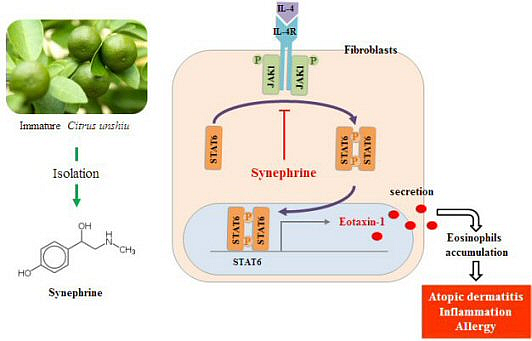
Synephrine Inhibits Eotaxin-1 Expression via the STAT6 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Immature Citrus unshiu Fruit Extracts Inhibit Eotaxin-1 Expression Induced by IL-4

2.2. Immature Citrus unshiu Extracts Contained more Phytochemical Contents than Mature Citrus unshiu Extracts

2.3. Synephrine Suppresses IL-4-induced Eotaxin-1 Production in NIH/3T3

2.4. Synephrine Inhibits STAT6, but not JAK1 Phosphorylation Induced by IL-4

2.5. IL-4 Induced Eotaxin-1 Expression is Mediated by JAK/STAT Signaling

2.6. Eotaxin-1 Induced Eosinophil Recruitment was Inhibited by Synephrine

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Materials
3.2. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.3. Cytokines and Pharmacological Inhibitors
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
3.6. Transient Transfection and Luciferase Assay
3.7. Immunohistochemistry
3.8. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative PCR
3.9. Cell Migration Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, I. An ephedra alkaloid in Citrus juices. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 1963, 76, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I.; Newhall, W.F.; Edwards, G.J. The isolation and identification of l-synephrine in the leaves and fruit of Citrus. J. Biol. Chem. 1964, 239, 930–932. [Google Scholar]
- Avula, B.; Upparapalli, S.K.; Navarrete, A.; Khan, I.A. Simultaneous quantification of adrenergic amines and flavonoids in Citrus aurantium, various Citrus species, and dietary supplements by liquid chromatography. J. AOAC. Int. 2005, 88, 1593–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Arbo, M.D.; Larentis, E.R.; Linck, V.M.; Aboy, A.L.; Pimentel, A.L.; Henriques, A.T.; Dallegrave, E.; Garcia, S.C.; Leal, M.B.; Limberger, R.P. Concentrations of p-synephrine in fruits and leaves of Citrus species (Rutaceae) and the acute toxicity testing of Citrus aurantium extract and p-synephrine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2770–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Fugh-Berman, A.; Myers, A. Citrus aurantium, an ingredient of dietary supplements marketed for weight loss: Current status of clinical and basic research. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2004, 229, 698–7004. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.G.; Midgley, J.M.; Chen, R.N.; Huang, W.; Bain, G.M.; McDonald, N.M.; Reid, J.L.; McGhee, C.N. Analysis of biogenic amines and their metabolites in biological tissues and fluids by gas chromatography–negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry (GC–NICI/MS). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1990, 8, 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- Takei, H.; Hirabuki, M.; Yoshizaki, F. Analysis of synephrine in the peel of Citrus fruit, immature Citrus fruit and decoctions of Chinese medicinal prescriptions containing these crude drugs by capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Sci. 1999, 15, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Torp, K.D.; Tschakovsky, M.E.; Halliwill, J.R.; Minson, C.T.; Joyner, M.J. Beta-receptor agonist activity of phenylephrine in the human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchi, R.; Chiellini, G.; Scanlan, T.S.; Grandy, D.K. Trace amine-associated receptors and their ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 967–978. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, P.D.; Marleau, S.; Griffiths-Johnson, D.A.; Jose, P.J.; Williams, T.J. Cooperation between interleukin-5 and the chemokine eotaxin to induce eosinophil accumulation in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, L.; Pinkston, P.; Kumaraswami, V.; Vijayan, V.; Yenokida, G.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Crystal, R.; Ottesen, E.A.; Nutman, T.B. Localized Eosinophil Degranulation Mediates Disease in Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stats: Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Gadina, M.; Schreiber, R.D. Cytokine signaling in 2002: New surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 2002, 109, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kisseleva, T.; Bhattacharya, S.; Braunstein, J.; Schindler, C.W. Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent advances and future challenges. Gene 2002, 285, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner, E.; Kliem, S.; Baus, D.; Litterst, C.M. The role of STATs in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. 