Dose-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects of Boldine in HepG-2 Cells—Telomerase Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
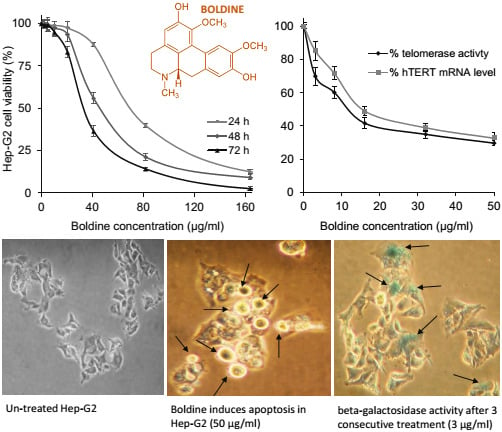
2.1. Dose and Time-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Boldine in HepG-2 Cells

2.2. Boldine Effectively Suppresses Telomerase Mainly by hTERT Down-Regulation

2.3. Boldine Induces Apoptosis in HepG-2 Cells


2.4. Boldine Induces p21 in HepG-2 Cells
2.5. Low Non-Toxic Concentration of Boldine Accelerates Senescence in HepG-2 Cells


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.3. Telomerase Assay (SYBR Green q-TRAP Assay)
3.4. Total RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time PCR
3.5. DNA ladder Formation
3.6. Fluorescence Microscopy of Apoptotic Cells
3.7. β-Galactosidase Staining as a Senescence Marker
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allsopp, R.C.; Vaziri, H.; Patterson, C.; Goldstein, S.; Younglai, E.V.; Futcher, A.B.; Greider, C.W.; Harley, C.B. Telomere length predicts replicative capacity of human fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10114–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, H.; Benchimol, S. Reconstitution of telomerase activity in normal human cells leads to elongation of telomeres and extended replicative life span. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, J.; Bacchetti, S. A survey of telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippi, C.; Loretz, B.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.M. Telomerase as an emerging target to fight cancer—Opportunities and challenges for nanomedicine. J. Control Release 2010, 146, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruden, M.; Puri, N. Novel anticancer therapeutics targeting telomerase. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013, 39, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocellin, S.; Pooley, K.A.; Nitti, D. Telomerase and the search for the end of cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureini, S.K.; Wink, M. Antiproliferative effects of crocin in HepG2 cells by telomerase inhibition and hTERT down-regulation. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2305–2309. [Google Scholar]
- Noureini, S.K.; Wink, M. Transcriptional down regulation of hTERT and induction of senescence in HepG2 cells by the benzophenanthridine alkaloid chelidonine. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3603–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi Noureini, S.; Wink, M. Antiproliferative effect of the isoquinoline alkaloid papaverine in hepatocarcinoma HepG-2 Cells—Inhibition of telomerase and induction of senescence. Molecules 2014, 19, 11846–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P.C.; Carrasco-Pozo, C.; Speisky, H. Boldine and its antioxidant or health-promoting properties. Chem. Biol. Interac. 2006, 159, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.X.; Ji, S.; Wang, W. Effects of boldine on tyrosinase, Inhibition kinetics and computational simulation. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, Y.C.; Kwon, O.S.; Han, E.S.; Song, J.H.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, C.S. Protective effect of boldine on dopamine-induced membrane permeability transition in brain mitochondria and viability loss in PC12 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stévigny, C.; Block, S.; de Pauw-Gillet, M.C. Cytotoxic aporphine alkaloids from Cassytha filiformis. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzberg, L.S.; Battle, T.; Rouleau, C.; Bagley, R.G.; Agata, N.; Yao, M.; Schmid, S.; Roth, S.; Crawford, J.; Krumbholz, R.; et al. Bone marrow and tumor cell colony-forming units and human tumor xenograft efficacy of noncamptothecin and camptothecin topoisomerase I inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3212–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Counter, C.M.; Meyerson, M.; Eaton, E.N.; Ellisen, L.W.; Caddle, S.D.; Haber, D.A.; Weinberg, R.A. Telomerase activity is restored in human cells by ectopic expression of hTERT (hEST2). Oncogene 1998, 16, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellert, G.C.; Dikmen, Z.G.; Wright, W.E.; Gryaznov, S.; Shay, J.W. Effects of a novel telomerase inhibitor, GRN163L, in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 96, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureini, S.K.; Esmaili, H. Multiple mechanisms of cell death induced by chelidonine in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 223, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwilaijareon, N.; Petmitr, S.; Mutirangura, A.; Ponglikitmongkol, M.; Wilairat, P. Stage specificity of Plasmodium falciparum telomerase and its inhibition by berberine. Parasitol. Int. 2002, 51, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talwalkar, S.S.; Vaidya, A.B.; Godse, C.; Vaidya, A.; Vaidya, R. Plasmodium DNA fluoresces with berberine, a novel approach for diagnosis of malarial parasites. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 124, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.; Jung, G. Positive association of long telomeres with the invasive capacity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.K.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.N.; Yoo, J.E.; Choi, J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.J.; Park, C. High telomerase activity and long telomeres in advanced hepatocellular carcinomas with poor prognosis. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.E.; Yoo, H.S.; Jin, C.-Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, Y.-W.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.-J.; Cho, C.K.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity in human lung carcinoma cells by the water extract of Cordyceps militaris. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, B.T.; Park, Y.-M.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity by trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in human leukemic U937 cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.E.; Park, C.; Kim, S.H.; Hossain, M.A.; Kim, Y.M.; Chung, H.Y.; Son, W.S.; Kim, G.-Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, N.D. Korean red ginseng extract induces apoptosis and decreases telomerase activity in human leukemia cells. J. Ethnopharm. 2009, 121, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yang, R.-C.; Chu, C.-J.; Wu, H.-T.; Pang, J.-H.S. Wogonin, an active compound in Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis and reduces telomerase activity in the HL-60 leukemia cells. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeb, D.