Is Promiscuous CALB a Good Scaffold for Designing New Epoxidases?
Abstract
:1. Introduction



2. Results and Discussion
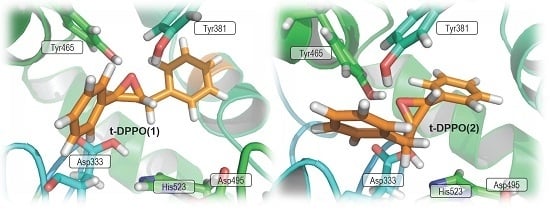
2.1. t-DPPO Hydrolysis Catalyzed by sEH


| (1)-DPPO | (2)-DPPO | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C1 | C2 | |||||
| Cluster | QM/MM a | Cluster | QM/MM a | Cluster | QM/MM a | Cluster | QM/MM a | |
| TS1 | 14.0 | - | 14.0 | - | 16.3 | - | 16.3 | - |
| I1 | 11.4(0.0) | 0.0 | 11.4 | 0.0 | 12.7 | 0.0 | 12.7 | 0.0 |
| TS2 | 39.9(28.5) | 23.5 | 41.5(30.1) | 24.5 | 42.5(29.8) | 18.4 | 40.2(27.5) | 27.6 |


2.2. t-DPPO Hydrolysis Catalyzed by CALB

| (1)-DPPO | (2)-DPPO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C1 | C2 | |
| RC | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| TS1 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| I1 | 2.6 | 2.6 | −0.5 | −0.5 |
| I1 | −0.8 | 0.3 | 2.0 | −1.8 |
| TS2 | 39.5 | 43.0 | 44.8 | 42.1 |



