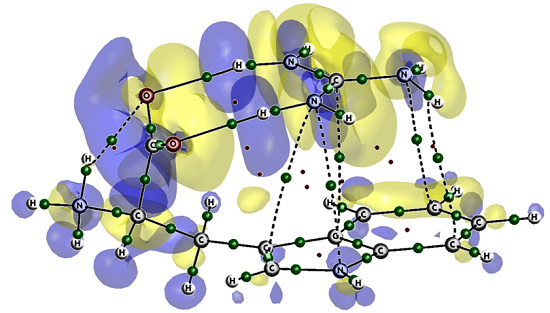
Aromatic Amino Acids-Guanidinium Complexes through Cation-π Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure and Energy

| M06-2x | Gu-Phe | Gu-His | Gu-Trp | Gu-Tyr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [a1] | −68.2 | −50.3 | −65.2 | −69.5 |
| [a2] | −60.8 | −41.1 | −60.1 | −64.3 |
| [b] | −65.6 | −48.1 | −55.7 | −66.8 |
| [c] | −21.4 | −21.4 | −15.9 | −19.8 |
2.2. Analysis of the Electron Density: AIM Analysis

| Complex | Type | ρBCP | ∇2ρBCP | Complex | Type | ρBCP | ∇2ρBCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gu-Phe[a1] | cation-π | 0.0072 | 0.0212 | Gu-Phe[a2] | cation-π | 0.0053 | 0.0152 |
| 0.0072 | 0.0214 | 0.0083 | 0.0254 | ||||
| O1…H1 | 0.0303 | 0.1204 | O1…H1 | 0.0283 | 0.1119 | ||
| O1…H2 | 0.0270 | 0.1130 | O1…H2 | 0.0220 | 0.0913 | ||
| Gu-Phe[b] | cation-π | 0.0053 | 0.0140 | Gu-Phe[c] | cation-π | 0.0064 | 0.0193 |
| 0.0059 | 0.0173 | 0.0071 | 0.0229 | ||||
| O1…H1 | 0.0372 | 0.1292 | N…H | 0.0047 | 0.0144 | ||
| O2…H2 | 0.0322 | 0.1149 | |||||
| Gu-His[a1] | cation-π | 0.0062 | 0.0215 | Gu-His[a2] | O1…H1 | 0.0270 | 0.1063 |
| 0.0088 | 0.0286 | O1…H2 | 0.0224 | 0.0940 | |||
| O…N | 0.0091 | 0.0295 | N…H | 0.0090 | 0.0296 | ||
| O1…H1 | 0.0299 | 0.1173 | 0.0125 | 0.0420 | |||
| O1…H2 | 0.0266 | 0.1141 | |||||
| Gu-His[b] | cation-π | 0.0041 | 0.0119 | Gu-His[c] | N…H | 0.0051 | 0.0148 |
| N…H | 0.0086 | 0.0264 | 0.0100 | 0.0337 | |||
| O1…H1 | 0.0374 | 0.1280 | |||||
| O2…H2 | 0.0350 | 0.1228 | |||||
| Gu-Trp[a1] | cation-π | 0.0064 | 0.0197 | Gu-Trp[a2] | cation-π | 0.00841 | 0.02968 |
| 0.0069 | 0.0204 | O1…H1 | 0.02628 | 0.09790 | |||
| 0.0074 | 0.0223 | O1…H2 | 0.02600 | 0.10560 | |||
| 0.0078 | 0.0280 | ||||||
| O1…H1 | 0.0305 | 0.1181 | |||||
| O1…H2 | 0.0256 | 0.1075 | |||||
| Gu-Trp[b] | cation-π | 0.00622 | 0.01993 | Gu-Trp[c] | cation-π | 0.00689 | 0.01947 |
| 0.00635 | 0.01843 | 0.00704 | 0.02092 | ||||
| 0.00661 | 0.01901 | 0.00725 | 0.02356 | ||||
| 0.00702 | 0.02466 | 0.00725 | 0.02218 | ||||
| 0.00715 | 0.02102 | ||||||
| O1…H1 | 0.03038 | 0.11460 | |||||
| O2…H2 | 0.02866 | 0.10782 | |||||
| Gu-Tyr[a1] | cation-π | 0.00847 | 0.02842 | Gu-Tyr[a2] | cation-π | 0.00740 | 0.02233 |
| O…H | 0.00786 | 0.02664 | 0.00858 | 0.02565 | |||
| O1…H1 | 0.02814 | 0.11408 | O…H | 0.01173 | 0.04084 | ||
| O1…H2 | 0.02953 | 0.11944 | O1…H1 | 0.02958 | 0.07545 | ||
| O1…H2 | 0.01837 | 0.11510 | |||||
| Gu-Tyr[b] | cation-π | 0.00581 | 0.01535 | Gu-Tyr[c] | cation-π | 0.00675 | 0.02034 |
| N…H | 0.00606 | 0.01805 | 0.00695 | 0.02257 | |||
| O1…H1 | 0.03793 | 0.13075 | |||||
| O2…H2 | 0.03164 | 0.11321 |

2.3. Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) Analysis
| Complex | Orbital Interaction | E(2) | Complex | Orbital Interaction | E(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gu-Phe[a1] | BD CC → LP* CG | 7.2 | Gu-Phe[a2] | LP CG → BD* CC | 4.4 |
| BD CC → BD* NGH | 1.6 | LP O → BD* NH | 70.4 | ||
| LP O → BD* NH | 63.3 | LP O → BD* NHʹ | 19.4 | ||
| LP O → BD* NHʹ | 49.5 | ||||
| Gu-Phe[b] | BD CC → LP* CG | 3.9 | Gu-Phe[c] | LP CG → BD* CC | 2.4 |
| LP O → BD* NH | 83.7 | ||||
| LP Oʹ → BD* NHʹ | 74.8 | ||||
| Gu-His[a1] | BD NCG → BD* NC | 1.3 | Gu-His[a2] | LP CG → BD* CC | 1.0 |
| LP O → BD* NH | 64.8 | LP O → BD* NH | 64.6 | ||
| LP O → BD* NHʹ | 43.8 | LP O → BD* NHʹ | 15.0 | ||
| Gu-His[b] | LP NG → BD* NH | 6.0 | Gu-His[c] | BD CNG → BD* NH | 2.3 |
| LP O → BD* NH | 104.2 | ||||
| LP Oʹ → BD* NHʹ | 89.4 | ||||
| Gu-Trp[a1] | LP N → LP* CG | 4.7 | Gu-Trp[a2] | LP NG → BD* CC | 5.6 |
