Metabolic Profiling of the Uncaria Hook Alkaloid Geissoschizine Methyl Ether in Rat and Human Liver Microsomes Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of GM Metabolites Using LC/MS/MS


2.2. Structure Elucidation of GM Metabolites in Rat and Human Liver Microsomes
2.2.1. Metabolites Produced by Demethylation (M1-1 and M1-2)


| No. | Parent Ion m/z | Retention Time (min) | Formula | Product Ions (MS2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM | 367.2 | 16.5 | C22H26N2O3 | 335.2, 251.2, 236.2, 170.2, 144.0 |
| M1-1 | 353.2 | 9.7 | C21H24N2O3 | 251.4, 170.2, 144.2, 108.2 |
| M2-1 | 365.2 | 9.9 | C22H24N2O3 | 223.2, 170.0, 144.2 |
| M3-1, M3-2, M3-3 | 381.2 | 6.1, 8.7, 9.5 | C23H28N2O3 | 237.2, 184.4, 144.0, 265.2, 144.2 |
| M4-1, M4-2, M4-3 | 383.2 | 6.6, 7.5, 9.7 | C22H26N2O4 | 267.0, 186.2, 160.2, 223.2, 170.2, 144.2 |
| M5-1, M5-2 | 385.2 | 3.9, 5.4 | C22H28N2O4 | 251.2, 170.4, 144.0 |
| M6-1 | 339.2 | 7.8 | C20H22N2O3 | 223.2, 197.2, 168.4, 154.2, 144.2 |
| M7-1 | 401.2 | 2.4 | C22H28N2O5 | 267.4, 160.2 |

2.2.2. Metabolites Produced by Dehydrogenation (M2-1)
2.2.3. Metabolites Produced by Methylation (M3-1, M3-2 and M3-3)
2.2.4. Metabolites Produced by Oxidation (M4-1, M4-2 and M4-3)
2.2.5. Metabolites Produced by Water-Adduct Metabolism (M5-1 and M5-2)
2.2.6. Metabolites Produced by Di-Demethylation (M6-1)
2.2.7. Metabolites Produced by Oxidation Followed by Water Addition (M7-1)
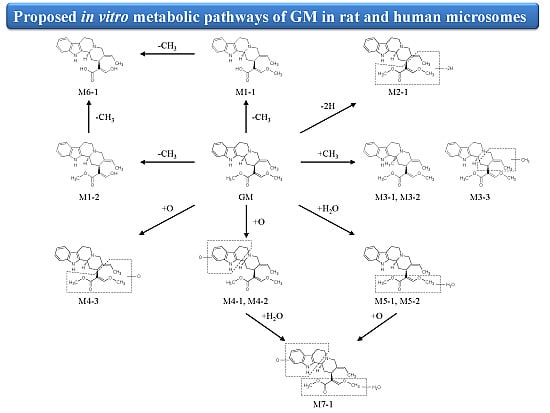
2.3. Biotransformation Pathway of GM