2004, 10, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, M.; Farrar, J.; Hilfiker, M.; Johnson, B.; Takatsu, K.; Hamaoka, T.; Paul, W.E. Identification of a T cell-derived B cell growth factor distinct from interleukin 2. J. Exp. Med. 1982, 155, 914–923. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.A.; Pierce, J.H.; Watson, C.J.; Falco, J.; Ihle, J.N.; Paul, W.E. B cell stimulatory factor-1/interlukin-4 mRNA is expressed by normal and transformed mast cell. Cell 1987, 50, 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Seder, R.A.; Paul, W.E.; Ben-Sasson, S.; LeGros, G.S.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; Finkelman, F.D. Production of interleukin-4 and other cytokines following stimulation of mast cell lines and in vivo mast cells/basophils. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1991, 94, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukara, S.; Stellato, C.; Plitt, J.R.; Bickel, C.; Miura, K.; Georas, S.N.; Casolaro, V.; Schleimer, R.P. Activation of eotaxin gene transcription by NF-κB and STAT6 in human airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6876–6883. [Google Scholar]
- Rankin, J.A.; Picarella, D.E.; Geba, G.P.; Temann, U.A.; Prasad, B.; DiCosmo, B.; Tarallo, A.; Stripp, B.; Whitsett, J.; Flavell, R.A. Phenotypic and physiologic characterization of transgenic mice expressing interleukin-4 in the lung: Lymphocytic and eosinophilic inflammation without airway hypersensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 7821–7825. [Google Scholar]
- Brusselle, G.; Kips, J.; Joos, G.; Bluethmann, H.; Pauwels, R. Allergen-induced airway inflammation and bronchial responsiveness in wild-type and interleukin-4-deficient mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1995, 12, 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, M.; Yano, M.; Matsuda, H. Pharmacological study on Citrus fruits. I. Anti-allergic effect of fruit of Citrus unshiu Markovich (1). Yakugaku Zasshi 1989, 109, 835–842. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, M.; Parmar, H.S. Evaluation of antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential of hesperidin and naringin on the rat air pouch model of inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Quelle, F.W.; Shimoda, K.; Thierfelder, W.; Fischer, C.; Kim, A.; Ruben, S.M.; Cleverland, J.L.; Pierce, J.H.; Keegan, A.D.; Nelms, K.; et al. Cloning of murine stat6 and human stat6, stat proteins that are tyrosine phosphorylated in responses to IL-4 and IL-3 but are not required for mitogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 3336–3343. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck, J.; Woisetschläger, M. STAT6 mediates eotaxin-1 expression in IL-4 or TNF-alpha-induced fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4507–4515. [Google Scholar]
- Mayumi, M. EoL-1, a human eosinophilic cell line. Leuk. Lymphoma 1992, 7, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, H.; Bourinbaiar, A.; Ginsburg, M.; Minato, K.; Ceresi, E.; Yamada, K.; Machover, D.; Bréard, J.; Mathé, G. Establishment and characterization of a new human eosinophilic leukemia cell line. Blood 1985, 66, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Ponath, P.D.; Qin, S.; Post, T.W.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Gerard, N.P.; Mackay, C.R. Molecular cloningand characterization of a human eotaxin receptor expressed selectively on eosinophils. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are commercially available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Roh, K.-B.; Kim, I.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.-A.; Jung, E.; Park, D. Synephrine Inhibits Eotaxin-1 Expression via the STAT6 Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2014, 19, 11883-11895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811883
Roh K-B, Kim I-H, Kim Y-S, Lee M, Lee J-A, Jung E, Park D. Synephrine Inhibits Eotaxin-1 Expression via the STAT6 Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11883-11895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811883
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoh, Kyung-Baeg, Il-Hyun Kim, Young-Soo Kim, Myungjae Lee, Jung-A Lee, Eunsun Jung, and Deokhoon Park. 2014. "Synephrine Inhibits Eotaxin-1 Expression via the STAT6 Signaling Pathway" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11883-11895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811883
APA StyleRoh, K. -B., Kim, I. -H., Kim, Y. -S., Lee, M., Lee, J. -A., Jung, E., & Park, D. (2014). Synephrine Inhibits Eotaxin-1 Expression via the STAT6 Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 19(8), 11883-11895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811883