| BD CC→ BD* NCG | 4.7 | LP CG → BD* CC | 4.3 | ||
| LP O → BD* NH | 41.2 | LP O → BD* NH | 45.1 | ||
| LP O → BD* NHʹ | 34.3 | LP O → BD* NHʹ | 33.8 | ||
| Gu-Trp[b] | LP NG → BD* CC | 4.6 | Gu-Trp[c] | LP NG → BD* NH | 2.9 |
| LP CG → BD* CC | 1.1 | LP CG → BD* NH | 1.4 | ||
| LP O → BD* NH | 57.4 | ||||
| LP Oʹ → BD* NHʹ | 56.7 | ||||
| Gu-Tyr[a1] | LP CG → BD* CC | 3.7 | Gu-Tyr[a2] | LP CG → BD* CC | 1.6 |
| LP O → BD* NHG | 5.6 | LP NG → BD* CC | 1.5 | ||
| LP O → BD* NH | 58.0 | LP O → BD* NHG | 9.9 | ||
| LP O → BD* NHʹ | 52.8 | LP NG → BD* NH | 6.1 | ||
| LP O → BD* NH | 89.6 | ||||
| LP O → BD* NHʹ | 3.3 | ||||
| Gu-Tyr[b] | LP CG → BD* NH | 3.0 | Gu-Tyr[c] | LP NG → BD* NH | 1.0 |
| LP NG → BD* NH | 2.2 | LP CG → BD* NH | 0.7 | ||
| LP O → BD* NH | 116.9 | ||||
| LP Oʹ → BD* NHʹ | 68.6 |
2.4. Effect on the Aromaticity
| Complex | NICS(0) | NICS(1) | NICS(2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | −7.5 | −10.5 | −5.2 |
| Phe | −7.5 | −10.4 | −5.1 |
| Gu-Phe[a1] | −7.4 | −10.3 | −5.2 |
| Gu-Phe[a2] | −8.5 | −10.9 | −5.1 |
| Gu-Phe[b] | −7.6 | −10.1 | −5.1 |
| Gu-Phe[c] | −7.9 | −10.8 | −5.2 |
| His | −11.5 | −10.1 | −4.1 |
| Gu-His[a1] | −12.5 | −10.9 | −4.4 |
| Gu-His[a2] | −12.2 | −10.9 | −4.6 |
| Gu-His[b] | −12.3 | −10.7 | −1.4 |
| Gu-His[c] | −12.0 | −10.4 | −4.2 |
| Trp | −9.0 (−12.3) | −10.9 (−10.6) | −5.3 (−4.3) |
| Gu-Trp[a1] | −9.6 (−12.9) | −11.0 (−10.5) | −5.6 (−4.6) |
| Gu-Trp[a2] | −9.0 (−12.7) | −11.0 (−10.3) | −5.5 (−4.6) |
| Gu-Trp[b] | −9.4 (−13.1) | −10.9 (−10.8) | −5.4 (−4.8) |
| Gu-Trp[c] | −9.3 (−13.0) | −10.8 (−10.9) | −5.3 (−4.9) |
| Tyr | −8.7 | −10.0 | −4.8 |
| Gu-Tyr[a1] | −8.5 | −10.0 | −4.8 |
| Gu-Tyr[a2] | −8.8 | −9.8 | −4.9 |
| Gu-Tyr[b] | −9.8 | −10.4 | −4.6 |
| Gu-Tyr[c] | −9.2 | −10.4 | −5.0 |

3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunner, J.; Nishizawa, K.; Kebarle, P. Ion-solvent molecule interactions in the gas phase. The potassium ion and benzene. J. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.C.; Dougherty, D.A. The Cation-π Interaction. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1303–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallivan, J.P.; Dougherty, D.A. Cation-π interactions in structural biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9459–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, D.A. Cation-π Interactions Involving Aromatic Amino Acids. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1504S–1508S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gallivan, J.P.; Dougherty, D.A. A Computational Study of Cation-π Interactions vs. Salt Bridges in Aqueous Media: Implications for Protein Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Thornton, J.M. SIRIUS: An automated method for the analysis of the preferred packing arrangements between protein groups. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 211, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.B.O.; Nandi, C.L.; McDonald, I.K.; Thornton, J.M.; Price, S.L. Amino/Aromatic Interactions in Proteins: Is the Evidence Stacked Against Hydrogen Bonding? J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 239, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, A.; Quiñonero, D.; Deyà, P.M. Cation-π and anion-π interactions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2011, 1, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estarellas, C.; Frontera, A.; Quiñonero, D.; Deyà, P.M. Theoretical ab initio study of substituted benzene trimer: Interplay between hydrogen bonding and π-π interactions. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2011, 975, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauza, A.; Deya, P.M.; Frontera, A.; Quinonero, D. Substituent effects in cation-[small pi] interactions revisited: A general approach based on intrinsic properties of the arenes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromiha, M.M.; Santhosh, C.; Ahmad, S. Structural analysis of cation-π interactions in DNA binding proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Petsko, G.A. Amino-aromatic interactions in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986, 203, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlin, S.; Zuker, M.; Brocchieri, L. Measuring Residue Association in Protein Structures Possible Implications for Protein Folding. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 239, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, F.; Kelly, B.; Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Rozas, I. Non-Covalent Interactions: Complexes of Guanidinium with DNA and RNA Nucleobases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 11608–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, B.; McMullan, M.; Muguruza, C.; Ortega, J.E.; Meana, J.J.; Callado, L.F.; Rozas, I. α2-Adrenoceptor Antagonists: Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling Investigation of Pyridinoguanidine, Pyridino-2-aminoimidazoline and Their Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Cecilia, E.; Kelly, B.; Perez, C.; Zisterer, D.M.; Nevin, D.K.; Lloyd, D.G.; Rozas, I. Guanidinium-based derivatives: Searching for new kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, I.; Kruger, P.E. Theoretical Study of the Interaction between the Guanidinium Cation and Chloride and Sulfate Anions. J. Chem. Theor. Comput. 2005, 1, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, I.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions in Guanidine/Guanidinium complexes: A computational case study. Struct. Chem. 2008, 19, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; Kelly, B.; Alkorta, I.; Rozas, I.; Elguero, J. Cation-π interactions: Complexes of guanidinium and simple aromatic systems. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 511, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.; O'Donovan, D.H.; O'Brien, J.; McCabe, T.; Blanco, F.; Rozas, I. Pyridin-2-yl Guanidine Derivatives: Conformational Control Induced by Intramolecular Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 9216–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sanz, A.; Cabaleiro-Lago, E.; Rodríguez-Otero, J. Effect of stepwise microhydration on the guanidinium···π interaction. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanz, A.A.; Cabaleiro-Lago, E.M.; Rodriguez-Otero, J. Interaction between the guanidinium cation and aromatic amino acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 22499–22512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleyer, P.R.; Maerker, C.; Dransfeld, A.; Jiao, H.; Hommes, N.J.R.E. Nucleus-Independent Chemical Shifts: A Simple and Efficient Aromaticity Probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6317–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Pople, J.A.; Binkley, J.S. Self-Consistent Molecular-Orbital Methods 25. Supplementary Functions for Gaussian-Basis Sets. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll (Version 14.11.23). TK Gristmill Software: Overland Park, KS, USA, 2014; Available online: aim.tkgristmill.com (accessed on 19 May 2015).