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.1.1. Isolation of GM
3.1.2. Synthesis of 23-O-demethyl GM and (±)-Geissoschizine
3.1.3. Other Reagents
3.2. Microsomal Incubations of GM and Sample Preparation
3.3. LC/MS/MS Analysis of GM and Its Metabolites
3.4. Identification of Demethyl GM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pengsuparp, T.; Indra, B.; Nakagawasai, O.; Tadano, T.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Kisara, K. Pharmacological studies of geissoschizine methyl ether, isolated from Uncaria sinensis Oliv., in the central nervous system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 425, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, Z.; Kanno, H.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Yokukansan, a kampo medicine, protects against glutamate cytotoxicity due to oxidative stress in PC12 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Imamura, S.; Tabuchi, M.; Kushida, H.; Nishi, A.; Kanno, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. The blood-brain barrier permeability of geissoschizine methyl ether in Uncaria hook, a galenical constituent of the traditional Japanese medicine yokukansan. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Imamura, S.; Tabuchi, M.; Kanno, H.; Nakai, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Geissoschizine methyl ether, an alkaloid in Uncaria hook, is a potent serotonin (1A) receptor agonist and candidate for amelioration of aggressiveness and sociality by yokukansan. Neuroscience 2012, 207, 124–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ueki, T.; Nishi, A.; Imamura, S.; Kanno, H.; Mizoguchi, K.; Sekiguchi, K.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Effects of geissoschizine methyl ether, an indole alkaloid in Uncaria hook, a constituent of yokukansan, on human recombinant serotonin 7 receptor. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 33, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, T.; Ugawa, S.; Ishida, Y.; Shimada, S. Geissoschizine methyl ether has third-generation antipsychotic-like actions at the dopamine and serotonin receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 671, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kushida, H.; Fukutake, M.; Tabuchi, M.; Katsuhara, T.; Nishimura, H.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kanitani, M.; Kase, Y. Simultaneous quantitative analyses of indole and oxindole alkaloids of Uncaria Hook in rat plasma and brain after oral administration of the traditional Japanese medicine yokukansan using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, T.; Banba, K.; Hata, K.; Nihei, Y.; Hoshikawa, A.; Ohsawa, K. Metabolites of hirsuteine and hirsutine, the major indole alkaloids of Uncaria rhynchophylla, in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Le Verge, R.; Le Corre, P.; Chevanne, F.; Döe De Maindreville, M.; Royer, D.; Levy, J. Determination of yohimbine and its two hydroxylated metabolites in humans by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectral analysis. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1992, 574, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Berlan, M.; Le Verge, R.; Galitzky, J.; Le Corre, P. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist potencies of two hydroxylated metabolites of yohimbine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 108, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Feng, F.; Xie, N. The metabolism of YiGan San and subsequent pharmacokinetic evaluation of four metabolites in rat based on liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 972, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Perez, J.M. Current and future trends in the application of HPLC-MS to metabolite-identification studies. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Yuzurihara, M.; Ikarashi, Y.; Goto, K.; Sakakibara, I.; Hayakawa, T.; Sasaki, H. Geissoschizine methyl ether, an indole alkaloid extracted from Uncariae Ramulus et Uncus, is a potent vasorelaxant of isolated rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 444, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Deiters, A.; Chen, K.; Eary, C.T.; Martin, S.F. Biomimetic entry to the sarpagan family of indole alkaloids: Total synthesis of (+)-geissoschizine and (+)-N-methylvellosimine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds of GM, 23-O-demethyl GM, and (±)-geissoschizine are not available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kushida, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Igarashi, Y.; Nishimura, H.; Watanabe, J.; Maemura, K.; Kase, Y. Metabolic Profiling of the Uncaria Hook Alkaloid Geissoschizine Methyl Ether in Rat and Human Liver Microsomes Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2015, 20, 2100-2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022100
Kushida H, Matsumoto T, Igarashi Y, Nishimura H, Watanabe J, Maemura K, Kase Y. Metabolic Profiling of the Uncaria Hook Alkaloid Geissoschizine Methyl Ether in Rat and Human Liver Microsomes Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2015; 20(2):2100-2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022100
Chicago/Turabian StyleKushida, Hirotaka, Takashi Matsumoto, Yasushi Igarashi, Hiroaki Nishimura, Junko Watanabe, Kazuya Maemura, and Yoshio Kase. 2015. "Metabolic Profiling of the Uncaria Hook Alkaloid Geissoschizine Methyl Ether in Rat and Human Liver Microsomes Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 20, no. 2: 2100-2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022100
APA StyleKushida, H., Matsumoto, T., Igarashi, Y., Nishimura, H., Watanabe, J., Maemura, K., & Kase, Y. (2015). Metabolic Profiling of the Uncaria Hook Alkaloid Geissoschizine Methyl Ether in Rat and Human Liver Microsomes Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 20(2), 2100-2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022100