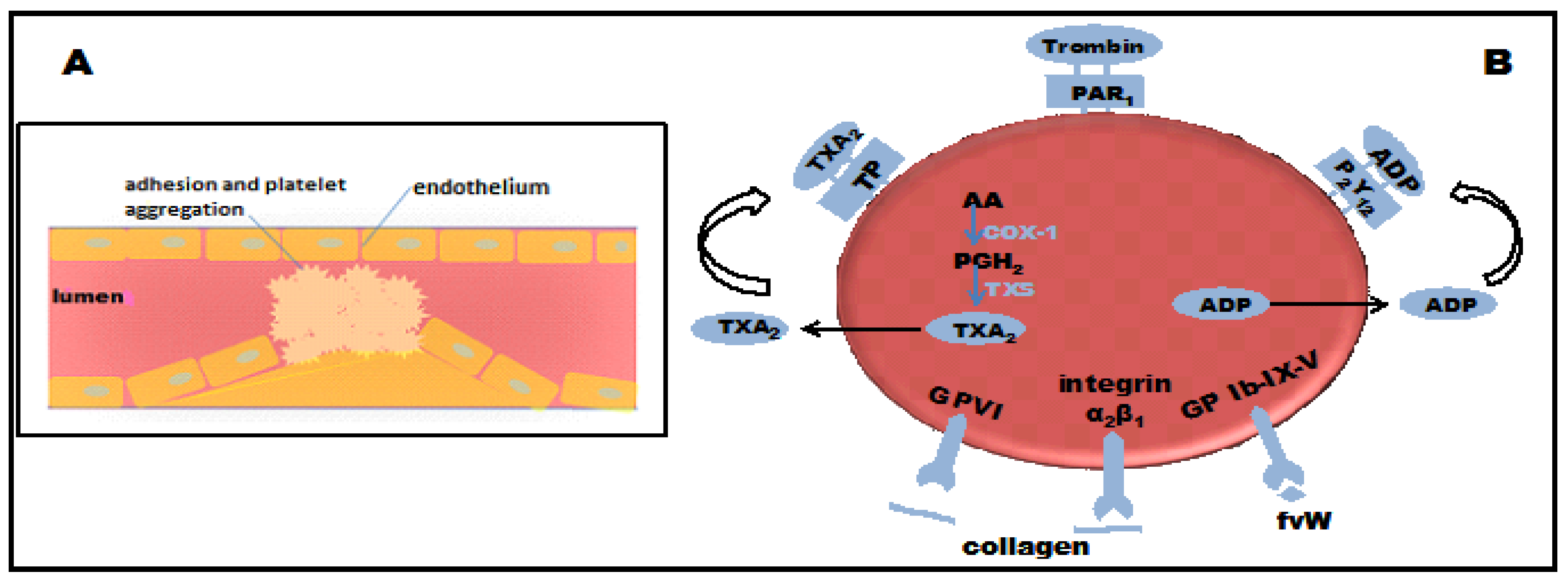

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antiplatelet Activity
| Compound | n | Concentration (μM) | ADP-Induced Platelet Aggregation (% Inhibition) | AA-Induced Platelet Aggregation (% Inhibition) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | – | 0 | 0 |
| ASA | 3 | 150 | 0 | 80 ± 1.6 * |
| 1 | 3 | 150 | 57.2 ± 2.1 *,† | 71.4 ± 2.2 * |
| 2 | 3 | 150 | 29.5 ± 1.8 *,† | 80.8 ± 1.1 * |
| 3 | 3 | 150 | 30.5 ± 2.3 *,† | 66.8 ± 1.7 * |
| 4 | 3 | 150 | 18.0 ± 1.7 *,† | 67.6 ± 2.1 * |
| 5 | 3 | 150 | 61.1 ± 2.5 *,† | 65.9 ± 1.3 * |
2.2. Bleeding Time in Mice
| Compounds | Bleeding Time (s) |
|---|---|
| Negative control | 343 ± 11.5 |
| ASA | 818 ± 21.8 * |
| 1 | 642 ± 18.1 *,† |
| 2 | 1271 ± 24.9 * |
| 3 | 671 ± 16.7 *,† |
| 4 | 1178 ± 25.3 * |
| 5 | 653 ± 14.1 *,† |
2.3. Collagen- and Epinephrine-Induced Pulmonary Thromboembolism Model in Mice
| Compound | Survival Rate (%) * |
|---|---|
| Control | 20 ± 1 |
| ASA | 30 ± 3 † |
| 1 | 40 ± 1 †,‡ |
| 3 | 20 ± 2 |
| 5 | 33 ± 2 † |
3. Experimental
3.1. General Information
3.1.1. Reagents and equipaments
3.2. Preparation of Compounds 1–5
3.3. Animals
3.4. Pharmacology
3.4.1. Antiplatelet Activity
3.4.2. Bleeding Time
3.4.3. Pulmonary Thromboembolism Model Induced by Collagen-Ephinephrine Mixture
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Go, A.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Roger, V.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2013 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013, 127, e6–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J. The framingham heart study and the epidemiology of cardiovascular disease: A historical perspective. Lancet 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininger, A.J.; Bernlochner, I.; Penz, S.M.; Ravanat, C.; Smethurst, P.; Farndale, R.W.; Gachet, C.; Brand, R.; Siess, W. A 2-step mechanism of arterial thrombus formation induced by human atherosclerotic plaques. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S. Understanding the mechanism of platelet thrombus formation under blood flow conditions and the effect of new antiplatelet agents. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 2, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Anand, S.S. Oral antiplatelet therapy in cerebrovascular disease, coronary artery disease, and peripheral arterial disease. JAMA 2004, 292, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.D.; Nylander, S.; Whatling, C. Anti-platelet therapy: Cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the use of aspirin with particular regard to dual anti-platelet therapy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosser, T.; Fries, S.; FitzGerald, G.A. Biological basis for the cardiovascular consequences of COX-2 inhibition: Therapeutic challenges and opportunities. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, J.P.; Barbosa, J.P.; Ramos, R.M.; Antunes, N.F.; de Melo, P.C. Relative cardiovascular and gastrointestinal safety of non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors: Implications for clinical practice. Clin. Drug Investig. 2013, 33, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juni, P.; Nartey, L.; Reichenbach, S.; Sterchi, R.; Dieppe, P.A.; Egger, M. Risk of cardiovascular events and rofecoxib: Cumulativemeta-analysis. Lancet 2004, 364, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosslien, E. Cardiovascular complications of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2005, 35, 347–385. [Google Scholar]
- McGettigan, P.; Henry, D. Cardiovascular risk and inhibition of cyclooxygenase: A systematic review of the observational studies of selective and nonselective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2. JAMA 2006, 296, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turajane, T.; Wongbunnak, R.; Patcharatrakul, T.; Ratansumawong, K.; Poigampetch, Y.; Songpatanasilp, T. Gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risk of non-selective NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors in elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2009, 92, S19–S26. [Google Scholar]