- Rozas, I. On the nature of hydrogen bonds: An overview on computational studies and a word about patterns. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Weak interactions between hypohalous acids and dimethylchalcogens. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 9880–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozas, I.; Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Solvent effects on guanidinium-anion interactions and the problem of guanidinium Y-aromaticity. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2013, 26, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, C.; Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Mó, O.; Yáñez, M. Resonance assisted hydrogen bonds in open-chain and cyclic structures of malonaldehyde enol: A theoretical study. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1048, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo, O.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Large Chiral Recognition in Hydrogen-Bonded Complexes and Proton Transfer in Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrrole Dimers as Model Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 7485–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, I.; Alkorta, I.; Molins, E.; Espinosa, E. Universal Features of the Electron Density Distribution in Hydrogen-Bonding Regions: A Comprehensive Study Involving H···X (X = H, C, N, O, F, S, Cl, π) Interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2442–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Electron density shift description of non-bonding intramolecular interactions. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2012, 991, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.; Curtiss, L.A.; Weinhold, F. Intermolecular Interactions from a Natural Bond Orbital, Donor-Acceptor Viewpoint. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas, R.; Martínez-Guajardo, G.; Jiménez-Halla, J.O.C.; Solà, M.; Merino, G. Not All That Has a Negative NICS Is Aromatic: The Case of the H-Bonded Cyclic Trimer of HF. J. Chem. Theor. Comput. 2010, 6, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.J.; Islas, R.; Osorio, E.; Harrison, J.G.; Tiznado, W.; Merino, G. Is Al2Cl6 Aromatic? Cautions in Superficial NICS Interpretation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 5529–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G. Aromatic behaviour of benzene and naphthalene upon pnictogen substitution. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Rozas, I.; Elguero, J. A theoretical study on the aromaticity of benzene and related derivatives incorporating a C–CC–C fragment. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 7333–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Alkorta, I.; Trujillo, C.; Elguero, J. A theoretical NMR study of the structure of benzynes and some of their carbocyclic and heterocyclic analogs. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 6548–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendening, E.D.; Reed, A.E.; Carpenter, J.E.; Weinhold, F. NBO, Version 3.1. Available online: http://www.gaussian.com/g_tech/g_ur/m_citation.htm (accessed on 20 May 2015).
- Bulat, F.; Toro-Labbé, A.; Brinck, T.; Murray, J.; Politzer, P. Quantitative analysis of molecular surfaces: Areas, volumes, electrostatic potentials and average local ionization energies. J. Mol. Model. 2010, 16, 1679–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samples Availability: Not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trujillo, C.; Rodriguez-Sanz, A.A.; Rozas, I. Aromatic Amino Acids-Guanidinium Complexes through Cation-π Interactions. Molecules 2015, 20, 9214-9228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059214
Trujillo C, Rodriguez-Sanz AA, Rozas I. Aromatic Amino Acids-Guanidinium Complexes through Cation-π Interactions. Molecules. 2015; 20(5):9214-9228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059214
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrujillo, Cristina, Ana A. Rodriguez-Sanz, and Isabel Rozas. 2015. "Aromatic Amino Acids-Guanidinium Complexes through Cation-π Interactions" Molecules 20, no. 5: 9214-9228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059214
APA StyleTrujillo, C., Rodriguez-Sanz, A. A., & Rozas, I. (2015). Aromatic Amino Acids-Guanidinium Complexes through Cation-π Interactions. Molecules, 20(5), 9214-9228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059214