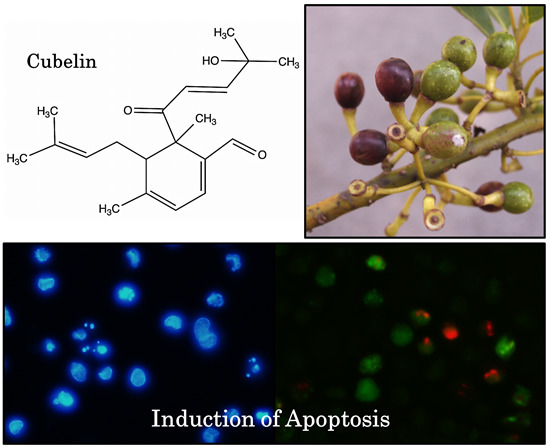
A New Diterpene from Litsea cubeba Fruits: Structure Elucidation and Capability to Induce Apoptosis in HeLa Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Elucidation
| Position | δ 13C | δ 1H | No. | δ 13C | δ 1H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.4 | 1.39 (3H, s) | 11 | 118.9 | 5.87 (1H, d, J = 5.52) |
| 2 | 17.8 | 1.52 (3H, s) | 12 | 121.8 | 6.54 (1H, d, J = 15.12) |
| 3 | 24.0 | 1.95 (3H, s) | 13 | 123.0 | 5.04 (1H, t, J = 1.38, 7.56) |
| 4 | 25.5 | 2.08 (2H, dd, J = 6.50, 7.56) | 14 | 132.6 | |
| 5 | 25.8 | 1.62 (3H, s) | 15 | 136.3 | |
| 6 | 29.2 | 1.28 (3H, s) | 16 | 148.4 | 6.83 (1H, d, J = 5.52) |
| 7 | 29.4 | 1.30 (3H, s) | 17 | 153.0 | 6.88 (1H, d, J = 15.12) |
| 8 | 46.2 | 2.73 (1H, t, J = 6.50) | 18 | 156.3 | |
| 9 | 52.9 | 19 | 193.0 | 9.46 (1H, s) | |
| 10 | 71.2 | 20 | 200.2 |



2.2. The Anticancer Potential of Cubelin
| Time/Sample | IC50 (µM) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell viability | LDH leakage | Cell proliferation | ||
| 24 h | Cubelin | 34.43 ± 4.87 | 179.21 ± 6.23 | 30.49 ± 4.29 |
| Etoposide | 62.90 ± 5.48 | No activity | 34.24 ± 5.59 | |
| 48 h | Cubelin | 21.92 ± 3.58 | 144.55 ± 2.43 | 24.07 ± 1.55 |
| Etoposide | 4.52 ± 1.02 | 201.17 | 3.17 ± 1.96 | |


3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction, Isolation and Identification of (+)-6-(4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentenoyl)-4,6-dimethyl-5-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-1,3-cyclohexadienecarbaldehyde (Cubelin, 1)
3.4. General Procedure on Cell Culture and Cell Based Assays
3.5. Cell Viability Assay
3.6. Cell Proliferation Assay (BrdU Incorporation)
3.7. Determination of LDH Leakage
3.8. Determination of Activated Caspase-8, Caspase-9 and Caspase-3/-7
3.9. Fluorescent Microscope Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nor Azah, M.A.; Susiarti, S. Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Persoon. In Plant Resources of South-East Asia No.19: Essential-Oil Plants; Oyen, L.P.A., Dung, N.X., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Coppen, J.J.W. Non-Wood Forest Products 1: Flavours and Fragrances of Plant Origin; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1995; pp. 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Si, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Zhan, Z.; Tian, S.; Cui, Q.; Wang, Y. Chemical composition of essential oil in Litsea cubeba harvested from its distributed areas in China. Molecules 2012, 17, 7057–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, Q. Transcriptosome sequencing and expression analysis of terpenoid biosynthesis genes in Litsea cubeba. PLoS One 2013, 8, e76890. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Tong, L.; Bi, K. Simultaneous determination of the 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one, limonene, linalool and citral in essential oil from Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Pers by capillary gas chromatography. Asian J. Tradit. Med. 2007, 2, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, J. Characterization of the volatiles and active components in ethanol extracts of fruits of Litsea cubeba (Lour.) by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS) and gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O). J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 3298–3303. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuinya, T.; Singh, P.; Mukherjee, S. Litsea cubeba—Medicinal values—Brief summary. J. Trop. Med. Plants 2010, 11, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Noosidum, N.; Prabaripai, A.; Charoenviriyaphap, T.; Chandrapatya, A. Excito-repellency properties of essential oils from Melaleuca leucadendron L., Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Persoon, and Litsea salicifolia (Nees) on Aedes aegypti (L.) mosquitoes. J. Vector Ecol. 2008, 33, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Qimei, L.; Yan, X.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, H.; Qin, Z.; Wang, M. The Fungicidal Terpenoids and Essential Oil from Litsea cubeba in Tibet. Molecules 2010, 15, 7075–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Jie-Pinge, O.; Liu, Y.; Hung, C.; Tsai, M.; Liao, P.; Wang, E.