Phytomelatonin: Assisting Plants to Survive and Thrive
Abstract
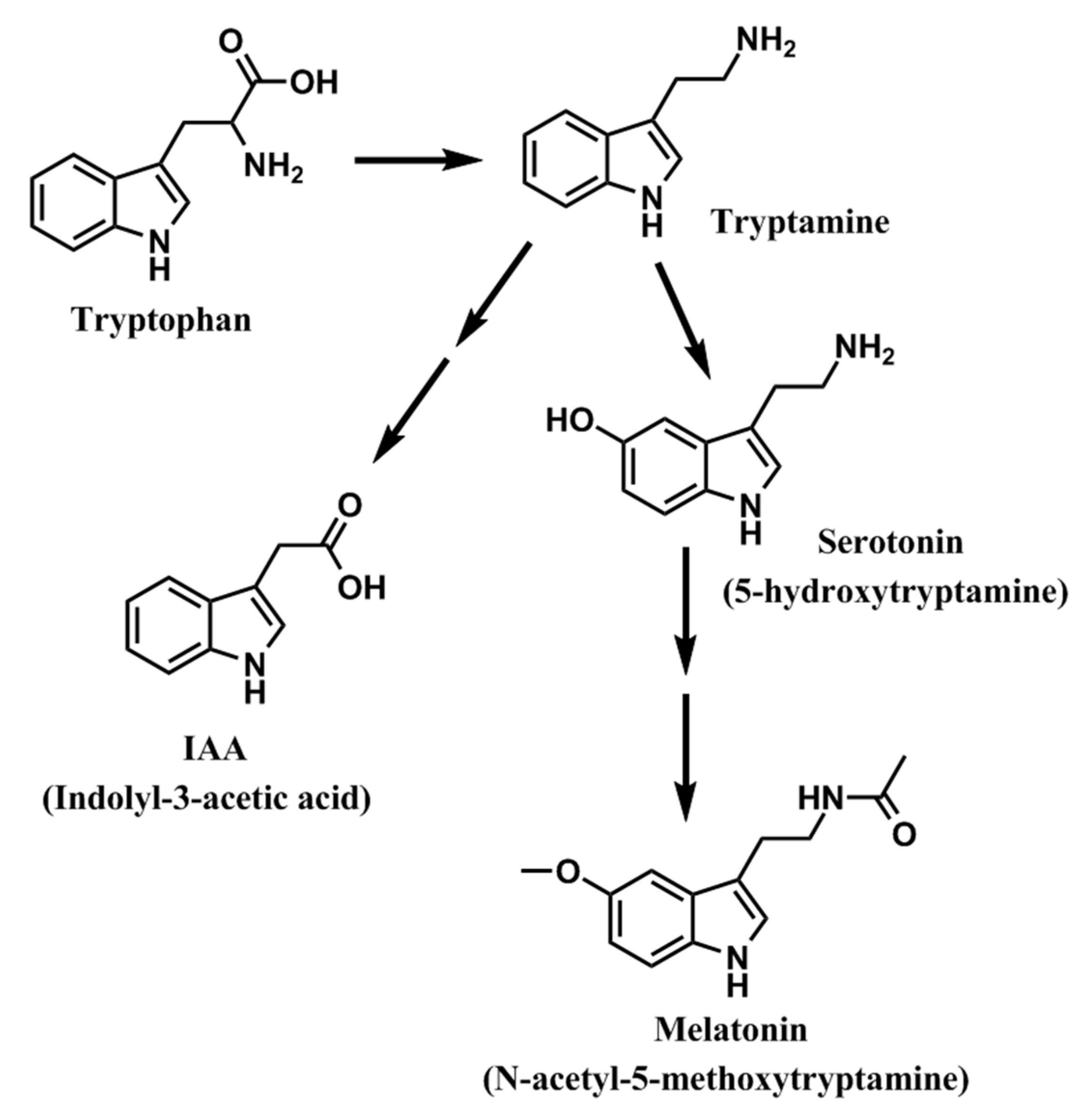
:1. Introduction
2. Melatonin in Plant Tissues: Expansion of the Field

3. Melatonin Rhythms in Plants

4. Effect of Stress on Plant Melatonin Synthesis

5. Melatonin Protects Plants from Abiotic Stresses


6. Melatonin Protects Plants from Biotic Stresses

7. Melatonin and Senescence in Plants


8. Melatonin Improves Plant Growth

9. Melatonin Improves Crop Yield and Provides Crop Protection


10. Plant Melatonin: Rules of Engagement
11. Concluding Remarks
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lerner, A.B.; Case, J.D.; Takahashi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Mori, W. Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightening melanocytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 81, 2587. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, A.B.; Case, J.D.; Heinzelman, R.V. Structure of melatonin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 6084–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, J.; Weissenbach, H. Enzymatic O-methylation of N-acetylserotonin to melatonin. Science 1960, 131, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, J.; Weissbach, H. Purification and properties of hydroxyindole-O-methyl transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1961, 236, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quay, W.B.; Halevy, A. Experimental modification of the rat pineal’s content of serotonin and related indoleamines. Physiol. Zool. 1962, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtman, R.J.; Axelrod, J.; Phillips, L.W. Melatonin synthesis in the pineal gland: Control by light. Science 1963, 142, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, E.W.; Wurtman, R.J.; Axelrod, J. An inhibitory effect of melatonin on the estrous phase of the estrous cycle of the rodent. Endocrinology 1964, 75, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, R.A.; Reiter, R.J. Pineal gland: Influence on gonads of male hamsters. Science 1965, 148, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, R.A.; Reiter, R.J. Influence of compensatory mechanisms and the pineal gland on dark-induced gonadal atrophy in male hamsters. Nature 1965, 207, 658–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Hester, R.J. Interrelationships of the pineal gland, the superior cervical ganglia and the photoperiod in the regulation of the endocrine systems of hamsters. Endocrinology 1966, 79, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quay, W.B.; Renzoni, A. Comparative and experimental study of the structure and cytology of the pineal body in the Passeriformes. Riv. Biol. 1963, 56, 363–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gundy, G.C.; Wurst, G.Z. Parietal eye-pineal morphology in lizards and its physiological implications. Anat. Rec. 1976, 185, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksche, A.; Hartwig, H.G. Pineal sense organs—Components of photoneuroendocrine systems. Prog. Brain Res. 1979, 52, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McNulty, J.A. Functional morphology of the pineal complex in cyclostomes, elasmobranches and bony fishes. Pineal Res. Rev. 1984, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Fraschini, F. Endocrine aspects of the mammalian pineal gland: A review. Neuroendocrinology 1969, 5, 219–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J.F.; Karsch, F.J.; Foster, D.L.; Takagi, S.; Dziuk, P.J. Effect of pinealectomy on estrus, ovulation and luteinizing hormone in ewes. Biol. Reprod. 1970, 2, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quay, W.B. Retinal and pineal hydroxyindole-O-methyl transferase activity in vertebrates. Life Sci. 1965, 4, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, P.C.; Hoff, K.M. Melatonin localization in the eyes of larval Xenopus. Comp. Biochem Physiol. 1971, 39, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Manchester, L.C. The universal nature, unequal distribution and antioxidant functions of melatonin and its derivatives. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Liu, X.Y.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D.; Reiter, R.J. Mitochondria and chloroplasts as the original sites of melatonin synthesis: A hypothesis related to melatonin’s primary function and evolution in eukaryotes. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiechmann, A.F.; Sherry, D.M. Role of melatonin and its receptors in the vertebrate retina. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 300, 211–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.; Brzezinski, A.; Brown, G.M. Melatonin and its analogs in insomnia and depression. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radogna, F.; Diederich, M.; Ghibelli, L. Melatonin: A pleiotropic molecule regulating inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, J.R.; Gonzalez-Yanes, C.; Maldonado, M.D. The role of melatonin in the cells of the innate immunity: A review. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Galano, A. Melatonin: Exceeding expectations. Physiology (Bethesda) 2014, 29, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Koppesetti, S. Medical implications of melatonin: Receptor-mediated and receptor-independent actions. Adv. Med. Sci. 2007, 52, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vivien-Roels, B.; Pevet, P.; Beck, O.; Fevre-Montagne, M. Identification of melatonin in the compound eyes of an insect, the locust (Locusta migratoria), by radioimmunoassay and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 49, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetterberg, L.; Hayes, D.K.; Halberg, F. Circadian rhythm of melatonin in the brain of the face fly, Musca autumnalis De Geer. Chronobiologia 1987, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finocchiaro, L.; Callebert, J.; Launay, J.M.; Jallen, J.M. Melatonin biosynthesis in Drosophila: Its nature and its effects. J. Neurochem. 1988, 50, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeggeler, B.; Balzer, I.; Hardeland, R.; Lerchl, A. Pineal hormone melatonin oscillates also in the dinoflagellate, Gonyaulax polyedra. Naturwissenschaften 1991, 78, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tassel, D.; Li, J.; O’Neill, S. Melatonin: Identification of a potential dark signal in plants. Plant Physiol. 