3. Computational Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devries, E.J.; Janssen, D.B. Biocatalytic conversion of epoxides. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.E.; Isaacs, N.S. Mechanism of epoxide reactions. Chem. Rev. 1959, 264, 9310–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.N. Asymmetric catalysis of epoxide ring-opening reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archelas, A.; Furstoss, R. Synthesis of enantiopure epoxides through biocatalytic approaches. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 491–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archelas, A.; Furstoss, R. Synthetic applications of epoxide hydrolases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wixtrom, R.N.; Hammock, B.D. Membrane-bound and soluble-fraction epoxide hydrolases: Methodological aspects. In Biochemical Pharmacology and Toxicology: Methodological Aspects of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes; Akim, D.Z., Vessey, D.A., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 1, pp. 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, M.F.; Grant, D.F.; Cheek, J.M.; Greene, J.F.; Williamson, K.C.; Hammock, B.D. Bioactivation of leukotoxins to their toxic diols by epoxide hydrolase. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, F.; Huse, L.M.; Morisseau, C.; Draper, A.J.; Newman, J.W.; Parker, C.; Graham, L.; Engler, M.M.; Hammock, B.D.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactiveepoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinal, C.J.; Miyata, M.; Tohkin, M.; Nagata, K.; Bend, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Targeted disruption of soluble epoxide hydrolase reveals a role in blood pressure regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40504–40510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, W.B. New role for epoxyeicosatrienoic acids as anti-inflammatory mediators. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.B.; Thompson, D.A.; Howard, L.L.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Weiss, R.H. Inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuate vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2002, 99, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Capdevila, J.H.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition lowers arterial blood pressure in angiotensin II hypertension. Hypertension 2002, 39, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Davis, B.B.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Olson, J.L.; Kroetz, D.L.; Weiss, R.H. Vascular localization of soluble epoxide hydrolase in humankidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2003, 286, F720–F726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yamamoto, T.; Newman, J.W.; Kim, I.H.; Watanabe, T.; Hammock, B.D.; Stewart, J.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M.; Imig, J.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition protects the kidney from hypertension-induced damage. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.D.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.H.; Davis, B.B.; Jiang, D.Q.; Zhao, T.T.; Xu, D.Y. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors and cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 11, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmquist, M. α/β-Hydrolase fold enzymes: Structures, functions and mechanisms. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beetham, J.K.; Grant, D.; Arand, M.; Garbarino, J.; Kiyosue, T.; Pinot, F.; Oesch, F.; Belknap, W.R.; Shinozaki, K.; Hammock, B.D. Gene evolution of epoxide hydrolases and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1995, 14, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Morisseau, C.; Maxwell, J.E.; Argiriadi, M.A.; Christianson, D.W.; Hammock, B.D. Biochemical evidence for the involvement of tyrosine in epoxide activation during the catalytic cycle of epoxide hydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23082–23088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busto, E.; Gotor-Fernández, V.; Gotor, V. Hydrolases: Catalytically promiscuous enzymes for non-conventional reactions in organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4504–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svedendahl, M.; Jovanovic, B.; Fransson, L.; Berglund, P. Suppressed native hydrolytic activity of a lipase to reveal promiscuous Michael addition activity in water. ChemCatChem 2009, 1, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świderek, K.; Martí, S.; Moliner, V. Theoretical study of primary reaction of Pseudozymaantarctica lipase B as the starting point to understand its promiscuity. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollis, D.L.; Cheah, E.; Cygler, M.; Dijkstra, B.; Frolow, F.; Franken, S.M.; Harel, M.; Remington, S.J.; Silman, I.; Schrag, J.; et al. The α/β hydrolase fold. Protein Eng. 1992, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świderek, K.; Pabis, A.; Moliner, V. A theoretical study of carbon-carbon bond formation by a Michael-type addition. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 5598–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Hu, J.; Miller, E.; Xie, W.; Cai, M.; Gross, R. Candida antarctica Lipase B chemically immobilized on epoxy-activated micro- and nanobeads: Catalysts for Polyester Synthesis. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svedendahl, M.; Carlqvist, P.; Branneby, C.; Allnér, O.; Frise, A.; Hult, K.; Berglund, P.; Brinck, T. Direct epoxidation in Candida antarctica lipase B studied by experiment and theory. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsdale, R.; Hoyle, S.; Grey, D.T.; Ridder, L.; Mulholland, A.J. Determinants of reactivity and selectivity in soluble epoxide hydrolase from quantum mechanics/molecular Mechanics modeling. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiriadi, M.A.; Morisseau, C.; Goodrow, M.H.; Dowdy, D.L.; Hammock, B.D.; Christianson, D.W. Binding of alkylurea inhibitors to epoxide hydrolase implicates active site tyrosines in substrate activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15265–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiøtt, B.; Bruice, T.C. Reaction mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14558–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrein, B.A.; Bauer, P.; Duarte, F.; Carlsson, Å.J.; Naworyta, A.; Mowbray, S.L.; Widersten, M.; Kamerlin, S.C.L. Expanding the catalytic triad in epoxide hydrolases and related enzymes. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5702–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, B.; Jones, A.D.; Pinot, F.; Grant, D.F.; Kurth, M.J.; Hammock, B.D. Mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase: Formation of an α-hydroxy ester-enzyme intermediate through Asp-333. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26923–26930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Robertson, A.D.; Jensen, J.H. Very fast empirical prediction and rationalization of protein pKa values. Proteins 2005, 61, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, D.C.; Rogers, D.M.; Jensen, J.H. Very fast prediction and rationalization of pKa values for protein-ligand complexes. Proteins 2008, 73, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; Søndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, C.R.; Olsson, M.H.M.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H.J. Improved treatment of ligands and coupling effects in empirical calculation and rationalization of pka values. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 2284–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, K.H.; Himo, F. Theoretical study of the full reaction mechanism of human soluble epoxide hydrolase. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 6898–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopmann, K.H.; Himo, F. Insights into the reaction mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase from theoretical active site mutants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21299–21310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.N. Enzyme-catalyzed detoxification reactions: Mechanisms and stereochemistry. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1987, 22, 39–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinot, F.; Grant, D.F.; Beetham, J.K.; Parker, A.G.; Borhan, B.; Landt, S.; Jones, A.D.; Hammock, B.D. Molecular and biochemical evidence for the involvement of the Asp333-His523 pair in the catalytic mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7968–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisseau, C.; Du, G.; Newman, J.W.; Hammock, B.D. Mechanism of mammalian soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition by chalcone oxide derivatives. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 356, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfström, L.T.; Widersten, M. Implications for an ionized alkyl-enzyme intermediate during StEH1-catalyzed trans-stilbene oxide hydrolysis. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppenberg, J.; Hansen, M.T.; Patkar, S.; Jones, T.A. The sequence, crystal structure determination and refinement of two crystal forms of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Structure 1994, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discovery Studio Modeling Environment; Release 3.5; Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015.
- Dewar, M.J.S.; Zoebisch, E.G.; Healy, E.F.; Stewart, J.J.P. The development and use of quantum mechanical molecular models. 76. AMI: A new general purpose quantum mechanical molecular model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. Density functionals with broad applicability in chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.J.P. MOPAC2007; Computational Chemistry: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. GAUSSIAN 09; Revision A.1; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng, H.F.; Laughlin, L.T.; Lin, S.; Armstrong, R.N. The catalytic mechanism of microsomal epoxide hydrolase involves reversible formation and rate limiting hydrolysis of the alkyl-enzyme intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 9436–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bordes, I.; Recatalá, J.; Świderek, K.; Moliner, V. Is Promiscuous CALB a Good Scaffold for Designing New Epoxidases? Molecules 2015, 20, 17789-17806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017789
Bordes I, Recatalá J, Świderek K, Moliner V. Is Promiscuous CALB a Good Scaffold for Designing New Epoxidases? Molecules. 2015; 20(10):17789-17806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017789
Chicago/Turabian StyleBordes, Isabel, José Recatalá, Katarzyna Świderek, and Vicent Moliner. 2015. "Is Promiscuous CALB a Good Scaffold for Designing New Epoxidases?" Molecules 20, no. 10: 17789-17806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017789
APA StyleBordes, I., Recatalá, J., Świderek, K., & Moliner, V. (2015). Is Promiscuous CALB a Good Scaffold for Designing New Epoxidases? Molecules, 20(10), 17789-17806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017789