- Trelle, S.; Reichenbach, S.; Wandel, S.; Hildebrand, P.; Tschannen, B.; Villiger, P.M.; Egger, M.; Juni, P. Cardiovascular safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Network meta-analysis. BMJ 2011, 342, c7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattenkirchner, M. Long-term safety of ketoprofen in an elderly population of arthritic patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1991, 91, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, W.A.; Varas-Lorenzo, C.; Chung, C.P.; Castellsague, J.; Murray, K.T.; Stein, C.M.; Daugherty, J.R.; Arbogast, P.G.; García-Rodríguez, L.A. Cardiovascular risks of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in patients after hospitalization for serious coronary heart disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2009, 2, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, M.C.; Altman, R.D.; April, K.T.; Benkhalti, M.; Guyatt, G.; McGowan, J.; Towheed, T.; Welch, V.; Wells, G.; Tugwell, P. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 465–674. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.B. Cardiovascular effects of the cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Hypertension 2007, 49, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.; Frattani, F.S.; dos Santos, J.L.; Castro, H.C.; Fraga, C.A.; Zingali, R.B.; Barreiro, E.J. Synthesis and anti-platelet activity of novel arylsulfonate--acylhydrazone derivatives, designed as antithrombotic candidates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, G.V.R.; Cross, M.J. The aggregation of blood platelets. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 1963, 168, 178–195. [Google Scholar]
- Rollas, S.; Küçükgüzel, S.G. Biological activities of hydrazone derivatives. Molecules 2007, 12, 1910–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A.M. Síntese de substâncias bioativas na cascata do ácido araquidônico: Antiinflamatórios, analgésicos e antitrombóticos (in Portuguese). Quim. Nova 1999, 22, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.A.; Zapata-Sudo, G.; Kummle, A.E.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Barreiro, E.J.; Sudo, R.T. Synthesis and vasodilatory activity of new N-acilhidrazones derivatives designed as LASSBio-294 analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 3431–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Sudo, G.; Sudo, R.T.; Maronas, P.A.; Silva, G.; Moreira, R.; Aguiar, M.I.S.; Barreiro, E.J. Thienylhydrazone derivative increase sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca+ releasein mammalian skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 470, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, A.G.M.; Rodrigues, C.R.; de Miranda, A.L.P.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A.M. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel heterotricyclic acylhydrazone derivatives, designed as PAF antagonists. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, A.R.; de Miranda, A.L.P.; Silva, K.C.M.; Parrini, S.C.; Barreiro, E.J. Synthesis of new 2-pyridinylarylhydrazones and evaluation of their analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet profile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 33, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, V.; Tehrani, K.H.M.E.; Amidi, S.; Kobarfard, F. Synthesis of novel indole hydrazone derivatives and evaluation of their antiplatelet aggregation activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, F.C.; Kummerle, A.E.; Lugnier, C.; Fraga, C.A.; Barreiro, E.J.; Miranda, A.L. Novel thienylacylhydrazone derivatives inhibit platelet aggregation through cyclic nucleotides modulation and thromboxane A2 synthesis inhibition. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 638, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.C.; Figueiredo, J.M.; Tributino, J.L.; Miranda, A.L.; Castro, H.C.; Zingali, R.B.; Fraga, C.A.; de Souza, M.C.; Ferreira, V.F.; Barreiro, E.J. Antiplatelet properties of novel N-substituted-phenyl-1,2,3-triazole-4-acylhydrazone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, K.H.M.E.; Sardari, S.; Mashayekhi, V.; Esfahani Zadeh, M.; Azerang, P.; Kobarfard, F. One pot synthesis and biological activity evaluation of novel Schiff bases derived from 2-hydrazinyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, M.; Lecchi, A. Inhibition of the platelet P2Y12 receptor for adenosine diphosphate potentiates the antiplatelet effect of prostacyclin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragam, K.G.; Bhatt, D.L. Antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndromes. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 16, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijajlovic, M.D.; Shulga, O.; Bloch, S.; Covickovic-Sternic, N.; Aleksic, V.; Bornstein, N.M. Clinical consequences of aspirin and clopidogrel resistance: An overview. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 128, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandvik, P.O.; Lincoff, A.M.; Gore, J.M.; Gutterman, D.D.; Sonnenberg, F.A.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Akl, E.A.; Lansberg, M.G.; Guyatt, G.H.; Spencer, F.A. Primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e637S–e668S. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.S. Aspirin, clopidogrel, and ticagrelor in acute coronary syndromes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A. Gastrointestinal bleeding associated with NSAIDs, antiplatelet therapy and anticoagulant agent. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 35, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Balaramnavar, V.M.; Hohlfeld, T.; Saxena, A.K. Drug/drug interaction of common NSAIDs with antiplatelet effect of aspirin in human platelets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 721, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhfi, H.; Belmekki, F.; Ziyyat, A.; Legssyer, A.; Bnouham, M.; Aziz, M. Antithrombotic activity of argan oil: An in vivo experimental study. Nutrition 2012, 28, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMinno, G. Mouse antithrombotic assays: A simple method for the evaluation of antithrombotic agents in vivo. Potentiation of antithrombotic activity by ethyl alcohol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 227, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dutra, L.A.; Chelucci, R.C.; Chiquetto, R.; Pires, M.E.L.; Marcondes, S.; Chung, M.C.; Santos, J.L. Synthesis of new NSAIDs derivatives designed as antiplatelet, analgesic and anti-inflammatory compounds. In Proceedings of the 6th Brazilian Symposium on Medicinal Chemistry, Canela, Rio Grande ds Sul, Brazil, 28–31 October 2012; OSPS-45. p. 1.
- Dejana, E.; Callioni, A.; Quintana, A.; de Gaetano, G. Bleeding time in laboratory animals. II—A comparison of different assay conditions in rats. Thromb. Res. 1979, 15, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejana, E.; Quintana, A.; Callioni, A.; de Gaetano, G. Bleeding time in laboratory animals. III—Do tail bleeding times in rats only measure a platelet defect? (the aspirin puzzle). Thromb. Res. 1979, 15, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–5 are not available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chelucci, R.C.; Dutra, L.A.; Lopes Pires, M.E.; De Melo, T.R.F.; Bosquesi, P.L.; Chung, M.C.; Dos Santos, J.L. Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Activities of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Containing an N-Acyl Hydrazone Subunit. Molecules 2014, 19, 2089-2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022089
Chelucci RC, Dutra LA, Lopes Pires ME, De Melo TRF, Bosquesi PL, Chung MC, Dos Santos JL. Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Activities of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Containing an N-Acyl Hydrazone Subunit. Molecules. 2014; 19(2):2089-2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022089
Chicago/Turabian StyleChelucci, Rafael Consolin, Luiz Antônio Dutra, Maria Elisa Lopes Pires, Thais Regina Ferreira De Melo, Priscila Longhin Bosquesi, Man Chin Chung, and Jean Leandro Dos Santos. 2014. "Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Activities of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Containing an N-Acyl Hydrazone Subunit" Molecules 19, no. 2: 2089-2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022089
APA StyleChelucci, R. C., Dutra, L. A., Lopes Pires, M. E., De Melo, T. R. F., Bosquesi, P. L., Chung, M. C., & Dos Santos, J. L. (2014). Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Activities of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Containing an N-Acyl Hydrazone Subunit. Molecules, 19(2), 2089-2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022089