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Pindolia, K.R.; Arbab, A.S.; Gautam, S.C. Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis by oleanane triterpenoid (CDDO-Me) in pancreatic cancer cells is associated with the suppression of hTERT gene expression and its telomerase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; Qin, Q.-P.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, Z.-F.; Liang, H. A platinum(II) complex of liriodenine from traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), Cell cycle arrest, cell apoptosis induction and telomerase inhibition activity via G-quadruplex DNA stabilization. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 137, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaczewski, C.V.; Saraiva, R.A.; Roos, D.H.; Boligon, A.; Athayde, M.L.; Kamdem, J.P.; Barbosa, N.V.; Rocha, J.B.T. Antioxidant activity of Peumus boldus extract and alkaloid boldine against damage induced by Fe(II)–citrate in rat liver mitochondria in vitro. Ind. Crop Prod. 2014, 54, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.S.; Tian, X.Y.; Huang, Y.; Murugan, D.; Achike, F.I.; Mustafa, M.R. Boldine protects endothelial function in hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress through an antioxidant mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthna, D.; Cmielova, J.; Tomsik, P.; Rezacova, M. Boldine and related aporphines, from antioxidant to antiproliferative properties. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konrath, E.L.; Santin, K.; Nassif, M.; Latini, A.; Henriques, A.; Salbego, C. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of boldine on hippocampal slices exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.; Shay, J.W. Actions of telomerase beyond telomeres. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chan, S.L.; Fu, W.; Mendosa, M.; Mattson, M.P. TERT suppresses apoptosis at a premitochondrial step by a mechanism requiring reverse transcriptase activity and 14–3-3 protein binding ability. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.H.; Meyer, J.N.; van Houten, B. Mitochondrial localization of telomerase as a determinant for hydrogen peroxide-induced mitochondrial DNA damage and apoptosis. Hum. Mol. Genet 2006, 15, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massared, C.; Zermati, Y.; Pauleau, A.L.; Larochette, N.; Métivier, D.; Sabatier, L.; Kroemer, G.; Soria, J.C. hTERT, a novel endogenous inhibitor of the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4505–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartel, A.L. The conflicting roles of the cdk inhibitor p21 CIP1/WAF1 in apoptosis. Leuk Res. 2005, 29, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Hurwitz, J.; Massague, J. Cell-cycle inhibition by independent CDK and PCNA binding domains in p21Cip1. Nature 1995, 375, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shats, I.; Milyavsky, M.; Tang, X.; Stambolsky, P.; Erez, N.; Brosh, R.; Kogan, I.; Braunstein, I.; Tzukerman, M.; Ginsberg, D.; et al. p53-dependent down-regulation of telomerase is mediated by p21 waf1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50976–50985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.R.; Cunningham, A.P.; Huynh, V.Q.; Andrews, L.G.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Evidence of extra-telomeric effects of hTERT and its regulation involving a feedback loop. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wink, M. The beta-carboline alkaloid harmine inhibits telomerase activity of MCF-7 cells by down-regulating hTERT mRNA expression accompanied by an accelerated senescent phenotype. Peer J. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubelj, I.; Pereira-Smith, O.; et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. p21 in cancer, intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.D.; Watanabe, K.; Broude, E.V.; Fang, J.; Poole, J.C.; Kalinichenko, T.V.; Roninson, I.B. Effects of p21 Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 on cellular gene expression, implications for carcinogenesis, senescence, and age-related diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival, application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.F.; Szalay, M.G.; Paskar, L.; Sahai, B.M.; Boyer, M.; Singh, B.; Green, D.R. Activation-induced cell death in T cell hybridomas is due to apoptosis. Morphologic aspects and DNA fragmentation. J. Immunol. 1990, 144, 3326–3333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ribble, D.; Goldstein, N.B.; Norris, D.A.; Shellman, Y.G. A simple technique for quantifying apoptosis in 96-well plates. BMC Biotechnol. 2005, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, D.; Bertola, G.; Dietrich, F.; Figueiró, F.; Zanotto-Filho, A.; Moreira Fonseca, J.C.; Morrone, F.B.; Barrios, C.H.; Battastini, A.M.; Salbego, C.G. Boldine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in T24 human bladder cancer cell line via regulation of ERK, AKT, and GSK-3β. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paydar, M.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Wong, Y.L.; Wong, W.F.; Looi, C.Y.; Mustafa, M.R. Evaluation of cytotoxic and chemotherapeutic properties of boldine in breast cancer using in vitro and in vivo models. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 719–733. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds boldine and berberine are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazemi Noureini, S.; Wink, M. Dose-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects of Boldine in HepG-2 Cells—Telomerase Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction. Molecules 2015, 20, 3730-3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033730
Kazemi Noureini S, Wink M. Dose-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects of Boldine in HepG-2 Cells—Telomerase Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):3730-3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033730
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazemi Noureini, Sakineh, and Michael Wink. 2015. "Dose-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects of Boldine in HepG-2 Cells—Telomerase Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction" Molecules 20, no. 3: 3730-3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033730
APA StyleKazemi Noureini, S., & Wink, M. (2015). Dose-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects of Boldine in HepG-2 Cells—Telomerase Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction. Molecules, 20(3), 3730-3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033730