1993, 102, 659, (Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dubbels, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Klenke, E.; Goebel, A.; Schnakenberg, E.; Ehlers, L.; Schiwara, H.W.; Schloot, W. Melatonin in edible plants identified by radioimmunoassay and by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pineal Res. 1995, 18, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, G.B. Tryptamines in edible fruits. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1958, 10, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenfriend, S.; Lovenberg, W.; Sjoerdsma, A. Physiologically active amines in common fruits and vegetables. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 85, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quay, W.B. Circadian rhythm in rat pineal serotonin and its modifications by estrous cycle and photoperiod. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1963, 14, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D.C.; Weller, J.L.; Moore, R.Y. Melatonin metabolism: neural regulation of pineal serotonin: Acetyl coenzyme A N-acetyltransferase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 3107–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champney, T.H.; Holktorf, A.P.; Steger, R.W.; Reiter, R.J. Concurrent determination of enzymatic activities and substrate concentrations in the melatonin synthetic pathway within the same rat pineal gland. J. Neurosci. Res. 1984, 11, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Chen, L.D.; Poeggeler, B.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: A potent, endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr. J. 1993, 1, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, A.; Migitaka, H.; Iigo, M.; Itoh, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohtani-Kancho, R.; Hara, M.; Sazuki, T.; Reiter, R.J. Identification of melatonin in plants and its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1995, 35, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brainard, G.C.; Petterborg, L.J.; Richardson, B.S.; Reiter, R.J. Pineal melatonin in Syrian hamsters: Circadian and seasonal rhythms in animals maintained under laboratory and natural conditions. Neuroendocrinology 1982, 35, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, D.S.; Goldman, B.D. Antigonadal effects of timed melatonin infusion in pinealectomized male Djungarian hamsters (Phodopus sungorus sungorus): Duration is the critical parameter. Endocrinology 1983, 113, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Simopoulos, A.P.; Maldonado, M.D.; Flores, L.J.; Terron, M.P. Melatonin in edible plants (phytomelatonin): Identification, concentrations, bioavailability and proposed functions. World Rev. Nutr. Diet 2007, 97, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tamura, H.; Tan, D.X.; Xu, X.P. Melatonin and the circadian system: Contributions to successful female reproduction. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J.; Park, W.; Monis, K.; Qi, W. High levels of melatonin in the seeds of edible plants: Possible function in germ tissue protection. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.X. Melatonin in walnuts: influence on levels of melatonin and total antioxidant capacity of blood. Nutrition 2005, 21, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladi, E.; Mohamadi, M.; Shamspur, T.; Mostafavi, A. Spectrofluorimetric determination of melatonin in kernels of four different Pistacia varieties after ultrasound-assisted solid-liquid extraction. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 132, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, G.M.; Pelham, R.W.; Pang, S.F.; Laughlin, L.L.; Wilson, K.W.; Sandock, K.L.; Vaughn, M.K.; Koslow, S.H.; Reiter, R.J. Nocturnal elevation of plasma melatonin and urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in young men: Attempts at modification by brief changes in environmental lighting and sleep and by autonomic drugs. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1976, 42, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.F. Melatonin concentrations in blood and pineal gland. Pineal Res. Rev. 1985, 3, 115–160. [Google Scholar]
- El Allali, K.; Sinitskaya, N.; Bothorel, B.; Achaaban, R.; Pevet, P.; Simonneaux, V. Daily Aa-nat gene expression in the camel (Camelus dromedarius) pineal gland. Chronobiol. Int. 2008, 25, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez-Pelaez, A.; Howes, K.A.; Gonzalez-Brito, A.; Reiter, R.J. N-acetyltransferase activity, hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase activity and melatonin levels in the Harderian glands of mate Syrian hamsters: Changes during the light:dark cycle and the effect of 6-parachlorophenylalanine administration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 145, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, C.; Garcia, J.A.; Escames, G.; Ortiz, F.; Lopez, A.; Doerrier, C.; Garcia-Corzo, L.; Lopez, L.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D. Extrapineal melatonin: Analysis of its subcellular distribution and daily fluctuations. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murch, S.J.; Simmons, C.B.; Saxena, P.K. Melatonin in feverfew and other medicinal plants. Lancet 1997, 350, 1598–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeggeler, B.; Hardeland, R. Detection and quantification of melatonin in a dinoflagellate, Gonyaulax polyedra: Solutions to the problem of methoxyindole destruction in non-vertebrate material. J. Pineal Res. 1994, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huo, Y.; Tan, D.X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Melatonin in Chinese medicinal herbs. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J. Functional aspects of the pineal hormone melatonin in combating cell and tissue damage induced by free radicals. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 134, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, S.; Reiter, R.J.; Tan, S.X.; Hardeland, R.; Cacrera, J.; Karbownik, M. DNA oxidatively damaged by chromium(III) and H2O2 is protected by the antioxidants melatonin, N1-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine, resveratrol and uric acid. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 33, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressmeyer, A.R.; Mayo, J.C.; Zelosko, V.; Sainz, R.M.; Tan, D.X.; Poeggeler, B.; Antolin, I.; Zsizsik, R.K.; Reiter, R.J.; Hardeland, R. Antioxidant properties of the melatonin metabolite N1-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AMK): Scavenging of free radicals and prevention of protein destruction. Redox. Rep. 2003, 8, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Reiter, R.J. One molecule, many derivatives: A never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species? J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.S.; Brown, G.M.; Spence, D.W.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin—A pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 350–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Cyclic 3-hydroxymelatonin, a key metaboite enhancing the peroxyl radical scavening activity of melatonin. Roy. Soc. Chem. Adv. 2014, 4, 4220–4227. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Galano, A. Melatonin reduces lipid peroxidation and membrane viscosity. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Hardeland, R.; Manchester, L.C.; Galano, A.; Reiter, R.J. Cyclic-3-hydroxymelatonin (C3HOM), a potent antioxidant, scavenges free radicals and suppresses oxidative reactions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, I.; Hardeland, R. Melatonin in algae and higher plants: Possible new roles as a phytohormone and antioxidant. Bot. Acta 1996, 109, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Fuhrberg, B. Ubiquitous melatonin: Presence and effects in unicells, plants, and animals. Trends Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 7, 25–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kolar, J.; Machackova, I. Occurrence and possible function of melatonin in plant: A review. Endocytobiosis Cell Res. 2001, 14, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Burkhardt, S.; Manchester, L.C. Melatonin in plants. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tassel, D.L.; O’Neill, S.D. Putative regulatory molecules in plants: Evaluating melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P.K. Melatonin: A potential regulator of plant growth and development? In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant. 2002, 38, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X. Melatonin: An antioxidant in edible plants. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 957, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caniato, R.; Filippini, R.; Piovan, A.; Puricelli, L.; Borsarini, A.; Cappaelletti, E.M. Melatonin in plants. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003, 527, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin, a potent agent in antioxidative defense: Actions as a natural food constituent, gastrointestinal factor, drug and prodrug. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2005, 2, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, J.; Machackova, I. Melatonin in higher plants: Occurrence and possible functions. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Craft, C.M.; Johnson, J.E., Jr.; King, T.S.; Richardson, B.A. Age-associated reduction in nocturnal pineal melatonin levels in female rats. Endocrinology 1981, 109, 1295–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J. Normal patterns of melatonin levels in the pineal gland and body fluids of humans and experimental animals. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 1986, 21, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Todini, L.; Terzano, G.M.; Borghese, A.; Debenedetti, A.; Malfatti, A. Plasma melatonin in domestic female Mediterranean sheep (Comisana breed) and goats (Maltese and Red Syrian). Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Allali, K.; Achaaban, M.R.; Vivien-Roels, B.; Bothorel, B.; Tligui, N.S.; Pevet, P. Seasonal variations in the nycthemeral rhythm of plasma melatonin in the camel (Camelus dromedarius). J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.A.; Love, R.J.; Hawton, A.; Arendt, J. Sleep and the endogenous melatonin rhythm of high artic residents during summer and winter. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 141, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: The chemical expression of darkness. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1991, 79, C153–C159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewy, A.J.; Wehr, T.A.; Goodwin, F.K.; Newsome, D.A.; Markey, S.P. Light suppresses melatonin secretion in humans. Science 1980, 210, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brainard, G.C.; Richarson, B.A.; King, T.S.; Matthews, S.A.; Reiter, R.J. The suppression of pineal melatonin content and N-acetyltransferase activity by different light irradiances in the Syrian hamster: A dose-response relationship. Endocrinology 1983, 113, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, I.M.; Norman, T.R.; Burrows, G.D.; Armstrong, S.M. Human melatonin suppression by light is intensity dependent. J. Pineal Res. 1989, 6, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolar, J.; Johnson, C.H.; Machackova, I. Presence and possible role of melatonin in a short-day flowering plant, Chenopodium rubrum. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 460, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Di Mascio, P.; Martinez, G.R.; Prado, F.M.; Reiter, R.J. Novel rhythms of N1-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine and its precursor melatonin in water hyacinth: Importance for phytoremediation. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J.; Manchester, L.C.; Yan, M.T.; El-Sawi, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Kohen, R.; Allegra, M.; Hardeland, R. Chemical and physical properties and potential mechanisms: Melatonin as a broad spectrum antioxidant and free radical scavenger. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Kynuramines, metabolites of melatonin and other indoles: The resurrection of an almost forgotten class of biogenic amines. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzen, S. Melatonin and synthetic analogs as antioxidants. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yan, J.; Fan, C.; Jiang, S.; Ou, Y. A review of melatonin in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury and clinical liver disease. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galano, A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. On the free radical scavenging activities of melatonin’s metabolites, AFMK and AMK. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, Y. Melatonin: A well-documented antioxidant with conditional pro-oxidant actions. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, S.; Hartzler, D.A.; Savikhin, S. Oxygen concentration inside a functioning photosynthetic cell. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 1882–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, O.; Haim, A.; Harel, O.; Gerchman, Y. Melatonin as an antioxidant and its semi-lunar rhythm in green macroalga Ulva sp. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, H.S.; Waaland, R.J. A molecular systemic study Ulva (Ulvaceae, Ulvales) from the northern Pacific. Phycologia 2004, 43, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnane, C.J.; McIvor, L.M.; Rindi, F.; Stengel, D.B.; Guiry, M.D. Morphology, rbcL phylogeny and distribution of distromatic Ulva (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta) in Ireland and southern Britain. Phycologia 2008, 47, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, S.; Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Hardeland, R.; Reiter, R.J. Detection and quantification of the antioxidant melatonin in Montmorency and Balaton tart cherries (Prunus cerasus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4898–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Poeggeler, B. Melatonin and synthetic melatonergic agonists: Actions and metabolism in the central nervous system. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandi, A.V.; Mosser, E.A.; Oikonomou, G.; Prober, D.A. Melatoin is required for the circadian regulation of sleep. Neuron 2015, 85, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, M.; Paredes, S.D.; Cubero, J.; Lozano, M.; Toribio-Delgado, A.F.; Munoz, J.L.; Reiter, R.J.; Barriga, C.; Rodriguez, A.B. Jerte Valley cherry-enriched diets improve nocturnal rest and incease 6-sulfatoxy melatonin and total antioxidant capacity in the urine of middle-aged and elderly humans. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigeon, W.R.; Carr, M.; Gorman, C.; Perlis, M.L. Effects of a tart cherry juice beverage on the sleep of older adults with insomnia: A pilot study. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howatson, G.; Bell, P.G.; Tallent, J.; Middleton, B.; McHugh, M.P.; Ellis, J. Effect of tart cherry juice (Prunus cerasus) on melatonin levels and enhanced sleep quality. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, M.; Gonzalez-Gomez, D.; Lozano, M.; Barriga, C.; Paredes, S.D.; Rodriguez, A.B. A Jerte Valley cherry product provides beneficial effects on sleep quality. Influence on aging. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y; Tan, D.X.; Lei, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.T.; Gao, Y.; Kong, J. Melatonin and its potential biological functions in the fruits of sweet cherry. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Wang, L.; Tan, D.X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X.D.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.T.; Zuo, B.X.; Kong, J. Identification of genes for melatonin synthetic enzymes in “Red Fuji” apple (Malus domesticus Borkh. cv. Red) and their expression and melatonin production during fruit development. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Collin, F. Melatonin: Action as antioxidant and potential applications in human disease and aging. Toxicology 2010, 278, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, J.; Loos, B.; Marais, E.; Engelbrecht, A.M. Mitochondrial catastrophe duirng doxorubin-induced cardiotoxicity: A review of the protective role of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. Chemical stress by different agents affects the melatonin content of barley roots. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, H.; Han, L.; Zhai, L. Characteristic montioring of groundwater—Salt transportation and input-output in inland arid irrigation area. J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Higuchi, K.; Hanawa, Y.; Shiraiwa, Y.; Ezura, H. Cloning and characterization of a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cDNA arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase and its use in the genetic engineering of melatonin content in the Micro-Tom tomato. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Back, K. Elevated production of melatonin in transgenic rice seeds expressng rice tryptophan decarboxylase. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, P.; Wei, Z.; Liang, D.; Liu, C.; Yin, L.; Jia, D.; Fu, M.; Ma, F. The mitigation effects of exogenous melatonin on salinity-induced stress in Malus hupehensis. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow-Walden, L.R.; Reiter, R.J.; Abe, M.; Pablos, M.; Menendez-Pelaez, A.; Chen, L.D.; Poeggeler, B. Melatonin stimulates brain glutathione peroxidase activity. Neurochem. Int. 1995, 26, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pablos, M.I.; Reiter, R.J.; Ortiz, G.G.; Guerrero, J.M.; Agapito, M.T.; Chuang, J.I. Rhythms of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase in brain of chick and their inhibition by light. Neurochem. Int. 1998, 32, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.W.; Kleszczynski, K.; Hardkop, L.H.; Kruse, N.; Zillikens, D. Melatonin enhances antioxidative enzyme gene experession (CAT, GPx, SOD), prevents their UVR-induced depletion, and protects against the formation of DNA damage (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxygaunosine) in ex vivo human skin. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas-Zapico, C.; Coto-Montes, A. A proposed mechanism to explain the stimulatory effect of melatonin on antioxidative enzymes. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostopoulou, Z.; Therios, I.; Roumeliotis, E.; Kanellis, A.K.; Molassiotis, A. Melatonin combined with ascorbic acid provides salt adaptation in Citrus aurantium L. seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 86, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.B.; Staub, B.A.; Natarajan, G.M.; Lasorda, D.M.; Poomima, I.G. Acute myocardial infarction associated with dietary supplements containing 1,3-dimethylamylamine and Citrus aurantium. Texas Heart Inst. J. 2014, 41, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; David, A.; Yadav, S.; Baluska, F.; Bhatla, S.C. Salt stress-induced seedling growth inhibition concides with differential distribution of serotonin and melatonin in sunflower seedling roots and cotyledons. Physiol. Plant 2014, 152, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syvertsen, J.P.; Garcia-Sanchez, F. Multiple abiotic stresses occurring with salinity stress in citrus. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 103, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, B.; Manchanda, V.K. Phytoremediation: Role of terrestrial plants and aquatic macrophytes in the remediation of radionuclides and heavy metal contaminated soil and water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 946–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Helton, P.; Reiter, R.J. Phytoremediative capacity of plants enriched with melatonin. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagriffoul, A.; Mocquot, B.; Mench, M.; Vangronsveld, J. Cadmium toxicity effects growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents and activities of stress related enzymes in young maize plants (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 1998, 200, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schützendübel, A.; Polle, A. Plant responses to abiotic stresses: Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, K.; Choo, K.S.; Pedersen, M.; Johansson, G.; Snoeijs, P. Effects of temperature on the production of hydrogen peroxide and volatile halocarbons by brackish-water algae. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolferus, R. To grow or not to grow: A stressful decision for plants. Plant Sci. 2014, 229C, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Parra, C.; Aranjuelo, I.; Pascual, I.; Erice, G.; Sanz-Saez, A.; Aquirreolea, J.; Sanchez-Diaz, M.; Irigoyen, J.J.; Araus, J.L.; Morales, F. Carbon balance, partitioning and photosynthetic acclimation in fruit-bearing grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Tempranillo) grown under simulated climate change (elevated CO2, elevated temperature and moderate drought) scenarios in temperature gradient greenhouses. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 174, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Savi, T.; Bertuzzi, S.; Branca, S.; Tretiach, M.; Nardini, A. Drought-induced xylem cavitation and hydraulic deterioration: Risk factors for urban trees under climate change. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Li, C.; Wei, Z.; Liang, D.; Ma, F. Long-term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought-induced leaf senescence in apple. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L; Zhao, Y.; Reiter, R.J.; He, C.; Liu, G.; Lei, Q.; Zuo, B.; Zheng, X.D.; Li, Q.; Kong, J. Changes in melatonin levels in transgenic “Micro Tom” tomato overexpressing ovine AANAT and ovine HIOMT genes. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, V.S.; Shukla, M.R.; Sherif, S.M.; Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P. Role of melatonin in alleviating cold stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Chan, Z. The cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor zinc finger of Arabidopsis thaliana 6-activated C-repeat-binding factor pathway is essential for melatonin-mediated freezing stress resistance in Arabidopsis. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.F.; Xu, T.F.; Wang, Z.Z.; Fang, Y.L.; Xi, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.W. The ameliorative effects of exogenous melatonin on grape cuttings under water-deficient stress: Antioxidant metabolites, leaf anatomy, and chloroplast morphology. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Tan, D.X.; Liang, D.; Chang, C.; Jia, D.; Ma, F. Melatonin mediates the regulation of ABA metabolism, free-radical scavenging, and stomatal behavior in two Malus species under drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Umezawa, T.; Urano, K.; Shinozaki, K. Regulatory metabolic networks in drought stress responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperry, J.; Hacke, U.; Uren, R.; Comstock, J. Water deficits and hydraulic limits to leaf water supply. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katul, G.; Leuning, R.; Oren, R. Relationship between plant hydraulic and biochemical properties derived from a steady-state coupled water and carbon transport model. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Jiang, C.; Ye, T.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Chan, Z. Comparative physiological, metabolomic, and transcriptomic analyses reveal mechanisms of improved abiotic stress resistance in bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L). Pers.] by exogenous melatonin. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 681–694. [Google Scholar]
- Weeda, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, X.; Ndip, G.; Guo, Y.; Buck, G.A.; Fu, C.; Ren, S. Arabidopsis transcriptome analysis reveals key roles of melatonin in plant defense systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.Y.; Zhu, R.Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Dai, Y.R. Attenuation of cold-induced apoptosis by exogenous melatonin in carrot suspension cells: The possible involvement of polyamines. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 36, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posmyk, M.M.; Balabusta, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Sliwinska, E.; Jana, K.M. Melatonin applied to cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seeds improves gemination during chilling stress. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, D.E.; Jang, H.; Byeon, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Back, K. Melatonin-rich transgenic rice plants exhibit resistance to herbicide-induced oxidative stress. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchiorri, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Sewerynek, E.; Hara, M.; Chen, L.; Nistico, G. Paraquat toxicity and oxidative damage: Reduction by melatonin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Sidhu, I.P.; Bhatti, G.K. Ameliorative action of melatonin on oxidative damage induced by atrazine toxicity in rat erythrocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 353, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afreen, F.; Zobayed, S.M.A.; Kozai, T. Melatonin in Glycyrrhiza uralensis: Response of plant roots to spectral quality of light and UV-B radiation. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posmyk, M.M.; Kuran, H.; Marciniak, K.; Janas, K.M. Presowing seed treatment with melatonin protects red cabbage seedlings against toxic copper concentrations. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 45, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Sawamura, K.; Konno, K. Diplocarpon mali sp. nov. the perfect state of apple blotch fungus Marssonina coronaria. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1974, 40, 412–418. [Google Scholar]
- Donghoon, S.; Hunjoohg, K.; Yangyik, S. Influence of defoliation by Marssonina blotch on vegetative growth and fruit quality in “Fuji”/M.9 apple tree. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 531–538. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.N.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, P. Out-break of Marssonina blotch in warmer climates causing premature leaf fall problem of apple and its management. Acta Hortic. 2004, 662, 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Wang, P.; Li, M.; Ke, X.; Li, C.; Liang, D.; Wu, S.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Zou, Y.; et al. Exogenous melatonin improves Malus resistance to Marssonina apple blotch. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Byeon, Y.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J.; Back, K. Arabidopsis seratonin N-acetyltransferase knockout mutant plants exhibit decreased melatonin and salicylic acid resulting in susceptibility to an avirulent pathogen. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.O.; Nam, H.G. The molecular and gentic control of leaf senescence and longevity in Arabidopsis. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 2005, 67, 49–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.O.; Kim, H.J.; Nam, H.G. Leaf senescence. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. Protective effect of melatonin agaist chlorophyll degradation during the senescence of barley leaves. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yin, L.; Liang, D.; Li, C.; Ma, F.; Yue, Z. Delayed senescence of apple leaves by exogenous melatonin treatment: Toward regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Chang, C.; Feng, F.; Liang, D.; Cheng, L.; Ma, F. Delay in leaf senescence of Malus hupehensis by long-term melatonin application is associated with its regulation of metabolic status and protein degradation. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Liang, D.; Ma, F. Melatonin regulates proteomic changes during leaf senescence in Malus hupehensis. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Chan, Z. INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBE 17 positively modulates natural leaf senescence through melatonin-mediated pathway in Arabidopsis. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, S.D.; Korkmaz, A.; Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Phytomelatonin: A review. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posmyk, M.M.; Janas, K.M. Melatonin in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2009, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig-Müller, J. Auxin conjugates: Their role for plant development and in the evolution of land plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1757–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, M.; Robert, S.; Kleine-Vehn, J. Auxin: Simply complicated. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2565–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. Melatonin: Plant growth regulator and/or biostimulator during stress? Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin in plants and other phototrophs: Advances and gaps concerning the diversity of functions. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Ruiz, J.; Cano, A.; Arnao, M.B. Melatonin: Growth-stimulating compound present in lupin tissues. Planta 2004, 220, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Ruiz, J.; Cano, A.; Arna, M.B. Melatonin acts as a growth-stimulating compound in some monocot species. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. The physiological function of melatonin in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2006, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. Melatonin in plants: More studies are necessary. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.P.; Cao, J.; O’Brien, R.; Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P.K. The mode of action of thidiazuron: Auxins, indoleamines, and ion channels in the regeneration of Echinacea purpurea L. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Higuchi, K.; Aouini, A.; Ezura, H. Lowering intracellular melatonin levels by transgenic analysis of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase from rice in tomato plants. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 49, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P.K. A melatonin-rich germplasma line of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Back, K. Enhanced production of melatonin by ectopic overexpression of human serotonin N-acetyltransferase plays a role in cold resistance in transgenic rice seedlings. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 49, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J. Genetic Transformation of Nicotiana tobacum L. and Hypericum perforatum L. by Agrobacterium tumefaciens Carrying Melatonin Synthetase Gene and Enhancement of Antioxidative Capacity in Transgenic plants. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Science, Northwest A and F University, Yangling, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.D.; Sun, Y.; Guao, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J. Effects of exogenous melatonin on ascorbate metabolism system in cucumber seedlings under high temperature stress. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2010, 21, 2580–2586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Hardeland, R.; Manchester, L.C.; Korkmaz, A.; Ma, S.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Reiter, R.J. Functional roles of melatonin in plants, and perspectives in nutritional and agricultural science. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peret, B.; Larrieu, A.; Bennett, M.J. Lateral root emergence: A difficult birth. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 3637–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanen, K.; Boucheron, E.; Vanneste, S.; Vercruysse, S.; Boucheron, E.; Aalard, P.; Chriqui, D. Auxin-mediated cell cycle activation during early lateral root initiation. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2339–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, P.J.; Park, C.M. Auxin homeostasis during lateral root development under drought conditions. Plant Signal Behav. 2009, 4, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murch, S.J.; Campbell, S.S.B.; Saxena, P.K. The role of serotonin and melatonin in plant morphogenesis: Regulation of auxin-induced root organogenesis in in vitro cultured explants of St. john’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 37, 386–393. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Qi, W.B.; Reiter, R.J.; Wei, W.; Wang, B.M. Exogenously applied melatonin stimulates root growth and raises endogenous indoleacetic acid in roots of etiolated seedlings of Brassica juncea. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarropoulon, V.N.; Therios, I.N.; Dimassi-Theriou, K.N. Melatonin promotes adventitous root regeneration in in vitro shoot tip explants of the commercial sweet cherry rootstocks CAB-6P (Prunus cerasus L.), Gisela 6 (P. cerasus × P. canescens), and MxM60 (P. avium × P. mahaleb). J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Arnao, M.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. Melatonin promotes adventitious- and lateral root regeneration in etiolated hypocotyls of Lupinus albus L. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelagio-Flores, R.; Munoz-Parra, E.; Ortiz-Castro, R.; Lopez-Bucio, J. Melatonin regulates Arabidopsis root system architecture likely acting independetly of auxin signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhao, B.; Sun, Q.Q.; Cao, Y.Y.; Li, R.; Wu, X.X.; Weeda, S.; Li, L.; Ren, S.; et al. The RNA-seq approach to discriminate gene expression profiles in response to melatonin on cucumber lateral root formation. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- De Tomasi, J.A. Improving the technique of the Feulgen stain. Stain Technol. 1936, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Byeon, Y.; Back, K. An increase in melatonin in transgenic rice causes pleiotropic phenotypes, including enhanced seedling growth, delayed flowering and low grain yield. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiryaki, I.; Keles, H. Reversal of the inhibitory effect of light and high temperature on germination of Phacelia tanacetifolia seeds by melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Li, Q.T.; Chu, Y.N.; Reiter, R.J.; Yu, X.M.; Zhu, D.H.; Zhang, W.K.; Ma, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, J.S.; et al. Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 695–707. [Google Scholar]
- Specht, J.E.; Hume, D.J.; Kumudini, S.V. Soybean yield potential—A genetic and physiological perspective. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Goldsmith, P.D. World soybean production: Area harvested, yield and long-term projections. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2009, 12, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Byeon, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.; Back, K. Light-regulated melatonin biosynthesis in rice during senescence process in detached leaves. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Functional analyses of three ASMT gene family members in rice plants. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Back, K. Cellular localization and kinetics of the rice melatonin biosynthetic enzymes SNAT and ASMT. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 56, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Melatonin synthesis in rice seedlings in vivo is enhanced at high temperatures and under dark conditions due to increased serotonin N-acetyltransferase and N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase activities. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Back, K. Tryptamine 5-hydroxylase-deficient Sekiguchi rice induces synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptophan and N-acetyltryptamine but decreases melatonin biosynthesis during senescence process of detached leaves. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Transcriptional suppression of tryptamine 5-hydroxylase, a terminal serotonin biosynthetic gene, induces melatonin biosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa, L.). J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Molecular cloning of rice serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate gene in plant melatonin biosynthesis. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, K.; Back, K. A rice chloroplast transit peptide sequence does not alter the cytoplasmic localization of sheep seratonin N-acetyltransferase expressed in transgenic rice plants. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, D.W.; Back, K. Chloropast-encoded serotonin N-acetyltransferase in the red alga (Pyropia Yezoensis): Gene transition to the nucleus from chloroplasts. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Lee, K.; Park, Y.I.; Park, S.; Back, K. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of serotonin N-acetyltransferase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Byeon, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, T.; Back, K. Cloning and characterization of a serotonin N-acetyltransferase from a gymnosperm, loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Back, K. Microarray analysis of genes differentially expressed in melatonin-rich transgenic rice expressing a sheep serotonin N-acetyltransferase. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Shi, J.; Li, R.; Weeda, S.; Zhao, B.; Ren, S.; et al. Melatonin promotes ripening and improves quality of tomato fruit during postharvest life. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 657–668. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, L.; Grierson, D. Ethylene biosynthesis and action in tomato: A model for climacteric fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 2039–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubocovich, M.L. Pharmacology and function of melatonin receptors. FASEB J. 1988, 2, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zee, P.C. Melatonin receptors: An overview for physicians. Postgrad. Med. 2004, 116, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doghramji, K. Melatonin and its receptors: A new class of sleep-promoting agents. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2007, 3, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slominski, R.M.; Reiter, R.J.; Schlabritz-Loutsevitch, N.; Ostrom, R.S.; Slominski, A.T. Melatonin membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: Distrubtion and functions. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 35, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekcioglu, C. Expression and putative functions of melatonin receptors in malignant cells and tissues. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2014, 164, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masana, M.I.; Dubocovich, M.L. Melatonin receptor signaling: finding the path through the dark. Sci. STKE 2001, 107, pe39. [Google Scholar]
- Reppert, S.M. Melatonin receptors: Molecular biology of a new family of G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Rhythms 1997, 12, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin: Signaling mechanisms of a pleiotropic agent. Biofactors 2009, 35, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuna-Castroviejo, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Menendez-Pelaez, A.; Pablos, M.I.; Burgos, A. Characterization of high-affinity melatonin binding sites in purified cell nuclei of rat liver. J. Pineal Res. 1994, 16, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, C.; Wiesenberg, I. The orphan receptor family RZR/ROR, melatonin and 5-lipoxygenase: An unexpected relationship. J. Pineal Res. 1995, 18, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Guerrero, J.M.; Lardone, P.J.; Reiter, R.J. A review of the multiple actions of melatonin on the immune system. Endocrine 2005, 27, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez-King, G.; Anton-Tay, F. Calmodulin mediates melatonin cytoskeletal effects. Experientia 1993, 49, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Calvo, J.R.; Guerrero, J.M. Inhibition of cerebellar nitric oxide synthase and cyclic GMP production by melatonin via complex formation with calmodulin. J. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 65, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussard, M.F.; Truche, S.; Rousseau-Rojas, A.; Briss, S.; Descamps, S.; Droual, M.; Wierzbicki, M.; Ferry, G.; Audinot, V.; Delagrange, P.; et al. New ligands at the melatonin binding site MT(3). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boutin, J.A.; Audinot, V.; Ferry, G.; Delagrange, P. Molecular tools to study melatonin pathways and activities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamini, B.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Boutin, J.A.; Mesecar, A.D. Kinetic, thermodynamic and X-ray structural insights into the interaction of melatonin and analogues with quinone reductase 2. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, H.; Takasaki, A.; Taketani, T.; Tanabe, M.; Kizuka, F.; Lee, L.; Tamura, I.; Maekawa, R.; Asada, H.; Yamagata, Y.; et al. Melatonin as a free radical scavenger in the ovarian follicle. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Flora, S.J. Structural, chemical and biological aspects of antioxidants for strategies against metal and metalloid exposure. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2009, 2, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, S.; Negro, S.; Tataranno, M.L.; Buonocore, G. Oxidative stress and antioxidant strategies in newborns. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 23 (Suppl. 3), 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurer-Orhan, H.; Suzen, S. Melatonin, its metabolites and its synthetic analogs as multi-faceted compounds: Antioxidant, prooxidant and inhibitor of bioactivation reactions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pablos, M.I.; Chuang, J.; Reiter, R.J.; Ortiz, G.G.; Daniels, W.M.; Sewerynek, E.; Melchiorri, D.; Poeggeler, B. Time course of melatonin induced increase in glutathione peroxidase activity in chick tissues. Biol. Signals 1995, 4, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchendu, E.E.; Shukla, M.R.; Reed, B.M.; Saxena, P.K. Melatonin enhances the recovery of cryopreserved shoot tips of American elm (Ulmus americana L.). J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Zhou, Z.; Cruz, M.H.C.; Fuentes-Broto, L.; Galano, A. Phytomelatonin: Assisting Plants to Survive and Thrive. Molecules 2015, 20, 7396-7437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20047396
Reiter RJ, Tan D-X, Zhou Z, Cruz MHC, Fuentes-Broto L, Galano A. Phytomelatonin: Assisting Plants to Survive and Thrive. Molecules. 2015; 20(4):7396-7437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20047396
Chicago/Turabian StyleReiter, Russel J., Dun-Xian Tan, Zhou Zhou, Maria Helena Coelho Cruz, Lorena Fuentes-Broto, and Annia Galano. 2015. "Phytomelatonin: Assisting Plants to Survive and Thrive" Molecules 20, no. 4: 7396-7437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20047396
APA StyleReiter, R. J., Tan, D.-X., Zhou, Z., Cruz, M. H. C., Fuentes-Broto, L., & Galano, A. (2015). Phytomelatonin: Assisting Plants to Survive and Thrive. Molecules, 20(4), 7396-7437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20047396