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y. Compositions and in vitro anticancer activities of the leaf and fruit oils of Litsea cubeba from Taiwan. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Seal, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Pal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Kundu, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhuyan, M.; Bhattacharya, P.R.; et al. Vapor of Volatile Oils from Litsea cubeba Seed Induces Apoptosis and Causes Cell Cycle Arrest in Lung Cancer Cells. PLoS One 2012, 7, e7014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Tseng, Y.; Chu, F.; Wen, T.; Cheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Tsao, N.; Wang, S. Neuropharmacological activities of fruit essential oil from Litsea cubeba Persoon. J. Wood Sci. 2012, 58, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, M.J.; Samundeeswari, A.; Sankar, P.D. Natural plant resources in anti-cancer therapy-A review. Res. Plant Biol. 2011, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chemotherapy Drugs and Side Effects. Available online: http://cancer.stanford.edu/information/cancerTreatment/methods/chemotherapy.html (accessed on 22 March 2014).
- Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, K.A. The cell cycle: A Review. Vet. Pathol. 1998, 35, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Nakagawara, A. Role of p53 in cell death and human cancers. Cancers 2011, 3, 994–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, B.; Kasten, M.; Giordano, A. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, W.C.; Martins, L.M.; Kaufmann, S.H. Mammalian caspases: Structure, activation, substrates and functions during apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 383–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Fang, K. Etoposide (VP-16) sensitizes p53-deficient human non-small cell lung cancer cells to caspase-7-mediated apoptosis. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandela, C.; Pera, M.F.; Wolvetang, E.J. p53 is required for etoposide-induced apoptosis of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2008, 1, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; Berghe, T.V.; D’Herde, K.; Vandenabeele, P. Apoptosis and necrosis: Detection, discrimination and phagocytosis. Methods 2008, 44, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwan, D.; Naruse, T.; Tamura, H. Effect of epoxides and α-methylene-γ-lactone skeleton of sesquiterpenes from yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) leaves on caspase-dependent apoptosis and NF-κB inhibition in human cervical cancer cells. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; D’Herde, K.; Vandenabeele, P. Clearance of apoptotic and necrotic cells and its immunological consequences. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 1709–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Sample of cubelin is available from the corresponding author (35 mg).
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Trisonthi, P.; Sato, A.; Nishiwaki, H.; Tamura, H. A New Diterpene from Litsea cubeba Fruits: Structure Elucidation and Capability to Induce Apoptosis in HeLa Cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 6838-6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056838
Trisonthi P, Sato A, Nishiwaki H, Tamura H. A New Diterpene from Litsea cubeba Fruits: Structure Elucidation and Capability to Induce Apoptosis in HeLa Cells. Molecules. 2014; 19(5):6838-6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056838
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrisonthi, Piyapat, Akihiko Sato, Hisashi Nishiwaki, and Hirotoshi Tamura. 2014. "A New Diterpene from Litsea cubeba Fruits: Structure Elucidation and Capability to Induce Apoptosis in HeLa Cells" Molecules 19, no. 5: 6838-6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056838
APA StyleTrisonthi, P., Sato, A., Nishiwaki, H., & Tamura, H. (2014). A New Diterpene from Litsea cubeba Fruits: Structure Elucidation and Capability to Induce Apoptosis in HeLa Cells. Molecules, 19(5), 6838-6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056838